Humans are part of living nature; they are constantly surrounded by multibillion-strong communities of bacteria and viruses that can cause serious diseases. For treatment, pharmacists offer a variety of medications that can lead to complications, so a possible allergy to Miramistin raises many questions. This drug, like Chlorhexidine, is prescribed by doctors for a number of diseases.
Characteristics of Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine bigluconate is a drug with a pronounced antimicrobial, antiseptic and disinfectant effect. It is actively used in dentistry, gynecology, otolaryngology, dermatology, and urology. It is quite possible to be poisoned by Chlorhexidine, but not with the kind sold in pharmacies. This is a 0.05% aqueous solution, transparent, without a specific smell or taste. This Chlorhexidine is capable of killing bacteria on the skin and mucous membranes, and when taken orally it causes only mild signs of poisoning. Another thing is a 20% alcohol dilution, intended for the needs of medical departments. It is diluted locally to 0.5%, 1%, 5% for antiseptic wiping of surfaces and disinfection of instruments.
If a 20% solution of Chlorhexidine is swallowed, a severe burn of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, incompatible with life, is possible.
Wound treatment with Chlorhexidine
The main purpose of the drug is precisely the antiseptic treatment of various surfaces, not only healthy skin, but also wounds of almost any origin.
The product belongs to the group of special germicidal antibiotics, and therefore Chlorhexidine is capable of not only stopping the growth of harmful microorganisms, preventing their reproduction, but also completely destroying pathogenic elements.
If we compare the product with other drugs of the antiseptic group, we can note that Chlorhexidine has no color or any odor, which means that this antiseptic is not toxic, does not leave marks on the skin, and does not cause pain to the patient when treating wounds, which is also significant advantages.
The drug does not have a negative effect on the healing process and does not lead to the formation of pronounced scars.
Chlorhexidine is completely safe , it does not cause allergic reactions or irritation of damaged tissues, and therefore is very often used to treat fresh skin lesions and disinfect them, along with regular hydrogen peroxide.
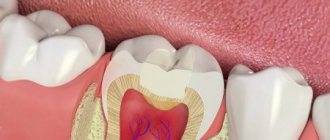
To treat fresh scratches, abrasions, various wounds, including postoperative wounds, in order to prevent the development of infection, a solution of the drug is used in a concentration of 0.05 - 0.1%. A solution of the same concentration can also be used to treat burns, as well as wounds in the oral cavity after tooth extraction.
A one-time treatment of the wound immediately after receiving it does not exclude the possibility of secondary infection, therefore, after washing, a sterile bandage should be applied, and if it is small, it can be sealed with a bactericidal plaster.
To treat wounds, it is recommended to simply pour a small amount of the drug onto the surface, wait a little, and then carefully blot the residue with a sterile napkin. Before carrying out such treatment, it is recommended to thoroughly wash the wound and the skin around it with water and laundry soap to remove any existing contaminants.
The drug in a concentration of 0.1 - 0.2% is often used for disinfection when performing various medical procedures , for example, when removing splinters, opening calluses and small abscesses, boils, when striking wounds that have dried to the surface of bandages, bandages, and plaster. A solution of this concentration is also used to treat the hands of medical personnel.
Drug interactions
- Concomitant use with iodine is not recommended.
- Chlorhexidine is incompatible with detergents containing anionic group (saponins, sodium lauryl sulfate, sulfonic acid, sodium carboxymethylcellulose) and soaps. The presence of soap can inactivate chlorhexidine, so before using the drug, any remaining soap must be thoroughly rinsed off.
- Forms a toxic compound when mixed with sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) - para-chloroaniline ( p
-NH3C6H4Cl).
Parachloroaniline is reported to be toxic (Chhabra et al., 1991; Burkhardt-Holm et al., 1999) [ incomplete references
] and can cause the formation of methemoglobin (Chhabra et al., 1991). [
incomplete reference
] - Ethanol enhances the effectiveness of chlorhexidine.
Causes of drug poisoning
Taking Chlorhexidine solution orally is strictly prohibited, but this method of use is used with alarming regularity. And it's not about suicide attempts at all. Fans of healthy lifestyle practice the method of treating various diseases in such an original and very dangerous way. It is not surprising that due to damage to the mucous membranes, pathologies that were previously mild in severity begin to progress and often recur.
Poisoning can also occur due to carelessness. This drug is often prescribed to treat the throat in the treatment of respiratory infections along with cough syrups and antibiotic suspensions. If you feel unwell, it is quite possible to mix up the bottles.
A 20% alcohol solution of Chlorhexidine can be converted into vapor. In a confined space, inhaling them can lead to severe intoxication.
What is the difference between these drugs?
