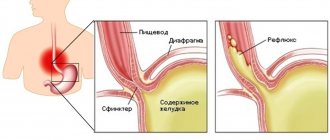
During the normal digestive process, bile is involved in the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates that accumulate in the intestines. After performing its function, bile enters the duodenum. There should be no bile in the stomach or esophagus. However, there are diseases in the process of which this scheme is disrupted and bile enters the stomach from the duodenum. There it mixes with gastric juice, after which bile refluxes into the esophagus.
Nocturnal acid reflux: how to stop it?
If you experience acid reflux at night, you may want to make a few dietary and lifestyle changes.
For example, because standing up helps with digestion, doctors recommend eating dinner a few hours before bed. Doctors also recommend raising the head of the bed to prevent gravity from moving food from the stomach into the esophagus.
If you suffer from this condition frequently, you may need medical help.
Research suggests that the hormone melatonin or medications with similar effects may reduce symptoms.
In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatment of acid reflux at night. We will also describe some methods for preventing and managing reflux.
Modern methods of diagnostic examination
As noted above, if symptoms of bile reflux into the esophagus recur regularly over the course of a week, you need to seek help from a medical specialist - a gastroenterologist. After the first visit to a specialist, a wide diagnostic examination is prescribed. The patient must undergo a set of tests: a general urine test, a clinical blood test.
In some cases, the doctor may require a biochemical blood test. Based on the examination results, the doctor decides on a treatment regimen. To undergo a diagnostic examination, the following methods are used:
Acid reflux: symptoms
Acid reflux, also known as heartburn, typically involves a burning sensation in the stomach, chest, and throat.
Other possible symptoms include:
- difficulty swallowing
- chest pain
- nausea
If the condition occurs regularly, it may indicate gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Trying to sleep
The International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD) notes that 79% of people with GERD symptoms experience them during sleep.
75% of people with the condition say symptoms affect their sleep, and 40% say loss of sleep affects their ability to get up.
Although GERD affects sleep, sleep deprivation also affects GERD. Lack of sleep can cause the esophagus to become more sensitive to acid.
Acid reflux that occurs after sleep has more severe symptoms than daytime acid reflux.
This combination of sleep disturbances and more severe symptoms means that acid reflux affects the quality of life of people with the condition.
Symptoms to help make the correct diagnosis
Bile reflux into the esophagus - a reason to visit a doctor
Sometimes the disease we are considering occurs when there is an ulcer in the stomach or duodenum. These are serious diseases, the treatment of which involves a more extensive range of measures. With ulcers, bile reflux is a symptom, and not a separate type of disease.
Today, doctors can, based on general signs, make a verdict as accurately as possible and make the correct diagnosis. The main symptoms that determine the reflux of bile in the esophagus include:
- the mouth feels constantly dry
- frequent occurrence of heartburn
- a feeling of heaviness forms in the stomach area
- constant belching and bouts of vomiting
- the presence of a yellow coating on the surface of the tongue
- there is a bitter taste in the mouth
If several of these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Acid reflux: causes
Acid reflux occurs when stomach contents flow into the esophagus. This occurs due to weakening of the esophageal sphincter.
The sphincter is a muscle that acts like a valve. It relaxes, allowing the swallowed food to enter the stomach. It then closes to prevent food from moving in the opposite direction. If the sphincter is weak, it may not function properly.
Why does the sphincter weaken?
Various factors can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter or cause it to relax when it should remain closed.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), these factors may include:
- smoking
- obesity
- pregnancy
- hiatal hernia
- certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and some medications that doctors use to treat depression
Reasons why bile is thrown into the esophagus
Bile reflux into the esophagus - unpleasant sensations
The entry of bile occurs in most cases from inflammatory diseases of the liver or gallbladder (hepatitis, cholecystitis). There may also be hydraulic reasons: disruption of the passage of bile flows, improper functioning of the sphincter, a kind of valve that is located between the stomach and duodenum.
With such deviations, bile refluxes into the esophagus. The possibility of the disease occurring due to poor diet and bad habits should not be ruled out. Experts have determined a list of the main reasons why bile is thrown into the esophagus:
- with excessively frequent consumption: carbonated drinks, strong tea, coffee
- from bad habits: alcohol, smoking, obesity caused by overeating
- with a hernia formed in the digestive tract, with cardiovascular diseases
- in the last months of pregnancy
- during bloating
- when eating quickly
The reflux of bile into the esophagus can be a single, rare occurrence - this should not happen regularly.
