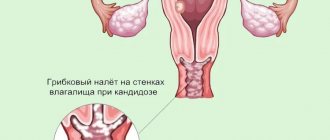
Thrush is an inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system of a fungal nature. It most often occurs in women in the form of vaginal candidiasis. It manifests itself as cheesy or creamy white discharge from the vagina, burning, itching and redness in the genital area, pain during intimacy and during urination. Treatment includes local and systemic use of drugs with antimycotic effects, as well as correction of immunity.
Urogenital candidiasis is a common infectious disease. Thrush occurs mainly in women of reproductive age. In men who are sexual partners of such patients, candidiasis balanoposthitis may occur. A child becomes infected with a fungal infection from a sick mother during childbirth.
Causes
The disease is caused by microorganisms of the genus Candida.
They are part of the opportunistic microflora that constantly lives on the skin and mucous membranes of humans. However, with decreased immunity or hormonal imbalance, fungi begin to actively multiply, suppressing the growth of beneficial bacteria and causing an inflammatory response. The following factors can cause thrush:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- excess weight;
- diseases of the female reproductive system;
- disturbances in the state of the microflora of the mucous membrane of the external genital organs;
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, drugs with cytostatic effects, immunosuppressants;
- radiation and chemotherapy;
- use of tight clothing, underwear made of synthetic fabrics;
- rare change of sanitary pads;
- intrauterine contraception - vaginal diaphragms, douching, spermicides;
- use of intimate deodorants, scented pads and tampons.
An exacerbation of the disease often occurs on the eve of menstruation and after significant stress. Diet is also important - consuming large amounts of carbohydrates contributes to the development of fungal infections.
Caring for a newborn boy: bathing
Caring for a newborn up to six months of age involves daily bathing. In the future, you can bathe the baby every other day or even two. Bathing is intended, first of all, not to cleanse dirt (a baby who cannot walk or crawl does not get particularly dirty yet), but to wash away the waste products of the sebaceous and sweat glands from the skin and give it the opportunity to breathe fully.
At the beginning of life, a newborn has a neutral skin pH and is therefore very vulnerable to bacteria and external influences. Only by six months the environment becomes more acidic and a protective glycolipid mantle forms on the skin. It should be protected from excessive use of detergents and maintained by lubricating the skin with natural oils. Olive, almond and other natural oils have a composition similar to that of sebum, so they easily penetrate deep into the skin and saturate it with beneficial substances that increase its protection. After each bath, you can carefully lubricate all the folds of the newborn’s skin with a thin layer of sterile hygienic oil, baby cream or milk. Close attention should be paid to the area behind the ears, where the delicate skin often gets wet and crusts form. After six months, you can moisturize your baby’s skin as needed.
Herbal medicine - the use of herbal decoctions - is at your discretion, just do not forget the fact that recently more and more babies are born with a predisposition to allergies.
| This is important to know! For diaper rash, especially associated with erosion, the skin should not be treated with oils, creams and alcohol-containing solutions. It is necessary to consult a pediatrician, he will select special disinfectants and drying agents. You can return to moisturizing your skin when your skin stops getting wet. You should also know that diaper rash in the perineal area is not necessarily a consequence of improper care. This may be the first symptom of atopic dermatitis. Consult a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist (for an appointment call: +7 (495) 229–44–10, +7 (495) 954–00–46). |
Classification
Vaginal candidiasis occurs in acute or chronic form.
In the latter case, the symptoms are less pronounced, but the disease has a long course and is more difficult to treat. Chronic thrush can be recurrent, with frequent exacerbations, and persistent, when episodes of deterioration are rare and associated solely with the provoking factor. The formulation of the diagnosis also specifies whether urogenital candidiasis is complicated or uncomplicated, depending on the number of exacerbations of the disease over 12 months and the severity of its manifestations. The congenital form of thrush is observed in children infected during childbirth from a sick mother. Candidiasis of newborns most often affects certain areas - eyes, mouth, respiratory tract, lungs, skin, but fungal sepsis cannot be excluded when a large amount of the pathogen enters the blood.
Soda rinses for older children
When the child is old enough to rinse his mouth on his own (this usually happens at the age of 1.5–3 years), he can use the soda solution himself to fight thrush.
- Add 2 tsp to 1 glass of water at room temperature. soda and mix well.
