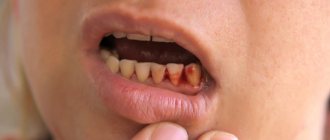
Situations requiring tooth extraction are familiar to most of us. Even if we are not talking about removal due to an advanced disease or inflammatory process, at least in childhood, each of us went through the period of changing milk teeth to molars. Sometimes everything happened by itself, and the tooth could be reached literally with your hand in one movement. And sometimes the task required a visit to the dentist's office. Remember what emotions we experienced at this age, what horror every trip to the doctor inspired. Inevitable associations with unbearable pain (which, most often, did not exist at all) and fear of the dental chair. However, with age, everything changes and adults, for the most part, understand that there is no need to be afraid of the dentist, but it is necessary to take care of your teeth, because it is thanks to regular visits to the dentist and careful oral care that it is possible to avoid dental problems and the very pain that comes with it. everyone is afraid.
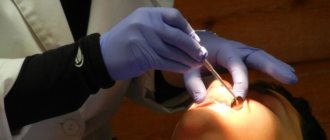
At the same time, even in cases where a person shows high responsibility towards his health, it may be necessary to remove a tooth. First of all, this concerns wisdom teeth. In addition to the fact that the procedure itself is often painful, due to the peculiarities of their location, as well as the different age of complete eruption, the removal of wisdom teeth can be accompanied by unpleasant complications. However, by entrusting the procedure to a qualified specialist, you can be sure of a positive outcome. However, in order to avoid problems during the healing process of the gums, you should strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations for hygienic treatment of the oral cavity.
Painless tooth extraction in Moscow - Selin aesthetic dentistry clinic
Content:
- A tooth has been removed: can you or can’t smoke?
- Why smoking after removal is undesirable
- Is it possible to smoke after tooth extraction if there are stitches on the gums?
- Smoking and anesthesia are an undesirable combination
- Useful information about the effect of nicotine on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity
- How to speed up the healing of a hole
A person who has just had a tooth removed is usually nervous. This is understandable - he has suffered stress and wants to relax. Smokers often use cigarettes to calm down, but the question arises: when can you smoke after dental surgery? We suggest you look into it.
Prevention of complications after tooth extraction
- Responsible choice of clinic and doctor is one of the most important conditions for successful treatment.
- X-ray monitoring of all performed manipulations allows timely detection and prevention of complications.
- Compliance with all dentist recommendations for oral care after surgery.
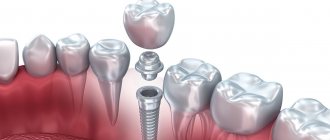
- Timely installation of an implant helps to avoid changes in bite.
- A thorough medical history allows you to choose the right anesthesia and calculate its dosage.
- Reducing treatment time, a comfortable environment and a friendly attitude allow you to avoid most common complications.
- Compliance with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis prevents and stops the development of inflammatory and purulent pathologies.
Tooth extraction is a surgical operation; this procedure must be handled responsibly. An informed and careful choice of clinic and doctor will help avoid most complications. Competent patient management and a friendly atmosphere will leave only positive emotions about treatment at the dentist, contrary to prevailing stereotypes.
Sources used in writing the article:
- “Outpatient surgical dentistry”, Bezrukov V.M.
- "Surgical dentistry", T.G. Robustova.
- “Guide to maxillofacial surgery and surgical dentistry”, A.A. Timofeev.
Please rate this article
Stanislav Mezheritsky
Chief physician, surgeon, orthopedist
The author of the article is Stanislav Mezheritsky, a practicing dentist with 19 years of experience, chief physician and one of the founders of the Matisse Dent clinic. The main focus is orthopedic and surgical dentistry. Author of numerous publications, regular participant in specialized seminars.
A tooth has been removed: can you or can’t smoke?
Dental surgeons prohibit smoking during the first two to three hours after extraction. This short period is relevant if:
- the operation was not very complicated;
- the bleeding has stopped completely;
- after removing the gauze swab, blood did not begin to flow again;
- a dense blood clot has managed to form, isolating the wound in the gum.
