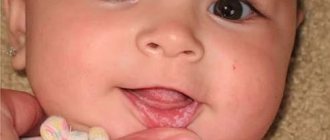
Factors contributing to the formation of bubbles:
- Oral diseases: caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, stomatitis;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Allergy to toothpaste or mouthwash;
- Injuries;
- Poor hygiene;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Immunity impairment;
- Alcohol and nicotine addiction.
Watery blisters on the mucous membrane in some cases can indicate the occurrence of serious diseases. Such manifestations occur with tuberculosis, syphilis or diabetes. Therefore, if such a pathology occurs, it is recommended to immediately make an appointment with a doctor and undergo the necessary examination. The first sign is the sensation of a strange object in the mouth that is in the way.
What to do if there are pimples on your lips?
Unlike other areas, white pimples on the lips are usually smaller, about 2 mm in diameter, and less prominent. In some cases, they may itch, but you should scratch them as they can become infected. You cannot squeeze them out, as this can cause microtraumas and scars.
It is necessary to consult a doctor who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. It may turn out that the rash on the lips is a completely different disease, for example, herpes or acne.
Symptoms
- Painful sensations when eating occur if a bubble has formed in the gum area or on the tongue;
- Pain when talking or smiling appears when a formation occurs on the inner surface of the lip;
- Pain in the throat area occurs if the bubble is located at the root of the tongue.
Transparent and bloody blisters can be not only inflammatory in nature. If the formation does not cause pain and is not accompanied by swelling, then you should consult a dermatologist. It is not recommended to treat yourself in such a situation, as it can be dangerous to health.
Symptoms of stomatitis and its classification
If a child has a white sore on the inside of his lip, it is better to take him to a dentist for an examination to prevent negative consequences. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children from one to 3 years of age; it is slightly less common in infants. Preschoolers and schoolchildren encounter the disease extremely rarely. The peak incidence usually occurs in the spring, when everyone feels their immunity weakens.
Experts distinguish 4 types of stomatitis: traumatic, infectious, allergic and chronic. First, small ulcers appear on the child’s lips, and then swelling of the mouth and lips becomes noticeable. The mucous membrane takes on a bright red color. Then the marks begin to spread to the tongue, palate and cheeks. Often they are the result of tissue injury from braces, a plate or a damaged tooth.
The appearance of bubbles indicates the infectious nature of the disease. Formations can make themselves felt on the face (on the nose, cheeks and lips). Such manifestations linger for several days, and then turn into traces of erosion, bringing with them headache, joint or muscle pain, as well as enlarged lymph nodes. Additional symptoms of stomatitis are dryness and burning in the mouth. Pain occurs when eating food. In extreme cases, the papillae located on the tongue may lose sensitivity.
Treatment methods depending on the cause:
- If the formation occurs due to a viral infection, then treatment will be based on the use of antiviral drugs;
- If the cause is injury, then it is necessary to eliminate the consequences and rinse the mouth with antiseptics;
- If an allergic reaction provokes an illness, then you should find out what the irritant is and not use it anymore. The doctor will also prescribe antihistamines;
- If a large bloody bubble has formed, then surgery is performed. After this, the doctor prescribes medications for rapid tissue regeneration and restoration.
Is it possible for acne to appear on the lips?
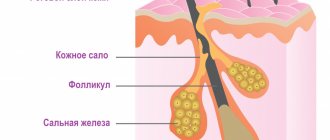
Acne is a disease of the sebaceous glands. Since there are very few of them on the red border of the lips, the likelihood of acne forming in this area is low. But acne can form in the area around the lips. If a dermatologist has diagnosed acne, he may prescribe azelaic acid preparations for treatment9. Azelik® belongs to this group of drugs. This is a 15% azelaic acid gel with the following properties5:
- the ability to normalize keratinization processes in follicles;
- anti-inflammatory effect exerted by reducing the metabolism of neutrophils and the free radical forms of oxygen they produce;
- reduction of free fatty acids in skin lipids;
- antimicrobial activity against propionibacteria and Staphylococcus epidermidis.
The results from the action of Azelik®, as a rule, become noticeable after 4 weeks of using the drug5.
Classification of rashes on the labia
Before answering the question of why acne appeared on the labia, for a correct assessment of the pathology process, it is important to be able to differentiate the elements that make up the rash.
According to dermatological terminology, primary ones are distinguished, appearing on unchanged skin.
And secondary elements, developing from primary ones.
Actually, in most situations, various types of acne on the labia belong specifically to the primary forms.
They are divided into cavity and cavityless.
Sometimes the transition from primary to secondary forms occurs very quickly.
