Sinusitis due to tooth pain is far from a rare occurrence. Doctors even distinguish a separate type of this disease - odontogenic sinusitis, that is, caused by inflammation and infection mainly in the roots of the teeth. Why does this happen? How to deal with this? And can, on the contrary, teeth hurt with sinusitis?
From the point of view of anatomy and physiology, it is not surprising that an infection from a tooth easily passes into the maxillary sinus and vice versa. Despite the fact that there is an anatomical barrier between them, it is very easy to overcome. Violation of its integrity can occur either through the fault of the patient or as a result of unqualified actions on the part of the dentist. However, when answering the question of whether it is necessary to treat teeth for sinusitis, doctors unequivocally say yes. But only with a competent specialist under the supervision of a radiovisiograph or x-ray. Dental treatment is best done outside the acute phase, however, in advanced cases, urgent surgical intervention may be indicated.
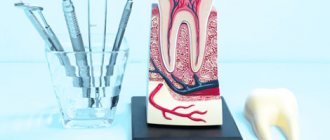
Structural features
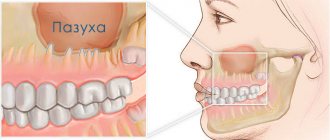
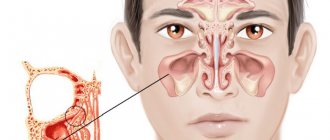
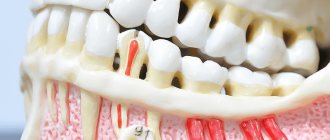
The maxillary (maxillary, main) sinus is located inside the bone of the upper jaw. It is delimited from the oral cavity by the alveolar process. It forms the bottom of the cavity. The volume of the cavity of the upper jaw can be up to ten cubic centimeters. She has a communication with the nasal cavity. The inside of the cavity is lined with mucous tissue.
The structure has features that make it easy to damage:
- Sometimes the thickness of the bone plate between the bottom of the cavity and the roots of the teeth does not exceed one millimeter.
- There is a variant of the location of the roots of the second and first molars, when they penetrate into the cavity and are delimited from it only by the mucous membrane that lines the sinuses.
- The bone plate quickly thins out during inflammatory processes.
- Small thickness of trabeculae of the upper jaw bone.
Such structural features cause slight damage to its wall, even when the doctor did not violate any rules and did not apply significant force.
What is perforation of the maxillary sinus?
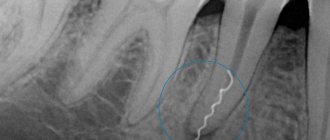
The formation of a defect in the maxillary sinus is a complication during manipulations on the upper jaw. A hole is formed between the oral cavity and the main sinus. This can happen when removing the molars of the upper jaw (molars and premolars) or during prosthetics. And also for complex endodontic treatment of tooth roots and removal of cystic formations. The defect is formed at the site of the tooth socket.
Rehabilitation after maxillary sinusotomy
In the period after surgery, the patient may need tamponade on the operated side for 8-24 hours. After endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy, it is enough to take painkillers according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician.
It is necessary to maintain oral hygiene: brush your teeth, gargle with antiseptics and follow all consultations with your doctor.
After studying the reviews about sinusotomy, you can understand whether maxillary sinusotomy is right for you. The price depends on the choice of operation.
Causes of perforation.
The dentist is not always to blame for this complication. It can often appear due to the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient. It may also be due to the course of the inflammatory process in the tissue surrounding the root.
The causes of perforation may be the following:
- Perforation of the maxillary sinus during tooth extraction occurs most often. Its bottom is perforated when a tooth is suddenly removed with great force.
- In some patients, the roots of the upper teeth penetrate into the sinus cavity. When teeth are removed, the integrity of the bone plate is automatically violated. During treatment, filling material may enter the cavity.
- For technically complex endodontic treatment. With this type of treatment, the inflammatory focus is located deep in the gums or under the root of the tooth. Instead of removing the diseased tooth, the dentist tries to save it. During this type of treatment, the bone plate is easily damaged.
- In the process of installing an implant in the upper jaw bone with subsequent dental prosthetics, the maxillary cavity can be easily damaged. This is because the implant is similar to a screw and must be screwed into the bone. If there are defects in this manipulation or anatomical and topographical features, the patient’s bone plate of the upper jaw may be damaged (the size of the implant was incorrectly selected, there were defects in preparation for implantation). Before placing an implant, the doctor does not take into account the fact that when a tooth is removed, the thickness of the bone plate quickly decreases.
- Perforation can occur due to chronic inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth (periodontitis). With this pathology, the bone plate delaminates and becomes thin. If a tooth has to be removed in such a situation, perforation almost always occurs.
- Carrying out manipulation to remove an impacted tooth from the maxillary cavity.
- Perforation often occurs during tooth root resection procedures. The need for this manipulation arises when extracting a root with a festering cyst.
