Modern medicine has specialized technologies that allow the patient to avoid discomfort after septoplasty and breathe through the nose.
Author:
- Gadzhiev Kamran Rafikovich
otolaryngologist, rhinosurgeon
4.33 (Votes: 27)
- Nose pain
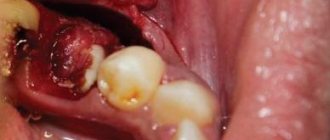
The most common pathology of the ENT organs is a deviated nasal septum. No one thinks that even the slightest curvature can cause serious diseases, such as sinusitis, nasal polyps. Why is this happening? When the ENT organs are healthy, only clean and warm air enters the lower respiratory tract, since it is warmed and disinfected in the nasal cavity. With a deviated nasal septum, these functions are disrupted due to the fact that the air stream hits the curvature of the septum.
Correction of a deviated nasal septum is called septoplasty. This operation helps the patient return to normal and natural breathing. But, unfortunately, many patients try to avoid it and continue to live with a deviated septum, which leads to complications in the future. What worries people before surgery:
- How to breathe through your nose after surgery?
- will tampons be placed in the nose?
- How long will I need to stay in the hospital after the operation?
These questions stop the patient from making the decision to undergo surgery.
How is rehabilitation after septoplasty?
With the development of technology, septoplasty has ceased to be uncomfortable. The operation begins with the patient being given anesthesia, then the doctor uses an endoscope, through a small incision, to enter between the layers of the mucous membrane and straighten the septum.
During the rehabilitation period, technologies were also created that allow the patient to avoid unpleasant sensations and breathe through the nose. Intranasal septal splints according to Reiter or splints were created. They are made of soft silicone, as it does not cause any harm to the nasal cavity and is painlessly removed from it. The splints have a seven-sided shape, which completely follows the shape of the nasal septum at the site of the operation. The essence of splints is that they keep the septum in the midline. After the operation, while the patient is under anesthesia, a silicone splint is sewn on.
Splints come in different modifications. Depending on the shape of the nose, they can be either large or small. A tube can also be inserted between the silicone of the splint, through which the patient can breathe immediately after the operation. The septal splint stays in the nose for about 5-7 days, during which time the nasal septum takes its position.
What is a sinus lift?
A sinus lift is a dental surgical procedure. Its essence is to create optimal conditions and prepare the area for the subsequent reliable placement of implants in the upper jaw. It is carried out according to certain indications, for example, in the presence of anatomical features or processes of bone tissue atrophy in a certain area in which the installation of a dental implant is impossible.
There are several types of such bone grafting: closed and open methods. The purpose of this operation is to raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus and build up bone tissue with certain substances. After which it is possible to perform implantation immediately after the operation or after some time. There are many nuances and certain difficulties in carrying out this surgical intervention. Therefore, there is always a small chance of developing complications, which will be discussed below.
Septal splints
Recently, septal splints or intranasal splints have become an integral part of operations on the nasal septum. For septoplasty, rhinoseptoplasty and closure of perforations of the nasal septum, the final stage of the operation is the installation of septal splints on both sides of the nasal septum.
The reason splints are so popular among surgeons is a number of advantages that improve the outcome of the operation, reduce the risks of postoperative complications and speed up the patient’s recovery.
The advantages of septal splints are reflected in the table
| Traditional septoplasty method | Septoplasty using septal splints | |
| Nasal discharge | After the operation, the mucous discharge in the nose and the remaining blood dry up. Crusts form in the nasal cavity, which adhere to the nasal mucosa and are difficult to remove. They also impair breathing and cause severe discomfort in the patient in the postoperative period. | Septal splints cover the entire mucous membrane of the nasal septum and prevent the formation of crusts on the mucous membrane of the nasal septum. And due to the fact that they are made of silicone, all the pathological contents in the nose do not find adhesion and are easily washed off with a nasal shower. |
| Swelling of the mucous membrane | After surgery, the nasal mucosa begins to swell and close the nasal passages due to surgical exposure. Because of this, the patient cannot breathe through his nose, he has to breathe through his mouth, and thus develops dry mouth, etc. | Silicone splints prevent the nasal mucosa from swelling and closing, as they are very flexible and quite elastic. And thanks to special channels, the patient does not have breathing problems after the operation. |
| Adhesions in the nose | Often, upon a second visit to the doctor, the patient is informed about the formation of adhesions in the nose (synechia). The reason for adhesions in the nose is that the mucous membrane of the nasal septum, due to swelling, begins to come into contact with the mucous membrane of the lateral (opposite) wall of the nose, as a result of which they stick together, and the patient faces additional surgery. | Being a barrier between mucous membranes, splints help to avoid this complication. |
| Re-displacement of the septum after surgery | High risk of displacement. | Splints, like a plaster cast, applied to a broken limb, keep the nasal septum strictly in the midline and give it additional support. Thus, splints help to avoid such complications as a secondary displaced nasal septum. |
| Nose bleed | Frequent nosebleeds. | By holding the nasal septum tightly in the midline, the splints compress the vessels and blood does not accumulate between the layers of the nasal septum mucosa. Thus, frequent complications such as nosebleeds or hematoma of the nasal septum do not occur with installed splints. |
| Tamponation | Mandatory packing. Tampons in the nose create additional discomfort. | It is possible to avoid packing of the nasal cavity. Due to this, the rehabilitation period for the patient is easier. But it should still be remembered that only the surgeon decides whether to pack the nasal cavity or not, depending on the circumstances after installing the splints. |
How to treat?
