This is a headache and a nightmare for any orthodontist: a patient who has had his braces removed and given a removable retainer and instructions for its use returns after some time with complaints about the curvature of his previously straight teeth. The retention period is the most psychologically difficult part of the treatment. Everything is already perfect, and then you have to wear a retainer. Yes, there are other reasons for the unsuccessful outcome of the correction. And although they are much less common, let’s talk about them in more detail.
Distal bite: what is it and how does it happen?
This is an anomaly in which the lower jaw “retracts” to the rear position, and the upper jaw protrudes forward.
The defect may be mild and almost invisible. Or it turns out to be too obvious.
Braces correct distal occlusion, but you need to seek help from a professional who has many successfully treated clinical cases.
This violation is divided into types:
- Horizontal. The incisors of the upper jaw are inclined, raised towards the lip. The lower antagonists rest against the sky.
- Vertical. The upper incisors are inclined inward, often touching the gums near the lower ones.
The chin visually appears small. Doctors name several signs
, which indicate the severity of the pathology:
- There is a minor problem when the sixth upper and lower teeth are in contact.
- If closure is not observed, the unit ends up between the fifth and sixth antagonists, then urgent intervention is necessary and a long treatment process will be required.
The distal bite can be corrected and after wearing braces the profile becomes symmetrical and proportional.
Indications for installation
There are many indications for installing a brace system; these devices help to cope with both minor malocclusions and very serious pathologies. Common anomalies: open and deep bite. In the first case, the rows may not have points of contact in the frontal zone or on the sides, and in the second, the lower jaw strongly overlaps the upper jaw in front.
Braces can also help with facial asymmetry, crossbite (one of the jaws is underdeveloped), diastal (severe protrusion of the upper jaw) and medial bite (protrusion of the lower jaw). Other indications include severe crowding, rotation of units around their axis, as well as the presence of slots of different sizes, etc.
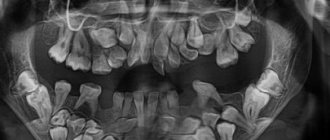
Only an experienced specialist can determine the need to install orthodontic structures and only on the basis of a preliminary examination of the patient’s oral cavity. The doctor will tell you which braces will be most effective and will solve existing problems as quickly as possible. The orthodontist will also tell you about all possible complications and symptoms that should alert you.
Signs of distal bite
Distal occlusion requires mandatory intervention from a specialist; treatment with braces is indicated; aligners can be used (especially when the diagnosis is made in childhood).
Signs of distal occlusion:
- The child spontaneously bites his lower lip
:
- The profile is slightly beveled. To define it, the term “avian” is used.
- The lips are thin and fall inside the oral cavity
. If you visually draw a line from the tip of the nose to the middle of the chin, then the lips will not appear on it:
- The lower third of the face is disproportionately small. A crease appears on the chin due to the jaw moving back.
It is possible to correct distal bite without braces when treatment is carried out in childhood. Aligners are approved for installation in children with baby teeth. They are installed in older preschool age, when the child can consciously follow the dentist’s recommendations.
In my practice, there are already more than 300 successful cases of bite correction using aligners. This is a promising method. Invisalign and FlexLiner aligners have proven themselves to be excellent in the treatment of distal occlusion. Star Smile aligners also correct this dental pathology quite well, although they require more careful attention from the attending physician. Whether correction of distal bite with aligners is right for you or your child can only be said with confidence during a consultation.
Standard consequences of treatment
After the installation of the glands, the patient may experience an unpleasant feeling, since the braces put pressure on the jaws. The oral cavity hurts, sometimes bleeds, and the teeth themselves often begin to loosen. Doctors explain: this reaction is associated with the complex structure of the jaw.
The incisors and canines are connected to the bone structure by strong ligaments, which are protected by thick tissue and are thus stable in one place. The intrusion of braces' locks into this structure forces the tooth to move with itself into the desired position. The tissue that holds the jaw tissue in place weakens. This is followed by a weakening of all elements of the oral cavity.