Surely many people do not even realize that these drugs differ not only in the additional name of the second one, but also in the purposes for their use. What is the difference between them should be known not only to those who often encounter this product. This information may be of great help one day.
- The first medication under consideration contains a large percentage of the active substance itself , unlike the second. For 1 ml. contents account for 0.2 grams of the active component, and per 1 ml. digluconate - 5 mg . The difference is significant.
- Chlorhexidine bigluconate contains the prefix “bi” , which means that it must contain, in addition to the active substance, either glycerol or water. This means that the drug is less concentrated and can be used in its pure form to gargle and treat open wounds.
- The products differ in their scope of application . For the treatment of mucous membranes, minor wounds and in gynecology, a bigluconate solution with a concentration of 0.05% is popular. For operations, such a percentage is not enough, so an analogue is used, where the content of the active substance is significantly higher.
- The usual solution is used mainly as needed , when it is really required. In the form of bigluconate, the medication is often used for prophylactic purposes, since the concentration is not high. For recurrent chronic skin diseases, it is sometimes necessary to carry out procedures in a state of remission.
- Chlorhexidine in the form of bigluconate, unlike the usual one, is not found in the form of an alcohol solution of 0.5%. This product is intended for disinfecting hands and medical instruments.
- In the form of vaginal suppositories, there may be only a second item under consideration, as in other medications sold over the counter.
Having an antiseptic in your home medicine cabinet is extremely important in today's active life. And chlorhexidine, like no other medicine, can cope with a problem of any nature. Thus, the development of infectious diseases can be prevented in time. Then your health will always be under control.
Medicine and healthComment
Description
In Soviet times, this drug was almost unknown in our country, while in the West it has been used for a long time. It was opened in Great Britain in the early 1950s. However, data on its high effectiveness and safety did not appear immediately. At first, the drug was treated with caution, since it was unknown what side effects its use could lead to. And only after they were not found did its widespread use begin.
Chlorhexidine is a universal, broad-spectrum bactericidal agent. There are few bacteria that can resist it. In addition, the drug is active against many fungi and even against some viruses, such as the herpes virus.
From a chemical point of view, the drug belongs to chlorine-containing biguanide derivatives. In finished dosage forms, chlorhexidine is contained in the form of bigluconate. The principle of action of the drug is based on its interaction with the membranes of bacterial cells. Chlorhexidine reacts with phosphate groups on the surface of membranes, which leads to disruption of osmotic balance and subsequent destruction of the membrane, as a result of which microorganisms die. Those fungi and viruses that, like bacteria, have lipid membranes, can also be affected by the drug. Although in this respect the drug is still inferior to antifungal and antiviral agents.
The drug is active against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It is characteristic that bacteria have not yet been able to develop resistance to the drug. Chlorhexidine is weakly active only against some strains of pseudomonas, bacteria of the genus Proteus, and bacterial spores. Fungal spores are resistant to chlorhexidine. The drug weakly affects the vital activity of lactobacilli.
How to replace Chlorhexidine when treating wounds
The most famous analogue of Chlorhexidine can be called Miramistin solution, which has the same properties and actions, has the same high efficiency and an almost similar list of indications for use.
Analogues of the drug:
- Miramistin is only a functional analogue, precisely because of its similar action, and although the main substance in these drugs is different, they can completely replace each other. The use of Miramistin, unlike Chlorhexidine, is not contraindicated for people suffering from any types of dermatitis.
- Akhdez-3000 , which has a pronounced fungicidal effect, suppressing harmful microflora in literally 30 seconds. After application to the skin or surface of wounds, the product remains effective for an hour if the injury remains open, and for at least 3 hours if a sterile bandage is applied or medical gloves are worn (when treating hands).
- Citeal is another analogue containing Chlorhexidine, along with Hexamidine and Chlorocresol. The drug belongs to the group of foaming antiseptic solutions used to treat hands and skin surfaces, as well as mucous membranes and all kinds of damage.
Symptoms of Chlorhexidine poisoning
Taking a concentrated alcohol solution is much more difficult for the body to tolerate than an aqueous solution. The main signs of such poisoning:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- pain in the throat, epigastric region and abdomen, heartburn, sour belching;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- migraine-like headaches;
- tremor of the limbs, turning into convulsions;
- facial redness;
- drop in blood pressure;
- thready pulse.
When inhaling vapors, shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of air when inhaling, redness of the eyes, and dryness of the nasal mucosa occur. If first aid is not provided, the victim loses consciousness.
Contraindications
Chlorhexidine is far from a harmless medicine. Frequent use leads to drying of the mucous membranes and the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the vagina. This applies to douching and washing. The microflora, altered due to vaginal dryness, may not be able to withstand it, then even more favorable conditions for the spread of candida will be formed in the body.
If you are allergic to the components, burning and redness appear in the groin and labia.
