Purulent nasal discharge can appear for many reasons and necessarily require treatment. You should not carry out therapy on your own due to the risk of severe complications if treated incorrectly. As soon as purulent discharge from the nose is noticed, you should immediately seek medical help from an otolaryngologist, or, in his absence, a therapist. The fact that pus, and not ordinary snot, began to come out of the nose can be understood by a special, extremely unpleasant odor, which does not occur with a simple runny nose. The yellow-green color of the discharge also differs from the usual one.
The appearance of pus from the nose can be associated with a number of diseases. In order to effectively treat a problem, it is necessary to accurately determine the reason why it occurs. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the therapy quickly produces positive results and nasal discharge disappears. If for some reason the disease turns out to be advanced, then treatment may take a long time and sometimes require surgical intervention. The appearance of pus from the nose occurs equally in adults and children and requires similar therapy. It is not uncommon for purulent nasal discharge to appear after viral infections as a complication of the disease. In order to prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary to fully treat the primary disease without suffering it on your feet.
When the pus is liquid and white, this is an indicator of the initial stage of the disease. In this case, it is released in large quantities, and also often flows down the back wall of the pharynx. If the particles of pus are viscous and more like lumps, then this is an indicator of severe neglect of the purulent process. Most often, with long-term disturbance, green nasal discharge occurs. The formation of pus is always associated with the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the nasal cavity. If they are absent, then a purulent process cannot occur. Because of this, in the viral form of rhinitis, the appearance of pus always indicates a secondary bacterial infection.
Causes of purulent vaginal discharge
Gynecological infections
With gonorrhea, thick yellow or green pus with an unpleasant putrid odor is released from the vagina. The amount of purulent leucorrhoea may increase after sexual intercourse. Yellow-green discharge from the vagina is accompanied by pain in the perineum with radiation to the sacrum and coccyx. When the infection spreads upward to the overlying genital organs, abundant purulent, creamy discharge with a characteristic odor is observed, sometimes streaks of blood are visible in it. Other infectious pathologies (mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis) may occur with scanty greenish leucorrhoea.
Pathologies of the uterus and appendages
Purulent vaginal discharge is characteristic of severe lesions of the uterus and its appendages - pyometra, pyosalpinx. Women note a constant flow of thick pus from the vagina with a foul odor, in which fragments of necrotic tissue or blood are found. The symptom is accompanied by severe pain in the lower abdomen, fever, problems with urination and defecation. Inflammatory causes of the disorder are endometritis (including postpartum) and endocervicitis, in which scanty purulent discharge is observed.
Bartholinitis
When the Bartholin gland is affected (bartholinitis), patients are bothered by the periodic leakage of yellow or greenish pus with a specific odor from the vagina. In the posterior third of the labia majora, the woman feels a lump; when pressing on it, suppuration intensifies. There may be throbbing pain in the perineum, worsening while walking. Lack of timely treatment and other unfavorable reasons provoke the formation of an abscess of the Bartholin gland, which, when spontaneously opened, produces abundant purulent discharge with a pungent odor.
Rare causes
- Staphylococcal infections of the genital tract
: bacterial vaginitis, cervicitis. - Intestinal-vaginal fistulas.
- Boils and carbuncles of the skin of the perineum
.
There may be explicit images of genitals hidden here.
Are you over 18 years of age?
Yes
No
Purulent discharge from gonorrhea
Abscess on the gum with periodontitis -
Gum suppuration can look completely different, but in any case, the formation of an abscess on the gum always occurs in the projection of the causative tooth. If the cause of suppuration is an infection in the root canals, then you will always see an old filling or crown on the causative tooth, or the tooth will be partially destroyed. In this case, infection in the root canals gradually leads to the development of a focus of chronic inflammation at the apex of the tooth root.
In dentistry, such inflammation of the tooth is called chronic periodontitis. From time to time, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation may occur, and in this case, pus begins to form at the apex of the tooth root, which comes out through the bone tissue and penetrates under the gum, forming an abscess there. Therefore, please note that with periodontitis, an abscess on the gum most often forms not at the gingival edge, but closer to the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth.