In such a situation, knowledge of the specifics and patterns of transformation makes it possible to determine the type of previous education.
Primary elements include:
- A spot (artificial, non-inflammatory and inflammatory vascular, pigmented) is a limited change in skin color without cavities or elevations. Vascular formations of an inflammatory nature up to a centimeter in size are called roseola, from one to five centimeters - erythema. Examples include roseola syphilitica, erythematous variants of dermatitis, and toxicoderma. Possible secondary forms are secondary pigment spot, scale.
- A blister is a raised, cavity-free formation, the result of edema with acute inflammation in the papillary skin layer, which quickly appears/disappears. It can form due to urticaria, insect bites, and toxicoderma. Such itchy pimples on the labia are usually pink, less often whitish in the central zone, and may be accompanied by a burning sensation.
- Papules, otherwise known as nodules, are hollow, raised elements that usually pass without a trace. Such formations vary in size, depth, and can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature. They may transform into cracks, scales, secondary pigment spots, lichenification (thickening, pigmentation disorders, deepening of the skin pattern). In some diseases, papules merge to form plaques.
- A tubercle is a hollow, raised, dense element up to a centimeter in size, which usually leads to the formation of scars and cicatricial atrophy. It can also develop into ulcers, growths, scales, and crusts. The formation lies deep in the skin and is observed in cases of tuberculosis, leishmaniasis, leprosy, and tertiary syphilis.
- A node is a hollow, raised element measuring over a centimeter (up to 10 cm). It may end without a trace or with the formation of a scar, ulcer, secondary pigment spot, or crust. Formed in the subcutaneous tissue. A subcutaneous pimple on the labia of inflammatory nature may turn out to be syphilitic gumma, a typical manifestation of tertiary syphilis. Non-inflammatory is formed due to the deposition of metabolic products (“pimple wen” on the labia) or as a result of neoplasms (lymphoma).
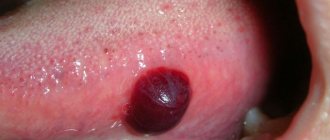
- A vesicle, otherwise known as a vesicle, is a cavitary single- or multi-chambered elevated formation, up to 5 mm in diameter, with a tire and a bottom. On the labia with genital herpes, watery pimples with serous contents appear on erythematous skin. Also, blisters on the labia are filled with serous-hemorrhagic contents (blood pimples). When the vesicles are opened, weeping erosions, scales, crusts, and secondary pigment spots may appear, but usually in the end there are no traces left on the skin.
- Bubble, bulla - differs in size from the bubble (its radius exceeds a quarter of a centimeter, and can even reach several centimeters). Resolves without a trace or with scarring. It is also possible to form erosions, scales, crusts, growths and age spots.
- Pustule, abscess - a cavitary deep or superficial raised formation with purulent contents (a pimple with pus is found on the labia). There are follicular, predominantly staphylococcal in nature, and non-follicular (superficial - phlyctena, deep - ecthyma), usually streptococcal. They can develop into crusts, erosions, spots, scars, ulcers, and growths. Follicular pustules form in the hair follicle, appearing on the labia as characteristic yellow pimples.
Secondary elements:
- scale – loosened horn cells in the form of a layer
- crust – drying contents of primary formations
- crack - a violation of the integrity of the skin that occurs due to a decrease in elastic properties
- abrasion - mechanical damage to the surface layer of skin
- erosion - a defect within the surface layer that appears when formations with a cavity are opened
- ulcer – deep skin defect
- scar - the formation of new connective tissue during the healing of skin defects
- cicatricial atrophy - cicatricial transformation without previous skin damage
- lichenification – thickening, dryness, compaction, staining, deepening of the skin pattern
- vegetation - growth of a skin area in an area of prolonged inflammation
- hyper- and hypopigmentation – weakening/increasing coloration of a skin area
Blisters on the labia
Blisters appear at the sites of insect bites (fleas, lice, etc.).
They are characterized by itchy rashes, the severity of which depends on the type of insect and the sensitivity of the bitten person.
Scratching the elements can lead to infection.
Spontaneous urticaria appears as itchy, sometimes burning, blisters.
The state is called:
- taking certain medications
- eating certain foods
- concomitant diseases (chronic gastrointestinal pathologies, diabetes, leukemia, etc.)
- pathological pregnancy, menopause, etc.
The elements first have a pale pink color, which becomes white as the swelling increases.
Usually such blisters disappear within 24 hours.
Diagnosis and treatment
First, a smear is given to analyze the infection, a conclusion is made from the blood whether there is inflammation in the body, and according to indications, a pelvic ultrasound is performed to eliminate the risk of any neoplasms. If you have conditions such as fever, pain in the lower abdomen or pain when urinating, immediately make an appointment with a specialist.
