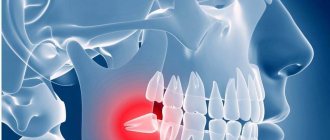
After the end of exposure to anesthetic substances, the pain syndrome returns to the patient who has survived tooth extraction. Pain can be a natural reaction of tissues to tooth extraction surgery, or a symptom of complications. To avoid a negative scenario, you should carefully prepare for the operation. Even successful treatment leaves the patient with many questions.
Preparing for tooth extraction
To avoid complications after dental procedures, simple preparation for tooth extraction is recommended.
- Do not delay going to the dentist: an inflammatory process quickly develops in the gum tissue, which stimulates increased blood supply to the sore spot, which is undesirable for surgery.
- Tooth extraction is not recommended for women during their menstrual period. On critical days, blood clotting is reduced, which leads to additional blood loss.
- It is better to contact the surgeon in the first half of the day, so that if unforeseen circumstances arise, you do not have to look for 24-hour dentistry.
- If an adult patient is going to the dentist, and the manipulation does not involve general anesthesia, then you need to eat first. The operation implies a mandatory reduction in the level of glucose in the body, which is already low in a hungry person. Lack of glucose causes a decrease in the rate of blood clotting, and after eating, the reverse process occurs.
- If general anesthesia is likely, contact your doctor in advance for an examination and consultation with an anesthesiologist. During general anesthesia, you cannot eat too much; the last meal should be taken no later than four hours before the operation. If this rule is not followed, the patient may vomit during anesthesia, and the vomit will enter the respiratory system, which will greatly complicate the work of doctors.
- Be sure to tell your dentist if you are allergic to certain medications.
- If you have heart disease, tell your doctor; this point is especially important if you are taking blood thinners. It is better to discuss this issue in advance with a cardiologist; sometimes taking medications that reduce blood clotting is temporarily discontinued.
The rules are simple, but this does not mean that you can ignore them. Tooth extraction is also an operation that sometimes leads to serious complications, especially if the patient and the surgeon are careless.
Flux (periostitis)
Description
An inflammatory process of bone tissue, which is accompanied by pain, elevated body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, and swelling of the oral mucosa. The seals have purulent contents. The cause is an infection of the oral cavity resulting from untreated caries.
Treatment
A visit to the doctor is required to treat the lump. The dentist opens the tooth, places special medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If treatment does not bring positive results, the tooth is removed.
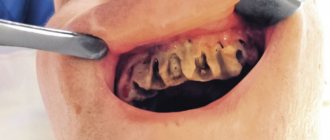
There's something white in the hole
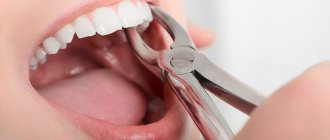
During tooth extraction, little depends on the patient. The doctor amputates the tooth and places a tampon in the wound; the patient has to hold it for at least 15 minutes. If the bleeding stops after this, the person is released. The dentist warns that pain for four hours after this is normal. From the hole left by the tooth, white ichor with streaks of blood comes out. This process is especially intense when a wisdom tooth is removed; discharge is sometimes observed within 24 hours.
It is normal if a bloody clot remains in the socket. It does not need to be removed; the clot performs important functions:
- prevents bleeding;
- protects the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria that live in the oral cavity;
- forms the basis for new tissue to replace the tooth.
Bleeding may last longer if the operation is not performed carefully or the patient takes certain medications or suffers from liver disease.
If the bleeding stops, and after a couple of hours it appears again, this is a variant of the norm, indicating the cessation of the effect of the vasoconstrictor drug.
What happens if you don’t treat a lump after a tooth extraction?
There are two options here:
- the neoplasm will resolve on its own within three to five days;
- the inflammatory process will progress and the situation will worsen.
Should we hope for a favorable outcome without medical help? Of course it is possible. Moreover, this is what happens in most cases. However, the risk of refusing to receive medical advice is always large and unfounded. There is no need to expect that the lump will resolve on its own. Having received medical advice, a person avoids many troubles.
If the doctor determines that the tumor does not pose a threat to health and is a normal variant, he will simply tell you to wait. If the diagnosis shows the presence of a dental disease, it will be treated. In both cases, the patient will benefit - he will maintain the health of his smile and avoid complications dangerous to the body.
Take care of yourself and don’t let dental problems take their course. Otherwise, very soon you will need prosthetics or implantation.
The wound is bleeding
In dental practice, there is only one known case in which a patient died after the removal of three adjacent teeth. The cause of death was not blood loss at all. The patient could not think of anything better after the operation than to drink a fair amount of alcohol and go to bed. Alcoholic drinks affect the liver, which increases bleeding. Due to alcohol intoxication, the sleep was sound, blood entered the respiratory tract, and the poor man choked.
