Also watch: Dental treatment under a microscopeTreatment of dental cariesEndodontic dental treatment
Any type of dental treatment is aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition and restoring oral health. Pain after dental treatment is a common problem that every person has encountered at least once. In some cases, pain and discomfort are an inevitable consequence of the treatment procedure itself and pass quickly, while in others they indicate the development of complications and poor-quality treatment. You should never ignore pain after dental treatment, but this symptom does not always require repeated dental treatment.
Main causes
Dental treatment can be therapeutic or surgical, and pain can appear after any type of intervention. In most cases, mild or moderate pain is a physiological reaction of tissues to the manipulation, can be easily eliminated by taking anti-inflammatory or painkillers and lasts several days after a visit to the dentist.
Also, pain after dental treatment appears due to complications and violations of the technique of performing medical manipulations. Pain is most often observed after:
- dental fillings;
- root canal treatment;
- removal of a diseased tooth, cyst or granuloma.
The dentist must advise the patient about how the recovery process will occur after treatment and for what symptoms it is necessary to come for another appointment. Also, for comfortable well-being after treatment, anti-inflammatory and, in some cases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. If, despite following all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain continues to bother you, then it is best to undergo another examination by a specialist.
Pain after dental filling
Dental filling is the most frequently performed treatment procedure in any dental clinic. Due to the high prevalence of caries, each dentist installs several fillings per day. However, even such routine dental manipulation in some cases leads to complications and pain in the patient after treatment.
Slight pain when putting pressure on a filled tooth normally goes away a few days after the filling is installed. To reduce discomfort, you can take anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed by your doctor. But if the pain does not go away and intensifies over time, then this may indicate a complication after dental filling. The main causes of pain are:
- Improper grinding of the filling . Grinding is one of the final stages of tooth restoration using filling materials. This procedure is performed to make the filling smooth and consistent with the patient's bite. If the dentist incorrectly polished the filling and it remains too high, this leads to improper closure of the jaws and injury to the mucous membrane. Also, an unsuitable filling increases the sensitivity of teeth to various irritants (exposure to cold, sour or sweet foods). In such cases, you need to contact your dentist again so that he can adjust the height of the filling and the associated discomfort will no longer bother you.
- Allergy to filling materials . Materials for filling teeth are being improved every year, but the use of even the most modern filling materials cannot completely eliminate the occurrence of an allergic reaction. Symptoms of individual intolerance include swelling, pain, redness of the gums, and a strange taste in the mouth. It is important to understand that similar symptoms occur if you are allergic to a local anesthetic drug. If you suspect that you are allergic to a temporary or permanent filling, you should immediately contact a dental clinic, where the placed filling will be removed from the tooth and filled with other materials.
- Violation of filling technique . Pain after dental treatment sometimes appears if the dentist performed one of the filling stages incorrectly. Pain may occur due to overheating of dentin when preparing a carious cavity with a drill, which leads to inflammation of the pulp. Pain also appears if a special acid is applied for a long time, which improves the fixation of the filling on the tooth, or if the drying technology is disrupted. Any mistake when installing a filling can lead to increased tooth sensitivity and pain. The method for correcting complications is selected individually.
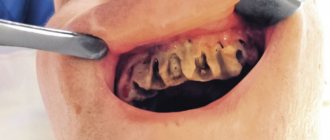
- Development of secondary caries . In some cases, an infectious process can develop under a previously installed filling. This occurs due to insufficient treatment of the carious cavity before installing the filling, as well as due to the loose fit of the filling to the natural tissues of the tooth. The danger of this process is that it is more difficult to visually notice secondary caries. Signs of pathology are darkening of the enamel and pain in the tooth affected by caries. In such cases, the dentist removes the old filling and re-treats the caries.
- Incorrect diagnosis . Pain after filling teeth occurs in cases where the dentist missed the presence of pulpitis in the patient and did not check the condition of the root canals of the tooth. Moreover, even after a high-quality filling is installed, complaints may remain of aching, intense pain of a bursting nature, which intensifies with chewing and biting. To prevent further spread of the inflammatory process, cleaning and treatment of the root canals and removal of the nerve are required. After these manipulations, the canals are filled and the tooth is restored.
To avoid complications and pain after dental filling, a thorough preliminary examination and treatment using high-quality materials by an experienced dentist is necessary. If you experience severe pain after installing a filling, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Treatment methods for headaches after dental surgery
If you have a headache for a long time, your dentist will prescribe treatment using the following medications:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - help relieve inflammation;
- Analgesics – eliminate pain;
- Antispasmodics – relieve spasms that cause pain;
If the cause of pain is inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, then the presence of toxins, which are eliminated by the use of antibiotics, should initially be eliminated, and only then the prescribed medications should be used.
Taking such medications must be done under the supervision of a physician. The use of such drugs is contraindicated for patients suffering from stomach diseases.
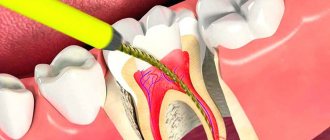
Pain after root canal treatment
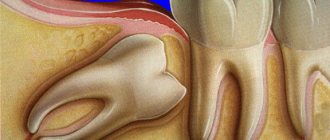
The need for root canal treatment worries the vast majority of patients in dental clinics. Many people are afraid of pain during and after the procedure. However, root canal treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating discomfort and pain in advanced stages of caries, when the nerve and pulp of the diseased tooth are involved in the pathological process.
To completely remove the affected tissue, the dentist opens, cleans, prepares and carefully fills the root canals of the tooth. This type of treatment is considered quite invasive and even after proper procedure, mild pain may bother the patient for 1-2 days. Unpleasant sensations do not affect general well-being or ability to work and are reduced by taking anti-inflammatory drugs (paracetamol, ibuprofen).
