- Operating principles
- Anesthesia methods
- Indications and contraindications
- Types of anesthesia
- pain relief in pregnant women
- Anesthesia for children
- Recommendations
- Complications
- Drugs used
- Price
Nowadays, it is possible to receive medical care not only fast and high-quality, but also painless. Almost any action of the doctor that can bring discomfort or unpleasant sensations to the patient is accompanied by dental anesthesia, or in other words, “freezing”. He stops experiencing pain and fear and relaxes, allowing the dentist to calmly do his job.
Operating principles
Anesthesia is carried out immediately before the start of treatment. The anesthetic comes in both liquid and gel form. The doctor injects into the soft tissues that are located near the diseased tooth. After some time, the tongue, gums and cheeks become numb and “freeze”. At this moment, the anesthetic acts as a blocker of nerve impulses that send a pain signal to the brain. The patient calmly endures dental procedures without experiencing stress.
The duration and effectiveness of dental anesthesia depends on the quality of the materials used and the location of the injection. The closer to the problem area the injection was administered, the more intense its effect. Each organism is individual, therefore the drug will be excreted at different rates.
Different types of drugs function in their own ways. For example, gel-like ones applied to the gums or surface of the cheek last only a couple of minutes. If they are installed in the upper part of the jaw, the effect will last for 2-3 hours. To treat the lower group of teeth, a deeper injection is required, so the result lasts up to 4 hours. After the solution is absorbed, the numbness disappears and sensitivity returns to the patient.
Is it painful to treat dental caries with anesthesia?
If you treat caries with an injection, anesthesia will be given at one of the first stages of treatment. Once the tooth is frozen, it will no longer hurt. Thanks to anesthesia, tooth sensitivity will noticeably decrease, and even with deep and complex caries there will be no pain. You will feel the touch of dental instruments, perhaps minimal discomfort, but not pain. When the treatment is completed and the anesthesia wears off, your gums will hurt a little for a while after the injection. But this feeling is tolerable and will soon pass.
There are people with intolerance or allergic reactions to anesthesia for whom injection pain relief is not suitable. This does not mean that they will have to endure pain when treating dental caries. For such patients, modern dentistry can offer an alternative painless treatment method - for example, using chemical dissolution of the affected tissue or using a laser.
Anesthesia methods
Depending on the goals and nature of the problem, the doctor chooses the method of pain relief. In medicine there are two main methods:
Anesthesia
It is most often used in surgery, and in dentistry much less often, in case of urgent need. It affects the entire body of the patient, inducing a state of sleep. At this time, all muscles relax and consciousness turns off. You can administer painkillers intravenously or inhale vapors through a mask. Deep anesthesia is used during complex operations when a person does not have enough strength to cope with pain or it is necessary to completely eliminate body movement. During sleep, the doctor monitors the patient's condition to avoid emergency situations.
Recovery from anesthesia is the body’s return to normal functioning after a long “freeze.” For all people, this process proceeds differently, some experience signs of nausea or a feeling of lethargy, while others wake up well-slept and rested.
General anesthesia in dentistry during pregnancy is applicable only in emergency cases when there is no other alternative.
Local anesthesia
Unlike anesthesia, it occurs locally, affecting only certain areas of the body. Can be used for children and pregnant women, without fear of unwanted consequences. In dental practice, this method is most often used, so we will talk about it in more detail.
How to perform the manipulation
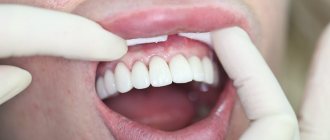
Anesthesia is administered depending on the area of the surgical intervention on the gums. For minor manipulations, the dentist uses a 2% lidocaine spray, sprinkling it on the injection site or applying an analgesic strip (Dentinox, Kalgel), waiting for the first manifestations of the analgesic.
If there are no undesirable reactions (allergic, inflammatory), the doctor proceeds to pierce the already numb gums. The injection site should be as close as possible to the diseased tooth to minimize damage to nearby healthy tissue (the development of gingivitis or periodontitis in the future).
Having opened the ampoules with the contents (analgesic), the medical specialist draws several syringes and injects the medicine into the gums layer by layer, starting from the outer layers.
Types of local anesthesia:
- Infiltration anesthesia – used in the treatment of caries, during the removal of dental nerves.