In severe cases, smoking after tooth extraction will have to be postponed for several days - the exact time period will be determined by the doctor. This is due to the fact that nicotine contained in cigarette smoke irritates the edges of the inflamed hole and causes spasm of blood vessels. Because of this, regeneration processes slow down and dangerous complications can develop.
Treatment of local complications after tooth extraction
The choice of treatment method is based on the causes of the pathology, its nature and the patient’s condition. Age is also taken into account, since not all medications are suitable for children. Therefore, the treatment regimen is developed individually for each patient.
Complications related to bone structures
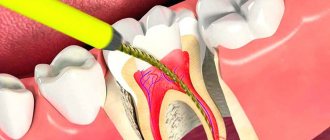
Most often, a fracture of the tooth root occurs during extraction. In this case, it is usually removed so as not to provoke an inflammatory process. If symptoms of infection have already arisen, and the pathology is discovered a few days after the operation, wait 1-1.5 weeks and perform surgical treatment again. In this case, the patient takes anti-inflammatory drugs to stop the inflammation process.
If during extraction a tooth that was located next to the extracted one is fractured, the doctor evaluates how reasonable and possible it is to save it. With minor damage, it is possible to build up the damaged area. If the fracture is serious, the tooth is removed.
During surgery, cases of dislocation of the tooth closest to the extracted one are not uncommon. For high-grade injuries, replantation is indicated. If the mobility of the tooth is preserved, it is strengthened with a stabilizer in the form of an endodontoendoxal implant. If the tooth tissue is completely dead, it is removed and replaced with an artificial tooth. If the dislocation is incomplete, strengthening is carried out using a splint.
A situation where the root is pushed into the jaw tissue from below is possible when the third molar of a large tooth is removed. If the hard part is palpable, it is removed through an incision made over it. If there are no objective signs of a root being located in any part of the jaw, an x-ray is taken, which is performed in two projections (side and front) - this is how the desired root is detected and removed.
When removed, the root of a tooth may end up in the sinus of the upper jaw. In this case, the root is urgently removed, as it can cause infectious sinusitis. The operation is not performed through the hole so as not to enlarge the hole in the sinus. First, perforation of the bottom is carried out, then an operation to remove the root is made - for this, a burr hole is made in the sinus of the upper jaw from the outside and in front. The operation is performed using endoscopic devices under continuous monitoring.
Trauma to the alveolar process is not considered a serious complication during tooth extraction. This condition does not cause discomfort and is not considered dangerous. It goes away on its own without affecting recovery after surgery. If the fragment has sharp edges, they are smoothed even during tooth extraction. The most commonly injured teeth are the upper and lower third molars.
Pathologies of soft tissues during tooth extraction
In case of injury to soft tissues or gums, the primary task is to stop bleeding: a hemostatic sponge is applied to the wound, and in case of severe damage, the wound is sutured with excision of those areas whose integrity cannot be restored.
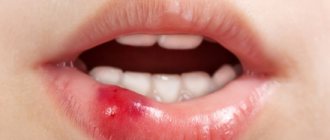
Some patients are concerned about swelling localized on the gum near the extracted tooth. In the first few days after surgery, it is considered physiological. But if the pain persists and the swelling grows, you need to consult a doctor - a purulent complication may develop, which requires opening and draining the resulting cavity.
If a blood clot does not form at the site of the extracted tooth, alveolitis appears. It is provoked by non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations for oral care (smoking, rinsing in the first few days, failure to perform hygiene procedures, aggressive foods). Sometimes the patient is bothered by pain that is subjectively felt in the temple area. Before starting treatment, the hole is sanitized, treated with an antiseptic solution and a cotton swab with an anti-inflammatory agent is placed in it.
If the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are not followed, osteomyelitis and other purulent complications may occur after tooth extraction. If left untreated, the pathology spreads to neighboring organs and also affects the jaw. To get rid of this condition, the patient undergoes an autopsy of the infectious focus and is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs.
Other damage after tooth extraction
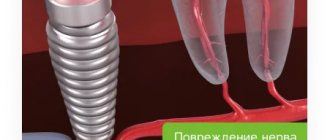
In some cases, paresthesia occurs due to tooth extraction. It is characterized by a lack of sensation in the cheeks, lips, chin and tongue. The condition lasts about two weeks, then passes. You can speed up recovery by taking B vitamins, ascorbic acid, dibazole and galantamine.