However, in some cases, severe pain indicates complications of root canal treatment:
- Exit of filling material beyond the root apex . A common complication of root canal treatment that occurs due to improper procedure technique. The patient may be bothered by aching pain that intensifies with load on the tooth. In combination with insufficient treatment of the canal, this can lead to severe periodontal inflammation, as well as intense pain after tooth treatment.
- Mechanical injury from tools . If, while cleaning the canals, the dentist does not fully comply with the accuracy and delicacy of the movements, then perforation (perforation) of the canal and damage to the periodontal tissues with the instrument are possible, followed by the development of inflammation and pain.
- Incomplete canal filling . In some cases, root canals have a complex structure and therefore are not completely filled with filling material. In unsealed areas, conditions are created for the development of an infectious process, which is accompanied by severe pain.
- Development of periodontitis . Advanced stages of caries and pulpitis can lead to inflammation of the periodontal tissues. At the initial stage of development of the disease, changes are not visible on an x-ray. Therefore, even after proper treatment of the tooth canals, the patient may complain of pain and an unpleasant feeling of fullness in the gums. As the disease progresses, granulation tissue or granuloma forms and must be removed surgically. In acute periodontitis, health worsens, the temperature rises, and general weakness is noted.
It is important to remember that during the first days after root canal treatment, slight pain (especially when putting stress on the tooth) is a physiological reaction. But if the pain is pronounced, interferes with meals, sleep and disrupts the usual daily routine, then it is necessary to be examined by a dentist and eliminate the complications that have developed as soon as possible. Treatment tactics in each case are selected individually, depending on the cause of the pain.
Pain depending on location and specificity, what does it mean?
Unpleasant sensations can be of a different nature, as well as their location.
- Pulsation at the implantation site, tingling, itching can be either normal or a sign of an allergic reaction to the material. You should continue to take antihistamines (as agreed with your doctor) and monitor the course of such manifestations;
- The unit located next to the installed artificial root is alarming. This may indicate nerve damage, gum inflammation or unsuccessful implantation, or it is possible that the crown is pressing, so the adjacent tooth hurts after the implant is installed;
- Severe pain in the ear after dental implantation in the lower jaw, which does not go away within a week, may indicate a violation of the integrity of the trigeminal nerve. The cause may be an incorrectly installed implant or injury from an instrument when preparing the bed;
- The answer to the question of why and how much gum pain after implant installation depends on the person’s health. Normally, the gums may ache for 5-7 days
. By the day the sutures are removed, usually on the 7th day, the pain goes away; - Bursting pain near the implant, the appearance of pus with light pressure, and temperature may indicate an inflammatory process. The main thing is to prevent the infection from joining. You should immediately consult a doctor.
Pain after tooth extraction
In some cases, effective treatment of advanced diseases involves the removal of a diseased tooth followed by prosthetics. After tooth extraction, pain, swelling and redness of the gums are a normal reaction of the body to tissue injury. You should be concerned if:
- the intensity of the pain does not decrease over time and is poorly removed by painkillers;
- the hole does not overgrow for a long time;
- purulent discharge appears from the wound;
- severe swelling of the mucous membrane occurs;
- body temperature rises.
The above symptoms indicate the development of an infectious process in the gum tissue. This happens if the tooth extraction technique is not followed or if the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations for oral care.
What does pain depend on during rehabilitation, on what days what sensations should be felt?
Pain after implantation begins when the anesthetic effect of the anesthetic drug ends. After 1.5-2 hours
.
Some tissue numbness may also be present. After 5-7 hours
, if normal sensitivity does not appear, you should consult a doctor, because There is a risk of damage to the facial nerve. Severe pain after dental implantation in the lower jaw can also be caused by trauma to the trigeminal nerve, because it is in close proximity to the roots.
The severity and degree of pain depends on:
- depending on the number of implants installed: one or several;
- depending on the type of operation: for implantation, the gum tissue was cut, followed by sutures - patchwork method (in rare cases) or a puncture was made (transgingival method);
- on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, his pain threshold;
- from additional surgical interventions: sinus lifting, bone tissue augmentation, etc.
How to cope with pain after dental treatment?
To feel comfortable after dental treatment, you must first take proper care of your oral cavity. The dentist must tell the patient in detail exactly how to carry out daily hygienic care of teeth and gums. After installing a filling or cleaning the canals, it is important not to put heavy stress on the treated tooth for some time. The following methods are also effective:
- Cold compress . Exposure to cold is good for eliminating swelling and dulling pain after invasive dental procedures. On the first day after treatment, you can apply cold compresses to the cheek in the area of pain. In order not to overcool the tissues, it is important to take a short break every 10-15 minutes.
- Baths with antiseptics or medicinal herbs . In some cases, it is recommended to take baths with antiseptic solutions several times a day to prevent infection and relieve pain.
- Taking medications . To improve your well-being in the first few days after dental treatment, you can take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that quickly and effectively relieve pain, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms. A safe remedy must be recommended by a doctor. Antibiotics after dental treatment are also prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain after tooth treatment will gradually decrease and completely disappear after a few days.
When do you need to see a doctor urgently?
Acute, throbbing pain after dental treatment, deterioration in general health and an increase in body temperature are a signal for immediate medical attention. The appearance of purulent discharge, severe swelling of the gum mucosa, or various sensitivity disorders in the oral cavity require a thorough examination by a dentist. You should also consult with a specialist if mild, aching pain bothers you for a long time after treatment or occurs when exposed to any provoking factor.