In any case of bleeding due to an extracted tooth, the patient should calm down.
You only need to seek medical help in one case, if blood flows out of the wound in a stream.
If the patient is worried about bleeding, it is enough to make a tampon from sterile material and press it with your teeth to the wound for half an hour. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe special medications to stop bleeding. Doctors do not recommend using hydrogen peroxide in such cases.
If bleeding continues for more than a day, this is a symptom of a complication. Only a dentist, upon examination, will determine the cause of these complications and prescribe further treatment.
Methods for diagnosing alveolitis
How long the alveolitis will take to heal depends on timely diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, at the first signs of illness, you should consult a dentist. Identification of pathology occurs after listening to complaints, collecting anamnesis (where there is recent tooth extraction) and examining the socket cavity.
Sometimes the doctor prescribes an x-ray examination, which helps to detect tooth fragments and other foreign fragments in the alveolus. In rare cases, when alveolitis of the tooth socket , computed tomography is prescribed for the purpose of differential diagnosis of other diseases (trauma, tumor, etc.).
Gums hurt
Often, after tooth extraction, the patient's gums hurt. Experts are confident that this is a natural reaction of the body to surgical trauma. In this case, the pain is moderate, but sometimes it indicates not only gum injury, but also inflammation. Medical statistics note that inflammation after tooth extraction occurs in 4% of operations. Gum pain as a result of inflammation becomes even more likely if not just one, but several hours of removal. How to determine whether a wound is healing? How to act in case of inflammation?
Normally, after a tooth is removed, a clot of dark blood forms in the socket, which over time acquires a white-yellow hue.
The duration of the pain depends on the level of injury and the appearance of inflammation; it usually hurts for no more than two days. The pain is much more serious if the inert tissue is severely damaged, which inevitably happens when cutting out bone using a bore. This surgical technique is used when it is necessary to remove a crown or extract a tooth in parts. In all other cases, prolonged pain indicates a medical error or problems in the body.
To relieve pain, the use of analgesics is allowed. Normally, they help a lot, but if the pill doesn’t work, this is evidence that the operation was performed incorrectly. Medical errors during tooth extraction occur frequently, especially in the following cases.
- When sawing out bone using a drill. Modern dental standards require the use of drill tips with a cooling component. But in domestic dentistry, most dentists use tips without cooling. As a result, the patient receives a burn, as a result of which superficial necrosis develops, accompanied by acute pain. If the pain does not go away after using NSAIDs, and a blood clot does not form in the socket, you will have to go to the doctor again. The doctor will clean the hole from dead tissue, after this manipulation the patient’s condition will return to normal.
- If there are sharp bones protruding from the socket. Such edges of protruding bones often injure the mucous membrane, especially if the bone is not completely covered by a clot in the socket. Most often, this problem occurs due to the fault of the surgeon who did not apply stitches to close the wound. The patient can independently determine the presence of cutting fragments by touching the tongue, as well as in case of severe pain when drinking drinks. In rare cases, bone fragments can be seen when examining the wound in the mirror.
- With mobility of parts of the bone in the wound. Sometimes the dentist does not notice significant pieces of bone that were formed when the tooth was rocked. Such pieces often cause pain and inflammation in the socket. The problem can only be corrected with a second visit to the dentist.
- Incorrect removal method. This is a common cause of complications after tooth extraction. Dentists have different experiences, so two doctors remove the same tooth in different ways. So, when removing, you can use forceps, but another doctor, to speed up the process, will divide the tooth into two halves and only then remove them.
- Excessive use of anesthetic, leading to spasm of the blood vessels of the gums. As a result of such an error, the hole after the operation does not fill with blood and a clot does not form. In an empty socket, the bone is exposed and reacts painfully to touch.
- The dentist did not apply stitches, which should be done even when removing some teeth with a single root. In the case of teeth with several roots, a suture is required in the vast majority of cases. A properly sutured wound reduces the intensity of pain and the likelihood of complications by half. With stitches, the wound heals much faster.
- The dentist did not prescribe antibiotics. These drugs are not always prescribed, but in difficult cases, inflammation and acute pain cannot be avoided without them.
Do not start taking medications without discussing with your doctor, relying on the recommendations of friends or the Internet. The pain normally lasts no longer than a couple of days and should be moderate. If the pain does not subside, bone particles are felt in the hole, the wound reacts to liquid, or an unpleasant taste appears in the mouth, you should immediately contact the dentist who performed the operation or any other similar specialist.
Indications and contraindications
If the formation is large, leads to inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, jaw deformation, or interferes with talking or chewing food, then it is removed. The operation is also prescribed before prosthetics, since even small bumps become an obstacle to the installation of implants.