Abscess on the gum with periodontitis: photo
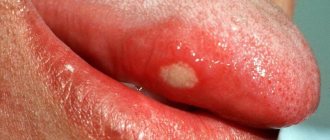
Symptoms - an abscess with periodontitis may look like a slight swelling of the gums in the area of 1 tooth or in the area of several teeth, if a significant purulent abscess has formed - flux (Fig. 4). Typically, the appearance of gum swelling is preceded by pain when biting one of the teeth. The pain can be acute, but sometimes purulent inflammation can occur without pain. Sometimes, in the projection of gum suppuration, swelling of the soft tissues of the face appears.
The abscess formed under the mucous membrane of the gums can burst with the formation of a fistula opening (Fig. 7-8). The fistula opening is connected through a fistulous tract to the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Therefore, gradual discharge of pus may be observed from the fistula openings. As soon as the acute inflammation at the root apex subsides and the process of pus formation stops, the fistula openings can close, but only until the process worsens again.
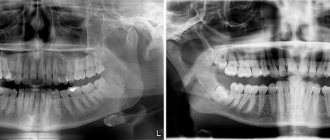
X-ray diagnostics - if you have a fistula or a purulent sac on your gum, treatment is only possible at the dentist. Before starting treatment, you need to take an x-ray to confirm the presence of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (24stoma.ru). The image will also show the quality of root canal filling, if it was performed previously. It’s sad, but according to official statistics, dentists fill root canals poorly in as many as 60-70% of cases.
The most common mistake dentists make is not filling root canals up to the apex of the tooth root, as a result of which infection begins to multiply in the part of the root canal that is not filled with filling material. As a result, a focus of chronic inflammation develops at the apex of the tooth root, for example, in the form of a cyst or granuloma. Below you can see what cysts and granulomas look like on a diagram, an x-ray, and also on the apex of the root of an extracted tooth.
Treatment of gum suppuration during periodontitis -
If, against the background of an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, an abscess appears on the gum, then what to do will depend on the results of examining the tooth and analyzing the x-ray. In some cases, it may turn out that the tooth can no longer be treated, and then you will be referred to a surgeon for removal. However, in most cases, it is possible to cure such a tooth, and then the doctor’s algorithm for further actions will depend on whether root canal filling was previously performed in this tooth.
1) If the root canals are not filled –
This greatly facilitates the doctor’s work, because... in this case, the dentist will not have to go through the trouble of unsealing poorly filled root canals. In this case, a standard method of treating periodontitis is used, which includes mechanical treatment of the root canals + treatment of the inflammation at the root apex. On your first visit, the dentist will remove your old filling or crown, drill out tooth tissues destroyed by caries, and perform a mechanical expansion of the root canals to allow pus to drain out through them.
After this, the dentist will prescribe you antibiotics, antiseptic rinses, and will most likely send you to a surgeon to make an incision in the gums, which is necessary to create a good outflow of pus. After 3-4 days, the dentist will make an appointment for you again to complete the mechanical treatment of the root canals and seal them. If the lesion is small at the apex of the tooth root, the doctor can immediately perform a permanent filling of the root canals with gutta-percha. But usually, the canals first have to be filled with temporary medicinal paste for a period of 1-2 months, and only after that permanent filling with gutta-percha is carried out.
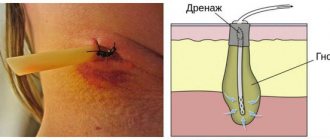
How the gum incision is made - the incision is usually completely painless and is performed under local anesthesia. If the abscess is small, the size of the incision usually does not exceed 5-7 mm, but if a large purulent abscess develops (as in the video below), the incision is made up to 1.5 cm. After opening, pus comes out of the gum, then the wound is washed with antiseptics and into it a small rubber drain is inserted. The latter prevents the edges of the wound from sticking together, which is necessary so that the inflammatory purulent exudate does not accumulate, but continues to separate from the wound. The drainage is usually left for several days.
