From this article you will learn:
- Why does pain occur after wisdom tooth removal?
- What are the complications after wisdom tooth removal?
- what to do if you have swelling of your cheek or bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth.
After wisdom tooth removal, patients may experience various symptoms - pain, swelling of the gums or cheeks, fever, painful opening of the mouth, painful swallowing, etc. Depending on the initial situation (for example, the removal was carried out against the background of inflammation, the removal was difficult...) - these symptoms may be natural, or they may, on the contrary, signal the development of complications.
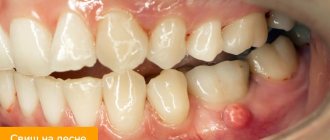
Possible reasons for the appearance of a lump on the gum after tooth anesthesia
Since the doctor makes the injection blindly, there is a risk of hitting a blood vessel. This explains why a bruise appears on the cheek or gum. In many cases it is considered the norm. Hematoma may also occur while taking certain medications that affect the blood's ability to clot. This could be, for example, Heparin, Aspirin, and many NSAIDs. A number of factors contribute to the appearance of a lump after the administration of an anesthetic:
- drinking alcoholic beverages before visiting the dental office;
- high blood pressure - hypertension;
- consuming too hot food or drinks shortly after dental treatment.
Swelling near the injection site is not considered a deviation from the norm. Often such manifestations are subjective in nature - a person may feel severe tissue swelling, although in fact the swelling is insignificant. But in some cases, these signs can lead to complications, so it is necessary to understand when the pathological process develops.
Temperature after wisdom tooth removal –
- If the tooth was removed not due to inflammation - If you have a wisdom tooth removed - the temperature can normally rise to 37.5 degrees, but only on the first evening.
The body sometimes reacts to injury with just such a low-grade fever, even if the tooth was not removed due to inflammation. This is especially true if the removal was difficult. Normally, the temperature should disappear the next morning after removal. When you need to sound the alarm - but if the temperature does not subside the entire next day after removal, and even more so continues to increase, then this clearly indicates the addition of an infection. You need to run to the dentist. - If the tooth was removed due to purulent inflammation, in this case the numbers on the first evening may be slightly larger than 37.5. Normally, from the next day the temperature should decrease progressively. If it persists and even increases, then you need to urgently go to the dentist.
Why does pain occur after an injection into the gum?
Since the needle is inserted into soft tissues, it injures them and provokes discomfort. The patient may feel pain at the injection site for 1-2 days, or even more. The duration of the recovery period depends on the characteristics of the body and the perception of stimuli at the neuropsychic level.
Overly sensitive patients should be prepared for aching pain. Most often, no action is required. Usually the pain subsides on its own. In the case when it does not go away and only gets worse over time, we can talk about the development of a complication. At the same time, other signs of disturbances may occur.
Sometimes the patient thinks that the injection site hurts, but the localization is in a different place. So, after caries treatment, you may feel aching pain that radiates to the gums. Removal of a wisdom tooth is accompanied by pain in the socket, while the patient thinks that the problem is localized at the injection site.
Hematoma after wisdom tooth removal –
This is a normal phenomenon, albeit an unpleasant one. This is due to the fact that some vessel in the soft tissues was injured. There is no point in blaming the doctor for this, since the doctor, when administering anesthesia, does not see where the vessels pass in your soft tissues. The needle can injure such a vessel. After a few days, the skin may appear blue. Gradually it will pass.
However, the formation of a hematoma may require additional measures. For example, already on this day or the next day after removal, the patient developed swelling of the cheek, a feeling of fullness, pain, and a slight fever. Such symptoms may also indicate the presence of a hematoma. You need to see a doctor; depending on the situation, you may need to take antibiotics, or make a loosening incision along the gum, or both.
If you experience such symptoms, then you should not postpone your visit to the dentist, because... in most cases, swelling and pain in this situation will only increase.
Complications after injection of anesthetic into the gums
Depending on the amount of blood released from the vessel and the individual characteristics of the body, it often takes 4 to 10 days for a bruise on the gum to disappear. Otherwise, this is already a complication.
| Type of complication | Features of manifestation | Symptoms |
| Accession of infection | There are always millions of bacteria in your mouth. In a normal state, they are in a certain balance, but under favorable conditions, for example, when immunity decreases, they can be activated. Thus, clotted blood becomes a nutrient medium for them. Pathogens begin to multiply. Pathogenic microorganisms can spread to periodontal tissue, the alveolar process that holds the tooth, periosteum and bone. Much depends on the type of pathogen and the location of the bruise. | Tissue infection is accompanied by the following symptoms: · painful sensations; · temperature increase – up to 39 ˚С; · weakness; · headache; Redness of the gum tissue. |
| Damage to the nerve trunk | If the doctor acts incorrectly, nerve fibers may be damaged as a result of the administration of anesthesia. In this case, it is important to contact a neurologist and maxillofacial surgeon as quickly as possible. | The patient feels a sharp pain immediately when the injection is given. It will subside for the duration of the anesthetic, but then resume again. It cannot be stopped even with the help of painkillers. If a large nerve trunk is affected, pain will be felt throughout the entire mouth, cheek and ear. It is even possible to turn off the chewing function and numbness of the face. Sometimes it is difficult to open your mouth completely; one side may sag. |
| Tissue necrosis | A very dangerous complication. The reason for its development may be the patient’s ailment, which he was silent about, vasospasm, too much anesthetic or its rapid administration. | The patient first feels a sharp, growing pain. It subsides for a short time, but this does not indicate that the danger has passed. The pain disappears due to tissue death. |
Complications after tooth extraction often occur due to the penetration of bacteria through the hole into various tissues of the dentofacial apparatus. Pus accumulates.
