Defects appear from tobacco smoke as a result of sedimentation of resins, from high levels of fluoride in the water that the patient constantly drinks. The situation is negatively affected by insufficient hygiene, as a result of which caries develops. Irregular cleaning of the chewing organs leads to the accumulation of soft and hard brown deposits. Such defects cannot be dealt with without the participation of a dentist. Contact your doctor in a timely manner to avoid complications.
Reasons for color change
Have you noticed that the filling on your tooth has darkened? Several factors could have contributed to the color change.
- Consumption of coloring products. A newly placed filling can become darkened by strong tea, black coffee, chocolate, red wine, grapes, and concentrated fruit juices. The composite can also become colored when consuming carrots, beets, blueberries, cherries, and carbonated drinks with dyes.
- Smoking. Tobacco smoke causes resins, plant alkaloids, and organic acids to settle on restored teeth, causing them to acquire a yellowish or brown tint.
- High levels of fluoride in water and food. Drinking low-quality water and foods high in mineral content can cause multiple stains on your teeth.
- Insufficient oral hygiene. If you don't clean your teeth well, stains will remain on them and bacterial plaque will accumulate. This can lead to secondary caries.
Who is susceptible to changes in the shade of the filling?
Unfortunately, some patients experience darkening of their fillings more often than others. There may be several explanations for this. The most common factors include, of course, smoking and poor oral hygiene. It is important to understand that teeth need to be cleaned of plaque not only in the morning and evening, but also after every meal.
The filling can also be affected by existing caries underneath or around it. If the professional does not completely clean the affected areas of the tooth, tooth decay can continue to destroy the tooth from the inside. Also, the filling may become stained due to frequent consumption of black tea, strong coffee, natural juices and red wine.
To prevent darkening, it is recommended to reduce the frequency of smoking and avoid foods and drinks that contain bright dyes. Also, do not neglect preventive examinations at the dental clinic, where you can periodically clean the oral cavity using any of the modern methods.
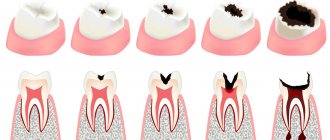
Types of darkening of restorations
Most often, fillings on teeth darken evenly. Fresh fillings may become stained in the first hours after placement if you consume coloring products. Old restorations are also subject to uniform discoloration:
- due to the effects of low and high temperatures,
- narrowing or expansion of the filling.
Less commonly, composite restorations darken around the perimeter. This occurs due to the fact that the filling material has not completely filled the carious cavity. Pathogenic microorganisms and food particles penetrate into a small crack, which leads to darkening and destruction of the filling.
Associated symptoms
In addition to blackening of the enamel, other symptoms may develop:
- The appearance of erosions, gouges, black spots or spots on the enamel.
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Mobility of the filling.
- Pain when pressing, tapping or chewing.
- Inflammatory process in the gums around the filling, bleeding of the mucous membrane, swelling. The appearance of bumps or gumboil in an advanced stage.
Changes in tooth color should not be ignored. This is a clear sign of a pathological process.
Diagnostics
The task of diagnosis is to determine why the filling material and the dental elements underneath have turned black. Professional techniques will help identify the presence of caries and the extent of damage in order to make a final decision on removal or treatment.
Diagnosis consists of a visual examination, as well as an x-ray examination. If concomitant diseases of the oral cavity are suspected, additional diagnostic methods can be used.
Prevention
You can prevent blackening of a tooth under a filling with the help of effective prophylaxis. To avoid the need for re-treatment, you should follow several rules:
Firstly, follow all the hygiene instructions of doctors - brush your teeth in a timely and regular manner, using the right toothpaste, floss, and rinses. Secondly, undergo preventive examinations in a timely manner in order to identify and treat any diseases in the early stages, before complications arise.
Try to avoid temperature changes - do not eat hot and cold food at the same time, do not drink hot drinks in the cold. Avoid traumatic effects - do not gnaw hard food (nuts, seeds) with filled teeth. Treat any infectious diseases in a timely manner, including those that are not directly related to the oral cavity.
Get rid of bad habits that disrupt the body’s activities and weaken its protective functions. Do not skimp on tooth restoration and, if the filling has darkened, replace it in a timely manner.
Treatment after diagnosis
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment begins. It depends on how much caries has developed again. Secondary caries can occur on the chewing surface, and if the lesion is small, the entire filling may not be removed. It is enough to clean only the affected area and drill out the filling a little, then seal the cleaned area with the same material.