2) If the canals in the tooth are sealed poorly -
If the dentist sees on an x-ray that the cause of suppuration lies in poor-quality root canal filling performed earlier, then there are 2 possible treatment options. This is either a standard treatment of periodontitis with preliminary filling of the root canals, or a minor surgical operation (resection of the root apex)…
- Standard therapeutic treatment - on the first visit, the dentist drills out the old filling, removes the crown and tries to unfill poorly filled root canals.
Next, the canals are washed with antiseptics, the tooth is left open for several days + antibiotics are prescribed. If necessary, the patient is also sent to a surgeon for a gum incision. Thus, unlike the previous treatment option, only 1 point has been added here - unsealing the root canals. When the inflammation subsides after a few days, first, either temporary filling of the canals with medicinal paste, or immediate permanent filling with gutta-percha can be carried out. The medicinal paste is left in the canals for a period of 1 to 3 months. During this period, an x-ray will be taken to record a decrease in the size of the focus of chronic inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. When the lesion disappears or becomes small, the canals will be sealed with gutta-percha and a permanent filling or crown will be placed. - Resection of the root apex (Fig. 13) –
This method allows you not to re-treat root canals or remove the crown from the tooth.
It consists of making a small incision in the projection of the apex of the tooth root on the gum, through which the doctor uses a drill to cut off the apex of the root with the unfilled part of the root canal from the tooth. Also, a cyst or granuloma is scraped out of the wound. However, the operation can only be performed on those patients whose root canal is poorly filled only at the very apex of the root. Root resection is a very simple operation and usually takes only 25-35 minutes. It is easiest to carry out on the front teeth, much more difficult on the side teeth. Low cost of the operation + no need to spend money on replacing the crown and re-treating the tooth. The operation is performed after the acute inflammation has been relieved, which may require an incision and antibiotic therapy.
→ Root apex resection operation
Diagnostics
Purulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor is a serious reason to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist to find out the causes of suppuration. The examination of patients involves a physical and instrumental examination of the genitals, various laboratory methods aimed at clarifying the etiological factor. The following have the greatest diagnostic value:
- Gynecological examination
. To obtain a complete picture of the disease, examination of patients with purulent leucorrhoea is carried out without preliminary preparation and toileting of the external genitalia. When examined in speculums, accumulations of thick pus can be detected on the walls of the vagina; hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane are typical. - Ultrasonography
. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs allows you to find out the reasons associated with purulent vaginal discharge. During standard or transvaginal sonography, the condition of the genital organs is assessed, the accumulation of hypoechoic fluid in the uterine cavity is detected, and signs of an inflammatory process are detected. - Endoscopic methods
. To determine the cause of scanty purulent discharge streaked with blood, colposcopy is necessary for a targeted examination of the cervix and cervical canal. The method helps to identify erosive changes and areas of tissue atypia. - Bacteriological method
. In order to identify the causative agent of a gynecological infection, microscopy of a vaginal smear is performed after staining, then the secretions are cultured on nutrient media. Modern methods - ELISA, RSK, PCR - are intended for rapid diagnosis of the cause of suppuration.
To identify laboratory signs of inflammation, general and biochemical blood tests are done. Serological tests help confirm the etiological factor of vaginal leucorrhoea with a pungent putrid odor. To exclude lesions of other pelvic organs, CT or MRI of the pelvic cavity is used. Diagnostic laparoscopy is prescribed if it is impossible to determine the causes of purulent discharge using other methods.
A vaginal smear examination is carried out to identify the causative agent of infection.
Pus in the gums with periodontitis -
Very often, the patient’s complaints that his gums near the tooth are festering are not associated with inflammation at the apex of the tooth root during periodontitis, but with the formation of periodontal pockets in local or generalized forms of periodontitis. With periodontitis, there is destruction of the attachment of the gingival margin to the necks of the teeth, destruction of the alveolar bone around the teeth, as well as periodontal fibers, with the help of which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue.