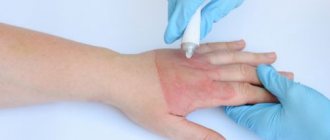
Depending on the appearance of the rash, treatment methods are selected individually. Before visiting a doctor, it is better if you treat the affected area yourself with an antiseptic (alcohol, brilliant green, iodine, chlorhexidine) and start taking multivitamins to increase immune resistance. For local therapy the following will be prescribed:
- cream for children, chamomile or powder with zinc;
- soda or herbal baths, which should be taken on a daily basis.
The systematic approach consists of applying:
- Vitamins and immunostimulating drugs.
- Drugs that fight allergies.
- Antifungal ointments.
- Preparations based on acyclovir.
- Tablets that normalize the activity of the central nervous system (Vitamin B, mint, valerian).
- Antibiotics of the penicillin group if the infection has entered the circulatory system.
- Surgical method. It is used to eliminate fatty cysts, papillomas, and dubious rashes that grow abnormally.
Acne in pregnant women: is this normal?
During pregnancy, a woman experiences enormous stress, and the change in hormones alone is worth it. Acne forms on the face, décolleté, back, and genital area. If you maintain daily hygiene, everything will go away on its own. The threat of miscarriage and taking strong medications increases the risk of strange lumps appearing in the delicate area.
The 2nd and 3rd trimester also provokes rashes on the genitals, this is due to the rapidly growing tummy, which prevents the penetration of air to the genitals. It is recommended to choose loose cotton clothing. During gestation, the work of the sweat and sebaceous glands is overloaded several times, so you should rinse more than once so that the pores do not become clogged with dirt. Continue taking vitamins to avoid the risk of vitamin deficiency, and as a result, a decrease in the protective functions of female microflora. By following all these tricks for 9 months, be sure that pimples will not affect the happy course of bearing a child.
You can ask your question to our author:
External and internal reasons for the appearance
A pimple in a woman’s intimate area will not just pop out. You may not even notice the pimple, so it is important to visit your personal gynecologist once a year. Household pathogens include:
- Synthetic underwear does not fit. This fabric does not allow moisture to pass through and is poorly ventilated, thereby provoking the growth of bad bacteria on the labia.
- Hypothermia of the internal genital organs, private wearing of skirts in winter, insufficient tightness of tights can lead to hypothermia in intimate places due to impaired blood circulation.
- Overheating of the body can provoke the proliferation of bacteria.
- Inflammation of hair follicles. When shaving and sugaring, the skin is mechanically injured and irritation begins.
- Poor hygiene or frequent washing wash away the protective microflora. Incorrectly selected care products for delicate areas can cause a rash.
- Allergic reaction to powder, pads, soap or synthetics.
- Hormonal changes.
- Abuse of unhealthy diet, a lot of sweets, flour.
These causes are easy to eliminate, the rash will go away without medical help, just follow the rules of hygiene and watch what you eat.
It’s worse if viral pathogens settle in the intimate area:
- herpes in the genitals;
- human papillomavirus;
- hormonal disorders;
- infections acquired through sexual intercourse;
- staphylococcus;
- untreated candidiasis;
- side effect of vaginal suppositories;
- weakening of the immune system.
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
Be sure to start treatment, a viral rash does not require delay.
Plaques on the labia
If a pimple appears on the labia, its size exceeds 1 cm, and in some cases, the skin in the affected area is thinned and whitened, we can talk about such primary elements as plaques.
Plaque lesions in women are typical for the following pathologies:
- neurodermatitis
- seborrheic keratosis
- lichen planus
- lupus erythematosus
- atopic dermatitis
- vulvitis candidiasis
- psoriasis
- Bowen's disease
- lichen sclerosus, etc.
With a disease such as candidal vulvitis (thrush), pimples on the labia and mucous membranes accompany the main manifestations.
These are curdled moderate/heavy discharge, swelling, redness.
Itching, which intensifies after sexual contact, a hygienic shower, during sleep, irritation, and a burning sensation in the perigenital area are also characteristic.
The problem is caused by the activity of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
Lichen sclerosus - otherwise white spot disease, lichen sclerosus, vulvar kraurosis.
It appears in the form of clearly defined light spots, plaques, papules (“white pimples”) on the labia, in the inguinal folds, and vulva.
The formation of bloody blisters and erosions is possible.
Scarring often leads to fusion of the labia minora.
Bowen's disease is an intraepidermal formation (carcinoma) in the form of a sharply limited plaque with an uneven surface.
Usually detected in old age, it can develop into squamous cell carcinoma.