Loose teeth do not mean illness. This may be a natural reaction to interference in the body. A slight change in the position of the tooth can accompany the entire process of wearing braces. If the gums are not red or bleeding, and the person himself does not experience pain, then there is nothing to worry about. But if doubts persist, you should contact the dentist for a consultation. Timely medical intervention helps avoid exacerbations.
Reasons for the appearance of distal bite, why it is dangerous
The causes of the defect may be genetic disorders, especially in cases where relatives had a similar diagnosis.
Sometimes the occurrence of pathology is facilitated by a lack of nutrients, microelements, as well as bad habits.
– sucking toys, pacifiers.
Often, instead of a pacifier, the child uses a finger to suck
- which undoubtedly contributes to the development of distal occlusion:
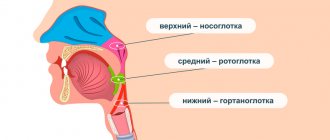
The structure of the dental apparatus is disrupted in the presence of untreated diseases of the nasopharynx - breathing through the mouth provokes weakening of muscles, ligaments and jaws shift.
Correction of distal bite with braces is necessary. If you ignore pathology, you will have to overcome many problems.
Problems arising from distal occlusion:
- Diction is broken.
- There is no adequate chewing of food, not all foods are convenient to eat. Gastrointestinal ailments or somatic diseases develop.
- It is difficult to get dentures in the future.
- Uneven load often leads to loosening of units and destructive changes in tissues.
The dentist will make an initial conclusion during the first examination and order imaging to clarify the diagnosis.
Loosen to move
When installing a turnkey bracket system , the orthodontist first of all takes care of making the teeth mobile under the traction of the orthodontic arch, after which they can be forced to move along the calculated trajectory. And if they started to stagger, it means everything is going according to plan. How is it possible to first move them from their usual position, and finally re-fix them in the jaw bone?
Teeth with braces become loose due to the coordinated work of cells such as osteoblasts and osteoclasts. The dental crown and root are connected by a ligament, which, in turn, is supported by bone tissue. When the tooth begins to tilt under the influence of traction, the distance between the crown and the ligament increases on one side and decreases on the other. Osteoblasts begin to make up for the lack of bone tissue in order to support the tooth in a new place, and osteoclasts begin to remove the “excess” and dissolve it. In this case, the compressed connective ligament straightens out over time, and the tooth has the full right to take the new position planned by the orthodontist.
The cycles of resorption and growth during orthodontic treatment are repeated many times, causing a kind of “rejuvenation” and strengthening of bone tissue and, of course, correcting the dentition. But since it takes a lot of time to increase tissue density, and resorption occurs faster, the teeth remain mobile for a long time.
Treatment: distal bite before and after braces
From 11-13 years of age (early adolescence), distal bite is corrected with braces, treatment gives good results. Within a year and a half, the pathology disappears. Adults will need more time. The structure is a metal arc fixed on overlays glued to the enamel. The wire has a “memory effect” - gradually the lower jaw develops and takes on a physiologically justified position.
But a child with baby teeth is not given braces. How to correct a distal bite without braces? In this case, aligners come to the rescue - mouth guards made of transparent synthetic, absolutely harmless to the body. The child can easily take them off and put them on, they quickly get used to them. Visually, custom-made mouth guards are almost invisible. The growth of the lower jaw is stimulated. Intervention from 7-8 years is considered optimal. The tissues are flexible, and the child already understands the importance and necessity of treatment. Plates are also effective in childhood, but as aligners develop, they are placed a little less frequently.
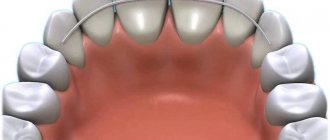
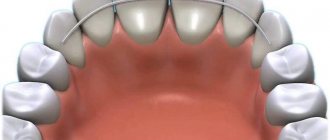
To consolidate the effect, after removing braces, retainers are installed or mouth guards are used. After the braces are removed and the distal bite is corrected, you can forget about the imbalances that were observed before the intervention. And pay attention to what changes have occurred after treatment: the face becomes symmetrical, facial expressions become varied. The lips are already expressive and take on clear outlines. The person becomes uninhibited.
