Dental diseases of the teeth are a group of pathologies that affect the enamel, gums, oral cavity, as well as the jaw and chewing muscles. Dentists call them harmless to humans, since the mortality rate is negligible. However, it is these disorders that determine the patient’s overall well-being: they affect self-esteem and an internal sense of comfort.
Experts recommend not to let the situation get worse and to closely monitor the condition of your teeth. Due attention allows you to avoid serious complications, as well as promptly identify defects that need correction.
In this article we examine in detail the most common problems, as well as methods of treating them.
Basic terms in dentistry: names and causes of inflammatory diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
It plays a vital function in the digestion process: it is responsible for grinding food and influencing its subsequent breakdown by enzymes. In addition, there is a huge number of microorganisms that create natural microflora, but are considered opportunistic. This nuance determines the fact that any dental disorders progress extremely quickly.
Among the key factors in the occurrence of dental diseases are:
- poor hygiene;
- mechanical injuries and damage;
- chronic illnesses;
- metabolic disorders and abnormalities;
- the presence of thermal irritants in the body;
- bad environment;
- hereditary predisposition.
The branch of medicine that studies the emergence and development of pathologies is called etiology. It is partially correlated with diagnostic procedures, as it helps in determining pathogenesis.
Classification: types of main dental diseases of the teeth
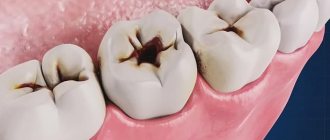
Conventionally, all violations can be divided into two broad categories - those associated with damage to the enamel, and those caused by processes occurring in periodontal tissues. There is another classification principle - based on “carious” affiliation:
- with existing caries lesions;
- non-carious deviations.
The second option is considered the simplest and most convenient to treat if the problem is detected at an early stage. In addition, it is easier for patients to comply with prescriptions, which simplifies the process of rehabilitation measures.
Note that congenital and hereditary pathologies stand apart. They are formed in the womb and are very difficult to correct.
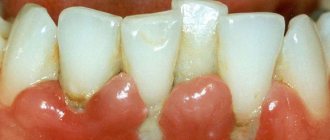
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is not treated, it can lead to the development of periodontitis . Periodontal inflammation means inflammation of not only the gums, but also the tissues that support the teeth. These include bone, gums, mucous membrane and dental ligament. Their defeat can lead to exposure of the roots of the tooth, its loosening and, as a result, loss. Periodontitis, like gingivitis, is accompanied by bleeding gums and bad breath; in addition, it is characterized by itching and pulsation in the gum tissue, and tooth mobility. As the process progresses, mobility increases, the necks of the teeth become exposed and become increasingly sensitive to temperature stimuli. Treatment of periodontitis requires a serious approach and is carried out using both conservative and surgical methods.
Developmental and eruption disorders
What are the different dangerous dental diseases? Perhaps the most serious problems are caused by congenital or hereditary causes. In these cases, the exacerbation does not begin due to pathogenic bacteria, pathogens or other factors. Such pathologies, as a rule, play a symptomatic role. They signal about malfunctions occurring in the body and force you to take immediate action.
Edentia
A pathological process accompanied by the loss of individual units or complete rows. In extremely severe stages, complete tooth loss occurs. The disease begins to develop during intrauterine development. The main factor is poor heredity or serious illnesses suffered by the mother while carrying the fetus. Due to jaw overload, even healthy teeth can become loose.
Superset
A disease in which excess elements appear in the oral cavity, which have an extremely negative effect on the state of the bite, and provokes additional speech and chewing problems. Dentists recommend removing such units, and the sooner the better.
Fusion and Merger
A rather rare deviation, expressed in the connection of tooth buds with dental cement. The main processes unfold during the formation of elements. Only 1% of people are prone to this disease. As a rule, the disease is diagnosed as part of a temporary dentition. In adulthood, pain is approximately 5-6 times less, so patients often do not suspect the presence of a problem until a visit to the dentist.
Spear-shaped teeth
A disease that affects crowns. It is considered infrequent - it occurs in one case in a thousand. It causes both aesthetic, psychological and physiological inconvenience. Usually it is a consequence of chronic injury to the inner surface of the cheeks, lips, and tongue. In some patients it is accompanied by hypoplasia.
Impacted teeth
An ailment in which the teeth are unable to fully erupt. As medical practice shows, the problem begins to bother people due to the gums being blocked by bone layers. Another reason is premature loss of elements.