If the entire tooth is destroyed and caries penetrates deep into the roots, the filling will have to be completely removed. Actually, the treatment continues according to the usual traditional scheme. First, the doctor cleans out the damaged tooth tissue. If the caries has reached the nerves, they will also have to be removed (here you will have to be patient, otherwise neither the patient nor the tooth may be able to withstand the third attempt to cure the tooth).
After this most painful procedure, you need to treat the drilled cavity with an antiseptic to make it sterile for sure. After this, fill the tooth and polish the surface of the filling so that frequent friction due to the uneven surface will deteriorate it and not break prematurely.
Sometimes, if the caries under the filling is deep and has reached the roots, sometimes the treatment is delayed for several visits to the doctor, but usually no more than two. Those who have a tendency to develop caries should be very careful about preventive measures and dental and oral hygiene.
When to eat mono after filling?
People who have ever had a filling installed know that you can eat no earlier than two hours later. This time is enough for the material to acquire the required hardness and be well fixed in the tooth crown.
Modern materials differ from classical composites, so the question of whether it is possible to eat after a light filling is relevant. Dentists have different opinions regarding how long after a light filling can be eaten without the risk of damage. Some experts are of the opinion that after a light filling you can eat immediately. This is explained by the properties of photopolymers. The material hardens under the influence of ultraviolet rays, which means that after the procedure is completed, the filling should not be exposed to external influences.
However, the risk is not completely excluded. For complete confidence in the readiness of the material, and most importantly, its reliable fixation in the tooth. For this reason, most experts, when asked “how long not to eat after installing a light filling,” recommend refraining from eating and drinking for at least 2 hours.
Errors during the preparation stages and secondary caries
When a tooth under a filling turns black and hurts, this may be the result of poor-quality endodontic treatment. Go to another clinic and be examined using a microscope. This will make it possible to recognize even microscopic errors in previous therapy. From this, secondary caries often develops. It is provoked by shrinkage of cement that is not placed tightly. At the same time, the size of the lining decreases, which creates cavities between the material and the tissues of the masticatory organ. Bacteria thrive in such holes.
Removing an old filling requires the dentist to thoroughly clean the cavity. However, it happens that blood, organic remains, and pus remain inside the unit. When destroyed, they cause a defect in the chewing organ in the form of brown spots. Leaky application of cement or incomplete removal of pathogenic pulp also leads to problems. Common mistakes made by doctors:
- The dentist may not completely dry the tooth cavity before placing composite cement.
- Laying the material in a thick layer at a time, instead of applying it in small portions.
- Careless polymerization.
- Incomplete cleaning of pathological dentin.
After such mistakes, caries forms again. Patients complain of increased sensitivity of crowns, changes in their shade, mobility of the embedded glue, and bad breath. In this case, therapy is needed. First, the defective material is removed, then the cavity is cleaned, then treated with an antiseptic. Finally, a new composite is installed and polymerized.
The tooth under the filling hurts. What does the treatment method depend on?
When treating secondary dental caries, the dentist must choose the right tactics: either correct the filling, or remove it and refill the cleaned and treated cavity. In some cases, after removing the affected tissue, the cavity turns out to be so large that to restore the dental crown it is necessary to use special inlays or cover the treated tooth with a crown made from an impression.
- There is no need to remove the entire filling if the chewing surface in the area of only one of the walls of the carious cavity has suffered from secondary caries. Necrotic tissue is removed, a cavity is formed and filled with the same filling material. Then the filling is ground and polished.
- If the infection has spread to several sides or around the entire filling, it is removed, the cavity is formed and treated, and the filling is refilled.
A filling fell out - how will they treat it?
It all depends on the specific case. Before treatment, the tooth cavity is cleaned with a drill machine to remove any remaining filling material.
- Part of the filling has fallen out - the remaining part is removed and re-sealed.
- A filling with a piece of tooth falls out - they make a filling or install an inlay (more reliable than a regular cement filling). In case of radical destruction of the crown, pins are installed, and then (for greater tooth strength) an artificial crown.
- A filling with a pin has fallen out - if the root is intact, the pins are re-installed into the tooth and covered with a crown. If, after a filling falls out, a tooth breaks (the entire crown part falls off) and the roots are damaged, it is necessary to remove the remains of the tooth and install a prosthesis (bridge or implant).