Prevention
Perforation of the maxillary sinus is a problem that is easier to avoid than to fix it later. Since perforation is caused by dental intervention, preventing the problem falls on the shoulders of the dentist. He is obliged:
- responsibly examine the patient before performing procedures;
- clearly understand the anatomical features of the client before major intervention;
- strictly adhere to the intervention technology.
The dentist is also obliged to respond adequately to any signs of perforation that has just occurred due to his fault. If for some reason the doctor has not fulfilled his own duties, then it is up to the patient - he must refuse self-medication and put aside the fear of dentists, in no case try to “endure” the discomfort, but immediately seek help.
Symptoms of perforation of the maxillary sinus
How does perforation of the maxillary sinus manifest itself? There are specific symptoms when this happens.
Signs of perforation:
- Bleeding from the tooth socket with the inclusion of air bubbles. When you exhale through the nose, the number of bubbles will increase.
- With perforation, bleeding occurs not only from the tooth socket. It may come from the nasal passage, which is close to the sinus.
- The patient speaks “in his nose” or nasally.
- Then there is a feeling of free passage of air through the tooth socket.
- The patient sometimes notes distension and a feeling of heaviness in the middle third of the face on the affected side.
If the perforation was not recognized immediately and treatment was not carried out, then the symptoms of sinusitis are added to the previous clinic.
Sinusitis manifests itself:
- Body temperature rises.
- The feeling of fullness in the projection of the maxillary sinus intensifies.
- Nasal breathing is difficult.
- The nasal mucosa on the affected side is swollen.
- General weakness increases.
- Aching pain in the nasal region.
- Purulent discharge from the nasal passage on the side where the manipulation took place.
Classification and manifestations of pathology
According to the duration of the disease:
- acute - no more than three weeks;
- subacute - duration of illness up to 6 weeks;
- chronic - the disease lasts more than 6 weeks.
Depending on the location of the inflammation:
- pathology on the left;
- pathology on the right;
- bilateral pathology.
When pathology develops due to an extracted tooth, unilateral sinusitis most often develops, but if left untreated, the infection can spread to both sides.
In any case, the disease manifests itself with the same symptoms, but in acute pathology they are more pronounced:
- nasal congestion;
- profuse mucous or purulent runny nose;
- pain from the extracted tooth (localized in the cheek or under the eye);
- throbbing headache;
- pain when tapping on the cheekbones;
- fever;
- general intoxication syndrome - fever, chills, weakness
A distinctive feature of odontogenic sinusitis is its connection with previous dental procedures.
Methods for determining perforation
This pathology can be identified only on the basis of a characteristic clinic. If there is any doubt, a full range of diagnostic procedures is performed, including instrumental methods.
To diagnose a bone plate defect and subsequently eliminate it, it is necessary to perform the following manipulations when examining the patient:
- Carefully examine the tooth socket after the tooth root has been removed.
- Perform sounding of its bottom.
- Ask the patient to pinch their nose and exhale through the nose. The air will escape into the mouth through the tooth socket.
- If the patient puffs out his cheeks, air passes into the nasal cavity. But this technique can provoke sinus inflammation and should not be used frequently.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- probing the dental and perforation canal using a thin probe;
- CT scan;
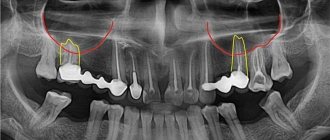
- radiography, in the pictures you can see the defect and foreign bodies;
- general blood analysis.
Treatment of sinus perforation during tooth extraction
The tactics for managing a patient with perforation depends primarily on the condition of the sinus itself and the time of detection of this defect. This defect should only be treated by a qualified specialist.
Treatment of perforation of the main sinus of the upper jaw has the following objectives:
- Closing the defect.
- Prevent the process of inflammation in the sinus.
- Prescribe treatment if there is inflammation.
- If there are foreign particles, they must be removed.
If the perforation was immediately noticed and there are no signs of infection, then the treatment measures are as follows:
- Preservation of a blood clot in a tooth socket.
- Take measures to prevent its infection (application of a tampon with iodine solution).
- Apply stitches to the gums, if necessary.
- Treatment is carried out until the granulations grow and the defect is closed.
- The tampon is not removed from the hole.
- If the defect does not close on its own, it is covered with a plastic plate. It is fixed to the teeth.
- Prescribing a course of drug therapy aimed at counteracting inflammation.
If the perforation is complicated by gum rupture and penetration of foreign particles into the soft tissues surrounding the tooth socket, plastic closure of the defect is performed on the same day. Or after some time, when you are confident that the fabric will hold the seams. Before this, all foreign bodies are removed and areas that have undergone necrosis are excised. The manipulation is performed under x-ray control to make sure that there is no foreign body. If penetration of a foreign body into the cavity occurs, then it is necessary to perform surgery in a hospital setting.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removal of a tooth from the maxillary sinus (its fragments) and other foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas.
- Closing the defect.
Why you should entrust treatment to the ENT department of dentistry
ENT dentistry is a symbiosis of two medical areas, a multidisciplinary approach to the treatment of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses of odontogenic origin. Only an experienced maxillofacial surgeon with ENT training can make an accurate diagnosis and create a sound rehabilitation plan.