- Conduction anesthesia is when a nerve bundle is blocked during the treatment of several teeth located close to each other.
- Intraligamentous anesthesia - injection of the drug into the peribuccal fold of the mucous membrane (in the treatment of painters and pre-painters).
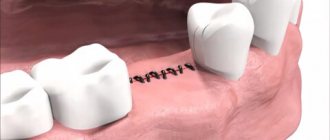
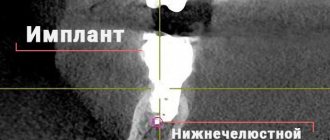
- Injection of the drug into the bone of the upper or lower jaw. Performed when implants are implanted or molars are removed, in particular wisdom teeth.
- Involvement of the nerve trunk - anesthesia for large-scale dental procedures. It is carried out with the support of an anesthesiologist in a hospital setting.
Indications and contraindications for the use of local anesthesia
Any dental intervention that causes pain must be accompanied by “freezing” of the required area of the oral cavity. There is a list of diseases for the treatment of which it is necessary to administer anesthetic drugs:
- Complex caries;
- Removal of a tooth or its roots;
- Periodontitis;
- Inflammatory processes in the dental system;
- During prosthetics.
Before drawing up a treatment plan and choosing medications, the doctor must interview the patient and find out from him the presence of contraindications in order to exclude the possibility of complications.
- Allergy to drugs used;
- Heart diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Problems with the endocrine system.
Why are gum injections used in dentistry?
Any surgical intervention (amputation of teeth, removal of nerve endings in the root of a tooth, placement of a filling) causes an unpleasant painful sensation of varying degrees. Due to fear of pain, patients often postpone visiting the dentist, which leads to deterioration of the condition of their teeth. Local injections are made to numb the gums.
Another reason for injections into the gums is the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics in the treatment of gingivitis and periodontal disease. The question arises about intramuscular injections, since such manipulations also reduce inflammation and pain sensitivity.
Dentists administer local anesthesia for greater effectiveness and speed of reaction. If the anesthetic is administered intramuscularly, its effect will occur over a longer period of time.
Contraindications
Despite the effectiveness of an anesthetic injection into the gums, there are many absolute and relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications to local anesthesia and anti-inflammatory injections on the gums:
- children under 3 years old;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- increased sensitivity to drugs;
- patients with malignant arterial hypertension;
- a history of diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
Relative contraindications to manipulation will be:
- children under 7 years old;
- presence of problems with the liver and kidneys;
- oncological diseases (refers to antibiotic therapy);
- reduced immunity;
- gastrointestinal disease.
Types of anesthesia
There are several methods in medicine; they differ in duration, effectiveness and location.
Conductor.
The most common type of local anesthesia in dentistry. Using a special needle, the drug is injected near the nerve trunk, blocking pain impulses that go to the brain. The injection is given in doses not exceeding a volume of 5 ml. To ensure a guaranteed result, the injection is placed at an angle of 90 degrees.
“Freezing” applies only to a certain group of teeth, in the place where the treatment will take place. After about 15 minutes, the medicine begins to work and the doctor can begin work.
The injection site can be additionally lubricated with lidocaine. If during the procedure the patient continues to feel discomfort, another dose may be administered.
Infiltration
It differs from the conductor only in the angle of the needle and the place of application. The drug is injected directly into the root apex area. This type is most effective for teeth and upper jaw. With infiltration anesthesia, you can “freeze” both a small area and a large surface of the oral cavity along with soft tissues.
Applique
This method is performed without a syringe. The dentist applies the necessary product directly to the diseased tooth and the soft tissues surrounding it using a cotton swab or fingers. Some doctors spray anesthetics using a special spray.
It is mainly used during simple and quick operations, since its effect is short-term and does not protect against severe pain. The result is stored for a maximum of 20 minutes. It is often used as the first stage before the injection “freezing” method.
Intraosseous
The dentist resorts to this technique much less often when other types of anesthesia have proven ineffective. An analgesic that is injected directly into the hard tissues between the teeth. The difficulty lies in the technique; to get to the bone, the doctor cuts the gum and drills a hole in it with a bur. This is the most effective method for quickly and permanently freezing the required area.
Intraligamentary
Its peculiarity is the high speed of injection, so numbness occurs almost immediately, but lasts only 20-30 minutes. The advantage of intraligamentary anesthesia in dentistry is that it acts directly on the tooth without touching the cheeks, lips and tongue. That is why the recovery process is much easier.
