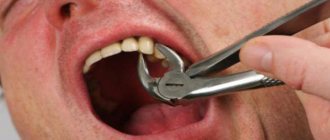
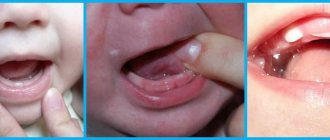
Stomatitis of various etiologies
The oral mucosa becomes inflamed with stomatitis. Whitish spots are located on the inner sides of the cheeks, on the gum tissue. Without therapeutic measures, painful ulcers will quickly appear. Such children exhibit restless behavior, fever, loss of appetite, and disturbed sleep. The disease may be:
- Viral, when it occurs against the background of influenza, chickenpox, bronchitis and other diseases;
- Allergic, if the baby develops asthma, atopic dermatitis appears;
- Bacterial, when the little one picks up some kind of infection, for example, a fungal one;
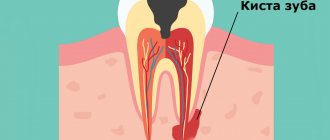
Purulent cyst
A white spot on a child's gum may indicate the development of cysts. They look like beads. Occurs against the background of infection of the body. A formation with purulent contents is detected on x-ray. Most often, the disease is caused by bacteria that penetrate into the chewing organs or soft tissues. This happens with complicated caries. When the accumulated pus begins to come out, swelling appears. If you do not visit the pediatric dentist on time, the pus accumulates, then the abscess breaks out, and the little one develops a fistula. Don't ignore rashes in your child's mouth! Contact your doctor promptly!
Lipoma and leukoplakia
With leukoplakia, keratinization of the mucous membrane is noted. This process is influenced by the following stimuli:
- sharp edges of affected teeth;
- hanging uneven fillings;
- hot and spicy food;
- malocclusion;
- improperly fitted dentures;
- crowns made of various materials;
With this disease, whitish plaques may have clearly defined edges or blurred ones. There is no discomfort. The rash may be rough, cracks and ulcers may appear. The doctor will take a sample of this tissue to send for a biopsy. Often the formation turns out to be a harmless lipoma, that is, a wen. It requires medical supervision. It is important that its size does not increase.
Treatment of white spots on gums
The first thing parents need to do is visit a pediatrician. If necessary, the child will be referred to a dentist. Pediatric dentistry is a department where the factors that provoke the disease are determined. Depending on your age, the doctor will carry out therapeutic measures.
- In case of improper hygiene, the mother will receive professional recommendations.
- When pimples are a consequence of vitamin deficiency, the nutrition of the mother and child is adjusted. You should drink enough liquid.
- Congenital masticatory organs, if they are mobile, are removed.
- Pathological diseases are treated with modern methods.
- The toddler should be protected from anxiety and stress.
- Stomatitis is treated with antiseptics, for example, Miramistin. The drug is prescribed by a doctor.
- Candida fungus is eliminated with drugs such as Flucostat. The baby's mouth is treated with chlorhexidine.
- If there is a lack of calcium, the necessary minerals are prescribed.
You cannot puncture the blisters yourself. The gum tissue may be damaged. After all, with such a procedure, infection can easily occur.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess
Young children do not properly care for their oral cavity. Poor brushing of teeth promotes the accumulation and proliferation of bacteria. Penetrating into the tissue, they provoke the development of inflammatory processes, including a purulent lump.
Other factors also influence the formation of an abscess:
- New teeth.
In some babies, the eruption of baby teeth is preceded by the appearance of small tumors filled with white fluid. If such a lump on the child’s gum does not hurt, then there is no reason to urgently consult a doctor.
- Gum injury.
Damage occurs due to the active lifestyle of babies, solid foods or accidental biting. The injured area becomes red and inflamed. Usually everything goes away on its own, but sometimes, when an infection occurs, ulcers and lumps appear.
- Oral diseases:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periostitis;
- cyst;
- fistula;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis.
Inflammatory processes on the gums are often accompanied by abscesses. Purulent complications can be avoided by promptly consulting a doctor.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of pathology, preventive measures should be taken.
- The baby’s mouth should be cleaned after any meal and rinsed with boiled water.
