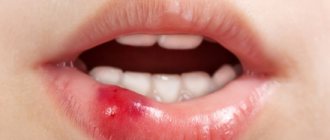
One of the most common diseases of the oral cavity is stomatitis. This is a pathology that most often takes an infectious-inflammatory course and is the result of increased activity of lymphocytes in response to the ingress of pathogenic molecules that the child’s body cannot recognize. Decreased immunity is the main factor that provokes inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. In newborns and infants of the first year of life, the immune system continues to improve and cannot cope with all negative factors, therefore children under one year of age are considered the most vulnerable group of patients for the development of various forms of stomatitis.
Stomatitis in babies
Treatment of stomatitis in infants differs from therapy that may be recommended for an adult, so you cannot prescribe medications yourself. This is also due to the fact that stomatitis has several varieties, each of which differs in clinical course, symptoms and characteristics of the therapy. To correctly determine the type of disease, laboratory diagnostics (scraping from the tongue and gums) may be required, so if symptoms of stomatitis are detected in an infant, you should immediately go to the hospital. The pathology is treated by a local pediatrician or pediatric dentist.
Childhood stomatitis - how to help your baby?
Why does the disease appear?
In order to quickly cope with the disease and prevent re-infection, it is necessary to find out the reason that provoked the growth of pathogenic flora on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The main factor leading to the development of infectious forms of stomatitis is non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards for the treatment of toys, premises and objects surrounding the child. Bacteria and germs can enter the child's body from rattles, the surface of the changing table, and pacifiers. The development of fungal flora is often caused by insufficient sterilization of bottles (in children who are bottle-fed or mixed-fed).
Aphthous stomatitis in children
If a child has had conjunctivitis or other infectious diseases, it is necessary to carefully treat all the furniture and toys in the children's room, and also wash the bedding on which the baby slept at high temperatures. If the type of fabric allows, it is best to wash at a temperature not lower than +90°C, then iron it on all sides using the steam mode.
Lack of hygiene is not the only reason for the development of infectious processes in the oral cavity. Experts believe that the main role in the mechanism of the appearance of stomatitis belongs to the immunological factor. If a child has a strong immune system, his body will independently cope with infectious agents and other provoking factors.
Candidal stomatitis in children
The following reasons lead to poor functioning of the immune system in infants:
- birth before 32 weeks of gestation and associated severe prematurity (low birth weight);
- early transition from breastfeeding to feeding with artificial milk substitutes;
- early introduction of complementary foods and associated disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, as well as allergic reactions;
- living in poor social and living conditions;
- poor maternal nutrition (in breastfed children), in which the child does not receive the required amount of useful and nutritious elements;
- short walks and poor hygiene.
Breast-feeding
If stomatitis in an infant in the first year of life is repeated more than 3-4 times, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. This picture can be observed in children suffering from indolent infectious diseases, for example, tuberculosis.
Important ! Heart disease and endocrine disorders can also lead to impaired immune activity. A decrease in local protective functions often occurs after taking antibacterial drugs, therefore, after antibiotics, it is recommended that the child be given drugs containing bifidobacteria or lactobacilli (“Bifidumbacterin”, “Acipol”, “Bifiform Baby”).
"Bifiform Baby"
What causes chickenpox?
The causative agent of this disease is human herpesvirus type 3. It belongs to the subfamily of alphaherpesviruses, which have the following features:
- a wide range of hosts (humans and animals);
- short reproductive cycle;
- rapid reproduction;
- volatility;
- rapid decay of affected cells;
- death under the influence of UV rays.
When the chickenpox virus enters the human body, for the first three to four days it is contained within blisters covering the skin. On the eighth day it ceases to be detected. Outside a living organism, type 3 herpesvirus dies in 15 minutes.
The rash usually appears 48 hours after infection. The carrier remains infectious for another five days. Infection occurs by airborne droplets. Contact-household infection is also possible.
