Scarring
Healing of a granulating wound occurs through scarring and epithelization. At the final stage of healing, collagen fibers appear among the cells of the granulating tissue, the number of granules decreases, and the number of fibers increases. Ultimately, the fibrous substance passes into the connective tissue and forms a scar.
When wounds heal by primary intention, delicate scar tissue is formed, which tends to resolve.
In case of healing by secondary intention, a rough scar is formed, which will not be easy to get rid of.
Home first aid kit
However, if we are talking about a universal remedy, which is better to have in a home medicine cabinet and which is suitable for all family members, then preference should be given to dexpanthenol preparations, which are approved for use in children from the first days of life, in pregnant women and women during lactation. Since at each stage of the wound process different forms of release of this drug are recommended, it would be optimal to have an ointment and a cream or gel combined with an antiseptic in the first aid kit.
Sources
- Abaev Yu. K. Biology of acute and chronic wound healing // Medical news. - 2003. - T. 6. - P. 3–10.
- Afanasyev V.V. // Solcoseryl: results and prospects. Collection of scientific and practical works. articles. St. Petersburg - 1997. - pp. 4–9.
- Butko Ya. A., Drogovoz S. M., Deeva T. V., Lyapunov N. A. Study of the reparative properties of creams with dexpanthenol and ceramides // Scientific bulletins of BelSU. Series: Medicine. Pharmacy. - 2013. - No. 18 (161).
- Zhilyakova E. T., Ivashchenkova A. O. Analysis of the Russian pharmaceutical market of drugs for the treatment of thermal burns // Young scientist. - 2022. - No. 39 (8).
Types of wound healing
According to the classification of I.V. Davydkovsky, the following types of wound healing are distinguished:
- closing the defect of the epithelial cover, which occurs when the upper epithelial layer is damaged;
- healing under a scab, or healing without a scar. Observed on mucous membranes in case of minor defects.
- healing by primary intention, or healing without suppuration. Characteristic of wounds with damage to the skin and tissue underneath.
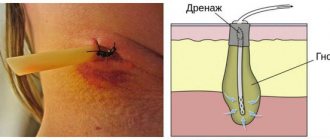
- healing by secondary intention, or healing through suppuration and granulation. Occurs with extensive wounds, accompanied by foreign objects entering the wound, tissue necrosis, microbes and infections.
Doctor's consultation: when is it necessary?
It is recommended to see a doctor, even if the wound does not seem serious. In addition, there are a number of cases when you cannot do without the help of a specialist. Such cases include:
- continued bleeding from the wound - it may be necessary to stop it by ligating the vessel, applying a suture, or using a hemostatic sponge;
- foreign bodies remaining in the wound, contamination;
- wounds caused by heavily contaminated, rusty, painted, grease-coated objects;
- wounds with signs of inflammation;
- wounds caused by animals;
- suspicion of a fracture, dislocation, ligament rupture.
In addition, it is not recommended to try to use certain medications on your own. The doctor prescribes an ointment for wound epithelization.
Stages of healing
The wound healing process goes through three main stages: inflammation, regeneration, and restoration of the epithelium.
The inflammation phase begins immediately after injury and in an uncomplicated state lasts for 4–5 days. During the hemostasis stage, platelets attach to sites of injury and cause a chemical reaction that activates fibrin, which forms a matrix network and binds platelets to each other. This is how blood clots form, blocking damaged blood vessels and stopping bleeding.
At the stage of proliferation and regeneration, the process of angiogenesis, collagen deposition, and the formation of granulation tissue (young connective tissue formed in places of defects) occurs. The regeneration stage can last 2–4 weeks depending on the size of the defect.
The final stage is the formation of the epithelium. Depending on the severity of the injury, the process can last from several weeks to a year or more.
The importance of the granulation phase for tissue repair
The granulation stage of the formation of new tissue is a complex process in which several groups of cells take part. It includes:
- Plasmocytes are cells that synthesize antibodies, which, in turn, are responsible for the body’s immune response.
- Histiocytes. They perform a protective function by inactivating foreign objects that enter the newly formed layer of tissue.
- Fibroblasts responsible for secreting the precursor protein collagen.
- Leukocytes - protect the body from any pathogenic agents.
- Mast cells are one of the components of formed connective tissue.
The entire maturation cycle of granulation tissue takes 20-30 days.
