- What kind of disease is candidiasis?
- Symptoms
- Causes
- Treatment
- Therapy methods
- Preventive measures
Many parents are aware of such a common problem in children as thrush, which is characterized by the appearance of a white coating on the tissues of the oral cavity. In medicine, this pathological condition is called “candidiasis” and refers to fungal diseases. Candidiasis most often develops in a child’s mouth in the first year of life. The symptoms of thrush are very disturbing for the baby, but timely treatment allows you to get rid of the fungus quickly and without consequences.
What kind of disease is candidiasis?
According to statistics, about 30% of infants experience candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of children is not yet formed and is not able to resist pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors.
With weakened immunity and the concomitant influence of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. Much more often, if thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.
Thrush: a common problem with improper treatment
Every woman knows what candidiasis (“thrush”) is. And each has a “proven” remedy. But what if symptoms return? Why can candidiasis persist? And how to find an individually effective medicine?
Why does Candida fungus “grow”?
1. Lactobacillus deficiency
As is known, the basis of female microflora is lactobacilli. The share of which, ideally, is at least 85%.
The remaining 15% are dozens of species of opportunistic bacteria and 4 species of Candida fungi. The presence of which is acceptable and safe, but only in limited quantities.
Control of the number of such pathogens is carried out by lactobacilli, which secrete lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide. And while there are enough of the latter, “conditionally harmful” ones are not capable of reproduction.
To maintain normal activity, lactobacilli need food - glycogen from the surface cells of the vaginal epithelium ("dead from old age").
And the rate of epithelium renewal, that is, “replenishment of food reserves,” in turn, depends on the balance of estrogen.
Thus, a decrease in lactobacilli and the “overgrowth” of fungi and other pathogens against this background is often associated with an imbalance of estrogen and is observed with:
- Diseases or decreased ovarian function,
- When taking certain oral contraceptives;
- Against the backdrop of acute stress
- Against the background of sudden weight loss (fat is needed for the synthesis of estrogens).
Mechanically, frequent douching and other similar procedures that “wash away” the surface layer of cells and a certain amount of beneficial flora can provoke disturbances.
Well, among other reasons:
- inflammatory diseases
- sexually transmitted infections
- long-term and/or “non-targeted” use of antibiotics
- and the use of antibacterial/antiseptic suppositories.
2. Insufficiency of immunity
“Thrush” may also be associated with immune disorders, since Candida is “under the supervision” of local defenses.
And another risk factor for candidiasis are:
- various immunodeficiency conditions
- chronic pathologies that adversely affect the immune system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies, oncological processes, etc.),
- taking glucorticoid hormones.
3. Household reasons
Well, the most “banal” provocateur of the violation may be the regular use of sanitary pads, wearing synthetic underwear and some other factors that create conditions for increased local temperature, oxygen deficiency and high humidity. That is, what fungi of the genus Candida “love”.
Candidiasis or “other”
If you suspect a risk of candidiasis, you can already based on the presence of the listed factors. It is not easy to distinguish candidiasis from vaginosis at first glance.
At the same time, the treatment of one and another pathology is fundamentally different. And the use of non-targeted therapy leads to chronicity of the process and the development of complications, including infertility.
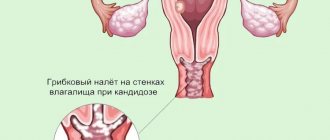
The nature of the discharge can help determine candidiasis by eye - white, cheesy, with a sour odor, accompanied by severe itching. However, not everyone has such “classic” signs and not always.
Vaginosis (bacterial vaginosis) often “has” copious white-gray, sometimes foamy, discharge, with an alkaline (“fishy”) odor, which intensifies after sexual intercourse. Sometimes with itching. However, even here the nature of the symptoms varies greatly. And, among other things, violations can be combined.
Thus, to accurately distinguish candidiasis from other forms of vaginal dysbiosis, a flora analysis will be required.
And the most complete picture can be obtained from the “Florocenosis” analysis.
The study includes calculations:
- lactobacilli,
- causative agents of bacterial vaginosis Gardnerella vaginalis
- and Atopobium vaginae,
- Enterobacteriaceae
- Ureaplasma urealyticum,
- Candida albicans
which makes it possible to differentiate several types of dysbiosis at once and apply the correct treatment.
Typing fungi of the genus Candida allows you to select an effective antifungal drug. After all, not everyone knows, but some of the listed types have pronounced resistance to popular means. You can get the typing result in the “Florocenosis” test or submit a vaginal smear for a separate fungal typing test in order to accurately determine the type of thrush pathogen and select the right antifungal drug.
Prevention of candidiasis
Summarizing all of the above and adhering to national clinical recommendations, we can conclude that the prevention of “thrush” in both women and men comes down to:
- maintaining personal hygiene,
- the use of barrier methods of contraception,
- abstaining from unprotected sexual intercourse with frequent changes of partners,
- avoiding uncontrolled use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs,
- exclusion from the “wardrobe” of tight, synthetic underwear,
- monitoring the state of general, hormonal and reproductive health.