- Mother and child should eat a balanced diet.
- It is necessary to protect the baby from kissing people who have sore gums, from traumatic games, and from chewing objects with sharp edges.
- Pacifiers, toys, bottles should be perfectly clean, like the hands of a toddler.
- See your dentist regularly for preventative checkups.
- The baby must use a separate towel and utensils.
Gingivitis in children: what are the causes and symptoms
Gingivitis, or inflammation of the mucous membrane around the teeth in children, is a fairly common phenomenon. Most often, gingivitis can be detected in a child aged 1–3 years, as well as in adolescence - in both cases, the “trigger” of the disease can be active growth of the body, hormonal changes and features of the formation of the immune system
Gingivitis in children develops quite quickly. If inflammation develops in a child’s mouth, the number of bacteria increases significantly compared to the norm. Within 72 hours, the process of stone formation from soft plaque begins, and the first signs of gum erosion appear. If the situation is neglected, this can lead to the loss of teeth in children - both milk and permanent.
Symptoms of gingivitis in children
How does gingivitis manifest itself in children? The symptoms are:
- bad breath
- discomfort, pain in the mouth
- bleeding gums
At the same time, the temperature with gingivitis in children does not always rise. Therefore, it is quite easy to miss the onset of the disease. A child may tolerate discomfort without attaching any importance to it, or endure it, fearing a visit to the dentist (especially if he has already had a bad experience with dental treatment). That is why it is necessary to unobtrusively check the oral health of your son or daughter from time to time. For kids this can be done during play, but for a teenager you will have to find a psychological approach. Perhaps it would be easier (and more correct!) to “introduce” your offspring to a professional dentist whom he can trust, and periodically take him for preventive examinations.
Types of gingivitis in children
Only a competent doctor can determine what form of gingivitis a child is suffering from and, accordingly, prescribe effective treatment that quickly relieves discomfort. The disease can manifest itself in different ways:
- Catarrhal gingivitis. Children aged 3–7 years are most often affected. It is accompanied by swelling of the tissues around the tooth, unpleasant taste in the mouth, pain when pressure is applied to the gums, the appearance of pink saliva, general malaise and tearfulness. This type of disease easily becomes chronic, when gingivitis occurs approximately twice a year, causes temporary inconvenience to the child and seems to go away on its own. In fact, each time the inflammatory process becomes more and more severe, hard dental deposits are formed, which can ultimately “develop” into periodontitis - a disease in which the bonds of the tooth with the surrounding tissues are destroyed, which leads to its loss.
- Hypertrophic gingivitis. Painful sensations in a child do not appear immediately. The area of the front teeth is most often affected - the gums swell, changing their color (up to purple-blue). Over time, the tissues grow, covering a significant part of the tooth area, gum pockets appear, pus begins to be released, and severe pain appears.
- Atrophic ginivitis. This form of gingivitis is characterized by “recession” of the gums: the neck (and sometimes even the root) of the tooth is exposed, the child feels discomfort from eating cold and hot food. In this case, the gums become pale and bleed slightly. This is not only unpleasant and unsightly, but also quite dangerous and difficult to treat: you will most likely have to restore the shape of the gums using mini-plastic surgery.
- Ulcerative gingivitis. This is one of the options for the development of catarrhal gingivitis: the inflammatory process does not become chronic, but intensifies. Bleeding ulcers appear in the child's mouth, covered with a gray film - this is dead gum tissue. The child cannot eat and sleep normally, experiences severe pain, his body temperature rises to 39 °C... This development of the disease can be avoided by consulting a doctor at the first signs of gingivitis in the child.
Causes of gingivitis in children
Of course, parents want to believe that they will not have to treat gingivitis in children, knowing the causes of its occurrence. It’s really important to know them - they can be:
- Systemic diseases of the body (failure of the endocrine, cardiovascular, digestive, hormonal systems, the influence of infection)
- Dental pathologies, bite defects and errors in their correction
- Incorrect installation of fillings or their deformation
- Advanced caries, careless attitude of parents towards the health of the child’s teeth
- Weakened immunity, lack of vitamin C, poor appetite
But the main and main reason for the development of gingivitis in both children and adults still remains poor oral hygiene. Remember this the next time you allow your baby to “so be it, don’t brush his teeth just once”!