It should be remembered that this is a temporary formation that will be replaced by dense scar tissue. Most of it consists of newly formed capillaries. Over time, the thin walls of the vessels are covered with new cells, which continue to divide, forming a dense layer that covers the site of damage.
Wound treatment
The choice of wound treatment method largely depends on their type (infected or necrotic, wet exuding or fibrous granulating, trophic ulcers or bedsores). Only a doctor can choose the optimal solution for treating each type of wound.
In addition, at each stage of wound healing, it is necessary to use a different agent: one that promotes the removal of exudate, the formation of granulation tissue, accelerating epithelization, etc.
When treating wounds, you need to remember that the wound does not heal on its own, but thanks to the body’s resources aimed at healing it. The immune, endocrine, and circulatory systems are involved in this process. A qualified doctor, along with treating the wound itself, will definitely prescribe a vitamin complex to maintain the body.
Correct form
The selection of the form of the healing agent is no less important than the choice of the active substance. Let's repeat the basic rules.
- Fat-based ointments are contraindicated in the first stage of the wound process - they create a film and prevent adequate outflow of exudate and cleansing of the wound.
- The drug used in the early stages must have a hydrophilic base and retain moisture for a long time. Dosage forms that meet such requirements include solutions, gels, aerosols and creams on a hydrophilic basis.
- Aerosols are convenient for treating burns when any touch to the wound is extremely painful.
- As granulations grow during the second phase of the wound process, more and more of the wound surface must be treated with ointment. And when the wound becomes dry and significantly reduced in size, it is necessary to completely switch to ointment forms. By creating a fatty film on the surface of epithelialization areas, the ointment will protect young sensitive skin cells from drying out and provide them with greater resistance to environmental factors.
How to speed up healing
The speed of wound healing varies. It depends on the nature of the injury and the individual characteristics of the patient, such as age, nutrition, and medications taken.
To speed up healing, it is necessary to provide optimal conditions for tissue regeneration at each stage. This role is fulfilled by therapeutic dressings designed for each stage of healing.
The method of hydrotherapy has a positive effect. Its essence consists in the sequential use of two dressings HydroClean and HydroTac. Using the first, the wound is cleaned, and then a second is applied, creating optimal conditions for granulation and epithelization.
What to do if the wound does not heal
Non-healing or chronic are wounds that do not respond adequately to therapy despite prolonged treatment. Such wounds are usually caused not by external factors, but by reasons hidden inside the body, leading to disruption of metabolic processes and, as a consequence, disruption of the wound healing process. This category includes trophic ulcers, bedsores, and diabetic foot ulcers. Before using any dressings, consult a doctor: therapy and treatment of wounds can only be prescribed to you by a doctor!
For the treatment of chronic wounds, HARTMANN has developed a two-bandage system - HydroClean Plus and HydroTac.
The HydroClean Plus cleansing dressing can be used at all stages of wound healing, effectively removing necrotic tissue and pathogenic bacteria from the wound surface. They get caught in the absorbent layer and die under the influence of the antiseptic. The HydroTac dressing has absorbent and moisturizing properties and also protects the wound from secondary infection.
With the help of the hydrotherapy system, many patients have been able to significantly alleviate suffering and improve their quality of life.
Types of wounds and their treatment
A wound is mechanical damage to body tissue, most often the skin, sometimes mucous membranes and internal organs. Wounds can be obtained at home, at work, especially often during physical labor, during games and sports. Falls, accidents, fights, animal attacks, and many other situations are accompanied by the appearance of wounds. It’s no coincidence that they rank high on the list of reasons to go to the emergency room.
Characteristic signs of a wound:
- divergence of edges in the damaged area (gaping);
- bleeding;
- pain.
Some wounds can be healed on their own at home, but often require qualified medical care to avoid purulent complications and ensure rapid healing.
Types of wounds
According to the severity of the wound, they are classified into:
- superficial—only the skin and/or mucous membranes are injured;
- deep - in addition to the skin, the soft tissues located underneath it, blood vessels, nerves, and internal organs are damaged. There are two types of deep wounds:
- penetrating—the wound channel ends in the cavities of the body (abdominal, pleural, pelvic, etc.), the internal organs located in them may be damaged, but not always;
- non-penetrating - the wound channel ends blindly in the soft tissues.
