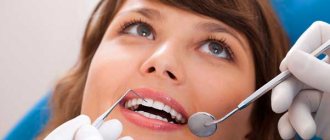
30.05.2019
Progress does not stand still! It is with this obvious truth that I would like to begin today’s article. This applies to all areas of our lives, and by a happy coincidence, dentistry included! Every year, more and more new materials enter the dental market: safer, more aesthetic, and more practical to use. A constantly developing dentist now has in his arsenal high-tech devices and modern materials that allow him to provide high-quality, comfortable, and most importantly, safe dental care.
However, this was not always the case. Just some 10-15 years ago, treatment methods were still actively used that were not only unaesthetic, but also far from safe. The most striking example of this is amalgam fillings.
In historical essays, fillings similar in composition began to be used more than 100 years ago. Amalgam was an alloy of various metals, such as mercury, silver, tin, zinc, copper, etc.
The creation of such a material was made possible thanks to the ability of mercury to dissolve other metals in itself.
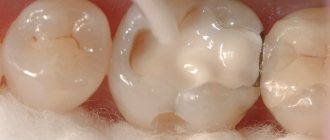
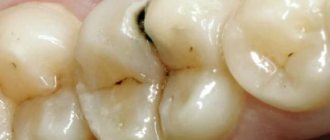
Example of an amalgam filling (work taken from the Internet)
Its main advantages were considered to be: strength, lack of visible abrasion and chipping, antiseptic properties of silver, and the ability to inhibit the progression of caries. The last point is very controversial, because under amalgam fillings, in the vast majority of cases, we find a recurrence of caries.
Obvious disadvantages include:
- Low aesthetic characteristics (metallic colored filling);
- Inability to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth (cusps and fissures);
- High thermal conductivity (increased sensitivity when eating cold and hot food);
- Technical difficulties at work.
And last but not least -
- Constantly released mercury vapor into the oral cavity.
The last point is now being studied especially carefully. After all, scientists have proven that mercury is a heavy metal that cannot be eliminated from the body on its own. Moreover, it has a destructive effect on human nerve cells. And if the patient has amalgam fillings in the oral cavity, on the side teeth, the structural elements of these fillings permanently enter the human body. Thus, chronic toxic effects of heavy metals occur.
Doctors all over the world have recognized the harm of amalgam and not only refused to place such materials, but also urgently recommend getting rid of such fillings.
Relatively recently, in the United States, the dental association created standards for the safe removal of amalgam fillings. This is called the SMART protocol. The essence of this protocol is that it is necessary to minimize the contact of the removed filling with the body of the patient, as well as the doctor and assistant.
Used in dentistry for about 200 years
It is known that amalgam dental fillings were invented a long time ago. The first mentions of it are found in the documentation of the Middle Ages. However, specialists began to use it widely and everywhere only in 1855. It was then that its composition was first patented and then improved by American dentists.
What you need to know about amalgam fillings
Until the early 2000s, dentists in Europe, the USA, the Soviet Union and the Russian Federation actively placed amalgam fillings on teeth. Later, a number of studies appeared that proved the harm and toxicity of the material, which is why many doctors stopped using it in their practice, and some countries even banned the use of amalgam.
To do this, the following requirements must be met:
- The skin, hair, and clothing of the patient and medical staff must be carefully covered.
- The seal is drilled with a special bur that does not create dust, with the supply of a large amount of water.
- The procedure for removing amalgam fillings is performed in a rubber dam using a hood or vacuum cleaner.
- It is necessary to ventilate the office after this manipulation.
The process of removing an amalgam filling (example provided from the Internet)
All these conditions must be observed, because during the removal of the filling, toxicity increases tenfold.
Important information! Patients during pregnancy and lactation should avoid removing amalgam fillings to avoid negative effects on the child’s body.
At the Atribeaute Clinique aesthetic dentistry department, strict monitoring of compliance with the SMART protocol is carried out. After excision of amalgam fillings, we carry out restoration with a composite material that can completely restore the aesthetic and functional characteristics of the tooth, while remaining 100% safe and hypoallergenic for the entire period the restoration is in the oral cavity.
Tooth restoration with Enamel composite material (the work of dental therapist Tamara Valerievna Kudzieva)
Important!