To minimize the risk of a filling falling out, contact the First Family Clinic of St. Petersburg. Experienced dentists provide high-quality treatment for caries and reconstruct teeth after the filling has been destroyed.
Signs of violations
Blackening of a tooth can be discovered by chance - for example, when replacing a bridge, one of the supporting teeth turned out to be dark. Or, the fact that there is a rotten or decaying tooth under the crown is indicated by indirect signs:
- An unpleasant odor that is noticed by the patient himself and those around him.
- The tooth reacts to temperature and strong tastes. If you run your tongue over the crown, you will notice a gap between it and the gum.
- Pain. Periodic or constant. Or itching or other strange sensations.
If one of the symptoms appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. Even when there is no sharp pain and unpleasant sensations appear and go away on their own. The tooth under the crown has already begun to deteriorate and the sooner treatment is started, the more effective it will be.
Uniform darkening
If after a few days or weeks you suddenly see that the installed filling has evenly changed its color and has become, for example, pink or yellow, this most likely indicates a violation of your dentist’s instructions. Perhaps you did not listen to the advice of a specialist and ate some coloring vegetable or drank strong coffee without milk.
To eliminate this defect, be sure to seek help from your doctor. He will be able to polish the composite material and perform a high-quality cleaning, as a result of which the filling will again become its original color. After this, you will not be able to eat food containing dyes for some time. Otherwise, all the efforts of the master will be in vain.
Old fillings are also susceptible to staining. This may be due to the fact that the patient exposes them to too sudden temperature changes, that is, he may eat ice cream and drink hot tea at the same time. All this leads to changes in the volume of the filling: it can imperceptibly narrow and expand. As a result, microbes and food particles penetrate into the small cracks and cracks that form. This filling can either be replaced or polished.
Methods for diagnosing and treating caries under fillings
It is quite difficult to determine the presence of secondary caries in the initial stages, due to the absence of symptomatic and visual manifestations. The disease is diagnosed during a follow-up appointment using diagnostic equipment (hardware diagnostics).
Diagnostics includes two stages:
- Anamnesis and initial examination of the causative tooth in order to detect visible structural changes in hard tissues;
- Hardware diagnostics (physiography) is aimed at detecting hidden changes in the structure of dental tissues.
If a pathology is detected, treatment is prescribed taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
A child's fillings fall out of his baby teeth
The destruction of fillings on baby teeth is associated with the following factors:
- Enamel and dentin in children are much weaker than in adults.
- The skills of proper brushing of teeth are not sufficiently developed.
- Frequent dental problems associated with dirty hands.
- Fidgets injure their teeth by falling and chewing hard objects.
- Children love to drink cola. With constant consumption of a drink containing phosphoric acid, teeth are destroyed and fillings fall out.
- Parents mistakenly refuse to install an inlay or crown on a badly damaged tooth for their child; instead, they insist on building it up.
What to do if a child’s baby tooth filling falls out? Re-filling is required. Tooth extraction is not advisable, as problems with bite may arise in the future. Leaving a damaged tooth without a filling is also not worth it. Repeated caries will negatively affect the condition of the rudiments of permanent teeth.
Causes of secondary caries
Can caries develop under a filling? The answer here is simple and categorical - yes. It is believed that in the first two to three years after filling, the likelihood of a problem occurring is highest, but this complication cannot be tied to a specific time frame. It is also necessary to understand the terminology: sometimes experts mistakenly combine recurrent, or recurrent, and secondary caries. The differences here are obvious: recurrent caries develops in the place of a poorly treated old carious cavity, while secondary caries covers previously healthy tissue under the filling. However, the recurrent carious process is also partly secondary, has a similar nature and is treated using the same methods.
Why does caries develop under a filling? The disease occurs due to an increased concentration of pathogenic microorganisms. Several factors can lead to this.
Causes of caries under fillings
- During the preparation process, not all affected tissues were removed (the main cause of recurrent caries).
- Violation of the rules of antiseptic treatment. During the treatment, an infection was introduced, which provoked the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Poor quality treatment of the tooth surface at the point of contact with the filling.
- Low quality filling material or significant shrinkage of the filling. Zinc phosphate and amalgam fillings are most susceptible to shrinkage. Caries under a light filling is less common, but this quality (albeit to a lesser extent) is also characteristic of them.
The above points are the main reasons for the development of secondary and recurrent caries, but there are also additional factors that increase the risk of such complications. These include poor hygiene, poor nutrition, bruxism, mechanical and thermal effects on filled teeth.