According to statistics, caries occurs more often in children than in adults. This is one of the most common reasons for visiting a dentist, because not only permanent teeth, but also baby teeth are susceptible to destruction.
Children do not like to be treated, and often parents feel sorry for the child until the last moment and do not take him to the dentist in order to avoid stressful situations. But you need to understand that the health of his teeth in adulthood will depend on how they care for their baby’s oral cavity in childhood.
What are the causes of caries in children
The appearance of caries can be due to various reasons.
Insufficient or incorrect hygiene
Children most often do not want to brush their teeth - they are capricious because they do not like the process itself or the taste of the toothpaste. And parents often follow the lead and let the situation take its course, without insisting on the need for this procedure. However, it is necessary to teach a child to brush their teeth from a very early age, so that by the age of two the child himself shows a desire to take care of his teeth. Dentists recommend starting caries prevention immediately after the first teeth erupt.
Prolonged contact with the pacifier
In dentistry there is such a thing as “bottle caries”. It can develop before the age of 1 year, when the child is fed too long and often from a bottle with a nipple. Most often, such caries affects the upper front teeth, and the consequences are really serious.
Transmission of infection from parents
Many people are familiar with the situation when a child suddenly dropped a pacifier on the floor, the mother quickly picked it up, licked it and returned it to the baby. It's not as harmless as it might seem. This is how bacteria are transmitted that cause caries. For the same reason, you should not lick the baby's spoon when feeding. The infection can be transmitted even through kissing, so parents and other relatives who are in close contact with the child should carefully monitor the health of their teeth.
Congenital problems
Often, dental problems are congenital in nature. This may be genetic or caused by health problems in the mother during pregnancy. Bad habits, past illnesses, deficiency of vitamins and minerals (especially calcium) - all this affects the dental health of the unborn baby.
Abuse of sweets and carbohydrate foods
This is the most common cause of dental caries. Too much love for sweets is not good for children's teeth. Sweets, juices, lemonades, buns and cookies - all this creates a favorable environment for the development of bacteria and subsequent destruction of enamel.
Lack or excess of fluoride
Fluoride is necessary for the normal formation of teeth and to protect them from damage. We get it from food and water, and it is better to periodically get tested for the content of this element in the body in order to adjust nutrition and care in a timely manner. Both deficiency and excessive amounts of fluoride provoke dental problems.
Causes
Causes of decay of baby teeth in children:
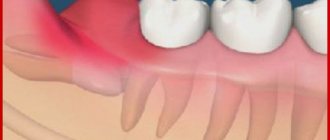
- Poor oral hygiene. Sometimes parents are too lazy to brush their child's teeth twice a day. If a child takes care of his hygiene on his own, his skills may not be enough for high-quality teeth cleaning. In both cases, bacteria accumulate on the surface of the teeth. They produce acids that corrode the enamel, leaching calcium and phosphates from it. This leads to the formation of foci of demineralization, which look like white, rough spots on the enamel. Later, the foci of demineralization transform into carious cavities. Plaque accumulates, hardens and forms tartar, which contributes to irritation and inflammation of the gums.
- Poor nutrition. If a child consumes a large amount of fast carbohydrates and there are no foods rich in calcium in the diet, this also leads to the development of caries. In children aged 1–1.5 years, night feedings (formula, sweet kefir, yogurt) may still be present. This is how the so-called “bottle caries” develops.
- Congenital enamel hypoplasia. This is insufficient development of enamel, which develops in a child in utero. Hypoplasia occurs due to metabolic disorders in the fetus. This is facilitated by colds and infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy, and severe toxicosis. Enamel contains few minerals and caries often affects teeth soon after they erupt.
- Fluoride deficiency in the body. A lack of fluoride is considered an important factor in the development of caries, since these elements strengthen the enamel. The main source of fluoride is regular drinking water. According to WHO standards, drinking water should contain 0.5–1 mg of fluoride per liter. The problem is that not all people consider it acceptable to drink tap water, because... it may have a repulsive odor or taste. But home filters for water purification, along with harmful impurities, also retain fluoride.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, and endocrine system also contribute to rapid tooth decay in children.
What are the stages of dental caries in children?
Tooth decay begins gradually, and with regular examination, parents and the dentist can catch the right moment in time and begin treatment.
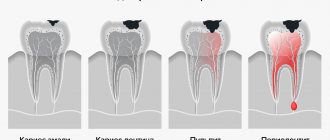
| Initial stage Specks appear on the enamel, which differ in color from the rest of the tooth, and over time they darken. | Superficial caries The tooth decay is still minor, but the child is already beginning to react to hot and cold. | Average caries A carious cavity appears at the site of enamel destruction; the tooth reacts very painfully to the temperature of food and drinks. | Deep caries The last stage is when not only the enamel is destroyed, but also the tooth tissue itself. If treatment measures are not taken, then inflammation of the pulp will gradually begin, and the tooth will have to be removed. |
It is better not to delay the examination, because caries in a child can develop quite quickly. The further you go, the more uncomfortable and worrying your first visit to the doctor will be.
Is it necessary to treat caries of baby teeth?
Despite the “temporary nature” of children’s teeth, treatment and care for them must be thorough and complete. Chronic inflammation in the oral cavity leads to serious problems.
- A baby tooth affected by caries can decay so deeply that it affects the germ of a permanent tooth. The infection will spread to it, and it will grow up with enamel defects or simply die.
- When a baby tooth is removed, the adjacent tooth moves into its place, causing the permanent tooth to erupt in a different place than intended. As a result, the bite is formed incorrectly, and in the future it has to be corrected with braces.
