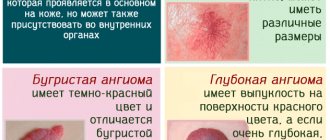
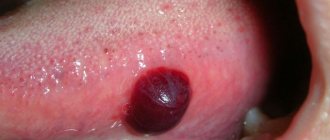
Factors contributing to the formation of bubbles:
- Oral diseases: caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, stomatitis;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Allergy to toothpaste or mouthwash;
- Injuries;
- Poor hygiene;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Immunity impairment;
- Alcohol and nicotine addiction.
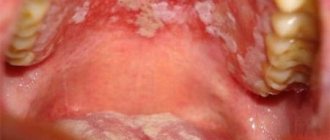
Watery blisters on the mucous membrane in some cases can indicate the occurrence of serious diseases. Such manifestations occur with tuberculosis, syphilis or diabetes. Therefore, if such a pathology occurs, it is recommended to immediately make an appointment with a doctor and undergo the necessary examination. The first sign is the sensation of a strange object in the mouth that is in the way.
Symptoms
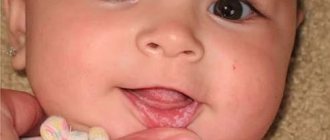
- Painful sensations when eating occur if a bubble has formed in the gum area or on the tongue;
- Pain when talking or smiling appears when a formation occurs on the inner surface of the lip;
- Pain in the throat area occurs if the bubble is located at the root of the tongue.
Transparent and bloody blisters can be not only inflammatory in nature. If the formation does not cause pain and is not accompanied by swelling, then you should consult a dermatologist. It is not recommended to treat yourself in such a situation, as it can be dangerous to health.
Acne on the face
Acne
Acne
Fungus
Allergy
27052 02 December
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Acne on the face: causes of appearance, what diseases cause it, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The sebaceous glands in human skin are located at the base of the hair follicle. They produce sebum, which moisturizes the skin and protects against the negative effects of the environment, bacteria and fungi. Hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands provokes the formation of pimples (acne, blackheads). On the face, they are most often localized in the locations of large sebaceous glands (on the forehead, temples, cheeks, nose and chin).
Types of acne on the face
In its most general form, acne falls into one of two types:
Non-inflammatory elements
(comedones) - look like small tubercles or dots of different colors. Comedones can be open or closed.
- Open comedones look like dense surface-type rashes, usually gray or black in color, which gives them the oxidative reaction of their contents with oxygen.
- Closed comedones, subcutaneous pimples (milia) look like white bumps or dots that look like small grains of millet. Accumulated sebum has no way out, which leads to painful inflammation. Closed comedones often turn into classic red pimples.
Inflammatory elements
are immediately noticeable due to their size. The skin around them becomes thinner and redder, and the purulent contents of the pimple are visible through it. When palpated, painful or uncomfortable sensations usually occur. There are several types of inflammatory rashes:
- Papules (red pimples) are inflamed comedones without obvious purulent content. They look like small red or pink balls protruding above the surface of the skin; there is no white head. If a papule has formed at the site of an open comedone, then a dark plug can often be seen through the skin.
- Pustules are infected papules or, more simply, pimples with purulent contents and a white head, surrounded by inflamed skin.
They appear when, in addition to sebum and bacteria, dead skin cells get into the pores. Pustules are cone-shaped, flat or spherical in shape. Their color can vary from white to yellow or green. Green color means the addition of a secondary infection, and if you squeeze it out on your own, there is a high probability of its penetration into the blood. - Nodules (nodules) are deep, hard subcutaneous papules of bright red, bluish or purple color, ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm, protruding to the surface of the skin, often accompanied by purulent discharge. After recovery, pigment spots and scars are left behind.
- Cystic acne is a sign of damage to the deep layers of the skin, indicating the presence of inflammation with the formation of pus. Cysts located at a short distance from each other tend to merge, forming a whole chain connected by fistulas.
Cystic acne is difficult to treat and always leaves noticeable marks on the skin.
Possible causes of acne on the face
So, acne appears as a result of excess sebum production, which clogs the skin pores. If the pore is partially closed and there is air access into it, acne begins to form. At first they look like blackheads surrounded by inflamed skin - the so-called blackheads. In a completely clogged pore, like in a container, anaerobic bacteria ( Propionibacterium acnes or Malassezia
), provoking the inflammatory process and suppuration.