Control
According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI), acid reflux can be relieved with remedies such as:
- raise the head of the bed 6-8 inches
- do not go to bed for 2–3 hours after eating
- Eat small meals more often and avoid heavy meals before bed
The side of your body you sleep on can also make a difference. A 2015 study found that sleeping on your left side reduces acid reflux.
To sleep calmly
The IFFGD recommends measures to promote restful sleep. A good night's rest can help prevent symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients with GERD.
The proposed measures recommend:
- go to bed and wake up at the same time every day
- sleep in a quiet, dark, and electronic-free environment
- avoid caffeine 8 hours before bed
Bitterness in the mouth during pregnancy
The taste of bile in the mouth is familiar to many pregnant women. It can appear either at the beginning of pregnancy or closer to the second half of the term. Sometimes the cause of bitterness is diseases of the biliary system that a woman had before conception.
In healthy women, the symptom occurs against the background of hormonal changes in the initial period of pregnancy, during an active increase in the size of the uterus due to pressure on the intestines, stomach, and bile ducts.
Regardless of the cause of bitterness in the mouth, you should not take medications to eliminate it without consulting a specialist. If the taste of bile has become intrusive, the doctor will recommend the appropriate medicine. Often the problem disappears on its own after childbirth.
Prevention
There are some changes you can make to your diet and lifestyle that can prevent GERD symptoms.
Lifestyle changes
AAAAI notes that the following lifestyle adjustments may help prevent acid reflux from occurring:
- reducing alcohol consumption
- to give up smoking
- achieving or maintaining a moderate weight
Dietary changes
Diet can also play a role in preventing acid reflux.
Foods to Avoid
IFFGD advises avoiding potential dietary triggers such as:
- chocolate
- fatty or fried foods
- carbonated drinks
- onion
- tomatoes and citrus fruits
Foods to include in your diet
IFFGD recommends a diet that includes the following foods in the diet that may help prevent or reduce acid reflux:
- fruits
- vegetables
- whole grains
- foods with healthy fats such as olives, avocados and fatty fish
- lean meat
- eggs
Reinforcement of therapy - proper nutrition
Proper nutrition - prevention of gastrointestinal diseases
To consolidate the positive effect after treatment, the patient must carefully monitor his diet and lifestyle. In other words, to prevent a recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to follow a diet, eat small meals (eating small portions throughout the day - 5-7 times a day) and give up bad habits. Excessively spicy and fatty foods must be completely excluded from the diet.
You should also avoid fried and smoked foods. Today, there are a lot of recipes for delicious and healthy food that is steamed or boiled. Nutritionists have developed dozens of diets that can prevent the reflux of bile into the esophagus.
Treatment
For GERD in general, doctors may recommend one or more treatments:
Medicines
Over-the-counter medications that reduce stomach acid levels may help relieve GERD symptoms.
An older study evaluating the effect of the proton pump inhibitor (PPI) esomeprazole found that it alleviated bedtime heartburn and related sleep disturbances.
Operation
Doctors may recommend surgery if behavior changes and medications do not improve symptoms.
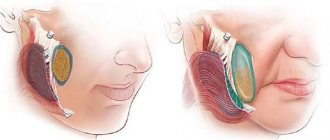
Surgical options may include fundoplication. During this procedure, the surgeon connects part of the stomach to the lower esophageal sphincter.
The Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons states that surgeons typically perform fundoplications using laparoscopy. This procedure involves making several small incisions instead of one large one.
Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone that the body produces before sleep. It helps us fall asleep and can help prevent or relieve symptoms of GERD, including acid reflux.
IFFGD found that deep sleep tends to improve GERD symptoms. This finding led them to believe that reducing the time spent awake after bedtime could reduce these symptoms.
They then conducted a study to test the effect of the sleep aid drug ramelteon, which works similarly to melatonin.
In the study, participants who took ramelteon before bed experienced fewer GERD symptoms at night. The benefit was attributed to the improvement in sleep produced by the drug.
What's more, a 2022 study reports that melatonin reduces acid secretion in the stomach and helps the lower esophageal sphincter stay closed when needed.
Given the results of two studies, it appears that melatonin may help by improving sleep quality and reducing the effects in the body that cause acid reflux.
Possible complications
Ignoring such changes in the digestive tract as the entry of bile into the stomach and esophagus, there is a high probability of complications and the emergence of dangerous diseases, among which should be highlighted:
- gastritis - the formation of an inflammatory process on the surface of the stomach due to the long-term negative effects of bile acids, which are themselves aggressive
- gastroesophageal disease - damage to the walls of the esophagus
- Barrett's esophagus is a precancerous condition in which the squamous epithelium of the esophagus becomes columnar
To avoid such pathologies, it is necessary to lead a correct lifestyle and regularly monitor your diet and diet.