- Advanced caries reduces immunity and causes ENT diseases and even allergies.
- Painful sensations prevent the baby from biting and chewing food correctly, which causes digestive problems.
- The child will be embarrassed about his bad teeth, which will prevent him from communicating with his peers.
It is necessary to treat caries at any age at the initial stage, and it is better to accustom your child to this in advance.
Can a filling be placed on a baby tooth?
If the doctor diagnoses not the first stage of tooth decay and insists that it is necessary to put a filling, it is better to agree with him. This is the fastest and most reliable way to solve the problem of infection and protect permanent teeth.
Modern filling materials are as safe as possible for children’s teeth. Depending on the stage of caries, the doctor will select a suitable filling option. Before installing a permanent filling, the dentist may place a temporary filling for several days to fix the medication inside the diseased tooth.
If the damage is not yet serious, the doctor will limit himself to preventive measures. There are different approaches and tools for different problems.
What are the treatment methods for caries in children?
Treatment methods depend on the stage of caries development. The more serious the problem, the longer it will take to fix it.
Preventive
At the initial stage, a delicate intervention is sufficient, which can stop or reverse the process of destruction that has begun. In this case, for example, remineralization (treatment of teeth with a solution of calcium and fluoride) or deep fluoridation (treatment with fluoride) is used. Such procedures are carried out in courses until the condition of the teeth is stabilized.
There is also a treatment method without drilling, which allows you to quickly and completely painlessly prevent the development of inflammation. The procedure is suitable for children from 4–5 years of age and causes them minimal discomfort.
Medicinal
For medium and deep caries, classical filling with preliminary preparation of teeth for the procedure is already necessary. To ensure that the treatment is calm and painless, the most modern and effective anesthesia is used. Your baby doesn’t even have to endure the pain of the needle because the injection site is first numbed. The drill is used to a minimum in the treatment of childhood caries - if something can be done manually, then the doctor will do so.
If a child has a complex case of caries, or is very restless in the dentist's chair, treatment is carried out under anesthesia. After consulting with an anesthesiologist and passing all the necessary tests, the baby will be selected the appropriate drug and dose, he will be put into deep sleep, during which the doctor will carefully monitor the condition of the body. Time will fly by in a dream - the child will wake up with healthy teeth, a clear head and an unspoiled mood.
Types of caries
Children under 3 years of age cannot develop only dental root caries; other types of this disease do not depend on age. It takes various forms - acute or chronic. In the first case, the carious process progresses rapidly; within a few weeks, the pathology passes through all four stages. It is accompanied by severe pain, which is not helped by analgesics.
Chronic caries is painless. However, it can develop over months and years, gradually destroying hard dental tissues. Often the carious process spreads to neighboring teeth. In such cases it becomes multiple.
Based on localization, caries is divided into cervical (near the gums), interdental and fissure (in the pits on the chewing surface). Dentists also often use the classification proposed by the American doctor Green Black. It allows you to determine the stage of caries and select a treatment method. Black divided this disease into classes:
- Carious lesions are localized in the fissures of the teeth.
- Pathology affects the contact surface of premolars and molars.
- Caries of the anterior teeth, localized on the contact surface of the canines and incisors.
- The pathological focus is located on the front teeth, the integrity of the cutting edge is compromised.
- Caries covers the vestibular surfaces of the tooth.
- Carious lesions are located on the cutting parts of the incisors and in the fissures of the molars.
With the help of instrumental diagnostics, the doctor can detect caries at any stage. Each of them is treated using different methods. Let us consider separately another type of carious process that develops on the front teeth. After this, we will tell you how caries is treated in children.
How to prevent tooth decay in children
The best way to combat tooth decay is prevention. To maintain the health of children's teeth, you need to follow several rules.
- Follow your diet. Reduce your consumption of sweets as much as possible. Make sure your child gets enough calcium from their diet - dairy products, nuts, legumes and sesame are especially rich in it.
- Teach your child to brush their teeth. From the first tooth that emerges (age 6–8 months), you can already use a small baby brush. Gradually accustom your child to self-care - buy tasty toothpaste, turn the process of brushing your teeth into a game, encourage your baby’s interest.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Children need to undergo preventive examinations, as well as professional hygiene procedures more often than adults - approximately once every three months. The doctor will be able to identify problems in a timely manner and give advice on the proper care of children’s teeth. In addition, visits to the doctor will become routine for the baby, and he will not be afraid of them.
Try to carefully monitor the condition of your child’s teeth and pay attention to his complaints. The sooner you see a dentist, the faster, more effective, and most importantly, painless the treatment will be. Explain to your child that dentistry is not scary. And our experienced doctors will help him make sure of this.
What to do if your teeth turn black
An important role is played by the structure of the child’s tooth enamel, which directly depends on heredity, as well as the composition of the saliva that washes the surface of the tooth. When the required composition of saliva is disrupted (which occurs when there is a deficiency of fats, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins or minerals), plaque appears on the teeth. This is what causes teeth to darken. Do not try to get rid of it by brushing your teeth - this is useless, as the plaque will appear again. The way out of this situation will be to revise the children's diet, which should include foods rich in calcium, iron and other substances useful for strengthening teeth, including carrots, apples, cottage cheese and other dairy products, and, of course, fish. If a child’s teeth turn black, the first thing you should do is consult a dentist to find out the reasons for this process. Don't neglect your baby's teeth, because childhood caries develops quickly and can lead to undesirable consequences in the future if it is not prevented in time.