Indications for treatment of periodontitis
There are two main ways to treat periodontitis: conservative and surgical. Each of them has its own indications and contraindications.
According to modern dental standards, a doctor should give preference to conservative methods. They are indicated for both acute and chronic periodontitis, including the appearance of cysts and granulomas, loose teeth, and increasing inflammation.
However, orthograde treatment cannot be used in all cases. Indications for surgical intervention are:
- obstruction of the tooth root canals;
- the presence of a stump tab or pin that cannot be removed without damaging the roots;
- multiple perihilar cysts or cysts growing into the maxillary sinus;
- wide affected area (over 10 millimeters);
- perforation of the tooth cavity or root wall;
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment methods.
Important!
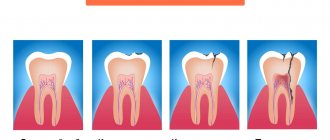
When we talk about periodontitis, we often mean apical (also known as periapical or apical) periodontitis - that is, inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. The cause of this disease is endodontic problems. Another type of periodontitis, marginal, affects the gums in the cervical area of the tooth, but it already belongs to the field of periodontology. This material is devoted to the treatment of apical periodontitis only.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Treatment methods for dental periodontitis
| Conservative treatment | Surgery |
Therapeutic:
Physiotherapeutic:
Conservative treatment of periodontitis is accompanied by the use of antibiotics. | Surgical treatment:
|
Important!
The probability of successful conservative treatment of periodontitis is 70 - 90%
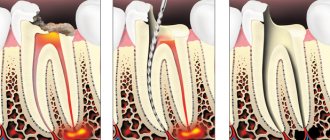
Stages of periodontitis treatment
The number of visits to the clinic for the treatment of periodontitis depends on the stage of the disease (acute periodontitis, chronic, chronic in the acute stage) and the chosen technique. Often, therapy is carried out in several stages and requires at least 2 - 3 visits to the attending physician, since it is not recommended to install a permanent filling until the inflammation is completely removed.
- Preparation for treatment: diagnosis using an x-ray, anesthesia injection.
- Drilling a tooth to access canals, removing a nerve, or removing an old filling.
- If necessary, expand channels.
- Antiseptic treatment of canals, application of medications, physiotherapeutic procedures.
- Installation of a temporary filling.
- Removal of the temporary filling, antiseptic treatment of the canals (this stage is repeated until the source of inflammation is completely eliminated; sometimes this may take several months).
- Installation of a permanent filling, control x-ray.
In parallel, the patient is prescribed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, as well as home rinses with disinfectant solutions.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis with fistula
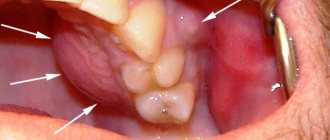
Odontogenic fistula is one of the complications of periodontitis, mainly granulating. It consists of holes in the mucous membrane, which are formed due to the proliferation of granulations and destruction of the tissues surrounding the tooth. In severe cases, a fistula can appear not only in the gum, but also in the cheek, and even on the skin of the face. Purulent contents are released through the hole, which appears due to the inflammatory process in the periodontium.
On the one hand, the formation of a fistula facilitates the course of the disease, since inflammatory products are eliminated through it (which means that the patient most likely will not suffer from severe pain). On the other hand, non-intervention over time can lead to tooth loss.
You can get rid of a fistula only by eliminating its cause - damage to periodontal tissue. Treatment follows a standard scheme: mechanical treatment of the canals, disinfection and thorough filling. Due to the outflow of pus through the fistulous tract, treatment is most often successful and takes less time. After creating suitable conditions, the fistula goes away on its own, but in severe cases, surgical removal of overgrown granulations may be necessary.
Causes of acute periodontitis
Among the main reasons for the development of acute periodontitis are:
- acute inflammation of the pulp that occurs against the background of teeth affected by caries; pulp and periodontal tissues are closely related;
- the use of arsenic for pulp devitalization, which provokes inflammation of the pulp tissue due to the toxic effect of the drug penetrating the periodontium;
- the use of strong antiseptics and various cauterizing agents that are injected into the root canal, which provokes inflammation in nearby tissues;
- entry of a large amount of filling material into the periodontal space.
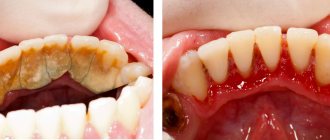
Treatment of chronic forms of periodontitis
There are three types of chronic periodontitis: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous.
- In fibrous periodontitis, the tissues surrounding the apex of the tooth are replaced by fibrous tissue. The patient usually does not feel pain, and the disease can only be determined by an x-ray.
