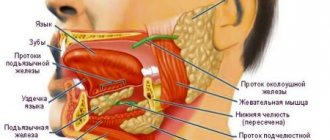
What is tongue swelling, and how dangerous is it?
Edema is an increase in volume of an organ. The tongue may swell and increase in width, and also partially, for example, when a tumor-like lump forms in some place. Such conditions are extremely alarming; they may indicate the progression of a dental disease or an allergic reaction.
Note! Tongue swelling should not be confused with a slight swelling on the tip of the tongue that appears after biting or eating hot, sour foods.
Edema may also be accompanied by the following symptoms of various diseases:
- choking cough and sneezing;
- profuse lacrimation;
- rash on the surface of the face and body;
- feeling of a “lump in the throat”;
- itching in the mouth and sore throat;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- difficulty swallowing;
- speech problems;
- swelling of the tissues of the oral cavity and face;
- feeling of a foreign body in the mouth, etc.
It is important! The most dangerous symptom is swelling of the tongue at its root, when the tissues block the airways, the person feels a sharp suffocation, blushes, and rolls his eyes upward. In such situations, you should urgently call an ambulance or provide emergency first aid to the patient.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Why does my tongue go numb?
External reasons
Short-term numbness of the tongue is provoked by the consumption of certain foods. The tip of the tongue often goes numb in heavy smokers. Sometimes the symptom occurs when drinking strong alcoholic drinks, in a state of intoxication. In young children, a temporary decrease in sensitivity may be caused by compression of the tongue when trying to insert it into small cavities, for example, a tube or a construction element.
Dental manipulations
The tongue becomes numb for a short time after dental anesthesia; normally, sensitivity is completely restored after a few hours. If the rules of the procedure are violated, the symptom may persist for a long time. Long-term paresthesia is sometimes observed after the removal of wisdom teeth, near which there are branches of sensory nerves.
Constant numbness often worries people with metal dentures and fillings. The reason is the interaction of several metals in a liquid medium. Under the influence of saliva, a galvanic current is produced, which irritates the mucous membrane, causing paresthesia and numbness.
Other medical effects
Taking medications with anesthetics (throat sprays, bellasthesin, which eliminates stomach pain) causes numbness of the tongue lasting up to several minutes. More severe reactions occur with the development of neurological complications of local anesthesia due to the absorption of a large amount of the drug or its erroneous injection into a vein. Numbness of the tongue and oral cavity is accompanied by dizziness, metallic taste, ringing in the ears, and tremors. Convulsions, disturbances of consciousness and speech are possible.
When performing a behind-the-ear blockade, numbness of the tongue is observed normally; it is a marker indicating that the needle has hit the right place. May persist for 24 hours after the procedure and may be associated with slight dizziness. Long-term or permanent loss of sensitivity sometimes results from operations on the ENT organs and facial structures and is associated with compression or mechanical damage to the nerves.
Numbness of the tongue
Glossalgia
It manifests itself as constant or periodic numbness, rawness, tingling, burning of the tongue. Symptoms become more pronounced during a conversation, with excitement and fatigue, and decrease while eating. The tongue and oral mucosa are not changed. Glossalgia is a functional disorder that often develops in patients with neuroses, depression, and psychosomatic diseases. Secondary glossalgia is provoked by the following conditions:
- Diseases of the digestive system
: gastritis, cholecystitis, hepatitis, pancreatitis. - Endocrine pathologies
: hypothyroidism, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, diabetes mellitus. - Damage to the central nervous system
: condition after ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, neurosyphilis. - Diseases of peripheral nerves
: sympathalgia, damage to the hypoglossal autonomic ganglion and glossopharyngeal nerve. - Connective tissue diseases
: dermatomyositis, scleroderma.
Glossodynia
Numbness, burning, tingling, itching, crawling sensation and the presence of hair are bilateral in nature, occurring on the tip or anterior 2/3 of the tongue, less often in the root area. At the initial stage, the attack lasts several minutes. Over a long period of time, the area of discomfort increases. Severe paresthesia persists for several hours; even outside an attack, patients are bothered by constant discomfort. Hyposalivation is often observed. Glossodynia is caused by:
- Gastrointestinal diseases
: colitis, gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer. - Endocrine disorders
: diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies. - Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels
: ischemic heart disease, hypertension, atherosclerosis. - Diseases of the nervous system
: vegetative-vascular dystonia.