But what makes the sebaceous glands work so actively? It is believed that one of the reasons lies in the high level of androgens (male sex hormones), which stimulate the production of sebum. The development of hyperandrogenism can be facilitated by digestive problems, stress, diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, endocrine and reproductive systems.
It is important to mention that rashes on the face that look like pimples can be a symptom and manifestation of other, sometimes very serious, dermatological diseases (acneiform dermatoses), which are in no way related to the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Acne on the face can be a symptom of a number of diseases (dysfunction of internal organs, hormonal dysfunction, lack of vitamins, decreased immunity), as well as poor environmental conditions and improper skin care. We list the main diseases, conditions and factors that result in skin rashes.
- Physiological changes in hormonal status: puberty, second phase of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, lactation, menopause.
- Diseases of the endocrine system: polycystic ovary syndrome, hypothyroidism, tumors of the endocrine glands.
- Thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis (hyperkeratosis), when dead cells of the epidermis are not exfoliated, but remain on the skin, clogging the sebaceous glands.
- Liver diseases and intoxication caused by them.
- Poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency:
- The predominance of fast carbohydrates (fast food, baked goods, fried, fatty foods) in the diet provokes an increase in blood glucose levels and a sharp release of insulin, which, in turn, affects the increase in testosterone levels.
- Excess omega-6 fatty acids can aggravate inflammatory processes in the skin (such phenomena can be observed when consuming large amounts of fish and poultry raised on animal feed).
- Abuse of dairy products, sunflower, peanut, soybean oils and margarine often causes hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands.
- Deficiency of zinc, vitamins A and E, Omega-3 fatty acids.
) also play a certain role in the formation of acne and, if not their direct cause, then certainly complicate treatment.
Which doctors should you contact if acne appears on your face?
If you have skin rashes, you should consult a dermatologist and cosmetologist. However, treatment often requires an integrated approach, which involves treating the disease of which acne is a symptom. In this case, consultations with a neuropsychiatrist are necessary.
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of acne
Pimples and their localization are a kind of messenger that transmits information about disruptions in the functioning of organs or systems. Most often, acne occurs in the so-called T-zone (forehead, nose, chin) - here the sebaceous glands are most active and the pores are enlarged. But acne is often found on the cheeks and cheekbones (U-zone). This is due to various reasons and the state of the body. A special guide map “Types of acne and what they mean” has been compiled. Thus, the middle part of the forehead corresponds to the lower part of the digestive tract, the small intestine and the bladder, the area near the ears - to the kidneys, the eyelids and the area around the eyes - to the liver, the temporal region - to the gallbladder, the middle third of the face, cheekbones - to the lungs, chin - to the stomach, the pelvic organs, the nose - the pancreas and heart, and the lower part of the cheeks and lower jaw - the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Diagnosis begins with a thorough examination of the skin, collecting anamnesis (information about past illnesses, operations, chronic diseases, heredity) and establishing a connection between the rashes and lifestyle, nutrition, and habits.
If the nature of the disease is not obvious, laboratory tests are prescribed.
- Clinical blood test.
Treatment methods depending on the cause:
- If the formation occurs due to a viral infection, then treatment will be based on the use of antiviral drugs;
- If the cause is injury, then it is necessary to eliminate the consequences and rinse the mouth with antiseptics;
- If an allergic reaction provokes an illness, then you should find out what the irritant is and not use it anymore. The doctor will also prescribe antihistamines;
- If a large bloody bubble has formed, then surgery is performed. After this, the doctor prescribes medications for rapid tissue regeneration and restoration.
Prevention of milia
To prevent the appearance of milia, careful facial skin care is required using cleansers and moisturizers appropriate to the skin type, scrubs, peels, cosmetic masks that normalize the activity of the sebaceous glands; elimination of provoking factors, proper and rational nutrition, healthy lifestyle. Salon cosmetic procedures, including mechanical, ultrasonic, vacuum facial cleansing, peelings (chemical, mechanical - microdermabrasion), laser resurfacing, are quite effective in preventing the appearance of milia.