The issue of going to the dentist during lactation is one of the most pressing. Dental treatment while breastfeeding is harmless, but necessary. A breastfeeding mother risks losing her teeth and passing on tooth decay to her baby by licking his spoons and pacifiers. Why does the fragility of mother’s teeth increase during this period? The fact is that, together with milk, it transfers calcium to the child, strengthening his body. At the same time, its lack in women provokes problems with the oral cavity. Therefore, the appearance of dental ailments during this period of time is not uncommon.
Indications for tooth extraction during lactation
During the procedure, drugs are used that can penetrate into mother's milk. If it is possible to postpone the date of the operation, then extirpation is carried out after the child is transferred to artificial nutrition. A dental unit is removed urgently during a purulent inflammatory process, as it contributes to the spread of infection throughout the body.
In what cases is surgery necessary:
- suppuration of a cyst, abscess, periostitis;
- unsteadiness due to periodontitis, periodontal disease of the third, fourth degree;
- odontogenic osteomyelitis, sinusitis, phlegmon;
- tooth root fracture;
- pulpitis, which cannot be cured due to the complexity of the canals;
- impacted figure eight, complicated growth of the third molar, pressure on neighboring teeth;
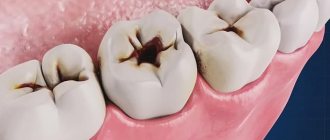
- deep caries that affected the root.
Unscheduled extraction is also performed in cases of severe, persistent pain.
The procedure has contraindications, including acute respiratory infections, chronic diseases in the acute stage, oral infections, sinusitis, severe pathologies of the liver, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, leukemia, bleeding disorders, and mental disorders.
Preparing for removal
If the tooth begins to ache, the gums are swollen, and the breath smells bad, then this may indicate severe inflammation in the dental system. At the appointment, the dentist collects an anamnesis, conducts a visual examination and sends the woman for an x-ray. It is important for a nursing mother to avoid psycho-emotional stress, so she is allowed to take sedatives in advance.
The best option for maintaining mental stability and eliminating fear is oxygen sedation with nitrous oxide (NAS). It is done in the doctor's office before the procedure. The patient inhales the gas and falls asleep. Additionally, a local anesthetic is injected into the gum.
Content:
- Is it permissible to use local anesthetics?
- Anesthetics that can be used by nursing mothers
- Is it possible to feed a baby immediately after dental treatment is completed?
- How to reduce the likelihood of developing dental disease after childbirth
Many women experience the need for dental treatment while breastfeeding. This is due to the increased load on the body of a young mother, calcium deficiency, and hormonal changes. If you have a toothache, it is very important to seek qualified dental care as soon as possible. The doctor will tell you whether the disease can be treated without interrupting lactation.
The process of tooth extraction in a nursing mother
The procedure for a woman during lactation is no different from that performed for ordinary patients.
Extirpation of a dental unit is carried out in stages:
- antiseptic treatment of mucous membranes;
- anesthesia with local antiseptics or general anesthesia;
- applying forceps and disconnecting the ligament;
- rocking or dislocation;
- extraction from the hole;
- stop bleeding.
If the third molar from below is removed, the operation becomes more complicated. In order to pull it out, the doctor cuts the gum, removes part of the bone, divides the roots into fragments and removes them separately. To prevent infection, the wound is treated with antibacterial drugs. After all manipulations, the gums are sutured with absorbable or non-absorbable suture material.
X-ray and anesthesia during lactation
Before extirpation of a dental unit, an x-ray or computed tomography is almost always done. This is necessary to assess the structure, position and condition of the root system. To protect the patient from x-ray radiation, she is wearing a lead apron. It blocks dangerous waves, but after the procedure it is better to express the first batch of milk and pour it out.
For local anesthesia, private clinics use drugs approved during pregnancy: Ultracain, Ubistezin, Artifrin, Alfacain and similar medications. They do not contain toxic components that can cause allergies and other side effects. Primacaine has a short half-life, so feedings may not be missed.
Anesthesia is used only in extreme cases, if a complex and lengthy extraction is being performed. If general anesthesia is necessary, the child is temporarily transferred to artificial nutrition. During this period, the mother must express milk regularly to ensure milk production continues.
If antibiotic therapy is necessary after a complex removal, then breastfeeding will have to be stopped for several days. During long-term withdrawal, doctors recommend giving artificial formula not through a pacifier, but through a spoon or even a syringe without a needle. Otherwise, the baby may refuse to breastfeed, since the process of sucking milk from a bottle with a nipple is much easier.
Anesthetics that can be used by nursing mothers
In dentistry, pain relief is usually classified into general and local. In the first case, we are talking about anesthesia - intravenous or inhalation. Local anesthesia is the numbing of an inflamed area using an injection, gel or spray. It is highly undesirable to use general anesthesia when providing dental care to nursing mothers. If this cannot be avoided, then until complete recovery the woman should feed the baby with a special infant formula or pre-prepared breast milk.