In addition, women should:
- limit the use of sanitary pads to menstruation days only,
- exclude douching, vaginal douche and other similar procedures,
- prevent long-term use of intrauterine devices and vaginal diaphragms.
And pregnant women require special attention, due to physiological weakening of the immune system, changes in hormonal levels and stagnation of lymph in the pelvis due to increased intra-abdominal pressure. Which creates “favorable” conditions for the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
Symptoms
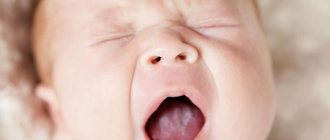
Oral candidiasis in children can have different forms of manifestation and severity of symptoms: mild, moderate and severe. As a rule, each form corresponds to the stage of development of the disease. If therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, the signs of fungal infection become more intense and the number of symptoms increases.
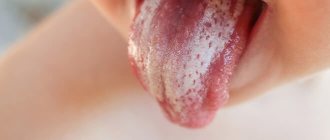
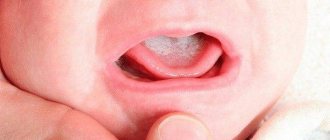
In mild forms of the disease, a red rash appears on the oral mucosa, which is covered with a white coating on top. At the next stage, the child experiences swelling of the tissues and the formation of localized white spots with a coating of curd consistency. Gradually these spots merge into a larger affected area. When plaque is removed, bleeding ulcers open. If thrush starts, the fungus spreads to the entire oral cavity, including the lips, tongue and throat. All fabrics are completely covered with a curd coating.
Common symptoms of candidiasis in children include:
- burning and itching sensation in the mouth;
- discomfort and pain when eating;
- frequent regurgitation in babies;
- formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
- temperature increase.
Children in the first two years of life report their condition by refusing to eat, constant whims and crying for no reason. It is not difficult to see the signs of candidiasis, so if a child has a sharp rise in temperature or refuses to eat, pediatricians and dentists recommend checking the oral cavity for the presence of white plaque. If you suspect thrush, it is not advisable to delay a visit to a specialist, since the fungal infection progresses quickly.
Complications of thrush
Thrush (candidiasis) is a disease, so its appearance requires special measures for immediate treatment. A mild form of candidiasis can develop into a more severe form if left untreated. The child’s body is designed in such a way that an infection from one place quickly spreads to another. Therefore, thrush as a disease cannot be underestimated. In weakened children, Candida fungi can spread into the intestines and disrupt its natural environment.
Fungi can enter the intestines, where they will also begin to multiply
Manifestations of thrush in the genitals of girls can become especially difficult to treat. Delayed treatment can lead to serious consequences: a fungus in the vagina can cause vulvovaginitis, which leads to fusion of the labia or vaginal mucosa (synechia). Treatment of this problem occurs only surgically. Therefore, treatment of white plaque in the mouth of girls should be accompanied by constant parental monitoring of the condition of the genital organs.
- How long does it take for drugs to leave the body?
Important! At the slightest sign of complications in the form of redness and discharge, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Synechia
The presence of a large number of bacteria in the oral cavity can cause them to enter the child’s blood, lymphatic system, and from them to all organs. It is necessary to start treatment on time to prevent such a serious complication of thrush.
Important! Treatment should continue until the child recovers completely. Otherwise, the disease can become chronic, which will significantly weaken the immune system, and this will cause the development of allergies and other diseases.
Bacteria can also enter the blood
Causes
The main reason for the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in children is weakened immunity. If a baby is born premature, the likelihood of developing thrush is very high. Children who are breastfed or have congenital pathologies are also often exposed to fungal infections.
Provoking factors include:
- the presence of vaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy (the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal);
- insufficient hygiene of the female breast during breastfeeding (the fungus is often localized specifically on the nipples due to the environment favorable for it);
- poor handling of the child’s initial things (bottles, pacifiers, etc.);
- parents’ habit of licking nipples (even if the adult has no signs of thrush, there may be a fungus in the mouth that can be passed on to the child);
- long-term use of drugs from the “antibiotics” group (medicines help reduce one’s own immunity);
- frequent regurgitation in infants (after regurgitation, an increased acidic environment will remain inside the oral cavity, favorable for fungus);
- excessive and frequent dry mouth (lack of saliva as a protective agent against the activity of pathological microorganisms).
Infection with Candida fungus in children over 2 years of age can occur as a result of consuming unwashed foods, raw milk or running water. If a child over 3 years of age suddenly shows signs of thrush, they should be examined not only for a fungal infection, but also for other possible diseases that may be accompanied by a “decay” of the immune system.
Signs of the disease
The key sign of the disease in childhood is the appearance of a whitish coating on the epithelial tissues, hiding eroded areas of tissue underneath. Lesions may appear on the tonsils, in the pharynx, on the tongue, in the corners of the mouth and on the edges of the lips.