The drug is not prescribed:
- if the patient is under 16 years of age;
- there is a high sensitivity to the components;
- during menstruation (therapeutic value is extremely low).
Douching with Chlorhexidine during pregnancy increases the risk of infection of the fetus.
First aid for Chlorhexidine poisoning
If a person swallows Chlorhexidine while gargling, it is advisable to induce vomiting. To do this, you need to drink warm water or a slightly pink dilution of potassium permanganate, and then press your fingers on the root of the tongue. In case of poisoning, it is strictly forbidden to rinse the stomach after taking a concentrated alcohol solution . When it passes, it will burn the esophagus and mouth, causing serious breathing problems.
In this case, you need to call a doctor, and before he arrives, help the victim:
- give any fast-acting laxative, for example, magnesium sulfate, as well as enterosorbent - Polyphepan, activated carbon, Enterosgel;
- drink hot, sweet tea.
The arriving doctor decides what to do next. He examines an adult or child and, if necessary, hospitalizes him.
For stomach pain that occurs after poisoning, you can give the victim any analgesic (Paracetamol, Analgin). But nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid by the gastric mucosa are strictly contraindicated.
Side effects
An important feature of the drug is its relatively low toxicity. It has almost no effect on the cells of the human body. However, this, of course, does not mean that the drug is completely harmless. It is still not recommended to use it internally. If this happens, then you should use sorbents, such as activated carbon, and perform gastric lavage. In addition, it can cause burns to mucous membranes. For this reason, chlorhexidine should not be used to treat eye infections such as conjunctivitis. If the drug gets into your eyes, rinse them thoroughly with water. You should also avoid getting the drug on the meninges, for example during open head injuries. It is prohibited to use the drug to treat ear diseases with a damaged eardrum.
Indications for use of miramistin spray
Miramistin is a medical drug that eliminates the inflammatory process . In the pharmacy you can find it in three forms - in the form of a spray, solution and ointment.
Miramistin spray, like chlorhexidine, has a wide range of applications. This remedy is used in such cases as:
- inflammation process;
- purulent abscesses;
- fungus on the nail plates;
- inflammation due to sexually transmitted diseases;
- burns and frostbite;
- bad breath;
- ear infection;
- sinusitis.
It is not recommended to use the drug for children under three years of age.
Treatment of intoxication
The toxicity of Chlorhexidine is high only at high concentrations. In this case, the victim is hospitalized for further treatment in a hospital. There is no specific antidote that can neutralize the active ingredient, so therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of poisoning.
The following clinical and pharmacological groups are used:
- enterosorbents;
- gastroprotectors;
- hepatoprotectors;
- regeneration stimulants.
For fluid loss with vomiting and diarrhea, treatment regimens include Hydrovit or Regidron. Their use allows you to replenish the reserves of essential macroelements. Severe poisoning requires intravenous administration of solutions of sodium chloride, Ringer, and glucose.
Predisposing factors
The antiseptic in question has been successfully used in medicine for more than fifty years. The development of pathological reactions to it can be explained by the fact that it is made on the basis of a complex of chemical components, therefore there are age restrictions on its use. Allergy to chlorhexidine is a fairly rare phenomenon, but in recent years such cases have become more frequent, and therefore new data have emerged about this drug, indicating its allergenic activity. In many cases, life-threatening pathological symptoms occur in patients in the postoperative period. There are risk factors that contribute to the development of inadequate immune responses to antiseptics:
- Genetic tendency to allergies.
- Presence of bronchial asthma.
- Hypersensitivity to other antiseptics and antibiotics.
- Weakened immunity due to chronic pathologies.
Indications for use of chlorhexidine
The range of applications of the universal antiseptic spray chlorhexidine is quite wide. This medicine is used:
- in open wounds or ulcers on the oral mucosa;
- for antiseptic purposes;
- if there are purulent formations in the mouth;
- with swelling of the larynx during allergic reactions;
- to get rid of an unpleasant odor after the adenoids have been removed;
- can also be used instead of soap; doctors often use this product before operations.
Features of intoxication
If you drink Chlorhexidine in the form of 0.05% aqueous dilution, then, with a high degree of probability, signs of poisoning will arise due to self-hypnosis. Exceptions are children, old people, and weakened patients. An overdose is manifested by nausea, dizziness, mild peristalsis, lack of appetite, and drowsiness.
In children
In pediatrics, Chlorhexidine is used from birth to destroy germs and viruses. It is used to treat diaper rash, abrasions, wounds, cuts, and skin rashes of allergic origin. If 1-2 tablespoons are accidentally swallowed, a slight disturbance of peristalsis is noted. But a concentrated solution of the drug that enters the child’s stomach is poisonous. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky warns parents against self-medication for any poisoning. If Chlorhexidine solution enters the stomach, the child must be immediately taken to the intensive care unit.