Expert opinion
There are many reasons for the development of gingivitis in a child, and not all of them are directly related to the condition of the oral cavity.
However, treatment should begin with a visit to the dentist: he will determine the form of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment, which will effectively relieve the symptoms - that is, quickly improve the child’s well-being. After all, sometimes inflammation of the gums causes real suffering to the baby, and he cannot even explain what is bothering him! A professional dentist will immediately understand what’s going on when he sees the clinical picture of the disease, and will definitely find an approach to the most capricious young patient. After this, parents (who will also immediately feel better after their child stops experiencing pain) should fully examine the child, starting with a clinical blood test.
Perhaps the inflammation is associated with teething, the formation of roots and the formation of a bite - this is the best option, it can be conditionally classified as normal. Otherwise, you will need to consult specialists from other medical specialties - you will need to look for and treat the cause of gingivitis.
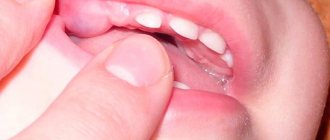
Reason No. 2. Bon's knots
White dots on the gums of a baby, as in the photo below, are Bon's nodules. A person who is not related to medicine is unlikely to be able to distinguish them from Epstein’s pearls outwardly, especially since they also consist of keratinized epithelium, but they take longer to disappear - within 3 months after birth. Benign and completely painless nodules got their name in honor of the famous German pediatrician who first described this phenomenon back in 1886.
Bohn's nodules consist of keratinized epithelium
Treatment of inflammation
Removal of a lump with pus on a child’s gum should be started immediately. Only a dentist can help the baby.
IMPORTANT! Self-medication, as well as piercing and squeezing are strictly prohibited! Such an intervention will lead to serious complications.
When an abscess forms over a baby's baby tooth, the doctor most often removes it. Such measures are necessary to exclude the possibility of destruction of the rudiments of the root. If a child has a lump on his gum next to a permanent tooth, treatment begins with a thorough examination. Sometimes the dentist will send you for an x-ray to assess the extent of the damage. Removal of a permanent tooth is carried out in extreme cases.
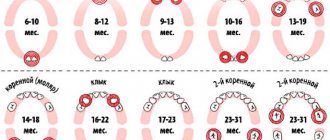
Approximate timing of eruption of permanent teeth
The first of the molar permanent teeth to appear are molars (at the 6th year of life), located at the end of the dentition. But it is they who are most susceptible to caries, since there are deep depressions on their surface where bacteria accumulate due to poor cleaning and neglect of flossing.
The second molar appears 4-6 years later, when the child reaches 11-13 years of age. Incisors erupt at 6-8 years of a person’s life, canines - after 9 years of age.
Like newly emerged milk teeth, permanent teeth contain few minerals (a tenth of their amount in a mature adult). It is for this reason that it is important to teach a child proper hygiene. It wouldn’t hurt to treat your teeth with gels containing a large amount of fluoride once a quarter.
Types of teething disorders
Teething in children, the sequence of which is clearly defined, can occur with a delay caused by various reasons (illness of the mother during pregnancy, diseases suffered by the child, etc.). Due to the delay, deformation of the jaws may begin, because There is not enough free space for teeth that have not yet erupted. In this case, only the dentist can decide on treatment after a thorough visual examination of the child and analysis of the photograph taken.
The next very common disorder is enamel hypoplasia, which manifests itself in spots of different colors on newly emerging teeth, pits or grooves. Hypoplasia causes complications during pregnancy.
Classification of candidiasis
Candidiasis can be acute or chronic.
According to the clinical course: According to the clinical course:
- pseudomembranous.
- atrophic.
- hypertrophic.
- erosive-ulcerative3.
By location:
- Stomatitis is a disease of the oral mucosa.
- Cheilitis is a lesion of the lips, with the lips being dry and covered with cracks. All lips, as well as just the corners of the lips (jams) can be affected.
- Gingivitis – the gums are affected and tend to bleed when brushed.
- Glossitis is a disease of the tongue.