If the patient opens his mouth excessively, the jaw may dislocate. This complication is typical for elderly patients, as well as during surgery on large and small molars of the lower row. When a dislocation usually affects one side, less often both. Patients have this defect corrected on the spot, immediately after detection.
In rare cases, a jaw fracture is detected. It is typical for surgery on the second or third molar. Diagnosis of a fracture is complicated by blurred symptoms, but is clearly visible on x-rays, so x-rays are often used to monitor the success of the operation. A jaw fracture is treated by repositioning the bones and fixing them with splints through the teeth or with the help of intra- and extrafocal bone tissue synthesis.
When removing small or large molars from above, perforation of the maxillary sinus is possible. It is characterized by the presence of a through hole in the hole. The condition may be accompanied by bleeding and discharge of pus. An important stage of treatment is to control the formation of a blood clot in the hole in the absence of inflammation. To speed up healing, an iodoform turunda, a gentamicin sponge or a tampon with an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent are placed on the hole. To ensure that the applications remain in place, they are fixed with a plastic mouthguard or bandage like a ligature in the shape of a figure 8 on the adjacent teeth. A removable denture can be used to cover the hole.
If clot formation does not occur, an iodoform tampon is secured to the socket to the edges of the gum using silk sutures or a mouthguard. The application should be worn for 5 to 7 days - during this time the wound begins to heal and there is no need for additional coverage. It is important to apply the tampon correctly so that it does not completely fill the hole, otherwise the patient faces sinus inflammation.
If a significant size hole is found at the bottom of the sinus, a blood clot may not form. Then the walls of the resulting hole are processed so as to remove all sharp parts, and then sutured without tension. If there is no positive effect, biological material can be applied to the hole, after which plastic surgery of the defect is performed with soft tissue. To speed up healing, an iodoform tampon is applied to the wound, which is fixed with a plastic plate.
If a root or whole tooth is inhaled, an emergency tracheotomy is performed to prevent the patient from suffocating. When an object passes into the lower parts of the respiratory system, it is removed using a bronchoscope, and for this the patient is transported to a suitable medical facility. If a tooth or part of it has been swallowed, the patient is monitored and the stool is independently monitored. Usually the object comes out naturally without causing significant discomfort.
If after tooth extraction the patient does not insert an implant in time, malocclusion develops over time - this is due to the natural displacement of the teeth towards the vacant space. If the dentition is not restored in time, bite correction with braces will be required, and the installation of a prosthesis will be accompanied by bone grafting.
Complications after tooth extraction in a child
Modern medical standards require that even children’s baby teeth be treated for caries. Until recently, they were simply removed, believing that healthy permanent ones would still grow in their place. But it turned out that this is not so.
Firstly, caries easily passes from baby teeth to permanent ones. Secondly, after the forced removal of baby teeth, a change in the bite often develops. As a result, it took a long time to correct the position of the child’s jaw using plates and braces. Therefore, doctors are increasingly deciding to place temporary implants even in childhood to maintain the correct bite.
The risk of developing malocclusion occurs not only in the postoperative period. There have been cases recorded when, during treatment, the doctor accidentally removed a baby tooth along with the germ of a permanent tooth. This is due to their close location in some children. Correction in this case is only possible with the help of a permanent tooth implant. Therefore, it is important to notice and treat carious lesions in children in a timely manner, rather than delay them and bring the situation to removal.
Why smoking after removal is undesirable
If you start smoking after leaving the dentist's office, you may experience dry socket problems. This means that the blood clot formed to protect the wound from the penetration of pathogens will collapse. Then the tissues will be left without a natural barrier. When smoking further cigarettes and eating food, irritating substances will enter the hole. In this case, there is no hope for quick healing.
The inflammatory process that has developed due to dry socket manifests itself:
- pain at the location of the torn unit;
- increased body temperature;
- accumulation of purulent masses in the wound;
- foul breath.
There is no point in hoping that the situation will normalize on its own. If you have a dry socket, you should visit your dental surgeon again as soon as possible.
What painkillers can be taken in the postoperative period?
Most often, when local anesthesia wears off after a tooth extraction procedure, the patient feels pain in the area of intervention. The best way to eliminate pain is to take NSAIDs. This group of drugs is the most effective in eliminating toothache.