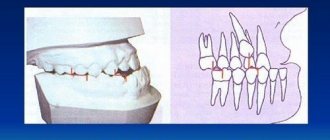
All this leads to the formation of so-called periodontal pockets between the gum and the surface of the roots of the teeth (Fig. 14). They create good conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the development of chronic inflammation. When one of the periodontal pockets becomes too deep, this can lead to disruption of the discharge of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate through the lumen of the pocket. As a result, an abscess forms in the projection of the periodontal pocket on the gum, which dentists call the term “periodontal abscess” (Fig. 15-16).
You can immediately suspect that gum swelling is associated with periodontitis, and not with periodontitis, if the tooth is completely intact (i.e., externally healthy and does not have a filling, crown or caries), if it has mobility, and mobility was present in this tooth and before the gums become suppurated, and also if, with slight gentle pressure on the abscess, pus comes out from under the gums (as in Fig. 16).
The differences between local and generalized periodontitis are that they are caused by completely different reasons and, accordingly, the treatment will also be different. With local periodontitis, the inflammatory process occurs only in the area of 1-2 teeth - due to exposure to a traumatic factor. For example, a pocket may appear as a result of trauma to the gum margin by the overhanging edge of a filling or crown. The cause may also be the premature closure of several teeth, which leads to chewing overload and destruction of the bone tissue around them.
But with chronic generalized periodontitis, gum suppuration occurs for other reasons. You can immediately suspect this form of periodontitis if you have symptoms of bleeding and pain when brushing your teeth, swelling, redness or bluishness of the gum margins in the area of most teeth. The cause of generalized periodontitis is soft microbial plaque and hard tartar, which accumulate on the teeth as a result of insufficient oral hygiene.
Bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins and various pathogens that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. With prolonged inflammation, first the dental-gingival attachment is destroyed, and then the periodontal fibers and bone tissue around the teeth are destroyed. With this form of periodontitis, pockets are found in almost all teeth, and not just in 1-2 (as with local periodontitis). When the outflow of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate in one of the pockets is disrupted, a periodontal abscess is formed in the gums.
Treatment of local periodontitis –
Based on the examination, the identified amount of tooth mobility, probing the depth of the periodontal pocket and analysis of the x-ray, the doctor will determine the possibility of saving the tooth and the algorithm for further treatment.
If the tooth can be saved, then the first thing to do in case of local periodontitis is to eliminate the impact of the traumatic factor. This means that you need to remove the overhanging edge of the filling or crown, and selectively grind the contacts of the chewing surface of the causative tooth and its antagonists. Next, under anesthesia, the periodontal abscess is opened to allow the outflow of pus and to rinse the periodontal pocket with antiseptics. If pus comes out of the pocket without an incision, but only little by little, then after anesthesia you still need to widen the mouth of the pocket with a stroker. Next, the doctor prescribes systemic antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiseptic rinses.
Opening of periodontal abscess –
Next, the issue of the need to fill the root canals in the causative tooth is resolved. This must be done if the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches 2/3 or more of the length of the root of this tooth. Removing the nerve from the tooth and filling the canals is required here because infection from a deep pocket very easily penetrates through the bloodstream into the neurovascular bundle (tooth pulp), as a result of which the pulp itself becomes a source of infection. But all this is just initial basic treatment!
The main treatment consists of open curettage of the periodontal pocket. This operation allows you to remove inflammatory granulation tissue (which forms at the site of destroyed bone tissue) from under the gums, as well as fill the periodontal pocket cleared of granulations with bone material, which allows you to partially restore the level of bone tissue around the tooth.
Progress of open curettage operation –
During open curettage, the gums are first moved away from the teeth and bone tissue to create good access to the periodontal pocket. Then the granulations are removed from the pocket, the root surface is polished and the pocket is filled with material based on artificial or bovine bone tissue. Next, the flaps of the gum mucosa are placed in place and the gum is sutured. Figure 19 shows that the bone level differs between radiographs taken before and 4 months after surgery (an increase in bone level of approximately 2.5 mm).