- Granulating periodontitis is characterized by the growth of granulation tissue: the process of bone resorption (resorption) starts, fistulous tracts are formed, through which inflammatory products are separated. As the granulations expand, the patient begins to experience periodic aching pain.
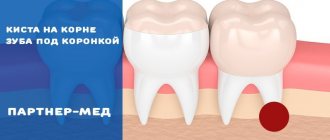
- Granulomatous periodontitis is accompanied by the appearance of a granuloma - a neoplasm at the root apex. It is a chamber of connective tissue filled with granulations. If the disease is not treated, the growth of granuloma can even lead to a jaw fracture.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis is often carried out using conservative treatment methods. According to modern standards, doctors, as a rule, do not carry out separate treatment for granulomas, cysts and fistula tracts: if the canals are disinfected and properly sealed, the neoplasms will disappear on their own. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is permissible.
Recommendations after fistula treatment
After treatment of the fistula, no special recommendations need to be followed. If the treatment was related to surgery and was carried out jointly with a therapist, then yes:
- baths with antimicrobial agents must be done carefully,
- eat soft food
- Do not put your tongue into the area of the healing wound.
If we are simply talking about therapeutic treatment, then there are no special restrictions at all.
How to avoid the appearance of a fistula on the gum
Are there any prevention methods to avoid the development of periodontitis? Of course, you can avoid the appearance of a fistula on the gums, and the prevention of these fistulas is a regular visit to the dentist in order to avoid these fistulas, not to lead to chronic periodontitis, and to keep your teeth healthy, beautiful and functional.
Therefore, once every six months
You need to come to the dentist for an examination and early diagnosis of any diseases, diagnosis of caries. It is better to cure caries at an early stage than to treat canals later, or to re-treat canals that can lead to the formation of a sinus tract and a fistula on the gum.
Can a fistula on the gum go away on its own?
Yes, it can only go away on its own if the causative tooth is removed, then it will go away on its own. It's a joke! In fact, the fistula cannot go away on its own as long as there is a chronic process that occurs in the gums, in the hard tissues of the upper or lower jaw. This chronic process is ongoing, and through this fistula there is an outflow, all purulent masses are drained along with exudate. And all this goes into the body, the body is certainly poisoned. There is a constant infection - these are staphylococci, which can then provoke all sorts of sore throats and various other diseases in the oral cavity. This is unhealthy flora that is constantly in your mouth, which constantly oozes, flows out and poisons you from the inside.
The fistula itself cannot go away
. It must be treated either therapeutically or surgically.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis in the acute stage
Exacerbation of periodontitis goes through two phases: intoxication and exudation (appearance of discharge). As the disease progresses, the patient first experiences aching and episodic pain, and then constant throbbing and tearing pain, so treatment cannot be delayed.
Acute periodontitis can be serous or purulent. In the second case, purulent exudate accumulates in the apical part of the tooth root, and the main task for the doctor is to remove it. Sometimes this is enough to clean the tooth cavity and treat the canals, but in severe cases it may be necessary to cut the periosteum for drainage.
Treatment of periodontitis at home
Periodontitis cannot be cured at home, since the disease is caused by bacteria that colonize the dental canals. The only way to get rid of them is to carry out antiseptic treatment and sealing of the canals, and this can only be done by a doctor, but by waiting for a visit to the clinic, you can alleviate the symptoms and reduce pain.
Disinfectants that do not irritate the mucous membranes can be used for rinsing 4 - 5 times a day. Doctors also recommend rinsing with a solution of salt and soda, including after treatment, to relieve swelling and reduce inflammation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for pain relief. All this will help relieve symptoms, but is not a cure.
You may experience pain after periodontitis treatment. Normally, they last 3–5 days and gradually fade away. If the pain does not subside or returns with renewed vigor, re-therapy is necessary.
Signs of the disease
The nature of toothache indicates the degree of neglect of the disease. A doctor will help you determine the properties of pain during your consultation.
Making an accurate diagnosis is the doctor’s task, but below are the symptoms of periodontitis:
- prolonged pain or painful throbbing in the tooth or gum;
- increased sensitivity when pressure is applied to the tooth surface;
- asthenia or increased body temperature;
- phantom feeling of tooth swelling;
- swelling of the gums;
- lack of response to cold, hot or sweet;
- easy mobility.
Note! Those places where deep caries treatment was previously carried out are examined. Often, untreated carious disease caused deep tissue damage.
In this case, chronic periodontitis, as a rule, is asymptomatic and is diagnosed only on an x-ray, or when it enters the acute stage.