Don't ignore the problem. Come to me for an appointment, and we will choose the appropriate method for correcting your distal bite, taking into account your characteristics.
Contraindications
In addition to the indications for installing braces, there are also contraindications. They are usually divided into relative and absolute. The first ones are only a temporary obstacle; they can be dealt with by contacting a highly qualified specialist. This usually includes the presence of small neoplasms on the soft tissues of the oral cavity, as well as inflammatory processes.
Periodontal disease and periodontitis are not absolute contraindications; after a course of therapy, you can begin installing braces. Also, structures can be installed after treatment of bruxism, if the patient has crowns and artificial teeth. Having an allergy to metal will not be a contraindication, since today braces are made from a variety of materials.
Absolute contraindications are those that cannot be eliminated (HIV, oncology, diabetes and others). In this case, the patient may be offered alternative solutions to existing pathologies.
How can I help the process?
While the tissues are weakened and the teeth are loose, it is necessary to prevent excessive stress on them.
- You should not chew whole hard carrots and hard apples, or bite caramels, nuts and seeds.
- Avoid viscous and sticky foods - dried fruits, toffees and chewing gum.
- Don't bite your nails, pens or pencils. In this way, you will not only protect weakened teeth, but also maintain the integrity of the braces system.
- Preference should be given to porridges, vegetable purees, and meat pates.
In order for bone regeneration to occur normally and the teeth to not become too loose by the time the orthodontic structure is removed, you need to include in your diet foods containing proteins, as well as all the necessary minerals and vitamins.
Mouthguards
Mouthguards or aligners are also used to correct malocclusion in adults. They are made from plastic or silicone. This device is placed on the teeth and the teeth are gradually straightened. The mouth guard is removable, making it easier to care for your teeth.
It is used if braces cannot be installed. Also, a mouthguard is always used after correcting the bite in adult patients with braces. This is a must, otherwise the teeth may return to their original position.
Mouthguards for teeth straightening are standard, thermoplastic, and individual. They are expensive and ineffective in complex cases.
What are braces
Braces are a surprisingly laconic design, where each element is assigned a significant role. The main parts of the device are:
- Orthodontic arch. A special feature of the wire component is the memory effect. This means that the arc has a given shape and always strives to return to its original position. During this process, the wire gently pulls the braces, and with them the teeth, which leads to alignment of the dentition and correction of the bite. The metal arc is the main element of the design, as it is responsible for the speed and quality of correction. The power element is made from medical alloys - with different stiffness and cross-section.
- The bracket is the plate that gives the name to the entire system. The bracket is fixed on the tooth with special glue in a place precisely calculated by the orthodontist. Each tooth has its own bracket; the plates differ in angle of inclination.
Types of braces according to the method of arch attachment
There are two ways to attach an orthodontic arch to braces:
- Using ligatures. Ligatures are special rubber bands or small wires that attach the arch to the bracket. This design is called ligature, and is especially loved by children and adolescents. Doctors' arsenal of rubber bands contains shades of all colors, which makes bite treatment more fun and brighter. Ligatures need to be changed every 1-1.5 months, which allows young patients to constantly update their appearance.
- With the help of locks - a groove and a closing lid. The system is called self-ligating or non-ligating and has its advantages. When wearing braces with locks, you need to visit the doctor less often, treatment is faster, and adaptation is smoother. During passive operation of non-ligature devices, the arc moves freely. With the active version of self-ligation, the lock rigidly fixes the arc, pressing it to the base of the metal groove.
Additional elements of braces
It is difficult to understand how braces work and how bite correction occurs if you do not take into account additional elements of the system. They are placed by orthodontists according to indications to solve specific problems:
- Springs - help to move the teeth apart in order to accommodate a separate protruding unit.
- Rubber chains – pull teeth together to eliminate pronounced gaps, threes, and diastemas.
- Elastics – create and strengthen the applied force vector to move the tooth.
The decision on the structure and features of the orthodontic structure is made by the doctor after diagnostics and diagnosis.