Etiology and pathogenesis
The development of periostitis most often occurs with inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and teeth, pulpitis and periodontitis. Also, the development of purulent inflammation of the periosteum can occur after jaw fractures, injuries and wounds of the soft tissues of the cheek, after treatment with anesthesia. Through damage to the dental tissue, gums or cheeks, the pathogen enters the jawbone, causing inflammation.
Acute periostitis can develop as a result of acute or chronic periodontitis, with suppuration of odontogenic cysts, and difficulty in teething. The process begins with the inner layer of the periosteum, gradually spreading to all other layers. Periostitis occurs when the focus of primary infection of the tooth canal or gum is blocked and its contents penetrate into the periosteum. The exudate penetrates through small holes in the alveolar plate through the channels.
Less commonly, flux develops in diseases of the pharynx (sore throat, pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis) or in the presence of a focus of infection in the body, from where it can be transferred to the periosteum with the blood or lymph flow.
When examining purulent contents during purulent periostitis, staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus is one of the main causes of flux development), streptococci, various types of bacilli and putrefactive bacteria are often found.
Reference! 25% of all pathogenic microflora during flux are aerobic bacteria, the rest is anaerobic forms.
General factors influencing the development of the disease:
- weak immunity;
- hypothermia;
- stressful situations;
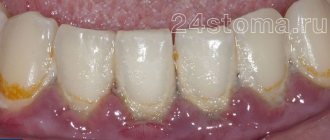
- poor oral hygiene;
- carious processes in teeth;
- old fillings;
- frequent medical interventions;
- bad habits.
Forms of periostitis
Depending on the cause of the flux and its course, we talk about its forms:
- Acute: simple – occurs as a result of a bruise of the face, with fractures and injuries of the jaw bones;
- purulent – penetration of periodontal infection to the periosteum;
- tuberculosis - when Koch's bacillus is carried into the periosteum and bone tuberculosis;
- syphilitic - as a complication of congenital or acquired syphilis.
- ossifying – chronic form with the development of compactions in the form of bone tissue;
Reason to see a doctor
If you were able to independently determine the cause of the gum swelling (an erupting tooth is visible, an injury is obvious, a tooth was recently removed, etc.) and it does not require the intervention of a doctor, you do not need to go to the clinic. But if the inflamed gum hurts for more than 3 days and there is no improvement in the condition, you should still consult a doctor.
If you have gum inflammation, you need to urgently go to the hospital in several cases:
- there was an unpleasant odor from the mouth and pus was found;
- not only the gums are swollen, but also the cheek;
- when you tilt your head to the painful side, you feel heaviness;
- there is a high temperature;
- swollen tissues are very different in color from healthy ones (white and yellow tumors indicate suppuration, and bluish and burgundy shades indicate blood stagnation);
- the pain seems to pulsate and is not relieved by analgesics.
Even in the absence of these symptoms, but if the cause of gum swelling is unknown, it is worth visiting a specialist. This will help avoid dangerous complications, as well as quickly alleviate the condition, relieve or reduce pain.
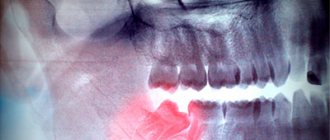
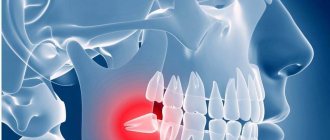
Clinical picture
The main symptom for all types of flux is severe toothache at the site of infection, sometimes diffuse (with extensive bone damage). Swelling gradually begins to increase: first it is localized above the site of inflammation, and then along the surrounding tissues, sometimes affecting the neck, temple and eye.
Important! Sometimes flux occurs painlessly or with a mild pain effect, which, as a rule, indicates the development of a chronic form with sluggish inflammation and periodic relapses.
Inflammation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pulsation at the site of the lesion;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile and febrile levels;
- headache;
- enlarged lymph nodes on the affected side;
- weakness, lethargy, lack of appetite;
- pain when swallowing, talking, opening the mouth;
- pain when pressing on the gum;
- redness of the oral mucosa at the site of the lesion.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, women often experience problems with gums. This is due to the radical restructuring that occurs in the body.
Do you want to know what causes teeth grinding during sleep in adults and how to start treatment with folk remedies? Then you need to read the following article. And you can see the photos before and after biorevitalization from the article provided at the link. Here you will find a lot of useful information about this procedure.
Also, pathological conditions develop against the background of decreased immunity, lack of vitamins, and unbalanced nutrition.
Therapy and rehabilitation
Treatment of the disease is carried out by two methods - conservative and surgical. The choice of method depends on the form of the disease, its severity, and the course of the disease. In the early stages of development of the pathological process, conservative treatment is possible by prescribing a complex of drugs:
- broad spectrum antibiotics
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- antipyretic.
IMPORTANT! Conservative treatment requires careful compliance with all doctor’s instructions until the process is completely eliminated. Otherwise, there is a risk of the disease becoming chronic.
Purulent periostitis is treated by wide opening of the purulent sac with dissection of the periosteum to the bone. At the same time, the issue of treating the tooth that caused the inflammatory process is being resolved. Most often, such a tooth is removed. After removing the pus, medications are prescribed, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Additionally, physical therapy may be prescribed: UHF, microwaves. The patient is recommended to frequently rinse the mouth with a solution of baking soda or sage tincture.
Simple periostitis requires complete rest of the injured area and treatment with physiotherapeutic procedures. All other types are reduced to treating the underlying disease or eliminating the focus of fibrous tissue growth.
IMPORTANT! Under no circumstances should you treat flux yourself. It is especially not recommended to pierce a purulent sac: there is a high risk of infection in neighboring tissues.
To speed up the treatment and recovery processes, you can resort to traditional medicine methods.