The patient himself can contact the surgeon if the bone spike spoils the aesthetics of the face. In this case, it is located on the buccal side and the protruding part is visible externally. An aesthetic defect gives a person more psychological discomfort than physical discomfort.
Before the procedure, the surgeon excludes contraindications. The list of restrictions includes infections in the mouth, acute respiratory infections, diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, poor blood clotting, exacerbation of chronic diseases, mental disorders, childhood, pregnancy and a number of other contraindications.
For children, surgery is delayed until they are 18 years old. This is due to the fact that the bones are still growing and the pathology can resolve on its own.
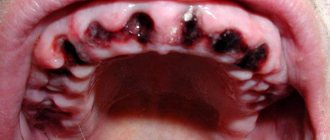
A growth has formed on the gum
After tooth extraction, there is often a complication such as the appearance of a lump on the gum. A growth in such a place indicates the onset of dangerous inflammatory complications. An infection can be caused if the clot is removed carelessly. Another source of infection is leftover food, so dentists prohibit patients from eating for several hours after surgery. During this time, a clot should form in the wound, protecting the gums from infection.
If a growth has formed on the gum, it may be an allergy to the anesthetics used or mechanical damage. Often a growth forms where the injection was given; such a new growth contains liquid inside, which in its structure is no different from a hematoma.
Such a lump will resolve in three days, unlike an infectious one, which often does not go away on its own and requires treatment.
Inside the growth, which is infectious in nature, there are purulent masses.
To determine the nature of the lump, the dentist performs palpation. By palpation, the doctor determines how hard the lump is and whether it contains liquid and pus inside. To make an accurate diagnosis, an x-ray or computed tomography may be prescribed. X-rays are not prescribed to pregnant patients. Based on the diagnostic results, the most appropriate treatment for the growth is prescribed.
- If there is no clot in the hole, it is cleared of inflamed tissues and treated with antiseptic materials. At the end of the manipulation, a hemostatic sponge is placed in the hole.
- The surgeon may decide to open the lump with a surgical instrument. After the procedure, the patient is invited to return for a follow-up visit in a few days.
- The general method of treating and preventing the growth is to take certain antibiotics.
Before coming to the dentist, the patient can rinse his mouth with furatsilin solution on his own. This drug cannot affect the size of the growth, but it will have an antimicrobial effect and reduce the intensity of inflammation. You can use dental ointments with an antibacterial effect. Folk remedies will not help get rid of the growth, but they can provide short-term relief. For this, soda and salt solutions are used. Rinsing should not be too vigorous, so as not to remove a blood clot that is beneficial for the body from the socket.
Therapeutic treatment
Treatment is carried out according to a standard scheme and it is important to start it in a timely manner:
- Cleaning the hole from food debris, plaque, and dead tissue;
- A thorough inspection of the hole, checking for the absence of roots and foreign elements;
- Washing the wound with hydrogen peroxide;
- Drying the wound;
- Putting anti-inflammatory drugs into the hole.
After treatment, the doctor gives recommendations to the patient on oral care. A few days later, the patient comes back for an examination to make sure that the treatment has given positive results and the wound is healing. It is important to rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions at home. Do not eat hard foods. For pain relief, you can use Nimesil or Ketanov.
Swollen cheek
Not all dentists tell patients what to do if their cheek is swollen after tooth extraction. Even in the doctor's office, some patients notice swelling on their cheeks. Anesthetic drugs cause not only numbness of the nerve endings, but also swelling - this is normal if the discomfort quickly passes after the end of the operation.
If a tumor appears after dental procedures, about a day or later after surgery, this is a dangerous sign. Pain, swelling and redness are caused by the presence of many blood capillaries in the oral mucosa. But the recovery process in the mouth is also much faster than in the arm or leg. If this does not happen in a timely manner, then the tumor is caused by one of the following reasons.
- Swelling of the cheek tissues that began even before the visit to the dentist. After surgery, such swelling only intensifies, although surgery in this case is not the main reason that the cheek is swollen.
- Removal of a wisdom tooth that has not yet fully erupted. The removal operation severely injures the gums, even if the surgeon is experienced. During the operation, the doctor cuts the tissue deeply, sometimes he has to further expand the wound to get to the tooth. When a wisdom tooth is removed, there is often profuse bleeding below, causing swelling of the cheek within a day.
- High blood pressure. Patients suffering from hypertension are more susceptible to edema than others.
- The patient is overweight. The thick layer of fat on the face is well supplied with blood, which contributes to swelling.
- Suppuration of the walls of the socket and blood clot also lead to swelling of nearby tissues.