Moreover, if an abscess on the gum occurs near a moving tooth, then in addition to all of the above treatment, splinting of the moving tooth may be required. For this purpose, fiberglass and filling material are used, with the help of which the movable tooth is fixed to the adjacent stable teeth. Detailed information on curettage and splinting in the articles:
→ How the open curettage operation is performed, → Teeth splinting technique
Treatment of generalized periodontitis –
With generalized periodontitis, periodontal pockets occur not in 1-2, but in almost all teeth. Typically, this form of periodontitis has a sluggish chronic course. Common complaints from patients include bleeding gums and inflammation of the gingival margin. In severe cases, tooth mobility, changes in the position and inclination of teeth, and suppuration from periodontal pockets occur.
Against the background of decreased immunity, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation may occur, and then abscess formation (i.e., the formation of purulent abscesses) may occur in the area of one or more periodontal pockets. Treatment of the generalized form of periodontitis is very complex, and we have devoted a separate article to this topic, which you can read at the link above. We hope that our article on the topic: What to do if your gums are swollen turned out to be useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook” ( Borovsky E.).
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The discharge of pus from the vagina is a symptom of serious disorders of the reproductive system, for which it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible. Self-medication can lead to the spread of the process to other pelvic organs or the peritoneum. Until the reasons for the purulent, foul-smelling discharge are determined, it is permissible to take analgesics to reduce pain. For high febrile fever, antipyretics are used.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the prevalence of purulent inflammation, the etiological factor of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathology in the patient. In the acute period, physiotherapy methods are not used; after the main manifestations subside, drug therapy is supplemented with UHF, electrophoresis, and ultraviolet radiation. Local treatment includes instillation of antiseptic solutions (miramistin, chlorhexidine) into the vagina. For sexually transmitted infections, medications are prescribed to both sexual partners. The most commonly indicated medications are:
- Antibiotics
. They are selected taking into account the causative agent of the infection and its antibiotic sensitivity. If severe purulent processes are detected in the uterus and appendages, a combination of 2-3 drugs with a wide spectrum of action is necessary. - Detoxification solutions
. Diseases combined with suppuration are characterized by severe intoxication of the body. To eliminate intoxication, glucose-salt agents are used for parenteral administration. - Immunomodulators
. Medicines increase the overall reactivity of the body, stimulate local immunity, and speed up the healing process. For chronic gonorrhea, a gonococcal vaccine is used for the purpose of immunostimulation.
Why gums fester: reasons
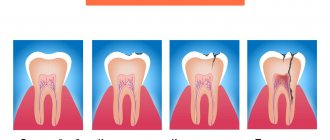
1) With an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis , infection in the root canals leads to the formation of a focus of purulent inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Depending on the type and size of such lesions, dentists call them by terms: granuloma, cyst or granulating periodontitis. You may not be aware of the presence of such foci for years, but sooner or later an exacerbation of chronic inflammation occurs, and then pus-filled abscesses form in the projection of these foci on the gums (Fig. 1-2).
2) Against the background of inflammation of the gums (with periodontitis) - in slightly less than half of all cases when the patient's gums near the tooth fester - the cause is a local or generalized form of periodontitis. Despite the fact that the causes of these two forms of periodontitis are different, the common thing is that the formation of a purulent abscess occurs in a deep periodontal pocket formed between the gum and the surface of the tooth root. Below you can see what an abscess on the gum looks like during periodontitis (Fig. 3).
The causes and treatment of an abscess on the gum will always be interconnected, and therefore, depending on the background of what disease (periodontitis or periodontitis) the suppuration occurred, either treatment of the root canals and the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root will be indicated, or treatment of the periodontal pocket using anti-inflammatory therapy , curettage and other methods. Below we will discuss in detail the treatment of gum suppuration in both cases.
Is it possible to cure an abscess at home?
Patients with acute conditions are admitted to dentistry without a queue. Therefore, if your health worsens, you should not postpone your visit.
The first question that a patient has is: why does pus appear in the gums and how to treat the pathology? The cause of infiltration is a weakened immune system and non-compliance with dental care measures. At the first symptoms of inflammation, you should immediately consult a dentist. Self-opening of a flux neoplasm threatens the addition of a secondary infection.
It is strictly forbidden to heat the inflamed area. Heat activates purulent-necrotic processes and accelerates the spread of infectious agents.
Timely sanitation of the inflammatory focus in a clinical setting prevents complications.