The position of the teeth with the jaws closed is called a bite in dentistry. Unfortunately, not every one of us can boast of perfectly straight teeth. Most people experience malocclusion. Most often, they are small and few people notice them, but there are situations when the malocclusion is pronounced and causes a lot of inconvenience. In these cases, it is customary to install braces. What to do if for some reason it is impossible to install braces? Dentistry has developed methods for correcting malocclusion using prosthetics, but doctors warn that they can only be used in specific clinical cases, strictly according to indications.
How is the bite formed?
The process of bite formation is long - from birth to adolescence. There are 5 periods.
- Initial (up to 6 months): no teeth, the upper jaw is larger in size than the lower jaw. At this time, an active feeding process is extremely important for the proper development of the jaw apparatus.
- Emerging temporary bite (6 months - 3 years): baby teeth and a bite appear, but it is still temporary. This stage is accompanied by inflammation of the gums, a rise in temperature, often grinding of teeth (bruxism), and emerging teeth may be crooked. It is important to maintain hygiene without taking any orthodontic measures.
- Formed temporary occlusion (3 - 6 years): baby teeth have erupted and can close in different ways, jaw growth continues. This is the time of active use of teeth. Characteristic wear of temporary teeth is considered normal before the upcoming change.
- Changeable dentition (6-12 years): jaw growth, loss of baby teeth and appearance of permanent teeth. Often new teeth, especially the lower ones, erupt unevenly. During this period, it is necessary to decide on a plan for further correction of the bite.
- Permanent dentition (12 - 15 years): replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones, all 28 teeth are visible, no wisdom teeth. The period is most favorable for orthodontic treatment.
In order for the bite to form correctly, there must be careful attention to teething, oral hygiene, and a timely plan to correct emerging problems.
Stage II - tooth implantation
After removing the braces, implant surgeon V.P. Alaverdov installed an Astra Tech dental implant for the patient. The operation lasted 30 minutes and was performed under sedation (in medical sleep). Healing took several months.
The fixed orthotic remains on the teeth until the final dental prosthetics. The dimensions of the orthotic will be harmoniously distributed between the antagonist teeth. Crowns on the teeth will fix the correct position of the bite.
Correct teeth bite
An ideal orthognathic bite implies the presence of the following features:
- The upper dental arch is slightly inclined forward and has the shape of a semi-ellipse, the lower, in the shape of a parabola, is slightly backward.
- When the jaws close, each upper tooth contacts the opposite tooth below.
- There are no obvious gaps between the teeth.
- The upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by about a third of their height.
Despite the fact that there are the above parameters for a perfect smile, the question “What should be the bite of the teeth?” cannot be answered unambiguously. In addition to the orthognathic bite, modern orthodontics allows for several options for the normal structure of the dentition and the location of the jaws.
Orthognathic
The upper row of teeth overlaps the lower one by 30% of the height, there are no gaps between the teeth or spaces between the rows.
Biprognathic
The dentition is slightly directed towards the vestibule of the mouth.
Progenic
The lower jaw moves forward slightly.
Straight
When the jaws close, the upper teeth come into contact with the lower cutting edges.
Partial or complete orthodontic treatment?
We offer different options. Sometimes full orthodontic treatment is necessary for an aesthetic and functional result. If we are talking about patients who already have quite a lot of orthopedic structures on the upper jaw, there are no lateral teeth, there is crowding, a close position of the front incisors on the lower jaw, then it will be sufficient to align the lower incisors and, as far as possible, raise the bite. In this case, we are talking about partial orthodontic treatment, lasting not 1.5-2 years, but much faster.
Local problems, such as tilted eighth teeth in the absence of seventh or sixth teeth, are solved by the support of two miniscrews without the use of a brace system or by using small systems for the lateral group of teeth. This will also be partial orthodontic treatment.