Dystopian teeth
A disease in which the incorrect location of units is recorded. The displacement occurs as a result of deviations of the alveolar ridges from the norm. It causes psychological discomfort, disrupts the beauty of a smile, and interferes with the correct functioning of the masticatory muscles.
Macrodentia and microdentia
Congenital hereditary anomalies that determine the specifics of development. Manifested in improper formation and scaling of teeth. They have a negative impact on the bite and the aesthetics of the smile. They are also extremely rare - in every 20 people (in the context of not a single state, but the whole world).
Dental clinic of Professor A.I. Doinikov
Often, a patient comes to the clinic and at the beginning of the consultation says: “You, doctor, just don’t be alarmed, I just really neglected everything in the oral cavity. Now I have a completely ugly smile and it’s uncomfortable to eat.”
Indeed, you often see a sad picture with many teeth completely destroyed down to the gums, large carious cavities and a lot of tartar.
You ask: “Why don’t you take care of yourself? We need to treat!”, and in response - “I don’t even know where to start... Probably, I just need to remove everything and insert prostheses, but, most likely, the treatment will be very expensive and I won’t be able to afford it.”
Let me note right away that there is no need to despair. Of course, you can’t do everything at once and quickly. The destruction process was long and the problem itself did not arise out of nowhere. Serious treatment and prosthetics undoubtedly require significant financial costs, but the treatment can be divided into several stages so that the financial issue is not so acute.
Let's draw up an approximate action plan on how to solve your problem.
The goal of treatment is, at the first stage, to reduce microbial contamination of the oral cavity, or, in layman’s terms, to remove the infection, and at the second stage, to restore chewing function and the aesthetics of the smile.
Treatment should begin, first of all, with those teeth that are currently causing you pain. It is necessary to prevent further development of the acute infectious inflammatory process.
After the initial “firefighting”, the approach to treatment should become planned and systematic.
First of all you should... change your toothbrush and learn how to brush your teeth properly again.
Yes, most people think that they brush their teeth quite normally, but their teeth are destroyed solely due to bad heredity, bad water, the environment in general, etc. This is wrong. This is where the treatment process begins - with training in proper hygienic oral care.
I recommend using a toothbrush with soft bristles and regular toothpaste (not whitening).
Look at the length of the working part of the toothbrush and estimate how many times this length can be measured along the dentition. So, on each section of the dentition, the length corresponding to the length of the bristles of the toothbrush, it is necessary to make 10 sweeping movements on the buccal and lingual sides of the tooth. The movements should be directed, figuratively speaking, from “red” to “white” - in the direction from the gums to the top of the crown of the tooth.
Remember - you are not just brushing your teeth - when brushing your teeth you are saving your own money! Think of it this way: if you brush your teeth, you put 100 rubles in your pocket! Few? Consider that you put in 500! And so on...
After you remember how to brush your teeth, you can begin further work on dental treatment and prosthetics.
And we start... again to hygiene! Now it's professional!
It is necessary for a dentist or hygienist to carry out professional oral hygiene for you - remove tartar with an ultrasonic instrument and clean your teeth with brushes and prophylactic paste.
An X-ray examination of all teeth should then be performed. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is best suited for these purposes, and less commonly, orthopantomogram (OPTG).
According to a visual examination of the oral cavity and x-ray examination, teeth should be classified into the following groups: 1) clearly hopeless teeth - subject to inevitable removal, 2) conditionally preserved - which can be tried to be preserved, but the prognosis is questionable, 3) requiring treatment, but definitely preserved 4) healthy teeth
After this the work becomes easier.
You should start by removing obviously hopeless teeth.
Patients are always tempted to “heal” their front teeth first to restore their smile, and leave everything else to the second stage.
What to say? We must fight this temptation and carry out complete treatment.
Removing clearly hopeless teeth as the first stage provides 2 advantages at once. Firstly, while you are treating teeth from the other groups listed above, your gums and jaw bone tissue will slowly heal, which is important for subsequent prosthetics or implantation. Secondly, after this it is already possible to pre-plan the type of future orthopedic structure.
At the next stage, we take a closer look at the teeth from the conditionally preserved group.
We are trying to treat. If the treatment is successful, great; if not, we remove it without regret. It is better to be a little more radical at this stage than to subsequently have problems with questionable teeth already involved in the prosthesis.
