All parents watch with trepidation how their newborn baby develops. Some changes bring joy, while others cause anxiety. So, many people don’t know what to do when their baby starts teething. To distinguish this natural process from a cold and not harm the baby, you need to listen to the opinion of the authoritative doctor Komarovsky.
- 2 When is there no reason to worry?
- 3 Warning symptoms
- 4 Colds or first teething
- 5 What should parents remember?
- 6 Komarovsky on teething
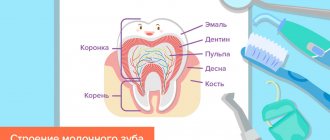
Features of teething
Young parents often come across stories on the Internet about how their children cut teeth. A couple of such stories are enough to begin to mentally prepare for sleepless nights , constant whims and crying. Of course, there is some truth in this, but in most cases, eruption is not as difficult as Dr. Komarovsky says.
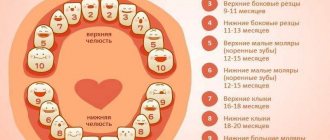
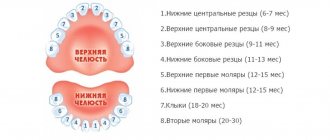
The timing of teething depends on various individual characteristics. So, one child’s first teeth appear at 3 months, while another’s teeth appear closer to a year. In some cases, a young mother notices the first tooth only during feeding.
How and what to feed a baby when teething
The reaction to teeth depends on the individual characteristics of the child, his sensitivity to pain, nutrition and even the climate. Teething is often painful, causing children to refuse to drink or eat for a while. What to feed your baby when teething, as well as what are the first noticeable signs of teething and simple remedies that will help ensure more comfortable feeding and return to normal sleep, we will find out in a conversation with pediatrician Anastasia Anatolyevna Nikulina.
— Anastasia Anatolyevna, when babies start teething, how long does teething last?
— Children can “show off” their first central incisors at about six months. However, the first symptoms of teething in infants may appear a couple of months before the tooth appears. And it is advisable to see the beginning of the process in time to help the baby survive the pain. In most babies, symptoms of discomfort are detected three to four days before teething and usually disappear on the fourth day after the tooth comes out.
Obvious signs of teething in a baby:
- increased salivation, rash on the face and chest from constant wetting;
- swelling of the gums, their increased sensitivity when sucking;
- The toddler is irritable and whiny, capricious, does not accept the breast/bottle;
- the baby gnaws, bites objects, trying to relieve soreness in the mouth;
- The baby's sleep is disturbed and wakefulness appears at night.
— Teething discomfort is often mistaken for a cold or allergy. How to distinguish one condition from another?
— Teeth growth is a physiological stage, and, as a rule, it does not have negative consequences for the child’s health, despite frequent crying, fever, and excessive anxiety. It is possible to differentiate childhood illnesses based on knowledge of their characteristic signs.
Table. How to tell if your baby is teething
| Frequent manifestations | A tooth appears through the gum | The disease develops |
| Cough |
|
|
| Nasal discharge |
A saline solution is recommended for rinsing the spout. |
|
| Increase in body temperature to 38 °C |
|
|
| Rashes |
|
|
| Immunity weakens |
|
| Cough | A tooth appears through the gum
| The disease develops
|
| Nasal discharge | A tooth appears through the gum
A saline solution is recommended for rinsing the spout. | The disease develops
|
| Increase in body temperature to 38 °C | A tooth appears through the gum
| The disease develops
|
| Rashes | A tooth appears through the gum
| The disease develops
|
| Immunity weakens | The disease develops
|
— Parents are often concerned that their children are not eating enough. Are a baby's first teeth and decreased weight gain related?
— Poor appetite is an alarming symptom that occurs against the background of teeth moving and pressure on aching gums during feeding. The baby does not attach well to the breast, pushes out the nipple and receives less nutrition, which leads to a cessation of weight gain. It is better to simply temporarily switch to a free feeding regime, but not to force feed the baby.
Poor appetite in an infant may be accompanied by the following behavioral changes:
- complete or partial refusal of breast/bottle;
- constant whims when feeding with body writhing;
- increased desire to put something in the mouth followed by refusal to eat due to increased discomfort and itching in the gums;
- loss of interest in solid foods, especially in children on a mixed diet.