Composition of modern amalgams:
- silver (66–73%), provides strength and resistance to corrosion, causes expansion when hardening;
- tin (25–29%), increases the plasticity of amalgam;
- copper (2–6%), gives strength and ensures that the filling adheres to the edges of the cavity, also has antibacterial and anti-corrosion properties;
- zinc (up to 2%), reduces the oxidation of other alloy metals;
- mercury (up to 3%), the main reagent, solvent, causing the formation of amalgam.
When is it better to choose a different composite?
Dental amalgam has a number of contraindications. Thus, its use is not allowed if the patient has an individual intolerance to the components included in its composition. The material is also not used if the patient has dentures or crowns with metal fragments in his mouth.
The remaining contraindications will be similar to all restrictions that are relevant for filling with any other materials. It should be noted that many refuse this option due to an exaggerated fear of mercury poisoning. The material is only suitable for restoring chewing teeth; for restoring a smile, you should choose a more aesthetic option.
What determines the service life of a filling?
As already mentioned, the average lifespan of a filling is about five years, but it is optimal to determine it individually, since it depends on a number of factors:
- Properties and characteristics of the filling material that was used;
- The dentist’s compliance with technological processes during installation;
- The condition of the unit being sealed (the degree of its destruction, the thickness of the walls);
- Hygienic measures of the oral cavity (regularity and correctness of their implementation, brushes and pastes used by the patient);
- Regular consumption of hard foods and sugar.
There are cases when, provided they are installed correctly and provided with good care, fillings can serve patients well for more than ten years.
Main advantages
The material turns out to be very plastic, and therefore easy to apply and simple to work with. After free mercury is released, it hardens on its own, meaning restoration does not require the use of expensive equipment.
What other advantages are there due to the composition:
- high strength and wear resistance, ability to withstand any chewing loads,
- long service life: from 10 years or more with careful care,
- possibility of installation in a damp tooth cavity,
- anti-corrosion properties,
- antibacterial effect,
- preservation of shape and color,
- good penetrating ability: in the presence of zinc in the composition, it penetrates well into small cracks in hard tissues and seals them,
- high radiopacity.
Amalgam was sent for MRI
But almost simultaneously with reports of regulation of the use of amalgam fillings in Europe, data from Turkish scientists appeared. And this time we were talking about the direct effect of the mercury they contain on the human body.
A laboratory experiment was conducted. Teeth with amalgam - removed, of course - were placed in a test tube with saliva and exposed to a magnetic field, as in an MRI. After exposure to a magnetic field of 1.5 tesla (this is what is used now in most tomographs), there was no significant increase in the mercury content in saliva. But in those test tubes that were exposed to a magnetic field of 7 Tesla, five times more mercury was released. Devices with such a powerful magnetic field are already used in laboratory research, but there are almost none in hospitals. True, their introduction into everyday practice is just a matter of time.
Scientists have not yet expressed a categorical opinion on how dangerous the release of mercury into saliva during MRI is. To do this, you still need to know how much of it can stay in the body.
Research will continue. And their benefits are undoubted. One hundred and fifty years of practical use of amalgam is a good argument. But our living conditions and technologies are changing. And what some time ago did not pose any danger can now manifest itself in unexpected ways.
Disadvantages of an amalgam filling
The use of silver-based filling material, with all its advantages, also has disadvantages that cannot be ignored.
- Metallic shine. Because of this, amalgams are used exclusively on the back teeth, since use on the “facade” would make the smile extremely unaesthetic.
- The lengthy hardening process of the material will require at least a second visit to the dentist for final grinding and adjustment to the bite.
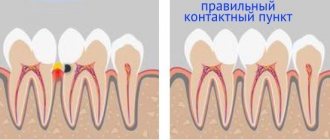
- Metal has the ability to expand and contract under the influence of temperature differences. Over time, this can lead to the formation of microgaps under the edge of the filling and, accordingly, the development of secondary caries.
- The high thermal conductivity of the material in some cases can increase the risk of thermal injury to the tooth with the subsequent development of pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Galvanosis. This reaction is associated with a mutual reaction to other metal products present in the oral cavity. Galvanosis has dangerous consequences for the stomach. That is why, if a crown needs to be placed on a tooth, the dentist will be forced to remove the amalgam filling.
If the patient decides to use a budget option, the doctor will first have to make sure that such material will not cause harm. In addition, due to the fact that dentists often switch entirely to working with composites, it is better, in order to avoid problems in the future, to find a specialist who will install such a filling as efficiently as possible.