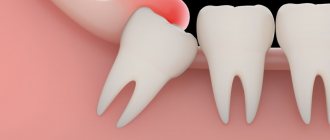
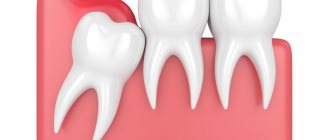
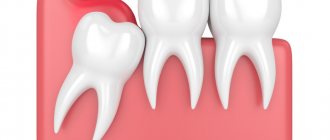
Pathology in tooth eruption
Usually in adults this problem is caused by wisdom teeth. however, nothing can be stated unequivocally; in each case, the problem is solved individually. For example, let’s look at wisdom teeth and the pathology of their eruption. The wisdom tooth begins to hurt as soon as it begins to “peck”. It moves nearby teeth and often grows in the wrong direction. Usually we drink painkillers and then go about our business. But the problem remains unresolved. The tooth continues to grow, begins to violate the integrity of the mucous membrane and forms a “pocket” in it, into which food debris gets trapped. These residues naturally begin to rot under the gums. And the pain becomes much more serious and acute. In this case, urgent medical intervention is necessary. The dentist will clean the wound and install a drainage gum so that it ensures the outflow of infiltrate. You may need to take antibiotics for some time to speed up recovery. After the situation has stabilized, the unfortunate wisdom tooth is removed. This is not done right away, because you had an active focus of inflammation in the gum, and the removal of a wisdom tooth could provoke infection into deeper tissues, which means the spread of this inflammation to the entire jaw. Such inflammation will be much more dangerous and more difficult to treat. Therefore, the treatment will be carried out in stages and will take you some time.
Prevention
Flux is easier to prevent than to treat. Prevention methods are simple and known to almost everyone. They consist of timely treatment of carious teeth, timely removal of the gum hood from wisdom teeth, the correct choice of toothbrush and toothpaste, and timely replacement of oral hygiene products. It is recommended that you visit your dentist at least twice a year and have your teeth professionally deep cleaned to remove plaque at least once a year.
IMPORTANT! Don’t forget about strengthening your immune system and giving up bad habits.
Dental flux is an unpleasant disease that requires treatment by specialists at an early stage of development. Self-medication in case of periostitis is unacceptable. With a favorable course and initial stage of development, conservative treatment is possible, but most often they resort to the surgical method.
What to rinse with?
To eliminate painful sensations, people are advised to rinse their mouths with special antiseptic solutions, for example:
- Chlorhexidine. The medicine is diluted in water in accordance with the recommendations specified in the instructions. Manipulations are carried out after brushing your teeth, no more than three times a day.
- Miramistin. The drug is able to eliminate pain and also destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
- Hydrogen peroxide.
Symptoms of wisdom tooth inflammation
To prevent a problem, you need to immediately notice the symptoms that cause it. To do this, special attention should be paid to the following points:
- there is a prolonged tugging pain;
- the gums become hard;
- the adjacent tooth becomes loose;
- body temperature rises;
- lymph nodes enlarge.
To alleviate his condition, the patient can take an analgin or paracetamol tablet at home before visiting a doctor, rinse his mouth with an antiseptic, and use only liquid food for nutrition.
If the pain is severe, you can take a painkiller pill, but you cannot suppress the pain with pills for a long time. You still need to go to the dentist.
Possible dental diseases
In 90% of cases, swelling of the soft tissues around the tooth appears with the development of periodontitis, gingivitis, periodontitis or an abscess. Other possible causes are extremely rare.
Periodontitis
With the development of periodontitis, the inflammatory process affects the bone tissue of the jaw. The cause of the pathology is the penetration of infection of the dental root canals and its spread. Swelling of soft tissues during periodontitis is caused by the accumulation of pus. If left untreated, pus may be released through the resulting fistula. The swelling subsides during this period, but the inflammation cannot be eliminated on its own. Treatment is mandatory.
Gingivitis
A distinctive feature of gingivitis from periodontitis is the development of an infectious and inflammatory process in the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. Swelling of the gums with gingivitis mainly occurs during the period of exacerbation. The swelling of the gums can be so severe that the tissue covers the tooth.
Periodontitis
The development of periodontitis occurs against the background of advanced periodontitis. Lack of treatment provokes a purulent process with a localized abscess area. With a periodontal abscess, a cavity forms under the gum in which pus accumulates. Externally, in addition to edema, a pronounced swelling in the form of a semicircle up to 1–2 cm in size appears on the soft tissue. Treatment is carried out surgically.
Traditional methods
To eliminate painful sensations, people can use folk recipes, provided there are no contraindications and individual intolerance to the components included in them:
- Soda-salt solution. To prepare it, you need to pour a glass of water into a deep container, into which soda and salt (a teaspoon each) are poured. After thorough mixing, it should be used for rinsing. You can add a few drops of iodine to the soda-salt solution. Manipulations should be carried out every two hours.
- For mouth rinsing, it is recommended to use herbal infusions made from eucalyptus, calendula or sage.
- A good effect is achieved by using chamomile infusion. To prepare it, dry and crushed grass (1 tbsp) is poured into a deep container, which is poured with boiling water (1 l). The contents of the dish should be infused for 15 minutes, after which it is filtered. The collected liquid is used to rinse the mouth.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation of the gums near the eighth tooth is accompanied by pain and discomfort. To diagnose the disease, it is necessary to take an X-ray of the tooth and take a blood test. Based on the results of the studies, the doctor makes a decision:
- Remove the tooth.
- Prescribe therapeutic treatment.
- Or cut the gum.
The gums can become inflamed and painful, most often due to the incorrect position of the tooth, which has difficulty erupting and grows in the wrong direction relative to the dental arch. The number eight can take a very long time to erupt, up to several years.