Painful sensations
Today, dentists use needles with a minimal diameter, so the moment they penetrate the gums is practically not felt by the patient. The damage to soft tissue is insignificant; many do not even notice that the procedure for administering the anesthetic has already been completed. That is why the issue of pain is more of a psychological nature.
Before injecting the drug into the gums, the doctor can calm or, conversely, slightly distract the person sitting in the chair. If the patient categorically refuses anesthesia, this may cause the termination of any intervention. This is explained by the fact that the slightest movements during treatment can lead to injuries and complications.
People who are prone to panic attacks or have a fear of needles may be offered treatment under general anesthesia. This will allow you to achieve the best result, because the patient will sleep, and at this time the doctor will be able to calmly carry out all the necessary manipulations in the oral cavity. You may also need to take additional sedatives, such as glycine or valerian tincture.
Features of pain relief in pregnant women
One of the most common misconceptions is that pregnant women are contraindicated for dental treatment. You should not trust unreliable sources; dentistry and pregnancy are completely compatible concepts. Expectant mothers should undergo a professional examination during planning and at 8, 18 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Untreated infections in the oral cavity contribute to the development of other dangerous diseases.
The question immediately arises: can the use of dental anesthesia harm the health of the unborn child? Modern technologies allow the use of drugs with lower concentrations of adrenaline. Accepted painkillers are ultracaine, primacaine or mepivacaine*. They do not penetrate the placenta, therefore, do not harm the body of a pregnant woman.
*A verified and accurate list of acceptable medications can be obtained from your doctor.
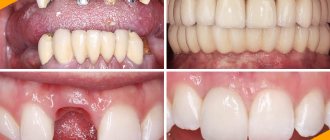
Painless dental implantation in Moscow
Some choose an implant for installation based on personal preferences or reviews of other patients, while others choose a specific design, listening to the recommendations of an experienced doctor. If you decide to restore the aesthetics of your smile and restore the healthy functionality of your teeth, we suggest having implantation done in a specialized dental office!
Our clinic employs high-level professionals with extensive experience. The initial consultation examination is free.
When treating and implanting teeth, modern technologies, high-quality materials and safe anesthetics are used to eliminate pain during treatment procedures.
Types and prices of dental implants
You can see the price list on our website. We also offer to leave your feedback on the work of our specialists and receive a 3% discount on all dental services as a pleasant bonus!
Anesthesia for children
Painless pediatric dentistry is a hot topic today. All parents know what a trip to the dentist means for a child. If this brings few pleasant emotions to an adult, then what can we say about children. The first scheduled visit is always scheduled for the age of 6-7 years - this is the time when baby teeth are replaced with permanent ones.
The psyche of children is not yet fully formed; one wrong word or action can provoke the development of unpleasant memories. Therefore, it is important to instill confidence in the child, to mentally prepare him for the procedure: explain why he is going there and what the doctor will do. The use of anesthetic agents in pediatric dentistry is an integral part of comfortable treatment.
The most suitable injection methods for babies are infiltration, conduction and application. The place where the drug is administered is “frozen” in advance and only then does the doctor give an injection. The child’s body is not yet fully formed, so in pediatric anesthesia, special medications are used that make it possible to carry out the procedure safely.
Recommendations
For the successful use of anesthetics, there are two conditions: 1) the patient must abstain from drinking alcohol at least 24 hours before treatment; 2) feel good.
Often, after the effect of painkillers wears off, the patient experiences pain, swelling, tingling at the injection site, and difficulty opening the mouth (trismus). Within 2-4 days, all residual effects should disappear.
After treatment, sensitivity returns gradually, so take the food carefully so as not to accidentally bite yourself. It is also recommended to quit smoking during this time.
How to get rid of pain after anesthesia
If the pain does not subside within a week after the manipulation, but, on the contrary, intensifies, becoming pulsating, you should consult a doctor. You should not self-medicate, since ordinary inflammation, which causes pain, can be complicated by the addition of an infection, and treatment will become more protracted and difficult.
At first, when the pain is still severe, strong non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help:
- Xefocam;
- Nurofen;
- Nimesulide;
- Ketanov.
It is important to take into account their harmful effects on the gastrointestinal tract and avoid overdoses.