According to statistics, about 70% of pregnant women do not visit the dentist. Neglect of treatment is justified by the opinion that anesthesia and dental procedures themselves can harm the fetus and the mother’s body. However, untimely seeking help and foci of infection can cause greater harm: caries, poorly treated root canals, inflammatory processes of the gums, plaque, abscess, periostitis. The neglect of pathological processes is fraught with the entry of microorganisms and their metabolic products into the general bloodstream and the development of a secondary infection.
It is important to remember that it is easier to prevent the disease than to resort to surgical treatment and medication in the future. That is why timely diagnosis and dental treatment during pregnancy is extremely important for maintaining the overall health of the mother and unborn child. In addition, a routine examination by a dentist is included in the list of mandatory examinations when planning pregnancy and during pregnancy.
Features of dental treatment for pregnant women
Dental treatment is a mandatory medical procedure, regardless of whether a woman is preparing to conceive a child or is already pregnant. The dentist’s tactics depend on the trimester of pregnancy, its course, the general somatic health status of the pregnant woman and indications for treatment. Peculiarities of management of pregnant women are characterized by the following features:
Treatment planning
During pregnancy, emergency dental treatment is performed, the indications for which are:
- Carious lesions of hard and soft tissues of teeth: pulpitis, periodontal inflammation (periodontitis).
- Pathological processes of soft tissues of the oral cavity, gums: gingivitis, stomatitis, cheilitis, glossitis, inflammation of periodontal tissues.
- Tooth injuries: fracture of the crown or root of the tooth, dislocation, cracks and chips of the crown part.
- Abscesses.
- Acute purulent inflammation of the jaw bone tissue.
Planned therapy (orthodontic, implantological and orthopedic treatment) is postponed to the postpartum period.
Pregnancy data
Before starting treatment, you should inform your doctor about the duration and course of pregnancy, taking medications prescribed before conception and during pregnancy, and bad habits. These data can significantly affect the treatment plan drawn up by the dentist.
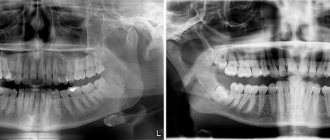
X-ray diagnostics
X-ray examination is extremely undesirable in all trimesters of pregnancy: failures in the formation of fetal cells can lead to irreparable consequences and abnormalities. The 1st and 3rd trimesters are especially dangerous for radiation diagnostics, however, the 2nd trimester is no exception, although it includes lower risks of developing pathology.
Dental filling
When filling teeth, materials of both chemical and light curing are used. Curing lamps used for curing are also not safe for the developing fetus.
Anesthesia
At the present stage of development of dentistry, painkillers are produced that are absolutely harmless to the pregnant woman and the fetus. High-quality anesthesia is half the success of treatment.
We know that it is possible to treat in a certain trimester
What equipment is safe to use for x-rays?
If necessary, any images (single, panoramic, 3D) are taken using modern digital equipment, which gives a very low radiation dose. But it’s better to avoid old film cameras
Digital radiovisiographs with narrowly directed radiation are now used for targeted images. The beam through the cheek “transmits” the tissue a couple of centimeters deep and “imprints” the image on a small sensor plate attached to the tooth. The image is immediately transferred from the sensor to the computer. The whole process takes a couple of seconds.
Contraindications and limitations to treatment
A contraindication to dental treatment for a pregnant woman is any procedure that can directly or indirectly harm the body and cause premature birth. Such procedures include the following:
Implant treatment
Both healthy fetal development and complete implant healing require large amounts of calcium. During pregnancy, the body is unable to produce enough mineral to support both processes. Even taking vitamin and mineral complexes sometimes does not give the desired effect. Therefore, every gram of calcium counts.
An additional danger during treatment is the need for X-ray monitoring of the implant installation, as well as the prescription of medications during the recovery period. The latter can have a general toxic effect not only on the pregnant woman’s body, but also on the developmental processes of the fetus.
Professional whitening
During bleaching, the enamel is damaged, which due to pregnancy may be somewhat depleted in mineral composition. Due to the fact that most of the calcium produced goes into the fetus's body, it may not be enough to restore the top layer of enamel. The result is increased sensitivity and microcracks.
