Stomatitis in a child is a very common phenomenon caused by an inflammatory process of the oral mucosa, which also occurs in newborns. We can say that raising a child and not knowing what stomatitis looks like in children is almost impossible. Quite often, the symptoms of the disease initially resemble those of a respiratory infection with a characteristic fever, stuffy nose and poor appetite. But after a short time, parents notice the appearance of blisters and ulcers on the gums, cheeks and inner lips, which can be caused by various pathogens. The child behaves anxiously, capriciously, sleeps poorly... Even for an adult, it is very difficult to endure the painful sensations that arise from stomatitis, not to mention children, who cannot always clearly explain what is tormenting them. Parents, of course, are concerned about the question of what causes stomatitis in children and whether the occurrence of such a disease can be prevented. Let's try to understand this thoroughly.
Types of stomatitis
Everyone is more accustomed to saying “stomatitis”, but it would be more correct to say “stomatitis”, since this is a generalizing concept for a whole group of diseases. Depending on the causes of stomatitis, it can be divided into several types, each of which has a number of characteristics.
Viral or herpetic stomatitis in children
One of the most common types of stomatitis in children is caused by the herpes simplex virus. Typically, a child becomes infected through airborne droplets. In addition, the virus is transmitted through dishes, toys, and household items. Most often, herpetic stomatitis appears in a child between the ages of one and four years. The disease begins with a cold, accompanied by lethargy and increased body temperature. Sometimes there is a runny nose and cough. Around the second day, small round or oval erosions of a light yellow color with a bright red border appear on the lips, tongue and inside of the cheeks. Swelling appears, the gums begin to bleed, and the child refuses to eat.
Traumatic stomatitis in a child
The disease is caused by mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. For example, burns from hot food, a too hard nipple, the habit of chewing a pencil. In addition, traumatic stomatitis often occurs in children with malocclusion due to frequent biting of the cheeks and tongue.
Candidal stomatitis
Appears in children under one year of age. The cause is Candida fungi. The main symptom is the appearance of a white coating in the baby’s mouth. It should be noted that this should not be confused with regular flowering after feeding. A cause for concern is if plaque persists and the baby refuses to eat.
Drug or allergic stomatitis in children
Caused by certain allergies or reactions to medications. If this type of disease is suspected, it is necessary to identify and remove the allergen, otherwise there is a risk of unpleasant consequences, including anaphylactic shock.
Each type of stomatitis is characterized by a certain childhood age. Young children often have candidiasis or fungus (thrush). At the age of “I want to know everything” in a child of 3-4 years, stomatitis is usually infectious in nature, when the infection is transmitted through dirty hands or objects. From one to four years, an acute herpetic form of the disease is often observed.
How to care for a child after stomatitis appears?
Without the help of parents, a child will never get rid of the disease, because strict discipline is needed. You must follow all the requirements of the pediatric dentist and pay special attention to diet and pain medications.
Prefer soft food with a temperature of no more than 28o C. It is important that it has a balanced composition of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Allergens, as well as spicy, sweet, sour and very salty foods, must be excluded from the diet. It is advisable to exclude citrus fruits due to their high acid content. After eating, rinse your mouth with filtered or boiled water.
Treatment includes the use of painkillers. The child will feel severe pain at first, which will interfere with sleep. Therefore, you need to regularly rinse your mouth not only with clean water, but also with medicinal balms. The affected area should be smeared with medicinal gel. All recommendations for treatment and pain relief will be given to you by your pediatric dentist during your consultation.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Causes of stomatitis in children
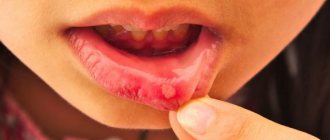
In childhood stomatitis, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity is affected: small, white or yellowish, fluid-filled pimples appear on its surface. In some cases, ulcers form.
Stomatitis is predominantly a childhood disease, although it can also occur in adults. The rash affects the inside of the cheeks, tongue and gums. The disease causes a lot of inconvenience: pimples hurt and itch, and their appearance is accompanied by a burning sensation in the mouth.
Among the main reasons for the development of stomatitis are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- mucosal injuries;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- burns of the oral cavity;
- pathogenic bacteria that enter the oral cavity with dirty hands, toys, etc.