During pregnancy and lactation
During the period of bearing a child, Chlorhexidine is prescribed to women for rinsing the throat, treating gums and teeth after visiting the dentist, and for otitis media for instillation in the ear. It quickly destroys pathogenic microorganisms without having a negative effect on the fetus. But during pregnancy, it is dangerous for a woman to come into contact with a 20% alcohol dilution of the drug, including its vapor. Its active substance is able to penetrate biological barriers, including placental ones.
What is Chlorhexidine and its action
Chlorhexidine is a very popular drug known to many people, since its scope of application is quite wide. Its main purpose is to remove pathogenic microorganisms of various categories.
Most often, Chlorhexidine is used to treat all kinds of wounds and abrasions, as well as to disinfect the doctor’s hands before examination or surgical procedures.
Can Chlorhexidine be used to treat open wounds? If previously brilliant green and iodine were most often used to treat abrasions, today Chlorhexidine is in first place among many pharmaceutical products, gradually replacing even hydrogen peroxide. The drug has no contraindications, does not cause adverse reactions, and is used not only for the treatment of injuries, but also in the treatment of certain diseases.
Chlorhexidine for wound treatment perfectly destroys microorganisms of various groups , including gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, Trichomonas vaginalis, protozoa, as well as most viruses, including the herpes virus. The drug is powerless only against Koch's bacillus, which is the causative agent of tuberculosis.
At the same time, an important advantage of the product is the absence of a resistant reaction to it in microorganisms, that is, the bacteria being destroyed do not get used to it, do not mutate, do not adapt, but simply die. Therefore, the effectiveness of the drug remains throughout the entire treatment, regardless of how often treatments are carried out.
Diagnostics
To accurately determine whether you may be allergic to Miramistin or Chlorhexidine, you must consult a doctor for a laboratory examination. Skin testing is a common way to determine allergies. The patient is given a minimal dose of the irritant and the body’s reaction is observed.
There are a number of contraindications for the procedure:
- infectious diseases;
- presence of HIV infection;
- risk of anaphylactic reaction;
- pregnancy, lactation period;
- asthma;
- malignant neoplasms;
- mental disorders;
- allergies during exacerbation.
Disadvantages include the fact that the analysis can only be carried out during remission. This diagnostic method is used less and less, since the introduction of allergens may lead to complications, especially in children. Laboratory diagnostic methods are used more often.
The allergist prescribes the following examinations:
- determination of total immunoglobulin E;
- histamine and leukotriene tests;
- ELISA for immunoglobulins;
- radiosorbent method for immunoglobulins;
- fluorescent method.
The material for analysis is venous blood. These modern methods allow you to quickly and accurately obtain results; for each patient, the allergist selects an examination regimen individually.
Prevention and precautions
More often, poisoning is diagnosed in children, and not even the smallest ones. If the bottle is left in a visible place, then the child’s curiosity will always prevail over the parent’s prohibition from touching the medicine. Out of curiosity, a baby may swallow a product that does not have an unpleasant taste or odor. The drug should only be stored in a locked box. Poisoning also occurs when taking expired Chlorhexidine. Chemical reactions have already begun to occur in it, increasing its toxicity. It is imperative to monitor the expiration date of the drug.
Indications
Photo: YJPTO/Shutterstock.com
The scope of application of the drug is varied. This is the treatment and treatment of wounds, cuts, pimples, acne, prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases. The drug is widely used for the treatment of diseases of the oral cavity - stomatitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, upper respiratory tract - pharyngitis and tonsillitis, for the treatment of dentures. Also, the drug is often used to disinfect the surgeon’s hands, surgical instruments, the surgical field during operations and other medical procedures, disinfection of medical equipment, thermometers, etc. In addition, the drug is necessary for disinfecting the hands of workers in catering establishments, the food industry and public utilities.
The drug has a high degree of safety. It can be used in childhood and pregnancy. True, since the drug has been used relatively recently compared to most other antiseptics, caution is recommended.
Treatment of wounds in children
Children of different ages very often receive all kinds of injuries and wounds. Kids are very actively exploring a new world for them, and in the process of getting to know it, they do not do without abrasions.
Children learn to rollerblade and bicycle, play outdoor games, climb trees, swing on swings, play various sports, communicate with animals, and quite often they get various injuries that require antibacterial treatment in order to prevent the penetration of harmful microorganisms and spread infections.
Since Chlorhexidine does not have a toxic effect on the body, does not cause adverse reactions or allergic manifestations, it can also be used to treat wounds, abrasions and other skin lesions even in very young children.
