Bad breath is a common problem that affects approximately one in three people. There is a medical term for bad breath - halitosis.
The appearance of an unpleasant odor may be a signal of health problems. In 90% of cases, halitosis is a consequence of poor hygiene or oral infections. Bad breath causes anxiety and embarrassment and makes it difficult to communicate with others, but it can be eliminated if the cause of its occurrence is identified and eliminated.
Causes of bad breath
The main cause of bad breath is the excessive proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity, which during their life processes release volatile gases with a characteristic unpleasant odor: hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan. Plaque on the tongue, pieces of food stuck between teeth or in gum pockets are a consequence of poor hygiene and a breeding ground for microorganisms that spread a foul odor. In most cases, treatment by a dentist helps get rid of halitosis. Other causes of bad breath include:
- food with a persistent pungent odor (garlic, onions, some spices). During the digestion of garlic, volatile sulfur compounds are formed, which enter the blood and are carried throughout the body, ending up in the lungs, larynx and mouth. They become the cause of unpleasant “garlic breath”, which disappears completely only after 72 hours;
- smoking. Tobacco smoke itself has a persistent foul odor; in addition, it can provoke gum disease, which is a common cause of halitosis;
- dry mouth. Saliva is necessary for natural cleansing of the oral cavity. It washes away food particles, preventing them from rotting, and contains antimicrobial substances that inhibit the growth of pathogenic microflora. With xerostomia (a pathological condition characterized by decreased secretion or absence of saliva), the number of bacteria in the mouth increases significantly, which contributes to the development of caries and halitosis. Xerostomia can be caused by taking certain medications (hypotensives, chemotherapy, antiparkinsonian, etc.), as well as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Saliva production also naturally decreases during sleep. This leads to an increase in the number of bacteria in the mouth (mainly on the surface and back of the tongue) and the appearance of stale breath in the morning. Drinking alcoholic beverages, coffee and smoking are other causes of bad breath due to dry oral mucosa;
- diseases of the throat and nasopharynx. Bad breath can be caused by purulent plugs in the tonsils due to tonsillitis, bacterial or viral infections of the paranasal sinuses (sinusitis), chronic bronchitis and other diseases of the upper or lower respiratory system;
- diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, reflux), liver, kidneys, diabetes;
- fasting and low carbohydrate diets. They lead to the fact that the body, experiencing a lack of energy obtained from food, begins to burn accumulated fat reserves. When fats are broken down, ketone bodies are formed. These are by-products of fat metabolism, which are excreted from the body by the lungs and have an acetone odor.
What does a healthy person's skin smell like?
The sweat of healthy people should not smell like anything. Each person is universal, has his own body aroma depending on how he lives and takes care of his health. Theoretically, people can be divided into 3 main groups:
- Sweat doesn't smell. This suggests that there is no large accumulation of toxins and bacteria in the body of such a person. Most likely, he leads a healthy lifestyle, watches his diet, exercises moderately and visits doctors. Or he was simply lucky to be born with a good immune system that does not allow viruses and bacteria. Strong immunity reduces the risk of catching a sore and acquiring the smell of viburnum from the body.
- Nice smell. 50% of people think their scent has a pleasant note. Men especially hold this opinion. In fact, this also happens. Some smell like paprika, rose, dessert. But a tasty body odor does not always indicate the proper functioning of organs. However, if you feel great and take care of your hygiene, then there is no point in steaming.
- The smell of hydrogen sulfide from a person. Nutritionists say that a person smells what he eats. And this is so, since fatty, spicy, high-calorie foods can negatively affect all organ systems. The more waste products remain in our body, the more toxins accumulate in it. And toxins come out through sweat and give off an unpleasant body odor.
The main thing to remember is that sweat is not to blame. On the contrary, with the help of sweating, all the “rubbish” comes out of a person, led by bacteria and harmful toxins. It also supports thermoregulation at different ambient temperatures. And the smell of sweat depends on the type of bacteria, and not on their number in the body.