If your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction, this does not always threaten your health. If this happens within 24 hours of surgery, it is likely not a problem and will go away on its own. To verify this, the patient only needs to measure his temperature. If it does not exceed 37.5°C, experts consider this a normal reaction to injury caused by surgery. In case of swelling, it is advisable to measure the temperature several times a day to ensure that there is no severe infectious inflammation. The second option is to examine your mouth with a mirror to make sure there is no worsening of the condition.
With the current level of technology development, experts recommend photographing the swelling every day to monitor its dynamics. The following are considered alarming factors:
- long-lasting bleeding;
- bad breath that was not there before;
- the appearance of pus from the wound when pressing on it;
- severe pain when swallowing.
Dentists recommend observing swelling of the cheek for the first 24 hours, but if the condition does not improve the next day, you need to contact the dentist again.
In what cases are molars removed?
Medical indications for extraction are:
- Progressive odontogenic osteomyelitis of the jaw. It is a purulent infectious-inflammatory lesion that affects not only the root of the molar, but also the tissue adjacent to it. Leads to increased body temperature, weakness, and abscess. For osteomyelitis of this type, tearing out the “causal” unit should be done in line order. Under no circumstances should surgery be postponed. Otherwise, the pathological contents of the abnormal focus will be evacuated into the jaw bone. There is a possibility of it entering the systemic circulation.
- Purulent periostitis, phlegmon, abscess, lymphadenitis, sinusitis of the maxillary sinus , if it is impossible to ensure a high-quality outflow of purulent masses from the infectious focus in the jaw.
- Lack of effect after conservative therapy for any purulent-inflammatory lesions of the oral cavity.
- Complete destruction of the crown and unsuitability of the remaining roots for prosthetics. Damaged root canals are a chronic source of odontogenic infection, so they have to be disposed of.
- The presence of teeth in the area of fracture of the alveolar process or jaw bone. Such units do not allow the correct composition of bone fragments and are regarded as conduits for infection.
- Impacted units, during the eruption of which a strong infectious-inflammatory reaction , tumor or cyst developed.
- Fangs, incisors and molars, due to which the mucous membranes of the mouth are constantly injured. They can be pulled out if standard sanding does not stabilize the situation.
- Progressive periodontitis , if loosening has reached the third or fourth stage.
- of a malignant tumor in the tissues of the periodontium or alveolar process
- Severe malocclusions , when “neighbors” do not allow the aligned units to take the correct position.
- Supernumerary teeth , causing curvature of the row, disrupting the aesthetics of the face.
Recommendations after tooth extraction
To reduce the likelihood of complications, the patient needs to follow simple rules at home.
- The gauze swab applied by the surgeon must be removed from the wound as carefully as possible so that the clot covering the bleeding wound does not accidentally come off. If you carelessly remove the tampon along with the clot, the wound may become infected, which will cause inflammation. It is recommended to remove the tampon 20 minutes after surgery, but not earlier. If the gauze has dried to the wound, you need to soak it with a chlorhexidine solution.
- Pain after tooth extraction is normal. To reduce pain, you can cool your cheek with an ice cube or a cold water bottle. A good folk remedy is to place a coin on the outside of your cheek. The cold cannot be kept for long, 10 minutes is enough. After an hour break, the cold manipulation can be repeated.
- It is not recommended to rinse your mouth immediately after surgery. You can resort to rinsing no earlier than 6 hours after tooth extraction.
- You should not eat for 2 hours after surgery. Until the wound has completely healed, food taken should be warm. You need to refrain from spicy and salty foods - this causes irritation of soft tissues.
- On the day of surgery, you should not drink alcohol, which dilates blood vessels and increases bleeding.
- You can smoke only three hours after surgery.
- Any medical procedures in the mouth can be resumed no earlier than 8 days after tooth extraction.
- After surgery, it is not advisable to touch the wound with your fingers or tongue, visit the sauna, or take a hot bath. Heavy physical activity and stressful situations are undesirable during the rehabilitation period.
- It is prohibited until the wound has healed to brush your teeth on the side of the dentition where the amputation was performed.
No dentist guarantees 100% that the patient will not have complications after tooth extraction. The result depends not only on the professionalism of the surgeon, but also on the characteristics of the patient’s body. If there is prolonged (more than a day) swelling, redness, severe pain and bleeding, you should seek medical help.
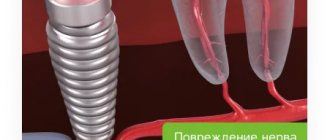
Why should jaw osteophytes be removed?
A bone growth on the gum is not dangerous until it begins to grow. Increasing in volume, the osteophyte puts pressure on the dentition and bone structures. This leads to tooth displacement, malocclusion, and jaw deformation. Large growths impede the movements of the tongue, complicate diction, and interfere with normal chewing of food. Large growths prevent prosthetics and implantation. Osteophyte of the jaw will not disappear on its own. The only effective method of treatment is surgical removal of the pathological formation.