Bleeding after wisdom tooth removal –
The doctor does not have the right to release you from the clinic if you are bleeding from the socket of the extracted tooth. Usually, in the socket of an extracted tooth, blood clots almost instantly. But with high blood pressure or if a large vessel has been injured, there may be prolonged bleeding.
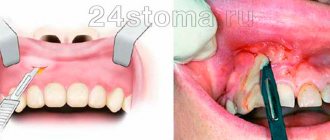
If significant bleeding occurs during the extraction process, then there is no big problem and the doctor will either suture the wound with suture material, or put a hemostatic hemostatic sponge into the hole of the extracted tooth, or all together (Fig. 8-9).
Often bleeding after tooth extraction occurs after leaving the clinic. Experienced doctors, to be on the safe side (especially if a large tooth is being removed, the patient has a history of hypertension) usually always put 1-2 sutures on the wound to bring the edges of the wound closer together and avoid bleeding. Applying sutures also allows the wound to heal faster.
If bleeding occurs, for example at night, then in this case you need:
- Make a tight gauze swab from a sterile bandage and place it over the socket of the extracted tooth. Clench your teeth so tightly that you feel that the tampon fits tightly to the wound surface.
- Measure your blood pressure. Such things happen very often in hypertensive patients. If your blood pressure is elevated, take the appropriate medication.
- Place ice (a piece of frozen meat in a bag will do) against your cheek, lip - in general, against the area where the removal was performed (Fig. 10). Ice is applied externally; there is no need to put it in your mouth. Usually the ice is kept 2-3 times for 5 minutes (at intervals).
- If none of the above helps and you have to constantly spit out blood clots, and also if you experience weakness or dizziness, then you definitely need to do the following: either feel free to call an ambulance, which will take you to the hospital, where they will put stitches on your wound and let you go home, or independently get to any 24-hour dental clinic, where they will do the same for you (they will put stitches to stop the bleeding).
Prevention of bleeding after removal: you cannot engage in physical labor, take a hot bath, smoke, drink alcohol, make active facial movements (sutures may come apart), and also - hypertensive patients need to control their blood pressure.
For information on how to behave correctly after tooth extraction, read the article: → “Memo on how to behave after tooth extraction”
Reason to see a doctor
The following symptoms require a visit to the dental office:
- severe pain at the injection site and its increase;
- significant swelling of the gums that remains after the anesthesia wears off;
- purulent or sanguineous discharge from gum tissue;
- temperature increase;
- compaction (“petrification”) of gum tissue in the affected area;
- looseness of the gums under the tooth, which was amenable to treatment, their slight displacement when exposed.
During the examination, the doctor will determine the cause of the development of undesirable effects.
Expert advice
To avoid complications after tooth extraction, you must follow your dentist's recommendations.
- For the first week after surgery, do not eat solid foods or drink drinks through a straw.
- Do not take a hot bath or visit the bathhouse or sauna until the wound has completely healed.
- Use a toothbrush with soft bristles to avoid damaging your oral tissues.
- If pain or other unpleasant symptoms occur, contact your doctor.
How long does swelling last?
The duration is directly related to the complexity of the surgical intervention. On average, after tooth extraction, swelling lasts for 3 days. Moreover, on the third day its development can reach its maximum. Then the swelling begins to gradually subside, at which time a hematoma may appear. The most important thing is to provide timely assistance to the body in treating the tumor and monitor whether the swollen area is amenable to simple therapeutic measures. However, if the healing period is prolonged, you should immediately consult your dentist.
Possible complications
If after seven days the tumor not only has not gone away, but has also grown and become denser, this indicates a progressive inflammatory process.
At the same time, other symptoms may appear: pain in the gums and cheeks (aching, cutting, throbbing), redness of the cheeks and gums, fever, weakness, loss of appetite, headache.
What complications can inflammation lead to:
- Alveolitis or “dry socket” - after a tooth is removed, a blood clot forms in the resulting socket. It serves as a protection and barrier to bacteria and protects the wound from infection. If it is somehow removed, the soft tissues are left without protection, pathogenic bacteria penetrate into them and suppuration begins. In advanced cases, inflammation spreads to other areas of the jaw; not only the cheek, but also the cheekbones and even the eye area swell.