- Your fidget should thoroughly rinse the mouth with the resulting solution, spitting out the liquid each time. One rinse should last at least 30 seconds.
- The procedure should be repeated 3-5 times a day.
Symptoms
The acute form of vaginal candidiasis has a clear clinical picture.
A woman is worried about intense itching, burning in the genital area and near the anus, pain when urinating, during intimacy, discharge from the genital tract of a white or yellowish color with a cheesy consistency and a sour odor. The latter can be abundant or adherent in moderate quantities on the mucous membrane of the vulva, in the posterior and lateral vaults of the vagina. Also in the affected area there is redness, swelling of the tissues, and possible cracks in the skin and mucous membranes. With persistent thrush, the symptoms are less pronounced. There may only be itching and discharge in small quantities, appearing, for example, only on the eve of menstruation. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis may be accompanied by striking manifestations during exacerbations. They leave dryness, atrophy, and lichenification on the skin and mucous membranes.
In newborns, thrush is often accompanied by damage to the oral cavity and tongue. A white coating appears on the mucous membrane; when you try to remove it, areas of redness and swelling are found underneath it. A child suffering from candidiasis from birth is capricious, and has sleep and appetite disturbances.
Thrush in men manifests itself in the form of candidal balanoposthitis and urethritis. The disease is accompanied by burning and itching, redness, and swelling in the area of the head of the penis. It may cause rashes, often covered with a white coating, and cracks. Just like in women, sexual intercourse and the process of urination become painful.
Candidiasis (thrush) in children
The following forms of thrush are distinguished:
- Thrush of the mucous membranes (oral cavity, tongue, gums, pharynx, tonsils, trachea, larynx, red border of the lips, corners of the mouth, teeth, vagina, vulva).
- Thrush of the skin and its appendages.
- Thrush is visceral, systemic.
- Allergic manifestations of thrush in children.
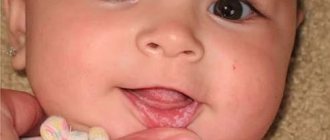
Candida infection most often manifests itself as thrush . It most often affects newborns, infants and preschoolers. The main symptom is curdled white deposits on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, gums, and palate. The overlays are initially located pointwise and then merged. Easy to remove. If treatment is not carried out in time, the overlays become denser and become grayish-dirty in color, they are increasingly difficult to remove, and the mucous membrane bleeds after removing the overlays. The general condition is not significantly disturbed if the children in the first days of life are not sick with anything else.
If the infection affects the mucous membrane of the tongue, then not only fungal overlays appear, but also areas without papillae. Swelling of the tongue, focal hyperemia and striations with furrows are recorded. The tongue becomes more sensitive to spicy and hot foods. Patients may complain of a burning sensation and dry mouth. It is difficult for infants to suckle milk, which is why they have difficulty eating.
Candidiasis tonsillitis , as a rule, appears against the background of candidiasis of the oral mucosa. It manifests itself by the appearance of loose whitish deposits on the surface of the tonsils, which can be removed with a spatula without effort. The tissue of the tonsils is practically unchanged. The child's general condition is almost normal. The temperature is elevated only if candidiasis of the tonsils occurs against the background of ARVI.
When diagnosed, fungal tonsillitis is distinguished from localized diphtheria of the pharynx by the absence of fever, the absence of hyperemia of the tonsils, and the normal size of the regional lymph nodes.
Candidiasis infection of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and tonsils can spread to the mucous membrane of the larynx, trachea, and esophagus. In such cases, symptoms such as hoarseness and difficulty breathing appear.
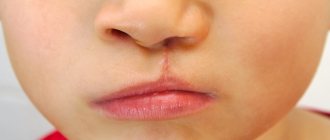
Candidiasis of the corners of the mouth (jam) in children occurs in rare cases. It is recognized by cracks in the corners of the mouth and erosion with perifocal infiltration. Usually both corners of the mouth are affected. The disease is distinguished from streptococcal infection - with it the inflammatory reaction is more pronounced.