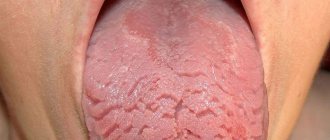
Desquamative glossitis
The disease may be asymptomatic or accompanied by numbness, tingling, and burning. Areas of whitish-gray plaque form on the tongue, in place of which red or bright pink smooth spots form. The affected areas quickly become covered with epithelium and are replaced by other lesions, so the appearance of the tongue is constantly changing.
Nervous diseases
Numbness of the anterior sections of the tongue develops when the third branch of the trigeminal nerve is damaged, the posterior sections are damaged by the glossopharyngeal nerve, and the root is damaged by the vagus nerve. The cause of damage is trauma, compression by a tumor or inflammatory infiltrate, or germination by malignant neoplasia. After irradiation for oncological processes, radiation neuralgia is possible. In addition, impaired sensitivity of the tongue is detected in the following diseases of the nervous system:
- Stroke.
The symptom appears suddenly, complemented by muscle weakness and sensitivity disorders of half the body, speech disorders, and facial asymmetry. - Epilepsy.
Numbness of the tongue is detected as part of the aura before partial attacks. May be combined with dizziness, weakness, nausea, drowsiness, chest pain, ringing and noise in the ears, and a feeling of a lump in the throat. - Acute encephalopathy.
The pathology is provoked by intoxications and dysmetabolic disorders. It manifests itself as numbness of the tongue, severe headache, unsteadiness of gait, vomiting, and visual disturbances. - Neurocardiogenic syncope.
The symptom occurs before fainting, lasts no more than 2 minutes, and is accompanied by nausea, dizziness, auditory and visual disturbances, anxiety, and a feeling of imminent fall.
Other reasons
The list of other pathological conditions accompanied by numbness of the tongue includes:
- Parasitic diseases
. The symptom accompanies many helminthic infestations, and is especially often found with ascariasis and acariasis. - Emergency conditions
. Loss of tongue sensation is observed in victims with delayed cyanide poisoning. Complemented by a metallic taste, pain and heaviness in the heart area. Gives way to convulsions and subsequent paralysis. - Mental disorders
. Numbness of the tongue sometimes occurs during panic attacks. Some patients with hysterical neurosis complain of paresthesia and sensory disturbances.
Why does swelling of the tongue still occur?
We list the most common reasons why an organ may swell:
- an allergic reaction resulting in Quincke's edema;
- glossitis disease or an inflammatory process that affects the tissues of the tongue;
- hypothyroidism or diseases of the endocrine system;
- infectious diseases, when the tongue may suddenly swell;
- injury caused by a broken piece of tooth, or incorrect prosthetics;
- disruption of the metabolic process;
- malignant formations;
- complications caused by piercing, etc.
An experienced doctor will help determine the true cause of swelling of the tongue, who will diagnose the oral cavity under the careful supervision of the patient.
How to help a child?
It is worth understanding that these habits do not arise on their own and not because of bad behavior. Comments and reminders that you should not stick your tongue out will not work - you need to work with the root cause of the disorder.
- Restore nasal breathing.
Orthodontists often prescribe consultations with an otolaryngologist, since the dental system and respiratory organs are closely connected. Removal of adenoids, treatment of chronic diseases, normalization of the microclimate at home to reduce the frequency of acute respiratory viral infections, hardening and other restorative procedures - all this can be prescribed by a doctor to achieve remission.
ENT can help restore health for proper tongue function
- Contact an orthodontist.
Only in this order, otherwise the treatment will not be effective. As soon as the child is able to breathe with his mouth closed, you can move on to correcting the position of the teeth and tongue.
For this purpose, children's orthodontic devices have been created:
- Plates.
- Trainers.
- Twin Block device.
- Children's aligners Kinder Smile.
All these devices are removable and act quite gently, guiding teeth during the period of their active growth. Wearing requires parental supervision, but with proper use, problems are solved quite quickly - within a few months.
Only after this can you begin classes with a speech therapist - when the malocclusion and the main manifestations of tongue dysfunction are eliminated, the correction of sound pronunciation will be much more successful.
First aid for angioedema of the tongue
We have already spoken above about first aid - here we will give an example using a specific clinical case with a patient.