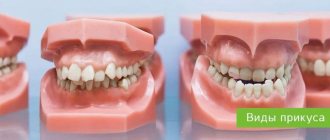
Malocclusion of teeth
Look at your reflection in the mirror. If you notice an excessively protruding upper or lower lip, teeth that “overlap” each other, or gaps between the dentition when the jaws are closed, this is a clear reason to consult a specialist. Descriptions of dental anomalies and photographs of teeth with malocclusion pathologies are presented in the table below.
Distal (prognathic)
In a distal bite, the upper jaw is more developed than the lower jaw.
Mesial (medial)
With a mesial bite, the lower jaw is pushed forward.
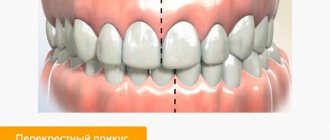
Cross
In a crossbite, the rows of teeth intersect in the manner of scissors when the jaws close.
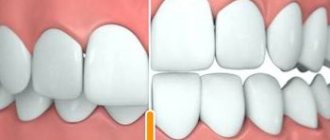
Deep
In a deep bite, the upper teeth significantly overlap the lower teeth.
Open
The presence of pronounced gaps between the dentition when the jaws are closed indicates an open bite.
Symptoms
Signs indicating the formation of a deep bite:
- The upper jaw grows and develops more rapidly than the lower jaw, surpassing it in parameters;
- The lower lip is too thin (in most cases!) and can be turned outward;
- Reduced depth of the gap located in front between the lips and cheeks;
- Lack of space between rows of teeth;
- Unnaturally small chin size.
Patients with a deep bite usually complain of difficulty biting and chewing foods, distorted pronunciation of certain sounds, and difficulty breathing.
Classification
Main types of deep bite:
| Name | Description | Peculiarities |
| Distal | The chin is reduced and slanted to the side, the face is shortened, the lower jaw is underdeveloped. When you smile, your teeth and part of your gums are visible. | Shapes:
|
| Neutral | It is not visually noticeable in either children or adults. The facial features are proportional. Accompanied by the formation of a supramental fold, in which the lower incisors overlap the upper ones. The chin is proportional to the rest of the face. | Affects the articulation of sounds and pronunciation. Only a specialist can determine a neutral deep bite. |
Consequences
A deep bite causes aesthetic discomfort and negatively affects the main function of the jaw – chewing. The mucous membranes are constantly injured, the front teeth are overloaded and bruxism (grinding) is formed.
Due to regular friction, tooth enamel wears down, which leads to increased sensitivity. A deep bite negatively affects the functioning of the maxillofacial joints, so treatment must begin as early as possible.
A long-term complication of the pathology is the gradual loosening of teeth and their loss already at 30-35 years of age. A deep bite provokes the development of many diseases - periodontitis, gingivitis and interdental gaps.
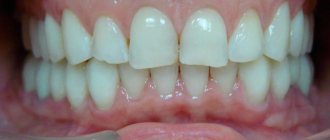
Photos before and after treatment
Diagnostics
To identify a defect and make a correct diagnosis, the orthodontist carefully examines the oral cavity and receives complaints from the patient. In order to recreate the exact contact of the dentition, casts are made from alginate mass. For a more detailed assessment of the condition of the oral cavity, computed tomography (CT), electromyography and orthopantomography are used.
Attention! Sometimes a specialist uses photographs of a person’s face taken from several angles to identify the occlusal relationships of the dentition.
Treatment
Correction of deep bites is recommended in childhood, but the necessary dental care is also provided to adult patients. The selection of treatment methods takes into account the form and degree of the anomaly:
- Plastic surgery for frenulum correction. The techniques used are frenectomy or frenulotomy. Laser exposure can be used;
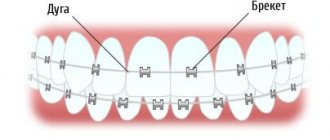
- Bracket systems. They are able to correct the bite when the position of the incisors and molars is fully formed. Vestibular and lingual structures are used for treatment;
- Veneers, crowns. A cosmetic method that masks a deep bite, BUT does not eliminate the causes of its occurrence;
- Osteotomy. A surgical intervention that involves separating the palate and upper jaw from the bones and fixing them with plates and screws.