Prosthetics
Installation of fixed dentures requires special preparation: preparing the tooth and forming a stump for the crown, removing the dental pulp, filling the root canals. The installation of crowns is contraindicated for pregnant women in the 1st and 3rd trimesters. In the 2nd trimester, in emergency situations, removable prosthetics are allowed.
Tooth extraction
Removal of teeth that are not the cause of discomfort (impacted or dystopic) is contraindicated during pregnancy. If there is a possibility of rescheduling the operation and there are no obvious clinical signs (pain, redness and swelling of the gums), then in order to prevent the development of infection, it is better to refuse the procedure before delivery.
Emergency cases requiring immediate tooth extraction:
- Fracture of the root or crown of a tooth.
- Pulpitis of wisdom teeth.
- Carious lesions of the tooth root.
- Periodontitis.
- Tooth root cysts.
- Destruction of more than 50% of the tooth, accompanied by unbearable pain.
Antibacterial therapy
Antibiotics during pregnancy are prescribed strictly according to indications and taking into account the duration of pregnancy. For treatment, those groups of drugs that do not have a teratogenic effect are selected.
Is it possible to reduce the effects of radiation?
With ultra-low doses of radiation, the body itself successfully restores the few damaged cells in the same way as it does every day (we are constantly exposed to background natural radiation).
After the procedure, it is useful to drink a glass of milk or fresh juice
The best support that can be recommended to pregnant women is a balanced diet that contains enough vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. Introduce fermented milk products, green tea, meat, eggs and fish, fresh fruits and fiber-rich vegetables, and whole grain bread into your diet. Also take vitamins, but only in consultation with your doctor based on your baby's developmental stage.
Source: Yandex.Zen channel Smile-at-Once. Read more and subscribe.
Dental treatment in the I, II and III trimesters
The dentist’s tactics when treating teeth in pregnant women depend on the specific stage of pregnancy - trimester.
Treatment in the first trimester
The first trimester is the time from the 1st to the 13th weeks of pregnancy. This period is characterized by the formation of the rudiments of the organs of the unborn child. At the same time, the placenta does not yet provide adequate protection of the fetus from the influence of factors of the external and internal environment of the mother’s body.
In the first trimester, a pregnant woman is worried about toxicosis, manifested by systematic nausea, short-term vomiting, hypersalivation, slight dizziness, and slight hyperhidrosis. Any, even minor, stress factor can cause a violent reaction in the body, even leading to miscarriage.
In dental treatment, courses of remineralization therapy and professional teeth cleaning without the use of ultrasound are acceptable. Filling, tooth extraction, prosthetics, dental implantation and x-ray diagnostics are contraindicated during this period.
Treatment in the second trimester
The second trimester lasts from the 14th to the 26th week. The placenta in this trimester is fully formed and provides reliable protection for the fetus. Dental treatment carries fewer risks, but still requires consultation with a gynecologist. During this period, you can perform dental fillings, surgical treatment (strictly according to indications), therapy for inflammatory diseases that may worsen by the 3rd trimester or after childbirth, professional removal of dental plaque (hard and soft).
Treatment in the third trimester
The third trimester is the period from the 27th week until birth. During this period, the woman’s body is actively preparing for childbirth, and therefore may be somewhat weakened. A pregnant woman experiences tachycardia, increased breathing, shortness of breath, decreased blood pressure, and increased anxiety. The woman constantly feels tired. Treatment in the 3rd trimester is exclusively emergency. Planned procedures are postponed until the postpartum period.
In all three trimesters, pregnant women are allowed to carry out professional oral hygiene, the method of which will vary depending on the timing of pregnancy and the condition of the body of the expectant mother.
I feel what I feel in my teeth
During pregnancy, it is especially important to eat right.
However, if hot and cold dishes cause severe aching pain, appetite disappears, in this case at least two suffer (mother and fetus).
The problem of increased tooth sensitivity is associated with the thinning of the enamel, which, like a shell, covers the underlying dentin, enveloping the vessels and the actual sources of pain - the nerves. The appearance of pain is an impetus that forces you to go to the dentist. There may be several reasons for thinning enamel. One of them, the most common, is the loss of calcium by the enamel, as a result of insufficient intake from food and increased consumption by the body. Another reason is early toxicosis, which was already mentioned above. Another reason that is not related to pregnancy, but does occur, is the wrong choice of toothpaste.