As a rule, odontogenic causes of sinusitis are simply ignored during routine examination by an otolaryngologist. Treatment in a city clinic without high-quality diagnostics or in the absence of it at all turns into a multi-part series with monthly visits to an ENT doctor, dragging on for many years, causing inconvenience and worsening the quality of life.
Unified drug therapy or traumatic sinus punctures are prescribed, which, if they bring relief, are for a short time. Inflammation from the acute stage becomes chronic with periodic exacerbations. A person runs from one doctor to another to no avail, but without identifying and eliminating the cause, odontogenic sinusitis cannot be cured !
Consequences of perforation of the maxillary sinuses
If the presence of a defect is not noticed and the patient, despite the symptoms, does not consult a doctor, this threatens the onset of serious and dangerous consequences for health.
Possible consequences:
- Severe inflammatory reaction.
- Formation of osteomyelitis.
- Generalization of infection.
- Development of abscess and phlegmon.
- Loss of healthy teeth in the fistula area.
- Chronic sinusitis.
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Cavernous sinus thrombosis.
To avoid the formation of complications, the patient should visit the dentist in case of any problems after tooth extraction.
Old sinus perforation
If the defect is not detected and eliminated in a timely manner, acute inflammation will subside. Within a month, the patient develops a fistula. It connects the gum surface and the sinus cavity. Signs of a chronic inflammatory process appear. This will be a serious complication.
The patient has complaints:
- The presence of dull pain in the upper part of the cheek, of a constant nature. They radiate to the eye area and temporal region.
- Feeling of nasal congestion on one side.
- Separation of pus from the nose and from the fistula on the upper jaw.
- Swelling of the middle third of the face on the affected side.
- Air movement through the defect.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Getting fluid from the mouth into the nose.
Therapy of old processes is associated with significant difficulties. Patients are indicated for surgical treatment in a hospital.
Operation stages:
- Opening of the main sinus of the upper jaw.
- Removing foreign bodies.
- Excision of necrotic areas and granulations.
- Excision of tissues forming the fistula.
- Closing the defect.
After the operation, drug therapy with the use of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs is mandatory for a course of two weeks.
Diagnostics
The odontogenic form of sinusitis often remains undetected by ENT specialists due to the lack of highly accurate diagnostics and banal ignorance of the “dental” cause of the disease. Such gaps lead to the fact that even after medical and surgical treatment the person continues to suffer.
Differential diagnosis is extremely important, which allows you to determine the form of sinusitis and select the appropriate treatment.
Only computed tomography provides informative 3D images for visualizing bone and adjacent soft tissues, the condition of the teeth, the presence of foreign bodies and neoplasms in the sinus.
In our Center, CT scans are performed on a Sirona Gallileos dental tomograph with ENT mode settings.
In some cases, it will be necessary to study the microbial composition of the sinus lining to rule out a malignant process.
Advantages of treatment in our clinic
Summing up, we can understand that it is very easy to get a septal defect in the cavity of the upper jaw. This depends both on the actions of the dentist and on the individual anatomical characteristics of the patient.
When seeking treatment at our clinic in Moscow, you can be sure that you are guaranteed not to have such complications. We prevent complications.
To do this, we prescribe a mandatory set of preventive measures to prevent them:
- We conduct a complete examination of patients before performing any dental procedures.
- We perform a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s anatomical and topographical features.
- We follow all stages of dental procedures.
You will be satisfied with the quality of dental services if you contact us at the clinic. Our clinic has the most modern equipment at the level of the standards of the best European and American dental clinics. We can offer you a full range of all diagnostic procedures in one place. Our doctors have been trained in the world's leading dental centers and are proficient in the latest treatment and prosthetic techniques. We will help even in the most difficult cases. We develop an individual course of treatment taking into account all the characteristics of the patient. We use only proven treatment methods and materials of the highest quality. Our clinic has made the highest quality dental services available. You can view the full range of our treatment and diagnostic capabilities on our website.
How to avoid
There are only two ways to prevent the development of odontogenic sinusitis:
- Treat your teeth in a timely manner, prevent infection of the dental canals and spread of inflammation beyond the apex of the tooth root.
- Contact proven clinics with experienced doctors, the opportunity to conduct a thorough diagnosis and provide for an emergency situation.
In our Center, not a single dental procedure, especially at the border with the maxillary sinuses, is performed without a thorough X-ray examination using a computed tomograph.
The study is carried out using
a high-precision Sirona device with the Galileos diagnostic software package.
Based on the results of computed tomography, we determine the location of the roots and the size of the bone septum. This makes it possible to plan treatment in such a way as to avoid risks.
Tooth extraction operations and other interventions in the area of the maxillary sinuses in our Center are performed only by maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training . Deep knowledge of the anatomy of the maxillary region allows you to avoid mistakes that a regular dentist might make. But each case is individual, and even if something goes wrong, our doctors are always ready for any turn of events and correct the situation.