- The drugs "Nurofen" or "Ibuprofen" cope well with pain after surgery. It is necessary to take the drug 500-800 mg three to four times a day, depending on the intensity of the pain.
- "Ketorol" is one of the most effective and powerful drugs from the NSAID group, which can eliminate pain after the procedure in a fairly short time. It is also used two tablets three to four times throughout the day.
You can take Nurofen, Ketorol
Smoking and anesthesia are an undesirable combination
Doctors insist that patients do not smoke for the next two to three hours after extraction for good reason. Anesthetics used during dental surgery make the tissue completely insensitive and reduce the activity of some muscles and can change the breathing rate. It is very important to wait until their effect ends.
Nicotine and carbon monoxide entering the oral cavity during smoking a cigarette cause spasm of blood vessels and reduce oxygen saturation in the blood. The combination of all these factors leads to a situation where the tissues of the mouth do not receive enough oxygen, which is important for their restoration.
Useful information about the effect of nicotine on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity
The mucous membranes of the human oral cavity are lined with very delicate and easily vulnerable epithelium. With the systematic use of tobacco products, nicotine and toxic tars damage tissue. The situation is aggravated by the negative impact of elevated temperature when inhaling cigarette smoke.
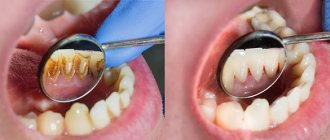
This is why smokers are often diagnosed with gingivitis and periodontitis. The components present in the smoke change the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth. The gums become inflamed. In the absence of adequate treatment and the persistence of a bad habit, the inflammatory process progresses. Then the unit becomes mobile.
Compounds present in cigarette smoke spasm peripheral blood vessels, disrupt tissue trophism and increase inflammation. Most often, the disease occurs without acute pain and bleeding, so the smoker is in no hurry to see a dentist. But, if you go to the doctor late, you can lose your tooth ahead of time.
How to speed up the healing of a hole
Dentists always give the patient individual recommendations that must be followed. But there are general rules that apply to all patients:
- Do not smoke for at least two to three hours.
- Promptly remove the tampon soaked in antiseptic from the postoperative wound. If you forget to do this, the fabric will become a suitable breeding ground for bacteria.
- Do not touch the blood clot covering the wound. It cannot be picked or felt. The speed of recovery directly depends on the state of the clot.
- When rinsing, do not make intense movements that will help wash out the clot. You just need to put the medicinal solution in your mouth and carefully hold it on the side of the extracted tooth.
- Do not apply medications to the affected area that have not been prescribed by a doctor. Such amateur activities can lead to dangerous complications.
- In the first three days after extraction, do not take a hot bath or steam in a bathhouse or sauna.
- Do not eat until the anesthesia wears off. Otherwise, you may bite the tissue of your cheek or lip.
- Take only those medications prescribed by your dentist. Sometimes doctors decide to prescribe antibiotics - they must be taken strictly according to the specified regimen.
How the regeneration process will proceed depends not only on the actions of the dental surgeon, but also on the behavior of the patient. Remember this!
Auxiliary medications for tooth extraction
If, after the tooth is removed, any complications begin at the intervention site, then modern pharmaceuticals can cope with them. With the help of various medications, the patient can not only eliminate the resulting secondary complications, but also strengthen his immunity as a whole. Quite often, specialists, to ensure against possible complications, in particular, various inflammations and suppurations, prescribe antibacterial drugs in the postoperative period. At the same time, the patient also needs to strengthen the immune system, which will help the wound heal faster. To do this, doctors prescribe vitamin complexes to the patient. Thus, in addition to the medicine placed in the hole and affecting its healing, the patient is recommended to take other drugs to speed up the process.
Your doctor may recommend taking medications to strengthen your immune system.
If during the procedure the patient was identified with any peculiarities or complications and tooth extraction was not without additional trauma, then a number of medications are prescribed in the postoperative period, since in this case there are additional risks of complications. The main thing is that the patient treats the postoperative period responsibly and does not neglect the doctor’s advice and the medications prescribed to him.
Important ! According to statistics, every third patient who has had a tooth removed needs to take antibiotics.