Signs and symptoms in infancy
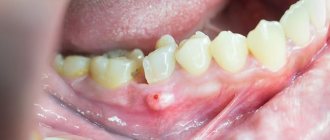
The main symptom of stomatitis is aphthous rashes on the surface of the mucous membranes, which can be single or have multiple courses. If the number of ulcers exceeds 20, the child is diagnosed with a severe form of stomatitis, requiring treatment in a hospital. Almost all babies experience an increase in the activity of the salivary glands and an increase in the production of salivary secretions - hypersalivation. Drooling can occur at any time of the day and does not depend on food intake. If you examine the oral cavity, you can see signs of an acute inflammatory process: redness of the soft tissues, fluid accumulation, swelling and bleeding of the gums.
Fungal stomatitis
Other signs of stomatitis include:
- What causes stomatitis?
- itching and soreness of the gums (the child puts everything into his mouth, making chewing movements that help relieve the soreness);
- temperature rise to +38°C;
- a dense coating of milky or dirty yellow color, having a creamy or curdled consistency;
- bad breath.
Stomatitis in a child
If you try to remove plaque from the surface of the gums or tongue using gauze or a napkin, underneath it there will be injured mucous membrane that will bleed and hurt. In very rare cases, a pinpoint rash of pale pink color may appear on the mucous membranes - this picture indicates the allergic nature of the disease.
Child's tongue is white
Types and forms of the disease
In order to prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to find out what type of stomatitis the baby has developed. To do this, you need to show the child to a doctor: he will examine the oral cavity, assess the condition of the mucous membranes, the number and size of ulcers and erosions. In uncomplicated cases, a visual examination is sufficient to diagnose the pathology, but sometimes the doctor may prescribe additional tests, for example, bacterial culture on nutrient media. This is necessary for selecting treatment tactics and prescribing treatment.
Table. Types of stomatitis and their manifestations.
| Type of disease | Cause of occurrence | Symptoms and signs |
| Fungal | Infection with single-celled microscopic microorganisms – fungi. In 80% of cases, the causative agent of infection is a fungus of the Candida family. | A cheesy coating on the surface of the gums and tongue, which has a dense consistency, bad breath, and an increase in temperature within the subfebrile range. |
| Aphthous (another name is ulcerative) | Systemic diseases that have a chronic course and have a negative effect on the activity of the immune system. | The formation of aphthae - round ulcers covered with a cloudy white film layer. Aphthae are always painful, and their number can reach up to 30 pieces. |
| Catarrhal | Poor oral hygiene and non-compliance with sanitary standards for the treatment of toys and premises. | Redness of the mucous membrane, swelling of soft tissues, increased production of saliva. |
| Bacterial | Gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms (mainly staphylococcus, chlamydia, streptococcus, klebsiella). | Yellow plaque, fever, signs of inflammation in the mucous membranes, pain during feeding. |
| Viral | Viruses of the herpes family (herpetic stomatitis) and viruses of the Vesiculorus genus (vesicular stomatitis). | Hyperemia of the mucous membranes, high temperature, increased salivation, blisters filled with cloudy liquid, which break through after 2-3 days. |
Note! There is another type of stomatitis - the allergic form. Allergic stomatitis develops as a result of interaction with irritating substances. These may be flavors and dyes included in children's toothpastes, or products used to treat toys and other items (antiseptics). This form of the disease is treated by an allergist.
Allergic stomatitis
How to treat: drug therapy
Treatment of stomatitis should always begin with identifying the cause and causative agent of the disease. If an infant is diagnosed with a viral form of stomatitis, the doctor may prescribe the use of antiviral agents in the form of ointments, gels or creams. They must be applied 2 to 4 times a day to previously cleansed mucous membranes. To clean and disinfect the oral cavity, you can wipe the gums, tongue and surface of the cheeks with a light cloth moistened with a decoction of calendula or oak bark or an antiseptic solution, for example, Chlorhexidine.
"Chlorhexidine"
Ointments that can be used to treat infants:
- "Oxolinic ointment";
- "Tebrofen ointment";
- "Viferon";
- "Gerpferon";
- "Acyclovir".
"Oxolinic ointment"
"Viferon"
For severe symptoms of viral stomatitis, a specialist may recommend combined regimens. Including the local use of antiviral ointments and the use of interferon-based rectal suppositories (“Viferon”).
To treat bacterial and fungal stomatitis, agents with a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity are needed. They can be used in the form of solutions, ointments or suspensions. Levorin and Nystatin suspensions have a good therapeutic effect. To destroy the fungus of the Candida family, the drug of choice is the Candide solution - it quickly copes with pathogenic flora and reduces the intensity of painful sensations after 2-3 days of use.