Our dentistry works with a wide range of materials, their latest variations. Our specialists hone their filling skills regularly, which guarantees high quality of service!
How to remove a filling and replace it
Removing filling material requires very careful cleaning of the cavity and complete disposal of used raw materials. A drill is not suitable for this - the seal is cut crosswise, after which it is carefully removed in parts. Instead of a diamond bur, special steel cutters are used. The surrounding space must be isolated with a rubber dam.
All seized items are placed in a sealed case and disposed of in accordance with established regulations. However, it is not recommended to remove the filling during pregnancy and breastfeeding. In all other cases, experts advise taking activated charcoal and vitamin C before removing or replacing.
Do you have mercury in your mouth?
Mercury in your mouth?
How is this possible! It turns out that it is very possible. Some people have no idea that they have been carrying this metal inside them for many years. And for the average person there is no more dangerous chemical element than mercury. It is used in dental practice in amalgam fillings. For those who don't know, these are fillings that look like metal patches. They are also called silver. They are not very aesthetically pleasing, so they are usually placed on chewing teeth. But it is quite reliable, some even consider them eternal.
Types of amalgam
Doctors use different amalgams to fill teeth. They differ in the concentration and ratio of metals in the composition. Some types contain a lot of silver and very little copper (less than 6%) - this is called silver amalgam in dentistry. In others, on the contrary, copper predominates - it can account for up to 30-37% - this variety is called high-copper and is considered the most advanced of the existing ones. There are options with and without zinc, as well as with the inclusion of expensive and rare metals (palladium, platinum).
Photo: mercury amalgam fillings
Read the article on the topic: types of dental fillings. Find out which ones are considered the best today.
A few words about components and properties
The material is obtained by dissolving metal alloys in mercury. The finished substance is moderately plastic, which allows you to accurately recreate the shape of the future filling. Free mercury gradually disappears and the material hardens. Sufficient strength for constant chewing load is achieved only after a day. The composition contains the following main substances:
- silver – prevents the spread of corrosion and provides high strength,
- tin – partly responsible for plasticity, prolongs the hardening process,
- copper – has anti-corrosion properties and provides an additional antibacterial effect,
- zinc – softens other components,
- Mercury – represents the main trigger or reactant.
The material contains many different metals.
In professional medical terminology, there is a definition that describes the chemical reaction of mercury leading to the formation of an amalgam - mechanochemical synthesis1.
How filling is carried out - description of the process in stages
The installation of an amalgam filling can be divided into several independent stages. Let's take a closer look at this sequence:
- preparatory measures: this includes cleaning the teeth from plaque and stone, administering anesthesia and fixing the rubber dam. Next, the doctor prepares the carious cavity, removes all affected tissue and carries out disinfection treatment. In this case, the thickness of the tooth walls should be slightly greater than required when filling with modern composites. A small cut should be left at the junction of enamel and dentin to improve retention. The tooth is washed and dried,
- application of a gasket: required to reduce tooth sensitivity, which can develop due to the increased thermal conductivity of the material. Its optimal thickness is 1-1.5 mm,
- amalgam mixing: carried out mechanically using a special electric mixer,
- installation of a filling - amalgam is applied in small layers using a special gun, waiting until it completely condenses before the next application. It is important to prevent the material from becoming porous and to remove all excess mercury. The cavity is filled, after which the edges are carefully removed, immediately forming a preliminary crown shape.
The amalgam is applied in small layers.
The final modeling of the restored area involves the application of tubercles and fissures. After this, occlusion control is required, for which special articulation paper is used. The filling itself is ground and polished only after a day. In this process, it is important to prevent overheating and evaporation of mercury, so water cooling is usually used.
Three hundred fillings are dangerous
Metal fillings consist of 50 percent mercury, the rest is copper, silver and other metals. It is impossible to do without mercury: thanks to it, the mixture retains plasticity at room temperature, which makes it possible to fill the prepared tooth cavity with the composition.
This material has been used for filling in the treatment of caries for a long time - more than one and a half hundred years. And this is the main argument of dentists in favor of the safety of amalgam. During all this time, not a single proven case of the adverse effect of such fillings on the human body has been recorded. Even if there are ten amalgam fillings in the mouth, the mercury content does not exceed a level that is harmless to humans. To cross this border, doctors reassure, you need to have 300 such fillings, which, of course, is impossible.