Next, we relatively calmly treat less damaged teeth from the group that require treatment, but are definitely preserved.
After this, the oral cavity becomes, as dentists say, “sanitized” - that is, healthier. Microbial contamination of the cavity is reduced.
Now you can think about the final type of prosthetics, we agree on the future orthopedic design (prosthesis) and proceed to the prosthetics stage.
Author : Surkin Alexander Yuryevich, candidate of medical sciences, dental surgeon, orthopedic dentist. Dental clinic of Professor A.I. Doinikov, 2022
Diseases associated with enamel
What are the possible dental problems due to enamel damage? In the vast majority of cases, they are associated with violations of the structure and integrity of the rows. Usually they are a consequence of internal failures in the body. They are eliminated only at the moment when the factor that provoked their exacerbation disappears.
Fluorosis
A chronic disease that develops during eruption. Accompanied by structural damage, darkening, and loss of dentin. The reason is excess fluoride, which is explained by long-term use of fluoridated water, medications, etc.
Cracks
Deviation, usually localized on the anterior chewing row. It looks like vertically or horizontally located defects of a non-carious nature. Appears due to sudden temperature changes, aggressive chemical exposure, or due to injury.
Turner teeth
An advanced form of local manifestations of hypoplasia. It is fixed long before the first eruptions and has nothing to do with carious lesions. Externally it looks like an enamel layer. Sometimes accompanied by excessive sensitivity.
Hypoplasia
Pathological phenomena of a congenital nature, which is characterized by a complete or partial absence of enamel. If we talk about the external picture, then it is worth noting depigmented or white spots, rather large grooves based on the surface, as well as small depressions. Caused by incorrect structure of hard dental tissues. If left untreated, it is complemented by acute forms of caries.
Wedge-shaped defect
Disadvantages expressed in wedge-shaped cavities in the cervical region of the units. This occurs due to the fact that certain areas of the enamel disappear, resulting in wedge holes. The problem can be registered on any element, but more often on fours and fives.
Jaw clicks
If, when you open your mouth, you hear a crunching sound and there is pain that radiates to the ear - these are symptoms of temporomandibular joint dysfunction.
The reasons may be different: for example, during dental treatment, the balance was disturbed and crowns were placed too large, resulting in muscle tension, which developed into constant pain. In this case, it is enough to grind the points of contact of the teeth with each other.
Another reason may be the loss of teeth, especially the lateral ones, which secure the bite. Because of this, increased stress is placed on joints and muscles. This problem can only be solved by restoring the dentition with implants.
Clicking jaws and pain when opening your mouth may indicate problems with the temporomandibular joint
The jaw can also click due to injuries, infectious diseases and musculoskeletal disorders. To establish the exact cause, you need to contact an orthopedic dentist.
Other dental diseases: list of dental diseases with photos
Next, we propose to analyze ailments that may appear as a result of teething or age-related changes.
Grinding
A pathology in which there is a rapid decrease in hard tissue. Provokes thinning of enamel and damage to dentin. It can affect both individual units and full-fledged rows.
Erosion
A process in which a violation of enamel integrity is recorded. Some areas are damaged symmetrically. Main signs: changes in pigment, various cosmetic defects, painful reaction to cold or spicy food.
Pathological resorption
Loss of root tissue caused by chronic diseases, advanced periodontal disease or progressive pulp disease. It can be one-sided or combined. In the absence of rehabilitation and therapeutic therapy, tooth loss occurs.
Deposits and build-ups
They are mineralized residues that form above or below the gums. The main material for formation is food particles, the results of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as components of saliva. They trigger processes that provoke periodontitis.
List of neurotic dental diseases
Stressful periods have a particularly detrimental effect on the state of the body. In addition, as practice shows, the quality of oral hygiene deteriorates sharply. A person simply forgets about cleaning or does not do it thoroughly enough, which increases the risk of developing caries. The parallel use of sedative medications disrupts the production of saliva and causes a feeling of dryness.
Gradually, all this is reflected in psychosomatics - muscle spasms and pain are detected. The most common occurrence is excessive clenching of the jaw.
Bruxism
A disorder characterized by uncontrollable grinding of teeth caused by emotional stress. As a rule, it makes itself felt during sleep. The causes of its appearance include stress, prolonged depression, and malfunctions of the masticatory apparatus.
Grinding
This is not so much a full-fledged disorder as a symptom. Occurs when muscle spasms occur when the patient clenches his jaw tightly. In the vast majority of cases, the person does not even know there is a problem. It is detected during routine dental examinations.