- If, in addition to the tumor, the patient experiences severe pain in the jaw, this may indicate the development of osteomyelitis - inflammation of the bone tissue. The swelling on the cheek grows, spreading to the cheekbones and other parts of the face, the pain spreads to both jaws, the patient experiences pain when opening the mouth. If you do not consult a specialist in time, the disease can lead to blood poisoning.
- A gum abscess is a purulent inflammation inside the gum tissue. It is dangerous due to the spread of inflammation to other tissues, loosening and loss of teeth.
- Periostitis of the jaw (flux) is an inflammation of the jaw, characterized by increased temperature and severe pain in the jaw and temporal part. If left untreated, the flux can spread to the infraorbital area. In chronic form it can develop into osteomyelitis.
- Neuritis is damage to the facial nerve, accompanied by severe pain and swelling. A distinctive symptom is swelling of the larynx, palate, tongue, and cheeks.
Each of these complications can cause serious consequences, which is why it is so important to diagnose and treat in a timely manner.
Swollen cheek
Not all dentists tell patients what to do if their cheek is swollen after tooth extraction. Even in the doctor's office, some patients notice swelling on their cheeks. Anesthetic drugs cause not only numbness of the nerve endings, but also swelling - this is normal if the discomfort quickly passes after the end of the operation.
If a tumor appears after dental procedures, about a day or later after surgery, this is a dangerous sign. Pain, swelling and redness are caused by the presence of many blood capillaries in the oral mucosa. But the recovery process in the mouth is also much faster than in the arm or leg. If this does not happen in a timely manner, then the tumor is caused by one of the following reasons.
- Swelling of the cheek tissues that began even before the visit to the dentist. After surgery, such swelling only intensifies, although surgery in this case is not the main reason that the cheek is swollen.
- Removal of a wisdom tooth that has not yet fully erupted. The removal operation severely injures the gums, even if the surgeon is experienced. During the operation, the doctor cuts the tissue deeply, sometimes he has to further expand the wound to get to the tooth. When a wisdom tooth is removed, there is often profuse bleeding below, causing swelling of the cheek within a day.
- High blood pressure. Patients suffering from hypertension are more susceptible to edema than others.
- The patient is overweight. The thick layer of fat on the face is well supplied with blood, which contributes to swelling.
- Suppuration of the walls of the socket and blood clot also lead to swelling of nearby tissues.
If your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction, this does not always threaten your health. If this happens within 24 hours of surgery, it is likely not a problem and will go away on its own. To verify this, the patient only needs to measure his temperature. If it does not exceed 37.5°C, experts consider this a normal reaction to injury caused by surgery. In case of swelling, it is advisable to measure the temperature several times a day to ensure that there is no severe infectious inflammation. The second option is to examine your mouth with a mirror to make sure there is no worsening of the condition.
With the current level of technology development, experts recommend photographing the swelling every day to monitor its dynamics. The following are considered alarming factors:
- long-lasting bleeding;
- bad breath that was not there before;
- the appearance of pus from the wound when pressing on it;
- severe pain when swallowing.
Dentists recommend observing swelling of the cheek for the first 24 hours, but if the condition does not improve the next day, you need to contact the dentist again.
Main reasons
Dental injuries can occur for various reasons, the most common of which are:
- accidental impact of the jaw on a hard object during a fall or in an accident;
- a blow to the front teeth with a glass, spoon or other utensil (sometimes such blows are so strong that they break off part of the incisor);
- a blow to the teeth with a fist or other blunt object (a professional injury that often occurs among fighters of various martial arts);
- chronic injuries associated with a person’s habits or lifestyle (tendency to bite nails, bite pens, frequent consumption of sunflower seeds, cracking pistachios and other relatively soft nuts with teeth);
- damage during the treatment of adjacent teeth (severe tooth bruising can occur both due to a dentist’s mistake, and due to the anatomical features of the patient, advanced diseases and other factors).
The likelihood of enamel fracture and other traumatic damage to dental tissue increases significantly with poor oral care and dental health. In this case, the enamel becomes more fragile, and the initial stages of caries may develop, significantly weakening the tooth. Timely treatment and proper oral health care significantly reduce the risk of injury to teeth as a result of a blow or other physical impacts.
Why does swelling occur after dental implantation?
In general, swelling is a completely normal reaction of the body to injuries. All this is nothing more than an influx of lymph to damaged tissues (i.e., accumulation of fluid in a certain area). This way the body’s natural defenses are activated. Swelling forms within 2-3 days - it reaches its peak on the third day after surgery. After this, the swelling of the tissues should gradually decrease and disappear completely within a week.
When installing classic two-piece implants, when the flap method with gum peeling is used, the likelihood of tissue swelling is much higher. Patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system and diabetes mellitus are also at risk.