Candidiasis of the red border of the lips (in the literature referred to as cheilitis) is often combined with candidiasis of the oral mucosa and erosions of the corners of the mouth. The red border of the lips swells and becomes hyperemic. The patient complains of dryness and burning of the lips. The disease lasts a long time.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis is symptomatically manifested by white discharge. The mucous membrane of the genital organs is moderately hyperemic, with loose cheesy deposits of a whitish or grayish tint visible on it. Rarely does it have superficial erosions. Overlays can be found in some cases on the vaginal mucosa and cervix. The external genitalia are very itchy and there is a burning sensation.
Intertriginous candidiasis occurs most often in infants in the area of large skin folds. The skin is hyperemic or eroded, and maceration of the stratum corneum is observed on it.
Smooth skin candidiasis in infants occurs mainly as a result of the spread of intertriginous candidiasis from skin folds. Candidiasis of the scalp is rare in children .
Chronic generalized granulomatous candidiasis is typical for children who are malnourished, suffer from gastrointestinal disorders, and bronchitis. The disease begins with oral thrush, then the process causes glossitis, cheilitis and seizures, which are treated poorly and ineffectively. In many cases, deep dental caries develops. The process subsequently affects the skin on the face and under the hair, and later on the torso, arms and legs. The appearance of hyperemic spots with a bluish tint, with infiltration and superficial peeling is recorded. These epidermal lesions gradually become granulomatous. Papules and tubercles appear, many of which are covered with a yellow-brown crust, under which papillomatous growths form. In almost all cases, the disease affects the nails and nail folds.
Microscopy results show the presence of yeast-like fungi in the urine and feces, and in some cases in the blood. Serological reactions in all sick children are positive.
In recent years, visceral candidiasis most often manifests itself as pulmonary candidiasis, which appears as a result of long-term therapy with antibiotics that were prescribed incorrectly. Pulmonary candidiasis manifests itself with a variety of symptoms. The disease can be acute or take a protracted, chronic nature. Relapses and exacerbations are possible.
Abscessing and cavernous forms of candidiasis pneumonia, pleurisy, which are difficult to distinguish from tuberculosis based on symptoms and radiographs, have been recorded in the literature.
Gastrointestinal candidiasis is distinguished by the fact that the deposits are abundant, sometimes completely fungal, they can cover the entire mucous membrane of the esophagus. Symptoms such as progressive dysphagia and the inability to swallow food are noted. Babies stop reaching for their mother's breasts and vomit. In especially severe cases of the disease, due to the massiveness of the deposits on the esophagus, its lumen may narrow, or even obstruction may occur. Histologically, deep destruction of the esophagus is revealed. In most cases, damage to the esophagus is also accompanied by thrush of the oral mucosa, which provides clues to diagnosticians.
Gastric candidiasis is a rare disease in children. It can only be detected by obtaining histological examination data. On the affected part of the stomach, hyperemia of the mucous membrane and small erosions are noted. Typical overlays, as with thrush, are quite rare.
With intestinal candidiasis, symptoms of enterocolitis or colitis, intestinal colic, and bloating are recorded. The stool is watery and may contain blood. The disease lasts a long time, there are relapses.
Damage to the urinary tract by Candida fungi manifests itself as urethritis, pyelitis, cysts, nephritis.
Generalized candidiasis in children can lead to endocarditis with damage to the heart valves or meningitis and meningoencephalitis, which is typical mainly for infants and preschoolers. With candidiasis meningitis, mild meningeal symptoms and a slight increase in temperature are observed. The disease progresses sluggishly, torpidly, and relapses are possible.
The most severe manifestation of candidal infection is candidal sepsis . This form of the disease occurs mainly in babies from 0 to 6 months. Before the disease, as a rule, there is another serious illness or microbial sepsis, which is complicated by an associated superinfection with the Candida fungus.
Candidiasis can spread through the oral mucosa to the esophagus, intestines or to the larynx, bronchi and lungs and end in sepsis . Also from the oral mucosa, Candida can spread through the blood. The symptoms of candidal sepsis are almost similar to ordinary bacterial sepsis. Diagnosis is made by isolating Candida from the blood of a sick child.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist diagnoses and treats thrush in women. If candidal balanoposthitis appears, you should seek help from an andrologist. During the patient’s initial visit, the doctor clarifies the nature of the complaints, the duration and frequency of appearance of signs of thrush, and conducts an external examination of the genital organs. Next, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests:
- a smear from the mucous membrane of the genital organs followed by a microscopic examination of the biomaterial;
- cultural seeding to determine the species of the fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic drugs;
- detection of pathogen gene material by PCR.