Have you noticed that there are people who sweat a lot, but don’t smell at all? And there are people who sweat a little during physical activity, but have a strong odor. This once again proves that it is not a matter of quantity, but of quality. In our case, the quality of the state of the body.
What causes sour breath?
The most common cause of sour breath is acid reflux. This is a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by heartburn, pain in the lower abdomen, and less commonly, belching. Symptoms of acid reflux occurring more than twice a week are already characterized as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and must be treated. The main cause of reflux is a weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter, a valve-like muscle that forms a barrier between the esophagus and the stomach. Normally, the sphincter opens when swallowing food and then closes tightly. With reflux, it remains open, allowing gastric juice mixed with bile and pieces of undigested food to flow back into the esophagus. This causes heartburn, a bitter or sour taste in the mouth, and bad breath that gets worse with belching.
In some cases, a person with GERD may feel their own bad breath without even opening their mouth. The sharp sulfuric acid smell of bile from the esophagus can even be heard through the nose. Less commonly, sour breath can be a symptom of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, accompanied by increased acidity of gastric juice.
Bad breath due to gastrointestinal diseases
Bad breath in some cases can be a consequence of gastroenterological diseases. Most often, halitosis is provoked by gastroesophageal reflux (a pathological condition in which gastric contents enter the esophagus), as well as infection of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. It can cause gastritis, ulcers and stomach cancer. In addition, the bacterium may also be present on the oral mucosa, which is also a cause of halitosis. There may not be any signs of gastrointestinal diseases.
The study, published in the journal Medical Principles and Practice, involved 18 patients with halitosis and confirmed H. pylori infection. 4–6 weeks after a course of antibacterial treatment, bad breath disappeared in 16 people. This study confirmed the relationship between Helicobacter pylori and halitosis.
Much less commonly, halitosis occurs due to intestinal obstruction. This is a health-threatening condition where food is unable to move through the digestive tract due to a blockage in the small or large intestine. Symptoms of the pathology: bloating, constipation, abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting and fecal odor from the mouth. If you have these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Bibliography:
- Maksimova E. V., Stetsyuk N. S., Shelikhova E. O. “Halitosis as a medical and social problem.” Crimean therapeutic journal, No. 1, 2020, pp. 32-37.
- Gorobets S. M., Romanenko I. G., Bobkova S. A., Dzherelei A. A., Kryuchkov D. Yu., Gorobets O. V. Risk factors for the development of halitosis (review). Crimean therapeutic journal, No. 3 (34), 2022, pp. 13-18.
- Karpishchenko S., Lavrenova G., Malay O., Milchakova A. Possibilities for correcting halitosis in chronic tonsillitis. Doctor, No. 2, 2022, pp. 50-52.
- Tyomkin E. S., Churikova A. S. Halitosis - modern diagnostic methods and their prospects. Volgograd Medical Scientific Journal, No. 3, 2022, pp. 15-18.
- Suyunova M. Kh. Everything about halitosis: diagnosis, treatment and prevention (review article). Bulletin of the Council of Young Scientists and Specialists of the Chelyabinsk Region, T. 1, No. 4 (15), 2016, pp. 68-77.
- GAUZ TO "Regional Center for Medical Prevention, Physical Therapy and Sports Medicine", Prevention of dental and oral diseases, methodological manual, 2022, 36 p.
- Namkhanov V.V., Pisarevsky Yu.L. The role of oral hygiene in inflammatory periodontal diseases. Bulletin of Buryat State University. Medicine and Pharmacy, No. 1, 2022, pp. 62-65.
- Prevention of dental diseases: textbook / S.I. Borodovitsina, N.A. Savelyeva, E.S. Tabolina; Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Ryazan State Medical University of the Russian Ministry of Health. – Ryazan: OTSIOP, 2022. – 264 p.
- Shavlokhova D. T., Dzgoeva M. G., Dzhanaev B. M. Study of antibacterial activity and clinical effectiveness of rinses: chlorhexidine, listerine and carsodyl. Medical and pharmaceutical journal "Pulse", T. 14, No. 4, 2012, pp. 319-320.