In children with unformed speech, acute candidiasis can manifest itself in the form of refusal to eat, irritability, tearfulness, somnological disorders, and bleeding from the gums. Older children may complain of pain in the mouth when eating, itching and burning of epithelial tissue in the affected area.
The main signs of chronic candidiasis are:
- swelling of the epithelium;
- the appearance of light brown plaque on epithelial tissues;
- dryness, pain in the mouth;
- systematic bleeding from gum tissue.
Treatment
Fungal diseases in children can be treated by a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist or a dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of oral thrush, then therapy can also be carried out by a dentist.
The diagnosis of candidiasis is determined in most cases based on an examination of the oral cavity performed by a specialist. If there is any doubt, the doctor refers the patient for additional examinations. More often, to confirm the disease, a laboratory test is used to test a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children requires an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe cases, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local agents and compliance with preventive recommendations.
Does COVID-19 affect the health of teeth and gums?
With Covid, skin symptoms may appear. Unfortunately, doctors often ignore examining the oral cavity of patients with suspected coronavirus infection for safety reasons.5
According to The New York Times, after suffering from coronavirus, a person may experience problems with teeth and gums. The newspaper cites several cases where people who recovered from COVID-19 experienced tooth loss.7
These observations support the need for dental monitoring of patients during illness and after COVID-19.
Therapy methods
Treatment of candidiasis begins with treatment of the oral cavity. The first procedure is performed by a specialist at the appointment. Antiseptic agents are used to remove plaque. The doctor may then apply an antifungal agent.
The parent should closely monitor the dentist’s actions, since in the future they will have to treat the oral cavity themselves at home. The necessary medications will be prescribed by a specialist. Local antifungal agents are dangerous in case of overdose, especially for children, so you must strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations.
In advanced cases, medications are prescribed in the form of solutions, drops or tablets. There are few drugs available to treat candidiasis in children. Replacing them with adult counterparts is also dangerous. The dosage must be strictly observed.
A mandatory addition to the main therapy is maintaining good hygiene, good sleep, proper nutrition and taking measures to strengthen the immune system (eating healthy foods, taking pharmaceutical vitamins if necessary, walking, etc.).
Cheilitis with COVID-19
Cheilitis is an inflammatory disease of the lips, the skin around the lips and the mucous membrane of the lip.
Main symptoms of cheilitis10:
- dryness and tightness of lips
- crusts on lips
- itching, burning
- redness
- soreness
- cracks
Less common:
- bubbles
- blood crusts
- exudate (liquid secretion)
The severity of symptoms and their presence depends on the type of cheilitis. Treatment of cheilitis is always complex and also depends on the form of cheilitis.
General treatment of cheilitis
- Normalization of nutrition, adherence to a diet that does not contain allergens, exclusion of spicy, irritating foods
- Taking vitamins, especially group B and PP (nicotinic acid)
- Antibacterial, antifungal and antiviral drugs for infectious cheilitis (Important! These drugs are taken only as prescribed by a doctor!)
- Antiallergic drugs
- Sedatives (Prescribed by your doctor!)
Local treatment of cheilitis
- Painkillers if necessary
- Antiseptics
- Proteolytic enzymes for cleaning erosions
- After inflammation and pain have subsided, healing ointments
- Corticosteroid ointments (Important! They are rarely prescribed and only by a doctor, as they have many side effects.)
- Physiotherapy
- Surgery
For actinic cheilitis, it is necessary to reduce sun exposure and be sure to use creams and lipsticks with SPF.
An important stage is oral hygiene; it is necessary to remove tartar, plaque and cure caries, otherwise there is a high probability of relapses.
It is necessary to treat not only the affected area, but also the entire oral cavity antiseptically, in order to avoid infection of the affected areas of the lip and reduce the risk of relapses.
To treat infectious cheilitis, you can use Tantum® Verde .
Why does thrush occur in a child?
The scientific name of the disease is candidiasis, but it is popularly called thrush. It is a lesion of the skin and mucous membranes by yeast-like fungi Candida albicans. Fungi are opportunistic organisms that live in the body of a child and every adult in normal quantities. But after creating good conditions, they begin to multiply and create unpleasant symptoms. The cause of the development of the disease is always the weak immunity of small crumbs. Let's find out what factors contribute to a decrease in the body's protective functions and can cause thrush. These include:
- cracks and injuries in the oral mucosa;
- burns and other damage to the skin;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (most often dysbacteriosis), regurgitation;
- long-term therapy with hormonal and antibiotic drugs;
- lack of hygiene or poor compliance with it;
- overeating sweet mixtures;
- eating a lot of sweets (for older children);
- period of teething;
- absolutely any inflammation, colds, infections;
- vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorder;
- prolonged stay in a damp room, wearing diapers.
Pediatricians, including Dr. Komarovsky, say that oral thrush most often develops:
- in a premature baby,
- in children after operations.
Also at risk are infants who do not receive all the nutrients and vitamins found in their mother’s breast milk, since artificial formulas are used for feeding. Fungi can be transmitted during childbirth if a woman has not cured genital candidiasis. Most often this is what happens.