If nothing serious was found in the images, sinusitis can be overcome conservatively, that is, with the help of medications and a number of physical procedures. Treatment must begin immediately, otherwise the implant may be rejected due to the inflammatory process.
If during diagnostic procedures damage to the maxillary sinuses was discovered, doctors will have to perform surgery. It looks like this:
- Administration of an anesthetic.
- Creating access to the damaged sinus.
- Drain accumulated liquid out.
- If necessary, the artificial structure is removed.
- Antiseptic treatment is carried out.
- Stitching.
In the future, the situation is resolved with the help of medications. A course of antibiotics is indicated, preferably in the form of injections. The course must last at least 14 days. Nasal drops are also prescribed to create free breathing.
Postoperative period
Nose pain
Often in the postoperative period, patients experience pain in the nose. This is due both to the surgical procedure itself and to the presence of tampons in the nose. If the pain is severe, the doctor may prescribe opioid-containing narcotic painkillers such as tramadol, promedol. Most often, patients themselves refuse opioid analgesics. In this case, doctors use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: ketorol, diclofenac, analgin. However, a contraindication to these drugs is the deterioration of blood clotting and an increased risk of postoperative bleeding, so doctors do not recommend using these drugs frequently, especially in the first days after surgery.
To reduce pain after septoplasty, it is recommended to raise the head of the bed if the patient is undergoing rehabilitation in a hospital. At home, you need to lie with your head elevated, using 2-3 pillows. It is also recommended to apply ice to the bridge of the nose and forehead for 5-10 minutes 2-3 times a day.
In the postoperative period, you should not touch your nose, especially avoid pressing on the tip of the nose. This can cause severe pain and will cause poor tissue healing in the surgical area. Also, trauma to the nose after septoplasty often causes a shift of the nasal septum to the side.
Antibiotics
During the rehabilitation period, antibiotics are prescribed to reduce the risk of infection. Usually these are penicillin antibiotics. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the duration and dose of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor.
Vasoconstrictors and nasal douche
The next day after removing the tampons, you will need to use vasoconstrictor nasal drops, for example, xylometazoline, Nazivin and saline solutions for the nose (Aqua-Lor, Dolphin). Vasoconstrictors are prescribed to reduce swelling in the nose and widen the nasal passages. This improves nasal patency during nasal shower with saline solutions. Saline solutions wash away mucus, congealed blood, and crusts from the nose, speeding up recovery. On average, vasoconstrictor drops and nasal douche are prescribed for 5-7 days.
General recommendations for the patient during the postoperative period
The postoperative period lasts for 3 weeks after surgery. At this time, the main thing is to speed up the metabolism in the body, which will speed up recovery. To do this, the patient is prescribed to drink plenty of fluids - up to 3 liters of fluid per day, and moderate walking - 3-4 hours during the day. However, you should not engage in physical exercise or strain yourself - physical activity is contraindicated during the entire rehabilitation period.
Causes of destruction of bone tissue of the upper and lower jaw and teeth
To better understand the problem, it is necessary to have at least some understanding of the structure of bone tissue.
Human bone is represented by certain specific cells and a compact substance, which is the main component of bone tissue. The main chemical compounds that serve as the basis of bones are Ca salts and phosphoric acid salts, which are called hydroxyapatites. Their percentage in bone tissue is quite high and ranges from approximately 65% to 75% (i.e., most bone consists of the above salts). The remaining 25-35% is due to the content of a certain protein (collagen) and specific cells in the bone tissue - osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Osteoblasts are islet cells. Their main task is the synthesis of collagen in bone tissue and the creation of trabeculae - the formation of the so-called “tubular frame” from collagen and Ca salts.
Osteoclasts are oval-shaped cells and contain a large number of special organelles - lysosomes. These structures contain proteolytic enzymes that can destroy or denature collagen (break down this protein structure into amino acids). The main task of these cells is to destroy bone tissue.
The work of cellular structures occurs continuously. The processes of bone destruction and construction do not stop for a moment. Because these processes occur slowly and balance each other, it seems that bone tissue is something inanimate and not renewed. However, this is not the case. Complete bone renewal in the human body occurs on average in about ten years. This happens until a certain age - 35-45 years. Further, metabolic processes in bone tissue slow down, and recovery occurs more slowly than destruction processes. The work of osteoclasts prevails over the work of osteoblasts. Age-related bone tissue atrophy occurs. As we age, bones become more fragile and lighter. This applies in particular to the maxillofacial apparatus. Due to these processes, there is not enough bone tissue for the necessary fixation of teeth. If the pressure on them increases, tooth loss may occur.
The causes of bone tissue destruction are also:
- Continuous inflammatory processes in bone tissue;
- Systemic pathologies. These most often include diseases of the endocrine system. Pathological processes of the thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and ovarian diseases reduce the content of hydroxyapatite in the bones of the human skeleton, which in turn makes them more fragile.
- Metabolic pathologies;
- Mechanical factor. This refers to the pressure of dentures on bone tissue. X-ray data show a decrease in bone tissue in the jaw area in people who constantly wear them.
All these reasons sooner or later lead to thinning of bones and a decrease in their strength. Such processes in the upper and lower jaws often lead to the development of dental diseases, as well as their loss. To solve these problems, consultation with a specialist is necessary and, most likely, bone grafting will be required. At the moment, there are various methods of plastic surgery for damaged jaws. One of the most popular is the sinus lift.