Toothpastes of the “Sensitive” type have been developed especially for those with teeth with increased sensitivity.
According to dentists, the most common cause of tooth sensitivity is improper brushing.
To learn how to properly brush your teeth, you must contact a dental center. Training is carried out individually in one session. The cost of this procedure is about 300 rubles. As a rule, the dentist invites the pregnant woman for a follow-up cleaning. To assess whether the patient is coping with the task correctly or not.
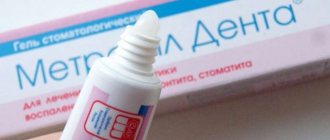
Tooth sensitivity can be caused by cervical caries, when a hole in the tooth is located at its base, next to the gum. Then the solution to the problem is only a filling in the problem area. If tooth sensitivity does not decrease, despite all efforts, then “Sensigel” will help, it contains special substances that reduce tooth sensitivity. The cost of the drug is 180-190 rubles. The dental office has pharmacological agents to reduce tooth sensitivity that have a prolonged effect (up to 6 months), but the cost of the procedure is much more expensive.
Principles of pain management
Modern painkillers used in dental practice do not penetrate the placenta and do not change uteroplacental blood flow. They include a lower dose of the vasoconstrictor component, while the analgesic effectiveness remains high.
The drugs of choice include:
- Ultracaine.
- Scandonest (Mepivacaine).
- Ubistezin.
- Alfacaine.
It is not advisable to use lidocaine for local anesthesia, as this drug can cause convulsions, pressure changes, severe dizziness, vomiting and muscle weakness. Carrying out pain relief during tooth extraction or therapeutic treatment must be done under strict monitoring of the pregnant woman’s condition – blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse.
Local anesthetics are not absorbed into the general bloodstream, as they are inactivated by local tissue factors. The entire volume of the anesthetic substance acts only at the site of its injection. Dental treatment during pregnancy under general anesthesia or sedation is strictly contraindicated.
Rotten tooth! Delete or wait?
Elena K.: “Before pregnancy, I had very bad teeth, some required removal, and I didn’t have enough time and courage to go to the dentist. Now that I'm pregnant, I'm afraid of being completely without teeth. What is the best thing to do?
Due to the environment, not everyone can boast of healthy and white teeth, especially those with average and low incomes. So if pregnancy threatens to deprive you of your last teeth, you need to take immediate action. Remove all rotten, damaged teeth that cannot be restored. Firstly, this will eliminate the source of infection from the mouth, and secondly, diseased teeth tend to worsen during childbirth. And then you may have to give birth in the dentist’s office with an acute toothache.
Thanks to the development of new anesthetics that do not pass through the blood-placental barrier, removal will not be a particular problem. New drugs “Ubistezin” and “Ultracain DS” will provide fast and reliable anesthesia.
The safest time for tooth extraction is the 3-6th month of pregnancy.
Carrying out procedures
All dental procedures are carried out after a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist and a general assessment of the need for dental intervention. A thorough examination and high-quality anesthesia are the key to effective treatment of diseases of the hard and soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Regular examination by a dentist and timely prevention of oral diseases are integral components of the health of the mother and fetus. You should not put off visiting a specialist and hope that the problem will solve itself. Modern dentistry has made a big leap in treatment, pain relief and treatment procedures for pregnant women, so if you doubt whether it is worth treating your teeth during pregnancy, then yes, it is definitely worth it.
Regular toothbrush or electric?
During the first half of pregnancy, a medium-hard toothbrush is suitable. By the third trimester, it is better to choose a soft brush, as this will avoid bleeding gums. Of course, unless there is a tendency to form hard plaque.
If you are used to using an electric toothbrush, then it is better to put it aside during pregnancy and use it only occasionally. Undoubtedly, the electric miracle removes plaque better. However, it has a greater traumatic effect on the gums than a regular toothbrush, and the gums are perhaps one of the most vulnerable places in a pregnant woman’s mouth.
If you really want to thoroughly clean your teeth, leave this procedure to a professional. Cleaning your teeth at the dentist's office will cost about 1,000 rubles.
Advantages of contacting PROFI-Dent
- Absolute safety of dental intervention at any stage of pregnancy.
- A team of experienced dentists of all specialties.
- An integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment.
- Unique proprietary therapeutic techniques.
- Affordable prices for the full range of dental services.