Causes and prerequisites for the development of aphthous stomatitis
The etiology of aphthous stomatitis has not yet been clarified. In the course of specially conducted studies, it was possible to establish only the factors contributing to the development of the pathological process. These include:
- inadequate immune response to the action of certain substances (components of hygiene products, dust, medications, waste products of bacteria and parasites);
- food allergies (potential allergens in such situations are buckwheat, rye, wheat, barley, pineapples, citrus fruits, tomatoes, strawberries, apples, seafood, figs, spices, cheeses, chocolate and food additives);
- mechanical damage to epithelial tissues of the oral cavity;
- neuropsychic stress;
- deficiency of nutrients in the body;
- menstruation in women;
- poor nutrition;
- immunodeficiencies;
- genetic predisposition;
- systemic blood diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- long-term use of antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- functional disruptions in the nervous system;
- chronic inflammatory lesions of the nasopharynx (tonsillitis, rhinitis, otitis).
Symptoms of stomatitis
Signs of stomatitis in a child have a number of features characteristic of a particular type of disease.
Herpetic stomatitis in children is considered very common and usually manifests itself as follows:
- in the initial stage, the disease is confused with a cold due to increased body temperature, often runny nose and cough;
- the inflammatory process begins abruptly, manifested by headaches and pain in the mouth and muscles due to intoxication of the body;
- submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful;
- feature - the formation of small bubbles filled with liquid.
Upon visual examination, redness of the gum tissue around the teeth, swelling of the mucous membrane and numerous vesicular rashes covered with a yellowish or whitish coating are noted. Candidal stomatitis in children can be clinically acute or mild. In this case, signs of stomatitis in a child appear as follows:
- very rarely an increase in temperature is recorded;
- in the oral cavity there are affected areas covered with a coating of cottage cheese;
- children behave restlessly, are capricious, refuse to eat;
- Locally similar stomatitis in children (or thrush, as it is often called) occurs on the tongue, cheeks, gums and inner lips).
Aphthous stomatitis in children is the most common form of the disease, but also difficult to treat due to the difficulty of identifying the specific pathogen. Similar stomatitis in children, the symptoms of which are more common in schoolchildren than in the younger age group, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- rash of single ulcers (feed) on the mucous membrane (on the cheeks, in the area of the tongue and the inside of the lips);
- Initially, such stomatitis in children in the mouth is manifested by characteristic redness, itching, burning, and an increase in temperature is also noted.
In this case, the ulcers do not look like blisters, but are whitish ulcers with a bright red outline around them. Then the ulcers are usually covered with a cloudy film, which can break through and cause a secondary infection, after which the baby’s condition will only worsen. Parents should know that stomatitis in a child is not a single type of infection with specific symptoms.
Each form of this inflammatory process has its own specific symptoms and causes. That is why, despite a number of individual similar points (temperature during stomatitis in a child, signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane, enlarged lymph nodes), the problem of treating stomatitis in a child is solved differently, taking into account the form of the disease.
Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is known as thrush. It can appear in children even in infancy, and it is caused by saprophytic fungi, which become pathogenic when immunity decreases. With this type of stomatitis, white spots appear in the child’s mouth. In addition, there may be an occasional increase in temperature and the appearance of photophobia. Infection of a child can occur through contaminated dishes, toys or pacifiers.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis involves undergoing daily procedures in the dental office, rinsing the mouth with alkaline solutions, and taking vitamins.
Treatment of stomatitis in a child cannot be delayed, otherwise this may lead to relapse of the disease. CELT pediatric dentists recommend regular preventive examinations that will help prevent the development of serious dental diseases, including stomatitis!
Diagnosis of the disease
The pathology of stomatitis is diagnosed by infectious disease specialists, pediatricians, and pediatric dentists. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical and epidemiological data.
Based on materials from smears, scrapings, and blood, the following studies are carried out:
- virological;
- bacteriological;
- immunological;
- cytological.
Diagnostics such as polymerase chain reaction and enzyme immunoassay are performed. In some cases, the child has a blood test for the presence of sugar, and a consultation with an endocrinologist, allergist and other specialists is carried out.
Correctly conducted diagnostic examinations will help establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment so that the situation does not worsen.
Treatment methods for aphthous stomatitis
The main goal of therapy for aphthous stomatitis is to achieve long-term remission of the disease or complete recovery of the patient.
At the same time, the standard treatment regimen for this pathology includes:
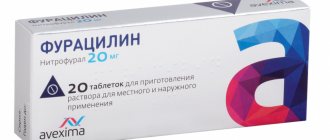
- treatment of affected areas with furatsilin or chlorhexidine;
- lubrication of the aft with a suspension of glycerin with novocaine or lidocaine (if allergic components are present in the pathogenesis of the disease, a mixture containing heparin, trasylol, hydrocortisone and novocaine is used);
- taking enzymes (chymotrypsin, trypsin);
- use of corticosteroid ointments (according to indications);
- taking antihistamines (Telfast, Claritin, Tavegil);
- vitamin therapy;
- the use of desensitizing agents (Histoglobin, Fenkarol);
- taking immunomodulators and immunoprotectors;
- prescribing sedatives (if the patient has neurological disorders);
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, laser therapy);
- adherence to a hypoallergenic diet that prevents injury to oral tissues.