Notes[ | ]
- Calibr ReFrame Drug repurposing library
- State register of medicines (unspecified)
. grls.rosminzdrav.ru. Retrieved April 21, 2022. - Zverkov A.V., Zuzova A.P.
Chlorhexidine: past, present and future of one of the main antiseptics // Clinical microbiology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. - 2013. - No. 4. - First study to link antibiotic resistance with exposure to the disinfectant chlorhexidine (undefined)
. EurekAlert!. Retrieved November 1, 2022. - WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 18th list (April 2013) (unspecified)
. - Ionov O.V., Nikitina I.V., Kirtbaya A.R., Balashova E.N., Lenyushkina A.A., Lyubasovskaya L.A., Rodchenko Yu.V., Priputnevich T.V., Zubkov V. .V., Degtyarev D.N.
“Chlorhexidine bigluconate solution and ethyl alcohol: which antiseptic is more effective in newborns?” (Russian) // Neonatology: News. Opinions. Training: Scientific journal. — Russia: All-Russian public organization for promoting the development of neonatology “Russian Society of Neonatologists,” 2022. — February 7 (No. 1). — P. 79-85. — ISSN 2658-7424. Archived from the original on February 27, 2020. - Alex Chin, Julie Chu, Mahen Perera, Kenrie Hui, Hui-Ling Yen, Michael Chan, Malik Peiris, Leo Poon.
“Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions” (English) // The Lancet Microbe : Medical journal[en]. - Hong Kong University: Elsevier, 2022. - April 2 (vol. 20, iss. 4). — ISSN 2666-5247. - doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3. Archived from the original on April 17, 2022. - Lai, P; Coulson, C; Pothier, D. D; Rutka, J (2011). “Chlorhexidine ototoxicity in ear surgery, part 1: Review of the literature.” Journal of Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery
.
40
(6): 437–40. PMID 22420428. - ↑ 12
Chhabra, R. S., Huff, J. E., Haseman, J. K., Elwell, M. R., & Peters, A. C. (1991). Carcinogenicity of p-chloroaniline in rats and mice. Food and chemical toxicology, 29(2), 119–124. - Zverkov A.V., Zuzova A.P.
“Chlorhexidine: past, present and future of one of the main antiseptics” (Russian) // Clinical microbiology and antimicrobial chemotherapy: Scientific and practical journal. - Smolensk: Interregional Association of Public Associations "Interregional Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy", 2013. - T. 15, No. 4. - P. 281. - ISSN 2686-9586. Archived from the original on April 18, 2022. - S. Malhotra, A. Dharmadasa, S. M. Yentis.
“One vs two applications of chlorhexidine⁄ethanol for disinfecting the skin: implications for regional anesthesia” (English) // Anaesthesia[en] : Medical journal[en]. - Association of Anesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland[en]: Wiley-Blackwell[en], 2011. - May 24 (vol. 66, iss. 7). — P. 574–578. — ISSN 1365-2044. - doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2011.06706.x. Archived from the original on April 20, 2022. - Shyh-Ren Chiang, Fang Jung, Hung-Jen Tang, Chung-Hua Chen, Chi-Chung Chen, Hsiu-Yin Chou, Yin-Ching Chuang.
“Desiccation and ethanol resistances of multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii embedded in biofilm: The favorable antiseptic efficacy of combination chlorhexidine gluconate and ethanol” (English) // Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection : Medical journal[en]. - Taiwan: Elsevier, 2022. - December (vol. 51, iss. 6). — P. 770–777. — ISSN 1684-1182. - doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2017.02.003. Archived from the original on April 20, 2020.
How to treat
The first thing an allergy sufferer should do is to refuse treatment with chlorhexidine. It must be replaced with an analogue or a drug with a similar effect.
Treatment for mild symptoms
Antihistamines are prescribed, as well as various ointments that eliminate the manifestations of an allergic reaction on the skin.
- Zyrtec;
- Suprastin;
- Loratadine;
- Claritin;
- Cetirizine and others.
- Hydrocortisone;
- Advantan;
- Flucinar and others.
IMPORTANT! Although hormonal ointments are more effective than non-hormonal ointments, they should nevertheless be used with caution. The course of treatment should not exceed more than one week.
Folk remedies
Various decoctions of herbs such as chamomile, mint, yarrow, sage and others will help cope with allergies, namely eliminate manifestations on the skin. It is enough to wash the affected areas of the body with such decoctions or use lotions from them.
You can prepare an ointment yourself that effectively relieves itching and irritation. To do this, you need to take celery root, as well as butter.
Oatmeal, which is steamed in milk, moisturizes the skin well.
How to relieve moderate symptoms?
An allergy sufferer who has a moderate severity of allergy should take an antihistamine. Both first generation, second and third generation antihistamines are suitable for this. Treatment should be symptomatic.