"Nystatin"
For bacterial stomatitis, it is necessary to treat the mucous membranes with any antiseptic solution 3-4 times a day. This can be “Miramistin”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Furacilin” (to prepare the solution you need to dissolve 1 tablet of “Furacilin” in 140 ml of hot water). The following medications can be used to heal and moisturize soft tissue:
- Which doctor treats stomatitis?
- "Vinilin";
- "Bura";
- Vitamin A in a gelatin shell.
"Vinilin"
If a child has a fever, it is better to use paracetamol-based products. It is better to give the drug to children older than three months in the form of a syrup with orange or strawberry flavor. Cefekon rectal suppositories are good for reducing fever and relieving pain, but they cannot be used for up to three months. If you need to bring down the temperature of a newborn, it is better to use products that contain ibuprofen - Nurofen or Ibuprofen.
"Ibuprofen"
Important! Antibiotics for the treatment of stomatitis are prescribed extremely rarely. If treatment is started at the initial stage of the pathology, in most cases it is possible to do without the use of potent antibacterial drugs. Only a doctor should prescribe and select the dosage of medications in this group.
At the dentist
Complications of chickenpox
In most cases, this disease is not dangerous; children tolerate it easily. The only threat is infection of the wound when combing with dirty hands. In such cases, staphylococci or streptococci may be ingested and a purulent infection may develop.
The chickenpox virus does not disappear from the body after recovery. Temporarily neutralized, it is localized in the spinal cord. As years pass, it can become more active and cause shingles.
In adults, complications may include:
- stomatitis (if a rash appears in the mouth);
- conjunctivitis (on the eyelids);
- inflammation of the middle ear.
The greatest danger is chickenpox pneumonia with a mortality rate of 40%. The consequences of infection with the chickenpox virus can manifest themselves in the form of neurological disorders, heart disease, and joint damage. A month after recovery, there is a risk of developing retinal inflammation and cranial nerve palsy.
Recommendations during treatment
It is very important to provide proper hygienic care for the baby during treatment. All toys must be thoroughly washed with hot water and baby or laundry soap. Wet cleaning should be carried out daily. It is best to wash the floors in the children's room with plain water, without adding disinfectants, as they often cause allergic reactions. It is necessary to ventilate the room in which the child spends most of his time at least 6 times a day. The last airing should be done before bedtime and last at least 30 minutes.
Children's dishes and bottles, as well as pacifiers and pacifiers, must be sterilized. To care for the skin, the baby must have his own towel - you cannot use towels used by other family members for this purpose, because the bacterial flora of an adult and an infant is very different.
Remedies for stomatitis in children
To speed up the healing of ulcers and the child’s recovery, you need to:
- keep plenty of fluids (breastfed children should be given breastfeeding “on demand”);
- if the child receives complementary feeding, make sure that all food is in liquid or puree form (the introduction of crackers and baby cookies into the diet should be postponed until complete recovery);
- increase the duration of daytime sleep - this will allow you to quickly restore strength and avoid overexertion, which is contraindicated for sick babies.
Feeding the baby
If, despite all the measures taken, the child’s condition does not improve after three days of treatment, it is necessary to visit the doctor again to rule out other diseases. After recovery, a preventive regimen and measures aimed at strengthening the immune system should be provided: hardening, gymnastics, frequent walks, water treatments. They must correspond to the age and physiological characteristics of the child, so before starting any health procedures it is better to consult a specialist.
How to help with chickenpox?
There is currently no cure for chickenpox. Usually the disease goes away on its own, and therapy is limited to smearing the rash with aniline dyes with bactericidal properties. A solution of brilliant green (“zelenka”) is usually used. You can take an antipyretic to relieve your general condition.
To relieve itching use:
- solution of iodine tincture (2-3%);
- solution of potassium permanganate (1:5000);
- hydrogen peroxide (3%);
- glycerol.
In some cases, antihistamines can help relieve itching. But you should not take them uncontrollably: it is better to call a doctor at home and determine acceptable medications. Showering is allowed, but without a washcloth to avoid damaging the bubbles. The same applies to the use of towels - after water procedures, you need to carefully pat your body dry with a cloth.