Attention! Elimination of malocclusion before the age of 6 years is recommended with the use of removable vestibular plates and retainers.
Treatment of a deep bite is accompanied by wearing a special plate and performing muscle gymnastics exercises.
At home
Self-treatment of deep bite is IMPOSSIBLE. However, at home you can speed up the healing process with the help of migymnastics. Provided that the exercises are performed correctly and regularly, it allows you to achieve excellent results.
When performing exercises, follow several rules:
- use all areas of the oral cavity,
- maintain the greatest amplitude of execution,
- take a break after each exercise,
- Perform exercises until your muscles feel slightly tired.
Prevention of functional disorders
A deep bite cannot be eliminated in 1-2 days; treatment with braces can take years. Simple preventive measures will help prevent functional disorders.
Among them:
- elimination of caries,
- correction of incorrect posture,
- eating solid foods (nuts, carrots),
- exclusion of pathologies of the skeletal system,
- prevention of somatic and chronic diseases.
The key to oral health is regular dental examinations (at least 2 times annually).
Patient reviews
“I wore braces for a long time - as a result, the bite improved a little, but still caused discomfort. To permanently solve the problem, the dentist suggested surgery. I had it performed under general anesthesia, the swelling subsided in just a few days, and 16 days after the operation I went back to work! Finally, my smile doesn’t give me any complexes, and eating food doesn’t cause any inconvenience!”
Lyudmila, 28 years old, Samara.
“After installing the braces system, I experienced severe pain for several days and could not even eat. The dentist warned about such consequences, so I bought painkillers in advance. After about a week I was completely accustomed to the braces. Now I’ve been wearing them for 6 months and the improvement in my facial proportions is already noticeable!”
Anastasia, 21 years old, Saratov.
“A deep bite has tormented me since childhood, but 2 years ago I finally decided to correct it and turned to an orthodontist. Initially, it was corrected with braces, but the doctor warned that it would be impossible to do without surgical intervention. Now my bite has been completely restored (after braces and surgery), even the oval of my face has visually stretched. For prevention, I continue to perform myogymnastics. I'm happy with the result."
Alexey, 34 years old, St. Petersburg.
Bite in the absence of teeth
A person without teeth has problems with the functioning of the temporomandibular joints, facial aesthetics deteriorate, and wrinkles appear due to loss of skin tone. To avoid unpleasant consequences, it is necessary to restore the bite using a complete denture made using a special technique.
Bite restoration with complete dentures
- The central ratio of the jaws is determined - the position of the lower jaw in relation to the upper in three planes: vertical, sagittal and transversal. The role of the dentition is played by wax rollers.
- Measurements are taken using a device consisting of an external facebow-ruler and an intraoral plate with a flat frontal part and curved distal parts.
- The plaster model marks the boundaries of the future structure, the line of the middle of the alveolar process, the tubercles of the upper and lower jaw, and the midline.
- Artificial teeth are placed in such a way that when you smile, the part of the prosthesis that imitates the gum is not visible.
Correction of the smile zone and missing anterior incisors
There is an aesthetic problem in the smile area associated with the absence of front teeth, for example, second incisors. Nowadays, it is not uncommon that even their rudiments are missing. It does not cause complaints as long as there are baby teeth in this place, but after their removal the question arises about restoring the defect. In such situations, the orthodontist, orthopedist and implantologist choose a comprehensive treatment strategy. Options are being considered with implantation and prosthetics in this area or orthodontic movement of adjacent teeth with their further restoration with veneers to create a harmonious smile.