In order to clarify the predisposing factors that contribute to decreased immunity and hormonal disorders, the following is carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of antibodies to HIV;
- blood test for the content of important microelements and vitamins;
- analysis of blood glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis, it is possible to conduct other tests, and if necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed - a therapist, gastroenterologist, dentist, immunologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist.
Artificial feeding, what measures to take
Attention! Infants who are bottle-fed are more susceptible to candidiasis than others. Therefore, they must be surrounded with special care. Parents should pay increased attention to caring for their baby's oral cavity.
The fact is that the mixtures contain sugar, which promotes the growth of fungal colonies. In addition, the remains of baby food stick to the roof of the mouth, which causes a lot of unpleasant sensations with oral candidiasis.
Be sure to give your baby boiled water after each feeding. 2-3 tsp is enough. liquids to wash away food debris from the mucous membrane. This will stop further growth of the fungus.
Treatment
Since fungi of the genus Candida belong to the opportunistic flora, treatment is required only in cases of vaginal candidiasis or balanoposthitis proven in laboratory studies, which have characteristic symptoms.
In case of uncomplicated course of the disease and early contact with a gynecologist, it is possible to prescribe only topical medications - vaginal suppositories and tablets for thrush, antifungal ointments, creams. In case of their ineffectiveness, as well as in case of chronic urogenital candidiasis, systemic antimycotics are prescribed - fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole.
Drug therapy for thrush during pregnancy is limited to topical antimycotic drugs for intravaginal administration. Children are prescribed systemic antifungal agents for thrush in a dosage adjusted based on body weight.
Local and general drugs are also used to treat balanoposthitis. To achieve greater effect from the use of ointments and creams, the head of the penis is first washed with a weak soda solution. If a man has a regular sexual partner, she also needs to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and, if necessary, a course of antifungal therapy, since infection with thrush is possible during intimate intimacy.
Stages of development of oral candidiasis
Photo: Depositphotos.com. Author: Mukhina1.
If a child has been diagnosed with thrush, it is worth immediately determining its stage:
- Easy. Small red pimples appear in the mouth, and after a few days the entire tongue is covered with a curd coating. At this stage, the disease does not bring much discomfort to the baby, so it is very important to detect and treat the fungal disease in time.
- Average. Plaque fills the entire space of the mucous membrane, erosions appear that bleed when cleaning the oral cavity. Candidiasis becomes sensitive for infants. The baby begins to experience discomfort and a burning sensation in the mouth, which can cause breast refusal.
- Heavy. The plaque spreads to the throat and lips. The disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, gastrointestinal dysbiosis, and elevated temperature. The child becomes capricious and lethargic. This is the most difficult and painful stage.
Prevention
Prevention of thrush consists of maintaining immunity, eliminating factors that provoke its decline or hormonal imbalance.
It is important to use antibiotics reasonably and only as prescribed by a doctor, and after completing the course of treatment with such drugs, restore the microflora with pro- and prebiotics. The following measures will also help to avoid the development of fungal infections:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely treatment of endocrine and urogenital pathologies;
- normalization of weight and nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives;
- having a permanent sexual partner;
- wearing underwear made from natural fabrics;
- refusal of scented personal hygiene products, intimate deodorants, and douches.
Baking soda in the fight against thrush
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate/bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate) has many beneficial properties that are of particular importance in the fight against thrush.
- It does not cause disruption to the microflora in the mouth and has a gentle effect on the mucous membrane, which is especially important when treating newborns.
- Creates an environment that has a detrimental effect on yeast fungus. It needs a sweet and sour environment to develop. Sodium bicarbonate alkalizes the body and restores acid-base balance. As a result, all pathogenic microflora die.
- Dries out the mucous membrane. Due to its physicochemical properties, sodium bicarbonate gives a good drying effect. This helps to quickly relieve itching and other unpleasant sensations in the mouth. After soda treatment, a protective environment is formed on the surface of the mucous membrane, preventing the growth of infection.
- This is a natural, safe remedy. Pregnant and young mothers can safely use soda without fear of negative effects on the body. It is also safe for infants when treating the oral mucosa (subject to precautions).