Be sure to consult a doctor as soon as possible for advice.
Help with complications
In very rare cases, allergies can be severe. Then the patient may experience anaphylactic shock, which is accompanied by a sharp decrease in pressure, loss of consciousness, and increased heart rate. An allergy sufferer with such signs needs urgent medical attention.
Properties used
Chlorhexidine is a drug that is not endowed with a specific taste and smell, does not leave marks on the skin, does not cause pain when it comes into contact with the surface of wounds, does not provoke the formation of scars and promotes tissue regeneration, extremely rarely, it can cause irritation and allergic reactions. These properties of the 0.05% solution, combined with a wide spectrum of action, distinguish it favorably from the most common means used for disinfection:
- iodine;
- brilliant green;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- alcohol and acid solutions,
as well as other common antiseptic agents.
What to replace
An allergy to Chlorhexidine requires complete exclusion of its use, as well as all drugs containing this substance. But if there is a need to use an antiseptic, then you can give preference to such agents as Miramistin, Furacilin, Vagotil, Octenisept, Malavit, Rotokan, Dioxidin, hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, Betadine, Vitaon, boric acid, Iodine, Iodizzerin. Tantum Verde, Ingalipt, Rotocan, Lugol, Malavit, Chlorophyllipt, Teraflu Lor are suitable for treating the throat.
What ways can you relieve the itching and burning sensation of thrush?
Thrush is a fungal disease caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida. If a fungal infection affects the genital mucosa, its main symptom is terrible itching and severe burning, with symptoms most pronounced in the evening and at night. The itching with thrush is so strong that it disrupts a woman’s sleep and normal rest. Moreover, in particularly sensitive people it can cause neuroses and neurosis-like conditions.
Itching can also intensify during the day - from water, when walking, from heat, during menstruation or just before it. Severe itching significantly worsens a woman’s quality of life and significantly affects her peace of mind, so many women strive to get rid of it at any cost in order to alleviate their condition at least for a short time.
How to eliminate unpleasant sensations
You can eliminate the burning and itching of thrush in several different ways. However, it is worth remembering that none of them brings complete recovery and does not cancel a visit to the doctor to prescribe full treatment.
All local methods of eliminating itching can be considered a kind of “first aid”, but a doctor will help you get rid of thrush completely.
Here's how to relieve severe itching and burning:
- Washing with baking soda solution.
For 1 liter of warm boiled water you should take 1 tbsp. spoon of soda, stir until completely dissolved. Gently wash yourself with the resulting solution and wipe the vaginal walls with a cotton pad soaked in the solution.
- Douching with hydrogen peroxide.
Under no circumstances should you just take a ready-made pharmaceutical solution! Hydrogen peroxide is dissolved in warm boiled water at the rate of 2 teaspoons per 1 liter of water. The resulting solution is used for 10-15 minutes of douching with a slow stream.
- Washing with herbal decoctions.
Decoctions of chamomile, calendula and oak bark soothe itching and reduce inflammation of the mucous membrane. For the best effect, it is advisable to use all three ingredients in one decoction.
- Treatment with antiseptic solutions.
A solution of miramistin or chlorhexidine applied to a cotton pad should be used to treat the vaginal walls and mucous membrane of the external genitalia.
- Antifungal ointment or cream.
Clotrimazole-based cream softens the mucous membrane well and can relieve itching in just a few minutes. It is highly advisable that the cream be prescribed by a doctor who will select the active ingredient in accordance with the severity of thrush and the individual characteristics of the body.
- Tea tree oil.
Dilute 2-3 drops of tea tree oil in warm boiled water, moisten a cotton pad or swab with the solution and treat the external genitalia and vaginal walls.
All these remedies will help relieve severe itching and alleviate the condition, but it should be remembered that they do not kill the fungal spores remaining in the glandular layer of the vaginal wall, so a relapse of the disease is possible after a while. For full treatment, systemic therapy, diet and proper care will be required.
Factors to consider
There are a number of factors that increase itching and provoke a recurrence of thrush, so they must be eliminated. Here's what you should definitely do to reduce discomfort and prevent it from recurring after treatment:
- Follow a diet: do not eat fatty foods, sweets, yeast baked goods, cheeses (especially blue cheeses), do not drink alcohol and carbonated sweet drinks. All these products create favorable conditions for fungus and provoke itching.
- Wear loose underwear made from natural fabrics. Tight synthetic underwear can cause severe itching and discomfort.
- Wash frequently with warm water without scented soaps and gels. It is better to use antiseptic solutions or herbal decoctions.
- Use only cellulose-based pads, without deodorizing or scented components. It is better to avoid tampons altogether and not use them even after treatment.