Superficial wounds can be treated independently; for deep, especially penetrating wounds, consultation with a surgeon is required.
Depending on the nature of the wound damage, there are:
- Pricked - they are characterized by a large depth with a small area of skin damage. Such wounds are inflicted with sharp long objects, such as a knife, an awl, or a nail. Puncture wounds can appear deceptively mild—they appear minor in appearance, the pain is mild, and there may be no bleeding at all. In fact, they are fraught with damage to deep-lying soft tissues, internal bleeding and suppuration - oxygen does not reach the interior, creating ideal conditions for the proliferation of anaerobic bacteria;
- Incised wounds are distinguished by smooth edges and shallow depth; They are applied by all types of flat sharp objects (blades, glass, sometimes even paper). The danger of incised wounds lies in damage to large vessels, nerves, tendons, internal organs, in other cases they heal quite quickly;
- Chopped wounds are similar to cut wounds, but they are inflicted by striking with a sharp object (saber, axe), so the cut is accompanied by a bruise, and there may be bone damage;
- Bruised wounds are inflicted with a blunt, heavy object, causing hematomas, sometimes internal ones. Skin lesions are usually small with minor bleeding;
- Lacerations have jagged edges, which makes them difficult to heal. They appear when a wounding object slides and simultaneously presses on the skin;
- Gunshot wounds are caused by bullets fired from a weapon. Due to strong pressure and burns, the skin, soft tissues, and bones are significantly damaged and do not heal well. In this case, the area of damage is small, and bleeding is insignificant.
An important characteristic of a wound is the presence of infection in it. Wounds made under sterile conditions are considered clean: these are surgical incisions performed by a doctor during operations. Wounds with purulent discharge are called infected, and all others are called contaminated. This means that microbes are present in the wound, there are no signs of an infectious process, but there is a risk of its development.
First aid for wounds
The wound must be properly treated immediately to reduce the risk of infectious complications and speed up healing:
- Remove dirt and foreign objects (chips, splinters, soil, etc.) from the damaged surface;
- Wash the wound with antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, which not only destroys germs, but also stops bleeding);
- If there is a lot of blood, apply a tourniquet or a pressure bandage to compress the damaged vessels; in this case, peroxide will not help;
- The edges of the wound can be treated with an alcohol solution of iodine or brilliant green;
- Apply an antibacterial healing cream to the cleaned wound surface and apply a sterile bandage on top.
When to go to the emergency room?
Professional medical help should be sought in the following cases:
- Deep wounds, suspected damage to internal organs, bone fractures;
- Severe bleeding that cannot be stopped on your own. If a tourniquet is applied, you also need to go to the hospital, since this is a temporary measure;
- Wounds with uneven edges;
- Heavy contamination, especially with soil, rust (high risk of tetanus);
- Signs of wound suppuration or deterioration of the patient’s well-being (fever, nausea).
When visiting on the first day, the doctor will perform primary surgical treatment (PST) of the wound: after anesthesia, he will remove dirt and damaged tissue, blood clots, and, if necessary, apply sutures. After this, a healing period begins, which takes on average 7-10 days.
For later visits, PSO is not performed; the wounds heal through suppuration or under a crust, which takes longer - about two weeks. Periodically, the doctor treats the wound, removing pus if necessary, and then applies bandages to speed up healing.
With severe defects, spontaneous healing may not occur. Then the patient is prescribed plastic surgery with a displaced or free skin flap.
Argosulfan® for wound treatment
Cream for external use Argosulfan® has a dual effect: antimicrobial and wound healing. The main component of the drug is silver sulfathiazole. When the ointment is applied to the wound, a chemical reaction begins, as a result of which silver ions and sulfathiazole are released. This is a gradual process, so the concentration of active substances remains at the desired level for a long time.
- Silver ions have a bactericidal effect - they kill bacteria by destroying their shell.
- Sulfathiazole has a bacteriostatic effect - it stops the formation of DNA in microbial cells, which is why they stop growing and multiplying.
Thus, Argosulfan® has both a bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, acting on most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Argosulfan® cream under the dressing maintains a moderate level of moisture on the wound surface, making dressings less painful.
Stimulation of cell division and metabolic processes in them promotes wound healing and reduces the likelihood of the formation of rough scars. Advertisement RUS-DRM-ARG-NON-09-2018-1319