After the tooth breaks through the gum, the inflammation goes away and the appetite is completely restored. Therefore, you should not worry about your child’s reluctance to eat. The baby can get the required amount of vitamins through breast milk or formula. The main thing is not to skip two meals in a row.
— What if the child often refuses to suck the breast or pacifier?
“Parents need to be patient. An inflammatory process in the mouth - which means nights without sleep and a moody mood - reduces appetite. Any touching of the gums is accompanied by discomfort, so the baby does not want to suck. In such a situation, force feeding is useless. But even if the child misses two or three feedings per day, nothing bad will happen, everything will get better soon. When he gets very hungry, he will still take the breast or bottle and will definitely eat.
— A restless baby is waiting for support - how to soothe itching and inflammation of the gums?
— Teeth do not appear before three months, and sometimes a “dental holiday” in the family is celebrated closer to a year. The parents' task is not to miss the moment the tooth comes out in order to facilitate the process.
Teether-pacifier
- Given with the appearance of the first incisor for scratching the outside of the jaw. The itching subsides as teeth grow along the edges of the mouth. It is better to look for a wide pacifier (it is so convenient to reach hard-to-reach places in the oral cavity) with a narrow handle-limiter (does not interfere with the grip and prevents the pacifier from being swallowed too deeply).
Materials:
|
|
|
Sippy cup
— Teething is accompanied by a strong secretion of saliva, therefore, in order to normalize the water balance, plenty of drinking is often given from a convenient sippy cup. Its spout is made of rubber, and the valve does not allow liquid to leak. In addition, convenient holders prevent the bottle from slipping out of the baby's hands. Children are delighted with this “toy” and drink from a beautiful bottle with great diligence.
Pain reliever, gum gel
- Your doctor will advise you on the best solution. A number of medications to relieve inflammation and soothe gums include lidocaine. But there is no clear dosage for them, and the baby may swallow the medicine. Therefore, when treating gums when a tooth is cutting, lidocaine can lead to intoxication of a small organism and cause serious undesirable consequences.
| Spray/gel with lidocaine dangerous, limited use | Homeopathy inappropriate, safety and effectiveness of drugs have not been proven | Pharmaceutical preparations with belladonna especially dangerous, contraindicated | Non-steroidal drugs for fever are allowed, but their abuse is unsafe for the gastrointestinal tract | Gels based on medicinal plant extracts most safe and effective |
Rules for using gels for pain in teething syndrome:
- at the first concern of the child, a teether and a sippy cup are first given, a circular massage of the gums is done from the wings of the nose to the corners of the mouth;
- the product is used only in case of severe discomfort;
- apply a thin layer up to 3-4 times a day, strictly following the instructions;
- manipulation is performed with a clean finger, accompanied by a circular massage;
- It is preferable to lubricate the gums after feeding and at night;
- Under no circumstances should you allow your baby to chew on a tube of gel.
— Anastasia Anatolyevna, what to feed and how to feed the child when teeth are being cut - do you need to follow a schedule, give the baby something to drink, heat up food? And what is better to give to a child: baby formula/puree soup/vegetable puree? Should I continue breastfeeding?
— When teeth are being cut, it is important to temporarily move away from a clearly planned feeding regimen. It is better to offer your baby breast or formula milk on demand. Everything will soon return to normal and return to the order that developed during life without teeth.
It is preferable not to force the baby to eat thick foods. It is better to prepare liquid, pureed, light meals, and also not to introduce new complementary foods, do not give stale bread or cookies, in order to eliminate the risk of choking on crumbs. The temperature of the food should correspond to the temperature of the child’s body, so as not to worsen the baby’s condition and he does not lose the desire to eat. In case of hyperthermia and drooling, it is advisable to give the baby water.
— Do breastfed and bottle-fed babies experience the same painful condition when a tooth comes out?
— It has been observed that breastfed children tolerate the appearance of teeth more easily. Mother’s breasts are not only a source of complete and healthy food, but also a bioregulator of the emotional state, a way to calm down. Mothers whose babies literally “hang on their chest” observe that periods of prolonged feeding coincide with the appearance of dental cusps.
You need to show extra attention to a bottle-fed baby - hold him in your arms more often, fall asleep with him, spend sleepless nights next to him - fortunately, the tooth comes out completely in just 3-4 days (in the worst case, in a week).