Angioedema is considered one of the most dangerous, often leading to death, as it occurs extremely quickly. Not only does a person’s tongue swell, but the neck, inner surface of the mouth, larynx, cheeks, eyelids, lips, and the entire face may also swell. The skin becomes blue, the tongue turns white, and tearing occurs.
What can be done first in case of angioedema of the tongue before the ambulance arrives?
- clear the airways of mucus;
- raise your head a little so that the swollen tongue does not block the airways;
- give an antihistamine, preferably administered intravenously;
- monitor the patient's condition and wait for an ambulance.
Tongue dysfunction: how it affects teeth
The habit of breathing through the mouth, including during sleep, leads to increased tongue dysfunction. The child begins to stick out his tongue more often (and the tongue is the strongest oral muscle), make additional efforts and press his tongue on the teeth.
What will happen to the teeth if such a habit develops?
- A diastema may form - a gap between the front teeth.
- The contacts of the teeth in the frontal region may be disrupted, then an open bite will appear - a pathology that is quite difficult to correct: it causes noticeable harm to the condition of the teeth, since the entire load falls on the chewing teeth in the lateral regions.
Open bite in a child
- The front teeth can rotate (turn around their axis) or form a protrusion - a forward tilt.
Children's teeth are quite pliable, as the child grows, the size of his jaws and the space in the row of teeth constantly increase. Therefore, the effort exerted by the tongue is quite enough to move the teeth, but they will no longer be able to return back to the correct position on their own.
One more problem
In addition to orthodontic disorders, difficulties with pronouncing sounds will increase. Speech therapy correction is designed for the correct structure of the teeth and the functioning of the tongue, so classes with a speech therapist will be very long and ineffective if the main cause of poor diction is not eliminated.
First aid for allergic swelling of the tongue
Another common picture is when the cause of swelling of the tongue is taking medications or foods that cause allergies.
The first aid for allergies is to stop taking the food or medication that caused the swelling.
You should definitely take antihistamines and report the situation to your doctor. If your allergy does not allow you to go to an appointment on your own, call a doctor at home.
You should also remember the drug or product that provoked the swelling and allergy, and exclude its presence (and drugs with a similar active ingredient) from your life for the future.
Principles of treatment
The treatment regimen proposed by the doctors of the Leto clinic is aimed at restoring normal psycho-emotional status, eliminating symptoms that bother the patient and preventing secondary complications. If the tongue twitches during neurosis or other symptoms of the syndrome are pronounced, drug treatment is indicated. It includes:
- sedatives;
- non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics;
- according to indications (for example, for severe insomnia) - antipsychotics;
- B vitamins, tocopherol, omega complex;
- nicotinic and ascorbic acid, drugs based on adenosine triphosphoric acid, glycine;
- iron supplements.
Various physiotherapeutic procedures that have a relaxing and calming effect have proven themselves well. We recommend:
- massage of the collar area;
- ozone and oxygen therapy;
- transcutaneous and transcranial electrical stimulation;
- hirudotherapy;
- laser therapy.
Regardless of clinical manifestations, neurotic disorders are an indication for consultation with a psychologist. The doctor will help the patient understand the cause of such unpleasant sensations, tell him how to properly respond to conflict and stressful situations, and help him find a solution to the problems that bother him.
Tongue neurosis is a rare disease, but quite amenable to outpatient treatment. You can get more detailed information from our consultants by calling 24/7 anonymous phone number 8(969)060-93-93 .
Causes
The causes of tongue swelling can be very diverse, ranging from injuries to allergies. It can be:
- mechanical trauma of the tongue;
- inflammation of the tongue or glossitis (causes and treatment of glossitis);
- infectious diseases;
- allergic reaction;
- anaphylactic shock;
- metabolic disease;
- thyroid disease (hypothyroidism);
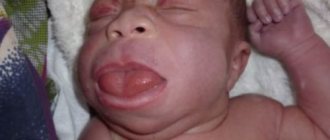
- genetic disorders (Down syndrome);
- malignant tumors (sarcoma, oral cancer);
- injury due to uncomfortable dentures;
- piercing;
- pellagra;
- pernicious anemia;
- pituitary disorders.
Only an experienced doctor can differentiate oral diseases that cause swelling of the tongue.
Swelling of the tongue and throat can be dangerous to the health and life of the patient. Don't self-medicate! At the first sign of swelling, you should consult a doctor for help. If swelling develops too quickly and begins to make breathing difficult, call an ambulance to avoid suffocation.