A condition in which a certain area of the tongue or an entire organ loses sensitivity is called paresthesia.
There are many reasons why the tip, middle or root of the tongue goes numb. These include both the impact of external factors and serious diseases that require immediate medical intervention.
Why does tongue paresthesia occur?
The main reasons that provoke numbness of the tongue include the negative influence of external factors and diseases, one of the symptoms of which is paresthesia. External factors include: excessive smoking, allergic reactions to foods and medications, injuries, injuries, burns, intoxication.
The tongue goes numb with the following diseases:
- A decrease in the sensitivity of the tongue may mean that a person has malignant tumors in the larynx or in the brain. This condition in neoplasms is not the main symptom; paresthesia accompanies severe headaches (in the case of brain cancer), nausea, low temperature and blood pressure. Oncological diseases of the larynx, in addition to numbness, are manifested by pain in the throat (as with ARVI), impaired sensitivity of the palate, unpleasant sensations and difficulties when swallowing.
- The tongue may become numb due to an incipient stroke or heart attack.
With this condition, paresthesia of the hands, tongue and lips is one of the main symptoms. Additional symptoms include acute headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can cause impaired mobility, damage and numbness of the nerve endings of the tongue. Osteochondrosis may cause pain and dizziness.
- Violation of the psycho-emotional background. Severe stress and deep depression can provoke severe headaches, impaired sensitivity of the face, lips, and mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Psycho-emotional disorders are the cause of migraine with aura - a disease in which the head hurts severely and the functioning of the senses is disrupted.
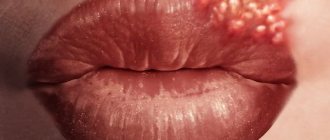
- If the tip of the tongue becomes numb and hurts, a burning or tingling sensation occurs, it means that the person has developed glossalgia or glossitis.
Manifestation of different forms of glossitis of the tongue
- Diabetes mellitus, which occurs as a result of impaired insulin production, leads to a feeling of thirst, dry mouth, and partial loss of tongue sensitivity.
- Anemia can cause decreased sensitivity of the oral mucosa, numbness of the extremities, low temperature, pale skin, and poor coordination.
- Age-related changes. A woman during menopause experiences hormonal imbalances that can cause tongue numbness.
- Oral candidiasis is a disease that is accompanied by pain, plaque formation on the mucous membranes, itching, swelling and partial numbness of the tongue.
- Impaired functioning of the facial nerves (Bell's palsy). The pathology is expressed in partial paresthesia.
Paresthesia can be caused by transformations that occur in the body of a pregnant woman.
Sore throat
Discomfort and sore throat with VSD occurs due to spasms of the muscles of the pharynx and larynx. If patients feel a lump in the throat during VSD, an experienced neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital will tell you how to get rid of this symptom.
A sore throat occurs in patients with VSD during the daytime. Many people experience serious stress when this symptom appears, as they consider discomfort in grief to be a manifestation of dangerous diseases, such as a malignant tumor or goiter of the thyroid gland. To eliminate throat discomfort, many people prefer to drink water, which brings temporary relief, but to completely eliminate the symptom, it is necessary to get rid of the root cause.
Determining the cause of tongue numbness by symptom localization
The tongue may lose sensitivity partially or completely. It is necessary to pay attention to which part of the organ is numb, since localization may indicate a specific disease.
Paresthesia begins with tingling of the tip of the tongue, then “running goosebumps” appear over the entire surface of the organ, and only after that there is a feeling of partial or complete numbness of the tongue.
In most cases, numbness in the tip of the tongue is a sign of the negative impact of external factors.
This condition manifests itself with excessive smoking, alcohol consumption, intoxication, imbalance of vitamins and minerals in the body, especially with a lack of vitamin B12. Loss of sensitivity of the tip of the tongue can be caused by an allergic reaction, in which case the symptom will be accompanied by swelling and paresthesia of the oral mucosa.
Numbness of the tongue and hands, accompanied by an acute headache, requires immediate consultation with a neurologist. Paresthesia in tandem with migraine can signal a sharp drop in insulin and an increase in blood sugar. In this case, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary.
Neoplasm in the larynx
Paresthesia of the throat and tongue indicates the occurrence of malignant neoplasms in the larynx. Numbness of the tongue and palate may be a manifestation of an allergic reaction. Injuries or damage to the glossopharyngeal nerve cause the root of the tongue to become numb.
A condition in which the tongue becomes numb and dizzy can be a symptom of VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), osteochondrosis, neurological disorders and disorders, pre-infarction or pre-stroke condition.
Sweating
Excessive sweating with VSD is a common symptom in which people try to get rid of the problem on their own. Self-medication for vegetative-vascular dysfunction can lead to the development of other manifestations of VSD.
Disorders in the functioning of the nervous system cause excessive sweating, which makes a person feel insecure. A lump in the throat with VSD and other symptoms if left untreated can cause consequences. Thus, with increased sweating, a favorable environment is created for the development of infections. The protective functions of the skin gradually deteriorate, so the skin can be affected by fungus.
To reduce sweating, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital recommend that patients get rid of bad habits, adhere to proper nutrition, and maintain a daily routine. During sessions, psychotherapists at the Yusupov Hospital help patients reduce anxiety and learn to relax.