Among the local anesthetics used by dentists are:
- Novocaine. Allowed during lactation only in cases where the expected benefit for the woman is much higher than the possible risks for the baby. Before administering the solution to the patient, the dentist must weigh the pros and cons. Sometimes the medication causes negative side effects: headaches, weakness, drowsiness, convulsions, dizziness, arrhythmia, bradycardia, swelling of the lips.
- Lidocaine. The official instructions state that only a doctor can prescribe medicine to breastfeeding women. The drug passes into milk in very small quantities, and its oral bioavailability is low. This means that the amount of active substance that is released in milk is minimal. Therefore, the potential harm to the child is low. Possible adverse reactions after the administration of lidocaine: numbness of the tongue, convulsions, drowsiness, tinnitus, blurred vision, angioedema, urticaria and some others.
- Articaine. A product approved for both pregnant and lactating women. Dentists use it if they need to perform infiltration or conduction anesthesia. Side effects of the drug include: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, low blood pressure, allergies.
Attention! Nursing mothers are prohibited from administering anesthetics that contain high amounts of adrenaline. Such drugs negatively affect the baby’s health, in particular, they provoke negative changes in the child’s cardiac activity.
Recommendations for the recovery period
In order to avoid complications after surgery, you need to follow all the doctor's advice. After the procedure, the doctor applies a cotton swab to stop the bleeding. It should be held for no more than 10 minutes, otherwise the blood clot will dry out and come off along with the cotton wool. With high blood pressure, bleeding continues for a longer time, so the tampon can be kept in place for 15 - 20 minutes.
In the first days you cannot:
- overheat the body, apply warming compresses;
- engage in heavy physical labor and sports;
- lick a blood clot;
- eat hot, spicy, rough food;
- drink through a straw;
- smoke;
- touch the socket with a toothbrush and other objects.
You are allowed to eat after 3-4 hours. The issue of feeding a child should be discussed with a doctor. Local anesthetics practically do not enter the blood, and components penetrate into mother's milk in minimal quantities. If the doctor has not prescribed other medications, then you can feed the baby within a few hours.
After the anesthetic wears off, pain appears. Possible increase in body temperature. To relieve acute symptoms, you can take Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Naproxen. You can reduce pain and swelling by using cold compresses.
Rinsing your mouth and brushing your teeth is allowed on the second day. For rinsing, pharmaceutical preparations are used: Romazulan, Chlorhexidine, Miramestin. They will prevent the development of infection and inflammation. You can rinse your mouth with an aqueous solution of baking soda and salt. To improve the healing of damaged tissue, decoctions of oak bark, chamomile, and calendula are used.
Prevention measures
Extraction of a dental unit is carried out in cases where the disease is advanced or therapeutic treatment does not have an effect. Since teeth decay faster during pregnancy, it is necessary to carry out proper oral hygiene and undergo a preventive examination by a dentist while carrying a child. If pathology is detected in the early stages, removal will not be required.
Doctors' recommendations during lactation:
- brush your teeth twice a day;
- rinse your mouth after every meal, use dental floss;
- eat well;
- limit consumption of sweet foods.
During lactation, teeth can and should be treated. Even if anesthesia is performed with lidocaine, there is no need to worry. You just need to check with your doctor for how long you should refrain from feeding. The components of the drug enter milk in minimal concentrations, so when used in small dosages they will not harm the baby’s health.
Is it permissible to use local anesthetics?
There is a myth that any dental painkillers are strictly contraindicated for nursing mothers. It is because of this that women put off a visit to the dental clinic - only a few are ready to treat a sore tooth without anesthesia.
In fact, local anesthetics can be used during lactation. Not all medications are suitable, but the list of safe options is wide. Therefore, the patient will definitely not have to endure severe pain during the treatment of a deep carious cavity, pulpitis or advanced inflammation.
It is very important that the patient warns the dentist in advance that she is breastfeeding. Then the doctor will be able to choose the optimal pain reliever for her.
If the upcoming intervention is very serious and requires the mandatory administration of a potent analgesic, you should discuss with your doctor the possibility of carrying out all the manipulations later - when the lactation period is over. If the disease does not tolerate delay, arguing with a specialist is not only pointless, but also harmful to health - you just need to trust him.
Often, after dental therapy, the dentist prescribes a course of antibiotics. This also confuses mothers, since all antibacterial agents are excreted in milk, which means they can pose a danger to the newborn. In fact, there is no need to worry. If the doctor is warned about lactation, he will choose exactly the medicine that will not harm the baby. But the mother’s independent refusal of antibiotic therapy can lead to serious complications.
It is important to understand: in most cases, postponing therapy until later results in serious problems. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether dental treatment is allowed during breastfeeding is affirmative. And the sooner a woman visits the dentist, the higher her chances of a speedy recovery.