A less common situation is the absence of one of the front incisors. If the defect has existed for quite a long time, then problems may arise with implantation in this area due to a lack of bone tissue. Then the orthodontist proposes a treatment plan with moving the lateral incisor to the place of the missing central one, and prosthetics on the implant is carried out in the freed area where there is enough bone tissue.
Bite after wisdom tooth removal
Some doctors are convinced that wisdom teeth are an atavism and must be gotten rid of. In ancient times, they were used to chew tough foods, such as raw meat. With the development of civilization, the human diet changed, his jaw began to gradually decrease - and the “eights” turned out to be superfluous. Most often, before starting to correct the bite, wisdom teeth are removed. This frees up space for the correct formation of rows, and the result of teeth alignment will be much better.
Initial consultation with an orthodontist
During the consultation, the following problems were identified: the absence of the 35th tooth (there is no place for its prosthetics), pathologically deep bite, bruxism, severely worn teeth in the lateral regions, minor chips on the front teeth, displacement of the jaw when opening the mouth, clicking in the TMJ on the left.
Bruxism, deep bite, increased tooth wear, TMJ dysfunction - all these problems, which are of the same nature, will only get worse without proper treatment. Treatment should be carried out comprehensively with the participation of several specialists: an orthodontist, an orthopedist, a neuromuscular dentist, an osteopath.
What affects the bite of teeth?
The negative impact of defects in the dental system on the condition of the entire organism has been repeatedly proven by scientists. The list of identified health risks is impressive even for ardent optimists.
- Due to improper distribution of the chewing load, tooth enamel wears off faster, teeth begin to react painfully to cold and hot, their necks become exposed, and noticeable gaps form between the teeth.
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joints occur, accompanied by headaches and a characteristic clicking sound when the jaws move.
- The aesthetics of the face suffers: its proportions change, wrinkles form, teeth become crooked, and the smile becomes unattractive.
- It becomes difficult to bite food, chewing functions are disrupted, causing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Speech defects appear, facial expressions are distorted, and self-esteem decreases.
- Crowding and crooked teeth cause accelerated tooth decay due to frequent chipping and carious lesions.
- The oral mucosa is injured - cheeks, gums, tongue, and the tissues of the oral cavity become inflamed.
- The quality of breathing deteriorates, which leads to diseases of the nasopharynx, trachea, and hearing aid.
Consequences
If dental malocclusion is not corrected in a timely manner, irreversible consequences may occur, including:
- Dental pathologies.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- ENT pathologies.
- Speech disorders.
- Central nervous system disorders, headaches and joint pains, development of psychological problems.
- Violation of facial symmetry, aesthetic defects.
This is a short list of the dangers of malocclusion. Each item has a number of medical diagnoses of varying severity.
Therefore, if you suspect the formation of a pathological bite, you should consult an orthodontist as soon as possible, who will conduct a thorough diagnosis and give recommendations for further treatment.
Treatment of dental malocclusion
How to change the bite of teeth? Pathologies of the dental system can only be eliminated through orthodontic treatment. An exception is the correction of a low bite, when the height of the teeth decreases with age due to their wear. In such cases, the bite is corrected by dental prosthetics with crowns or veneers, as well as by implantation. Other anomalies of teeth and bite can be removed at any age with special orthodontic structures or through surgical intervention.
However, maxillofacial operations are performed only in case of serious deviations from the norm. Usually, to correct dental malocclusion, doctors suggest correction with braces or aligners.
Now that you know about all the health risks that can cause pathologies of the dental system, and how to correct your dental bite, all that remains is to take specific actions. Even if at first glance it seems that your teeth are straight, make an appointment with an orthodontist. Diagnosing the condition of the dentition will help maintain the health of other organs and systems. And timely orthodontic treatment will make your smile more attractive and significantly reduce the number of future visits to the dentist.
Causes of pathological bite
Factors that provoke improper closure of teeth can be divided into congenital and acquired.