— Do baby formulas have any effect on the baby when teeth are being cut?
— The best food for a newborn is, of course, breast milk. But there is no tragedy in transferring a child to artificial or mixed feeding if it is really necessary. This decision is made by the mother together with the pediatrician.
Fortunately, now there are alternatives to breast milk, and among them are MAMAKO® Premium infant formulas. They have an excellent composition and pleasant taste. One of their main advantages is the base of goat’s milk, which is closer in composition to breast milk than cow’s milk. The peculiarities of the protein component of goat mixtures make them easier to digest.
The eruption of the first teeth through soft, tender gums can cause the child to be whimsical when feeding. But the basic milk nutrition is preserved, and pureed complementary foods will make it easier to eat when there is soreness in the mouth. Also, the growth of teeth will bring less trouble if you pay more attention to the baby, communicate gently with him, distract him by singing or playing. It is important to massage the gums and offer the baby teethers. On the recommendation of a doctor, in case of intense pain, ointments and gels can be used to calm the baby and help teeth break through.
Pediatrician Anastasia Anatolyevna Nikulina
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
When is there no reason to worry?
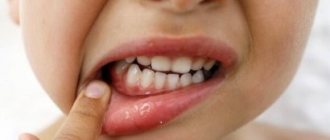
During the appearance of the first teeth, the baby’s behavior, as well as the reaction of the small organism, may change. The main symptoms are:
- Increased salivation . It is observed in almost all children. Saliva production increases from 10 weeks and lasts up to 4 months. At this time, it is enough for the young mother to prepare a set of bibs and change them regularly.
- Skin irritation on the chin and around the mouth. The cause of this phenomenon is the aforementioned excessive salivation. To avoid irritation, you need to wipe your baby's face with gentle movements and regularly apply a little emollient cream to the skin. It is best to use it before bed, so that the product is completely absorbed.
- While feeding a baby who has started teething, the mother experiences discomfort as the baby tries to bite the nipple . This is explained by the fact that the baby wants to scratch his gums, which is why he squeezes any objects.
Alarming symptoms
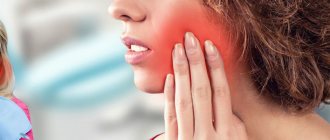
In some cases, teething causes great discomfort for the baby. This is explained by the fact that everyone has a different pain threshold. Accordingly, breaking through the soft tissue can be really painful.
This is especially true for the eruption of incisors and the very first teeth. During this period, some babies refuse food, even if they are hungry. Komarovsky explains this by the fact that painful sensations during sucking intensify significantly. If the baby missed no more than 2-3 feedings, there is nothing to worry about. If the baby refuses to breastfeed for 2 days or more, you should consult a pediatrician. Most parents are sure that diarrhea always accompanies teething . Some doctors agree. So, a large amount of saliva that a child swallows can lead to disorder. However, other experts do not share this point of view, so it is best to consult a doctor if your baby has loose stools.
Physiological diarrhea in a child
Diarrhea in a child may occur due to changes in climatic conditions.
Doctors have a definition of “physiological diarrhea,” which is quite common in young children for various reasons, such as:
- teething;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- the body's response to the introduction of a new food product.
With “physiological diarrhea,” the child behaves as usual: sleeps peacefully, is active, and does not cry for no apparent reason.
This situation is the norm; usually diarrhea goes away quickly without medical help; you can, perhaps, make adjustments to the diet of the mother and child (if he is already eating complementary foods).
But if symptoms such as vomiting and fever appear, then immediately consult a doctor to prevent complications.
What should parents remember?
- When teething, the baby's sleep is disrupted. If your baby begins to cry at night and fidget restlessly in the crib, you need to let her calm down on her own. There is no need to rock your baby to sleep or feed him milk right away.
- In some cases, , that is, small bumps, forms on the gums They dissolve on their own. If anxiety is severe, you can use a cold compress.
- Severe pain often spreads to the child’s ears and chin. Most often this happens when the incisors begin to appear. However, children may rub their chin and face when they have an ear infection. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
- When teething, a cough may occur , because the child does not always have time to swallow saliva. If there are no other symptoms, then there is no need to worry. This also applies to a runny nose caused by saliva entering the nasopharynx. If you have other alarming symptoms, you should consult your pediatrician.