- Khromova M.I., Suzanskaya M.A. The influence of balms-rinses on the microbiota of the oral cavity. FORCIPE, T. 3, No. 5, 2022, pp. 486-487.
- Internal research dated 07/09/2010. Internal reports for studies by Minoli G., October 3, 2008 Ilg D et al, Febriary 20, 2009.
- Kuzmina E.M., Lapatina A.V., Smirnova T.A. The use of antibacterial rinses for the prevention of periodontal diseases. Tutorial. Moscow. 2012 (from brands)
- "Tooth Discoloration: Article by Jonathan A Ship, DMD. Addy M, et al. J Dent. 1995; 23: 95-99.
- Overholser CD, et al. J Clin Periodont. 1990; 17:575–579.
- Minach et al. The effect of 6 months of use of an antiseptic rinse on the microflora of supragingival dental plaque. Journal of Clinical Periodontology. 1989. July; 16(6):347-52
- https://www.ncbi.nlnn.nih.gov/
- Cortelli et al. Gum health benefits of using an essential oil mouthwash and a CPC-based mouthwash: a 6-month randomized clinical trial. American Dental Journal. 2014; 27(3): 119-126
- Modern methods of diagnosis, elimination and prevention of halitosis: textbook / R.V. Ushakov, N.B. Eliseeva, N.P. Polevaya, N.M. Belova, V.V. Korkin. GBOU DPO "Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education". M.: GBOU DPO RMAPO, 2016. 81 p. ISBN 978-5-7249-2549-5
How to remove bad breath from reflux?
Medication treatment, as well as making some changes to your usual lifestyle, can help prevent sour breath from developing with GERD. First of all, you need to stop smoking. Nicotine causes the sphincter muscles in the lower esophagus to weaken, which is the main cause of stomach acid refluxing into the esophagus. In addition, smoking itself causes bad breath and increases the risk of developing cancers of the throat, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver and colon. How to prevent bad breath from reflux:
- do not lie down immediately after eating - in a horizontal position, gastric juice flows into the esophagus, and the longer it stays there, the more irritated its mucous membrane is. You must wait at least 2–3 hours;
- Place a wedge-shaped pillow under your head to elevate your upper body while you sleep. This way the esophagus will be located above the stomach and gastric juice will not flow back and irritate its walls;
- eat small meals throughout the day;
- Maintain a normal weight to avoid pressure on the stomach. Obesity increases the risk of hiatal hernia, which can worsen GERD symptoms;
- Chew gum to freshen your breath and reduce the risk of heartburn.
Changing your diet can also relieve symptoms of GERD and prevent bad breath. Many foods can reduce the tone of the sphincter muscles of the lower esophagus and increase the acidity of gastric juice, thereby exacerbating the problem. Foods and drinks to avoid if you have GERD:
- alcohol;
- coffee and tea containing caffeine;
- onion and garlic;
- citrus fruits and juices from them;
- carbonated drinks;
- tomato juice;
- mint;
- spicy food;
- chocolate;
- fatty and fried foods.
Include more fiber-rich foods in your diet. These are pears, apples, avocados, artichokes, lentils, beans, broccoli, bananas, carrots and beets. They help improve digestion and avoid halitosis. Consume natural sourdough yogurt without fillers and milk, and drink enough water. Drug therapy for GERD involves the use of several types of drugs that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid or neutralize it:
- histamine blockers;
- proton pump inhibitors;
- calcium carbonate, aluminum or magnesium hydroxide.
Only a doctor can prescribe medications. Self-medication can be harmful to health.
How to eliminate unpleasant odor from the stomach?
The first step in dealing with bad odor caused by stomach problems should be to determine its true cause. To do this, you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist, since attempts at self-medication can harm your health. After examining the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor will prescribe a treatment regimen that will help solve the problem of bad breath. Taking probiotics (beneficial microbial cultures that improve the functioning of the digestive system) also helps normalize the acid balance of the stomach and reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria.
How to remove the smell of acetone from your mouth?