- To prevent itching from returning after treatment, the normal microflora of the vagina should be restored. To do this, you can use Lactagel topically, as well as drink natural yogurt with live cultures of lactic acid bacteria every day.
To prevent itching after treatment, you should follow a diet for another 2-3 weeks after the therapeutic course.
It is also necessary to observe the hygiene standards given above for a long time after treatment. And it’s better to give up synthetic underwear forever.
Sometimes burning and discomfort after treatment indicate vaginosis - vaginal dysbiosis caused by the treatment itself and the use of antiseptics. To avoid such complications after treatment, care should be taken to restore normal vaginal microflora.
Thrush is the most common disease, affecting every third woman. Vaginal candidiasis causes a lot of inconvenience and disrupts the usual way of life. One of the popular means of relieving discomfort is the common antiseptic Chlorhexidine. It is available without a doctor's prescription and has an affordable price.
Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine
(Latin
chlorhexidinum
, English
chlorhexidine
) is a drug widely used for antiseptics and disinfection. In surgical practice, treatment of wound infections, prevention of sexually transmitted diseases, in dentistry, in the treatment of otorhinolaryngological diseases as an antimicrobial agent. Chlorhexidine bigluconate is one of the most active local antiseptics. It is well tolerated and has a rapid and strong bactericidal effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, while it has weak antifungal activity and does not have a destructive effect on viruses and spores. The drug remains on the skin of the hands and the surgical field and continues to have a bactericidal effect.
Chlorhexidine bigluconate and has a stronger bactericidal effect on gram-positive bacteria, especially sensitive strains of Staphylococcus aureus
, which are most often the causative agents of infectious skin diseases.
Chlorhexidine is less active against gram-negative pathogens. Some Pseudomonas
and
Proteus
are resistant to chlorhexidine. The use of creams that create a semi-permeable film that does not interfere with transepidermal moisture loss helps restore the natural barrier function of the skin. Chlorhexidine has a broader antiseptic effect compared to antibiotics; it forms a film on the surface of the wound, providing a long-lasting effect (Abelevich M.M.).
Chlorhexidine is mildly toxic to living cells. Maintains antimicrobial effect when impregnated into a dressing. Due to long-term persistent bacteriostatic activity, chlorhexidine prevents the proliferation of microorganisms for at least 6 hours after use of the drug. The activity of chlorhexidine is reduced in the presence of organic material such as pus or blood, so washing infected wounds and changing the dressing 2-3 times a day is recommended.
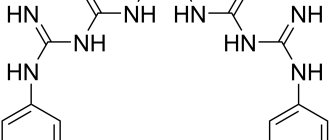
Chlorhexidine is a chemical compound
Dichlorinated biguanide derivative. The chemical name is 1,6-Di-(para-chlorophenyl-guanido)-hexane. The empirical formula of chlorhexidine is C22H30Cl2N10. Molecular weight 505.5 g/mol.
Chlorhexidine in ATC
Chlorhexidine is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of the drug. In ATC, chlorhexidine is included in a number of different groups, each of which has its own code, in particular:
- "A01 Dental preparations", "A01AB Antimicrobial preparations for local treatment of diseases of the oral cavity", code A01AB03
- “B05 Plasma replacement and perfusion solutions”, “B05C Irrigation solutions”, code B05CA02
- “D08 Antiseptics and disinfectants”, “D08AC Biguanides and amidines”:
- code "D08AC02 Chlorhexidine"
- code “D08AC52 Chlorhexidine in combination with other drugs”
According to the pharmacological index, chlorhexidine belongs to the group “Antiseptics and disinfectants”.
Microorganisms against which chlorhexidine is active or inactive
Chlorhexidine is active, in particular, against:
- gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Clostridium spp
. - gram-negative bacteria: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Gardnerella vaginalis, Treponema spp., Bacteroides fragilis, Chlamidia spp.
- prostists: Tricyomonas spp.
Bacteria of the genus Ralstonia
.
Indications for use of chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine, as a medicinal or disinfectant, is most often used in the form of chlorhexidine bigluconate. Chlorhexidine is used for:
- hand hygiene:
- surgeons
- medical personnel
- food industry workers
- catering workers
Chlorhexidine in oral hygiene products
The main hygienic carrier of chlorhexidine in dentistry is traditionally mouth rinses.