Congenital malocclusion is caused by a genetic mutation, hereditary predisposition or pathology of intrauterine development of the fetus. Such anomalies are more difficult to correct and are often an indication for surgical intervention.
Acquired factors can manifest their effects both in infancy and in adulthood. Thus, the main reasons for the development of malocclusion starting from early childhood are:
- birth trauma of the skull;
- improper latching on the breast when feeding;
- long-term breastfeeding or bottle feeding;
- chronic diseases of the endocrine and respiratory systems;
- lack of essential microelements in the diet, unbalanced nutrition;
- previous rickets;
- bad habits – finger or foreign objects (pencil) in the mouth;
- early tooth extraction, jaw injuries.
With age, factors such as errors in prosthetics, gum disease, the absence of most teeth, and pathologies of the motor joint of the jaw are added.
Measurement methods
Anatomical method
The use of this method of measuring bite height is aimed at identifying the physiological transformation of the lower part of the facial zone.
Calculation of central occlusion using this method is based on identifying features of facial anatomy.
A decrease in bite height is expressed in the following points:
- sunken lips;
- increasing the depth of nasolabial folds;
- moving the chin forward;
- reduction in the height of the lower part of the face.
When using the anatomical method, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- the lips should be mobile and in contact with each other along the entire length without effort;
- the functionality of the orbicularis oris muscle should be high;
- The elevation of the corners of the mouth and the severity of the nasolabial folds should be determined.
Experts in the field of dentistry note that this research method is quite subjective , so it is practically not used at present.
Information content of teleroentgenograms in orthodontics in lateral and direct projection.
This material is devoted to modern diagnostic methods in dentistry.
Here https://orto-info.ru/ortodonticheskoe-lechenie/podgotovitelnyiy-period/miogimnastika.html we’ll talk about the effectiveness of myogymnastics in orthodontics.
Anatomical and physiological
The anatomical and physiological method for determining the height of the bite is based on identifying the height of physiological rest.
The technique for performing the procedure is as follows:
- The dentist places two marks on the patient's skin - at the base of the nasal septum and in the central part of the chin.
- Next, the patient is asked to make a couple of swallowing movements or pronounce several phrases, the pronunciation of which involves the lips.
After completing these actions, the lower jaw row comes to a state of rest. At the same time, the lips touch each other without tension, without stretching or sinking, and the nasolabial folds are moderately visible. - The dentist, using a special ruler with divisions, measures the distance between two points that were previously applied to the patient’s skin.
- Special templates with occlusal ridges are placed in the patient’s oral cavity, which must be lightly bitten.
- The specialist re-measures the distance between the points located on the nose and chin. The resulting indicator determines the occlusal height, which normally should be less than the previously determined height of physiological rest by 2-3 mm.
If, when determining the height of the bite, the occlusal height is equal to the indicator determined at rest, then the specialist concludes that the bite is elevated. Conversely, when the occlusal distance exceeds the resting height by more than 3-4 mm, this indicates an underbite.
After determining the bite index, the specialist removes or increases the height of the lower bite ridge until the occlusal height reaches the norm.
In this case, the dentist evaluates the condition of the tissues around the mouth. When the physiological occlusion is restored, the contours of the lower part of the face are normalized, the corners of the mouth are raised, and the nasolabial folds become less pronounced.
Basis of construction
The construction of the bite height is based on determining the distance between the two jaws in the position of maximum intercuspal closure of the teeth.
This indicator is of great importance in dental practice, since it allows one to determine the correct location of the elements of the dentofacial row.
A change in the physiological height of the bite as a result of the loss of some teeth or their displacement relative to the jaw line entails a change in the position of the main anatomical elements that surround the oral cavity.
In this situation, the patient is diagnosed with sunken lips, an increase in the depth of the nasolabial folds, a significant protrusion of the chin forward, and a decrease in the height of the lower sector of the face.
In addition to being aesthetically unattractive, this situation significantly complicates further orthodontic and orthopedic therapy.