The smell of acetone on the breath usually appears when the body switches to the mode of burning accumulated fat due to the lack of carbohydrates from food to support all vital processes. This is a common side effect of low-carb or keto diets, but it is not harmful to your health. Breath with the smell of acetone or rotten apples disappears on its own a couple of weeks or a month after starting the diet, when the body fully adapts to the transition to a new source of energy.
In other cases, a sweetish fruity odor from the mouth may be a sign of an acute complication of type 1 diabetes - ketoacidosis. This dangerous health condition is caused by high levels of ketone bodies in the blood due to a lack of insulin. Symptoms of ketoacidosis:
- strong thirst;
- frequent urination;
- labored breathing;
- stomach ache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- confusion.
If these signs are present, you should urgently call an ambulance, since without timely treatment the patient may fall into a diabetic coma and die. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels will help prevent the development of ketoacidosis in the future.
The following tips will help minimize keto breath while dieting:
- increase your water consumption. Ketones are excreted not only by the lungs, but also in the urine. Dehydration increases their concentration in the body and increases the unpleasant odor;
- eat less protein. When it breaks down, ammonia compounds are formed - another metabolic byproduct with a strong, unpleasant odor, which is excreted through the lungs and urine;
- Maintain oral hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss and mouthwash;
- Sugar-free mints or chewing gum will help freshen breath and increase the production of saliva, which has an antimicrobial effect and neutralizes bad odors;
- increase your daily carbohydrate intake.
Methods of treating and getting rid of odor
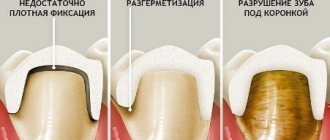
Modern dental treatment methods enable patients to maintain oral health. New materials, drugs, technologies are based on the use of computer technology and digital radiology. Today, lasers are often used and ozone is used to treat the affected areas of the masticatory organs. Sanding is often done with air.
Therapy for bad breath involves identifying and eliminating the cause of the disease. A specialist can determine the provoking factor. Since more than 65 percent of problems relate to diseases of the oral cavity and poor hygiene, you should visit the dentist on time. It is necessary to thoroughly clean the crowns, spaces between units, and tongue. For this purpose, dental floss, rinses, and tongue brushes are used. You need to choose the right toothpaste and use fluoridated products on the advice of your dentist.
What to do if your breath stinks?
The fight against bad breath should begin with a visit to the dentist, since most often halitosis is a consequence of poor oral hygiene and the resulting diseases of the gums and teeth. If the doctor does not find any problems, then the cause probably lies in gastrointestinal diseases, and you need to visit a gastroenterologist. Following these recommendations will help get rid of halitosis:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly at least twice a day (especially after meals), using a toothpaste containing fluoride, as it helps strengthen the enamel. Using a toothpaste or mouthwash with antibacterial ingredients kills bacteria in the mouth that causes bad odor;
- floss at least once a day to remove food particles stuck between your teeth;
- clean the surface of your tongue daily with a special scraper or toothbrush to remove plaque, which is a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria;
- Clean your removable dentures regularly (at least once a day or as directed by your dentist);
- avoid dry mouth - drink more clean water, chew sugar-free gum to stimulate saliva production;
- Avoid consuming garlic, onions, hot spices, alcohol and coffee. Limit your sugar intake - it promotes the growth of microbes, which turn it into acid, which destroys tooth enamel;
- change your toothbrush every three months;
- Get a routine check-up with your dentist every six months.
In what cases should you be concerned about such a symptom?
In any case, it is logical to consult a physician, dentist or gastroenterologist when halitosis appears to rule out the presence of serious health problems. Having found out the true causes of the unpleasant “aroma”, together with the doctor it is necessary to determine further tactics of behavior.
If halitosis is associated only with dietary restrictions or fasting, then only successful “masking” of it will be a sufficient measure. Otherwise, you should immediately begin treatment of organs that are malfunctioning in the body.
Another important note: it is advisable to carry out any dietary restriction only under the “supervision” of a qualified specialist (nutritionist or doctor), otherwise it is possible that there will be many more health problems than the expected benefits.
also necessary to “enter” and “exit” the diet gradually : the body may experience severe stress, which will not have the best effect on its condition.