Their formula makes it possible to provide the necessary therapeutic concentrations, and the inclusion of stabilizing additives in the composition significantly increases the stability and bioavailability of the drug. Numerous clinical studies have confirmed the high effectiveness of rinses with chlorhexidine as an anti-inflammatory and anti-plaque oral hygiene product. The severity and nature (bactericidal or bacteriostatic) of the antimicrobial effect of chlorhexidine have a clear dose-dependent effect. Chlorhexidine bigluconate has the widest spectrum of antimicrobial activity in a high therapeutic concentration of at least 0.2%. The introduction of chlorhexidine into toothpastes has long been problematic. The reason is the incompatibility of anions (both inorganic and organic) with chlorhexidine, which has cationic properties. Abrasives traditionally used in the manufacture of toothpastes interact with chlorhexidine, leading to its rapid inactivation during storage. In recent years, abrasive system formulas have been proposed that allow this drug to be incorporated into toothpastes. However, to date, the clinical effectiveness of toothpastes with chlorhexidine has been extremely insufficiently studied (Solovyova A.M.).
| Chlorhexidine mouthwash |
There are studies that substantiate that patients with GERD with frequent reflux of acidic contents into the oral cavity are recommended to use toothpastes containing chlorhexidine and calcium, which increases the pH of saliva, which leads to neutralization of the acidic environment and enhancing the antibacterial effect of chlorhexidine (Polikanova E.I. .).
In addition to limitations in the choice of hygiene products, topical use of chlorhexidine in a personal oral hygiene program may be limited by the following side effects:
- superficial staining of teeth and other surfaces in the oral cavity
- increased formation of tartar
- temporary reversible change in taste sensations
- serious allergic reactions (rare); See FDA Alert 2/2/2017.
The use of chlorhexidine for rinsing the oral cavity in pregnant, breastfeeding and children
FDA Category of Risk to the Fetus is B for chlorhexidine mouthwash in pregnant women (animal studies have not shown any risk of adverse effects on the fetus; there have been no adequate studies in pregnant women).
There have been no adequate studies on whether chlorhexidine is excreted into human milk. In this regard, rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine by nursing mothers is allowed only under the special supervision of a specialist.
There have been no studies regarding the safety and effectiveness of chlorhexidine mouthwash therapy in children and adolescents. Therefore, its use by children and adolescents under 18 years of age is not recommended in this capacity.
Professional medical publications addressing the role of chlorhexidine in healthcare
- Polikanova E.I. Clinical and laboratory study of soft dental tissues in patients suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Abstract of dissertation. Ph.D., 14.00.21 – dentistry, 14.00.05 – ext. diseases. MGMSU, Moscow, 2005.
The use of chlorhexidine in the disinfection of medical products
Chlorhexidine gluconate (alcohol solution), according to MU 287-113 “Guidelines for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical products,” can be used as a disinfectant for the disinfection of medical products made of glass, metals, plastics, rubber, including endoscopes, instruments for them for viral and bacterial (except tuberculosis) infections.
The concentration of the solution is 0.5%, the exposure time is 30 minutes for viral infections and 15 minutes for bacterial infections. Alcohol solutions of chlorhexidine are used to disinfect hands and instruments. Surgical instruments and endoscopes are disinfected with a 0.5% alcohol solution by immersing in the solution for 30 minutes, with the exception of the optical part, which is disinfected by wiping with a solution of the same concentration. After this, instruments and equipment are washed twice in distilled water.
FDA Warning for Rare but Serious Allergic Reactions
The US Food and Drug Administration, in its communiqué dated February 2, 2017, warns that rare but serious allergic reactions have been reported with the use of commonly used topical antiseptics containing chlorhexidine digluconate.
Although the number of reports of serious allergic reactions to these drugs is not large, it is trending to increase. The FDA requires manufacturers of over-the-counter (OTC) antiseptic products containing chlorhexidine digluconate to add a warning about this possible risk to the labeling of these drugs. Prescription mouthwashes and oral chips used to treat gum disease that contain chlorhexidine already have a warning on the labels. Consumers if they experience symptoms of a serious allergic reaction should stop using products containing chlorhexidine digluconate and immediately call a doctor or call 911. These reactions may occur within minutes of exposure to the drug. Symptoms include: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath; swelling of the face; urticaria, which can progress quickly; severe rash; shock, which occurs due to insufficient blood flow and is a life-threatening condition.
Health care professionals, before recommending or prescribing a chlorhexidine-containing product, should always ask patients if they have ever had an allergic reaction to any antiseptic and advise them to contact their doctor immediately if they experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction with their use. If such reactions are documented or suspected, the healthcare professional should consider using alternative antiseptics such as povidone-iodine, alcohols, benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium chloride, or chloroxylenol.
general information
Medicines containing the active ingredient chlorhexidine are (have been) registered in Russia: Amident, Hexicon, Hexicon D, Hibiscrub, Kategel S, Plivasept, Plivasept P, Chlorhexidine, Chlorhexidine bigluconate, Chlorhexidine Gifrer, Chlorhexidine S, Chlorhexidine-Ferein, Chlorhexidine bigluconate, Citeal .
Chlorhexidine has contraindications, side effects and application features; consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Back to section