Timely initiation of treatment in a dental clinic and compliance with all doctor’s instructions allows you to completely get rid of aphthous stomatitis or achieve long-term and stable remission.
Treatment of stomatitis in children
After a medical diagnosis of stomatitis in children under one year of age, a specialist prescribes highly effective drugs to combat the existing type of disease. Experts recommend that parents, at the first suspicion of stomatitis in a child, increase the amount the child drinks to irrigate the oral mucosa and remove toxins from the body. Clean drinking water without gas, fruit drinks or compotes that are not too sweet or sour; herbal teas are perfect for this. During this period, it is worth refusing to drink the child from concentrated juices and drinks with gas in order to avoid irritation of the mucous membrane.
After this, the specialist begins medical manipulations to cure stomatitis in the child.
Anesthesia
The first step is to numb the mucous membranes so that the child can eat and drink properly and generally reduce the child's stress level. Choline preparations with salicylate or lidocaine are commonly used as pain relievers in children. For this purpose, medications to facilitate teething, for example Kamistad or Dentinox gel, are suitable. Gel products are preferable for children because they are almost instantly absorbed into the mucosal tissue. Prepare with lidocaine in the form of a spray should not be used in children under one year of age - this may lead to bronchospasm.
Direct treatment of stomatitis
After anesthesia, you can begin treating your baby’s stomatitis. Firstly, all rashes and wounds must be treated with a special preparation, depending on the type of disease. Antiviral drugs are used for herpetic stomatitis, antibiotics and antiseptic drugs for bacterial stomatitis, antifungal drugs for candidal stomatitis. Not only the affected area, but also adjacent areas must be treated - this will stop the spread of the pathogenic process.
An important condition for eliminating infection is thorough and timely oral hygiene. The surface of the child's tongue and teeth should be brushed twice a day; experts recommend rinsing the mouth after every meal or drink. For young children, hygiene procedures are carried out using a piece of gauze or a silicone fingertip.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
If a specialist has identified the presence of allergic stomatitis or severe swelling of the oral cavity is observed, then the drugs Fenistil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine are used.
Treatment of viral stomatitis
For herpetic stomatitis, antiviral agents should be used in the form of ointments containing acyclovir - Gerpevir, Virolex, Acik, Viferon, oxolinic ointment.
For relapses of viral stomatitis, experts recommend a general strengthening of the immune system with the help of Immunal, Interferon, Viferon in suppositories. The duration of treatment and dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor. Often, medical experts recommend using the drug Cholisal in gel form. Perfectly relieves swelling, inflammation, pain, fever, eliminates pathogenic microflora. The drug does not contain sugar, has no taste and has a light anise aroma. To treat stomatitis in a child under one year old, it is necessary to rub a strip of gelatin preparation no more than 0.5 centimeters long into the palate, gums and inner surface of the cheeks, teeth, 2-3 times a day after brushing the teeth.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
For candidal stomatitis, the doctor uses antifungal drugs in the form of an ointment, for example, Clotrimazole, Candida, Candizol, and often prescribes soda rinses.
This helps create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity, harmful to pathogenic fungal microflora. Procedures with soda are especially effective in the treatment of candidal stomatitis in children under the age of one year, because at this age most drugs are contraindicated. To treat the oral cavity, you need to dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water, then wrap a piece of gauze around a clean finger and wipe the palate, inner surface of the cheeks, gums and sublingual space of the child, periodically dipping your finger into the solution. The procedure should be done after every child eats or drinks. Older children can rinse their mouths with baking soda themselves.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
With aphthous stomatitis, the first priority is to unload the affected area and speed up the healing of the poop. An aqueous solution of blue (methylene blue) has long been used for this purpose. It is not recommended to use a blue alcohol solution for this, since the ethyl alcohol in its composition will cause poisoning or burn the baby’s mucous membrane.
Wounds are treated with a blue cotton swab 3-6 times a day.