Specifics of adolescent teeth
Teenage teeth are in the same transitional state as their owners - no longer children's milk teeth, but not quite adults either. The permanent bite has been formed, the teeth have been replaced by molars, but the structure of these teeth is not yet perfect. Main characteristics of teeth in a teenager:
- thin enamel - it is formed within 2 years after the eruption of permanent teeth;
- there is little hard dental tissue - it is also still in the formation stage;
- many pulp tissues;
- deep fissures - depressions and tubercles on chewing teeth;
- short and thick roots are formed within another 2–3 years [1].
Dental diseases proceed in their own way: caries develops rapidly (due to the vulnerability of the enamel) and quickly turns into pulpitis (the pulp is very close). The layer of hard tissue is thin, so immature teeth are fragile and susceptible to injury.
The fissures of an immature tooth are deep, with hidden cavities - plaque easily accumulates in them, and the rapid development of caries is observed. The walls of the roots are thin, so such a tooth is not able to withstand heavy loads.
The main dental diseases in humans: what they are and how to treat them
Modern medical practice, implemented in the Dentika dental clinic, actively uses innovative methods of diagnosis and treatment. Almost any disease can be eliminated provided that you seek help in a timely manner, as well as follow all doctor’s prescriptions and prescriptions. Among the measures used by dentists are:
- filling;
- surgical intervention;
- prosthetics;
- implantation;
- aesthetic correction.
In addition, professional hygiene methods are used: bleaching, restoration, etc.
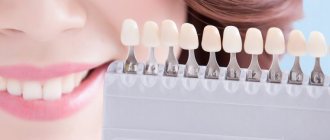
Aesthetic dentistry
A beautiful smile affects the impression we make on other people. Even white teeth have always indicated high social status, health and prosperity. To get the smile of your dreams, you can resort to the achievements of aesthetic dentistry.
Teeth whitening can be combined with strengthening the enamel and professional cleaning of the oral cavity from plaque and tartar. This will not only improve your appearance, but also prevent the spread of caries and periodontal disease. If the teeth are generally healthy, but have uneven edges and chips, the tooth can be restored using modern restoration methods.
Veneers and lumineers can significantly improve the appearance of your teeth without the aggressive treatment required for crowns.
This technique allows you to install a thin porcelain plate on the surface of the tooth, which will hide color defects resulting from metabolic disorders or other incidents.
Prevention
Above, we examined in detail what dental diseases are called and what are the main reasons for their occurrence. Now let's talk about preventive measures to avoid serious problems and pathologies.
If you experience any strange sensations in your mouth, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your dentist immediately. He will conduct an initial examination and draw up an individual treatment program. However, in some cases it is possible not to resort to aggressive measures of influence and limit oneself to supportive manipulations.
So, what needs to be done to prevent the development of diseases?
- Do not ignore the symptoms that appear - go to the doctor immediately.
- Do not let the disease worsen, follow all dental recommendations and prescriptions.
- Get professional examinations every six months.
- Maintain hygiene at home, use only high-quality products.
- Don’t forget about professional hygiene - ultrasonic cleaning should be done once every six months to a year.
In addition, it is important to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and give up bad habits.
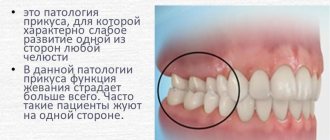
Facial asymmetry
As the jaw forms and teeth emerge, pressure and stress on some areas of the gums may be greater than others. This entails uneven development of the masticatory muscles and can lead to asymmetry in the lower part of the face or worsen the appearance of the lip area.
Correcting your bite by installing “advanced” braces allows you to make your teeth straight. Which, firstly, will promote chewing of food, and therefore improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract; secondly, it will brighten your smile and appearance, which will raise self-esteem and have a positive impact on your well-being and psychological health.
The range of services that modern dentistry offers is diverse and goes beyond just health care. A visit to the dentist can improve the quality of life, solve psychological problems, and relieve pain and discomfort.
Let's sum it up
Dentistry studies the etiology, symptoms, and treatment features of the most common dental diseases. There are a huge number of reasons that provoke oral problems. Some of them are easily eliminated, others are subject to only partial correction. However, for both cases the rule is true: the sooner you start working on dental treatment, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. That is why it is important not to let things take their course and undergo regular medical examinations.