Comments
My child has developed a white dot on his gum right next to his front baby tooth. The teeth are healthy, without holes, the child is 7 years old. What could it be?
Alexey (08/02/2020 at 00:22) Reply to comment
- Dear Alexey, perhaps your child’s permanent tooth has begun to erupt, and since the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, it simply does not have enough space and has changed the direction of growth. In this case, the baby tooth will have to be removed, otherwise there is a risk that the permanent tooth will move into the second row or will be severely curved, and the bite may be disrupted. Contact your pediatric dentist to clarify the situation and agree on a further plan of action.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (08/04/2020 at 09:12) Reply to comment
I still don’t understand whether it is possible to independently treat a child if such a white spot occurs. After all, it usually goes away quickly when you spread it with brilliant green.
Alisa (08/21/2020 at 06:38) Reply to comment
Stomatitis will probably be treated in a baby with some safe ointments or pastes? Are such remedies completely safe for children or can they offer another method of treatment?
Olga (08/21/2020 at 08:56) Reply to comment
Hello, my child is 5 years old, the front tooth is much lighter than the rest, it is very noticeable (the rest of the teeth are normal white, but the front one is just snow-white.) Tell me, what is this connected with and what to do?
Vladimir (08/21/2020 at 08:58) Reply to comment
Recently we were talking to a girl on the playground and she said that her daughter often has stomatitis. I would like to know if this is contagious to other children? After all, they play with the same toys and can transmit bacteria through them.
Olga (08/21/2020 at 09:35) Reply to comment
Hello! Thanks for the useful article. After reading the article, I thought about it: my son had small dots right on his gums with a size of 0.5 mm, very small. I thought it was teething and didn’t pay much attention. The teeth are cutting through, everything is fine, thank God. I have a question: can such dots just appear before teething? Or should I also contact a pediatrician or dentist?
Kamila (08/21/2020 at 10:56 am) Reply to comment
My son has white spots on his gums and mucous membranes, has a slight fever, eats poorly, he is 1 year and 2 months old. It looks like stomatitis. Can I buy medicine for stomatitis at the pharmacy, or is it better to go to the dentist?
Olesya (08/21/2020 at 11:08 am) Reply to comment
Could white spots be an allergic reaction of the baby to spicy and salty foods in the diet of a nursing mother? The habit of generously salting and peppering food has been around for many years. For now, I’m trying to eat more neutral in taste, but sometimes I break down.
Alina (08/21/2020 at 11:26 am) Reply to comment
Why did my one-month-old baby start to have white spots on his gums, although this had never happened before? What measures would you recommend to take in this case and will these white dots harm the child?
Laima (09.23.2020 at 14:43) Reply to comment
How can white pimples on the gums and oral mucosa cause harm? These white spots have been formed for several weeks; what should the baby’s oral cavity be treated with to get rid of them?
Tanya (09.23.2020 at 14:45) Reply to comment
Tell me, can these white spots on the gums cause stomatitis in an infant? How to treat these white spots in a baby if the child is still breastfed?
Kira (09.23.2020 at 15:29) Reply to comment
The child suffers greatly due to the appearance of small white spots on the gums, as well as on the inside of the cheek. In appearance, these white dots look like leftover milk from a baby; they cannot be removed with a cotton swab; the child is constantly capricious. Please advise what can be done to rid the child of these white spots in the mouth?
Lyudmila (09.23.2020 at 15:41) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Vulnerability zone
Let's look at gum disease in children. Your child's healthy gums are delicate and very vulnerable tissue of a pale pink color. Unlike adult gums, they can be easily injured, but they are capable of rapid regeneration. Another peculiarity of children's gums is that they often reflect the general condition of the body, being a litmus test for systemic diseases.
The most common diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues: gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs as a result of the adverse effects of local and general factors, occurring in 80% of children; gum atrophy, which develops in more than half of the child population; various types of childhood stomatitis, which most often occurs in infants and preschoolers; Periodontitis is a disease in which all periodontal tissues become inflamed and affects up to 5% of young patients. Periodontal disease (dystrophic changes in periodontal tissue) and other pathologies practically do not occur in childhood.