Treatment of traumatic stomatitis
According to experts, traumatic stomatitis most often occurs in children 1-2 years old. This type of disease is accompanied by bacterial microflora, so the use of medicinal and antiseptic agents will be required. For children under 2 years of age, use Cholisal, Solcoseryl, Actovegin gel, and also wipe the oral cavity with a solution of chlorhexidine or soda.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
For the treatment of bacterial stomatitis, drugs such as Tantum Verde, Orasept and Hexoral in the form of a spray, Doctor Theiss and Septolete in the form of lozenges and many others are effective. Experts do not recommend using lozenges to treat children under 6 years of age due to the risk of asphyxia, and sprays are suitable for treating bacterial stomatitis in children over one year of age. Antiseptic rinses and gel preparations with metronidazole are also effective.
Among solutions with an antiseptic effect, the drug Miramistin is especially recommended, as it promotes the regeneration of the affected mucous membrane and eliminates most pathogens. The aerosol can is convenient for treating children under one year of age. To do this, you need to make 3 injections and rinse your mouth with them for several minutes 3-4 times a day. Babies under the age of one year are treated with gauze soaked in the drug.
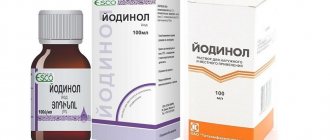
How does furatsilin work?
Furacilin, consisting of nitrofural and sodium chloride, has pronounced antiseptic properties, so many believe that this is the best remedy for stomatitis. One of its main features is the ability to act on most bacteria known to medicine. For this reason, it is widely used for a variety of purposes, from treating wounds to gargling.
The drug not only eliminates symptoms; upon contact with pathogenic microflora, it dissolves the cell membrane, which leads to their death and a reduction in the number of colonies.
Several forms of the drug are used in different fields of medicine:
- solutions (alcohol, water);
- pills;
- ointment;
- aerosol.
In dentistry, solutions are most often prescribed - ready-made or prepared independently from tablets.
Caring for a child with stomatitis
Parental involvement in treatment and proper care of children is not only important, but also necessary. With stomatitis, it is necessary to strictly follow the treatment plan, which is often very labor-intensive, so the result depends on parental care and control. The oral cavity is a kind of epicenter of pain, so it is not surprising that the child is very temperamental. Therefore, it is important for parents to be patient and persistent.
Most mothers and fathers are concerned about what to feed their child with stomatitis. Firstly, you need to eat only soft, warm and pasty foods, such as purees. The main thing is that the food is high in calories and not heavy, because the child’s immunity is already weakened. After eating, be sure to rinse your mouth so as not to provoke the development of stomatitis and not to add an additional infection. Spicy, sour, sweet and citrus foods should be excluded from the child's diet.
For stomatitis in children, it is necessary to relieve pain. This is done with the help of various medications to avoid food refusal and poor sleep. Also, for stomatitis in children, adequate oral treatment is very important. Your doctor should recommend how to handle your child and rinse his mouth.
How to make a solution of furatsilin
Ready-made liquid cannot always be bought at a pharmacy. More often Furacilin is found in tablets. The treatment regimen, duration, and dosage form are determined by the doctor, and each patient’s prescriptions are different. The doctor takes into account individual characteristics. Usually 1 – 2 tablets are crushed to a powder and stirred in a glass of warm water.
For faster dilution, it is recommended to use boiling water. For stomatitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, a solution is prepared to rinse the oropharynx: per 100 ml - 2 mg (1 tablet) of furatsilin. The duration depends on the nature of the localization of the infection. Take a small sip of the prepared product, throw back your head and rinse your larynx for 2 – 3 minutes.
Prevention of stomatitis in children
Irritative stomatitis can be prevented with good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups and proper nutrition. Because many adults and children carry the herpes virus and can transmit it even without symptoms, there is no practical way to prevent herpetic stomatitis. However, parents may discourage their child from kissing, eating, or playing in close contact with people who have an active herpes infection.
Ulcers can be minimized by teaching children to avoid injury, even minor trauma to the mouth. If our doctor determines that a child has a nutritional deficiency, parents can make sure the child is taking appropriate supplements and eating recommended foods. It won’t hurt to visit the dentist once every six months if we have previously discovered stomatitis in the child. Regular visits to our clinic will help prevent serious complications and detect the disease in time.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults is a reaction of the immune system to certain types of irritants, which are any substances. The causes of stomatitis have not been clearly identified; presumably, the body exhibits an individual reaction to certain substances or microorganisms.
Possible causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults:
- bacteria and infections of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of an infectious or viral type;
- respiratory diseases (ARVI, influenza, etc.);
- frequent injury to the tongue by orthopedic or orthodontic structures;
- damage to the tongue due to a chipped tooth;
- fungal infection;
- bad habits (smoking or alcoholism);
- burning the tongue or eating “spicy” foods.
In addition to the listed causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, inflammation of the mucous membrane can be caused by the herpes virus (herpetic stomatitis).