Professional treatment for tongue numbness
Loss of tongue sensitivity is not an independent disease, but a symptom accompanying the underlying pathology. Only after identifying the reason why the tongue is numb will the specialist prescribe treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease or irritating factor.
In cases where paresthesia is caused by osteochondrosis, the following are indicated:
- physiotherapy;
- massage manipulations;
- physiotherapy;
- taking painkillers and drugs that enhance bone tissue regeneration.
Injuries that cause the feeling that the tip of the tongue is numb are treated with antiseptic rinses and dental gels. Allergic reactions that reduce the sensitivity of the organ are eliminated with antihistamines.
VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia) is treated with drugs that increase blood circulation and dilate blood vessels in the brain. It is recommended to change the diet, introduce a nutritious diet, follow the rules of rest and work: 8-hour sleep, active lifestyle.
Oncological diseases require surgical intervention coupled with drug therapy
, at the initial stage of the disease, endoscopy can be done. In case of laryngeal cancer, the affected tissue is removed; in case of pharyngeal cancer, partial removal is performed, followed by restoration using plastic surgery.
Trigeminal neuralgia can be treated surgically, but destruction of the nerve is often required. Radiosurgery, a minimally invasive (bloodless) operation, is sometimes used.
Numbness caused by diabetes mellitus is eliminated after a course of treatment of the underlying disease. Injections or tablets are prescribed to normalize insulin levels, which eliminates dry mouth, thirst and loss of sensitivity.
Possible complications
This disease does not threaten health, but significantly reduces the quality of life. If you ignore an unpleasant symptom, glossalgia can become chronic. Its symptoms will occur from time to time, exacerbating the unstable psycho-emotional state. Against the background of pain, anxiety, eating disorders, sleep disorders, nervousness, and phobias can develop. As the condition worsens, treatment should be carried out not only by the dentist, but also by other specialists - a neurologist, psychiatrist or psychotherapist.
A long-lasting symptom can cause forced dietary restrictions, which can affect the overall health and cause vitamin deficiencies, weight loss, and lack of minerals.
Possible complications include inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. For example, a lack of saliva can lead to aphthous stomatitis, and when exposed to adverse factors or injuries, the likelihood of glossitis, gingivitis and other ailments increases.
Treatment of tongue numbness with folk remedies
Depending on the cause of numbness in the tip, root, or sides of the tongue, treatment may include alternative medicine methods. Rinses and compresses can significantly improve the condition and speed up the restoration of sensitivity.
Common traditional medicine recipes used for diseases of the oral cavity:
- A spoonful of soda and 4 drops of iodine are dissolved in a glass of warm water. Rinsing is done daily, morning and evening.
- If the cause of numbness in the mouth is a disorder of the nervous system, the use of chamomile and sage in therapy is effective.
In addition to pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, plants have a calming effect. Two tablespoons of dry herb are brewed with a glass of boiling water, the decoction is infused for 15 minutes. The resulting infusion is used for daily rinsing of the mouth and for oral administration: take 1 tablespoon. - A tablespoon of St. John's wort and the same amount of celandine are poured into a glass of boiling water and infused for about 30 minutes. The resulting infusion should be used to rinse your mouth morning and evening.
- You can fight lost sensitivity of the tongue with the help of garlic. To do this, take a garlic clove and roll it in your mouth. The procedure should be done as often as possible. After using garlic, apply a compress with sea buckthorn oil to the tongue, which will prevent possible irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Dried femoral grass is poured with a glass of water, brought to a boil, and then boiled for about 5 minutes. The broth must be filtered and cooled. Rinsing is done twice a day, after which 1 tablespoon of infusion is taken orally.
Numbness of the tongue is a sign of a serious pathology, and not a separate disease. It is important to determine the root cause that caused the loss of organ sensitivity, and only a doctor can do this. Therefore, it is necessary to contact a therapist as soon as possible, who, after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures, will redirect the patient to the right specialist. Timely identification of the cause of numbness and timely treatment will help prevent the development of the underlying disease and possible complications.
Diagnostics
The cause of tongue numbness is determined by a dentist. Patients with neurological symptoms are referred for consultation to a neurologist. In the absence of manifestations of dental and neurological diseases, an extensive examination is carried out with the involvement of a gastroenterologist, psychiatrist, and other specialists. To make a diagnosis:
- Dental examination.
The doctor assesses the condition of the tongue, identifies areas of epithelial desquamation, cracks, and signs of inflammation. Examines the oral cavity for other changes, specifies the type of fillings and dentures. - Neurological examination
. For isolated pathologies, curtain and pharyngeal reflexes and the excitability of the muscle fibers of the tongue are examined. For neurological diseases, reflexes, muscle strength, and sensitivity in various parts of the body are examined. - Saliva studies
. The water indicator is determined using special strips. Potential differences are measured to detect galvanic currents. The subjects are prescribed sialography and ultrasound of the salivary glands. - Other instrumental techniques
. For glossodynia and glossalgia, electromyography is performed. If diseases of the digestive system are suspected, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and gastroscopy are performed. - Lab tests
. As part of a laboratory examination, microscopic and microbiological examination of saliva, general and biochemical blood tests, and determination of the acidity of gastric juice can be performed.
Examination of the tongue