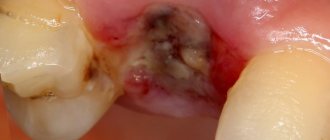
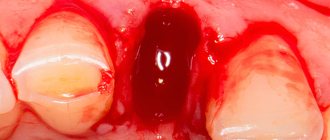
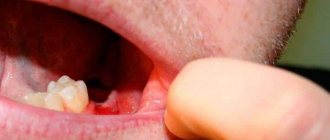
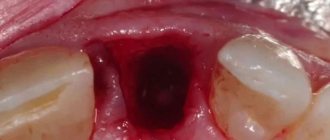
The doctor makes the diagnosis of “post-extraction alveolitis” based on a visual examination. To confirm the diagnosis, X-ray diagnostics is prescribed. An x-ray can show changes in tissue, identify tooth fragments, a cyst or granuloma, which could cause inflammation.
The final result of treatment of alveolitis should be:
- Elimination of inflammation;
- Cleaning the hole from foreign bodies;
- Complete healing of the hole;
- Exclusion of the development of complications.
Treatment at the dentist
The doctor begins treatment by washing the socket and treating it with antiseptic solutions, and then cleans the socket from the remains of the blood clot using a surgical curette. Then the wound is dried with a gauze swab and treated with an anesthetic and antibacterial agents. The wound is covered with a bandage, which is designed to protect the open surface of the wound from possible biological, chemical or mechanical irritants. To check the possibility of detecting pieces of the extracted tooth in the socket, an x-ray can first be taken.
The procedure for cleaning the hole as a whole is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Local anesthesia is performed;
- The well is washed with an antiseptic solution (hydrogen peroxide solution 3%, chlorhexidine 0.05% or furatsilin 0.02%), and food debris and necrotic masses are removed;
- If there are foreign bodies in the hole (root fragments, cysts and granulomas), they are removed using special instruments;
- After cleaning the hole, it is treated with antiseptic solutions, dried with a sterile gauze swab, and turunda with an antiseptic and an anesthetic is injected into it. With a mild degree of inflammation, a turunda may not be necessary; thorough cleansing of the hole and subsequent care for it is sufficient;
- In case of a pronounced necrotic process in the hole, rinsing and application with trypsin is carried out - this is an enzyme preparation that accelerates the breakdown of dead tissue. Trypsin has anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effects, helps clean the socket from necrotic masses and pus;
- After completing all the manipulations, the patient goes home, the doctor appoints appointment days when he needs to come for antiseptic treatment of the hole and change the turunda, if one has been installed. If necessary, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
For alveolitis, antiseptic baths (not rinsing) with solutions of chlorhexidine 0.05% or miramistin 0.01%, which can be purchased ready-made at the pharmacy, are effective. When performing baths, the solution is taken into the mouth and held for several minutes, then carefully spat out. To relieve pain and reduce the degree of inflammation, nimesulide or ibuprofen are prescribed.
To prevent the turunda from falling out of the socket, during treatment you need to eat soft, pureed food and do not chew on the sore side. If the turunda does fall out, you need to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine solution and immediately consult a doctor.
If this is not possible, you should rinse the hole yourself from food debris: to do this, bite off the sharp tip of the needle from a 5 ml syringe, bend it a little, and disinfect it with pure alcohol. A chlorhexidine solution is drawn into the syringe, the needle is inserted into the hole (not too deep) and the piston is pressed intensely to create a liquid pressure that can remove food debris.
All cases of alveolitis treatment are individual, so it may be necessary to visit the dentist up to several times.
With a favorable course of the healing process, the pain goes away, and the inflammatory process gradually subsides and disappears after a few days.
If the process, despite the procedures performed, progresses, then after antiseptics, gauze tampons soaked in propolis tincture or camvorophenol solution (10%) are inserted into the hole. A tetracycline-prednisolone cone inserted into the well has a good antibacterial effect.
Treatment of alveolitis -
If alveolitis develops in the socket after tooth extraction, treatment at the first stage should be carried out only by a dental surgeon.
This is due to the fact that the hole may be filled with necrotic decay of a blood clot; there may be inactive fragments and fragments of bone or tooth. Therefore, the doctor’s main task at this stage is to scrape it all out of the hole. It is clear that no patient will be able to do this on their own. Antiseptic rinses and antibiotics (without cleaning the socket) can only temporarily reduce the symptoms of inflammation, but do not lead to healing of the socket. But at a later stage, when the inflammation in the socket subsides, patients will be able to independently treat the socket with special epithelializing agents to speed up its healing.
Thus, the main method of treatment will be curettage of the hole, but there is also a second method - by creating a secondary blood clot in the hole of the extracted tooth. Read more about these methods...
Curettage of the tooth socket for alveolitis -
- Under anesthesia, a festering blood clot, food debris, and necrotic plaque from the walls of the socket are removed. Without removing the necrotic plaque and the disintegration of the blood clot (containing a huge amount of infection), any treatment will be useless.
- The hole is washed with antiseptics, dried, after which it is filled with an antiseptic (iodoform turunda). Usually, the turunda needs to be changed every 4-5 days, i.e. you will have to go to the doctor at least 3 times.
- The doctor will prescribe you antibiotics, antiseptic baths, and painkillers, if necessary.
Doctor's prescriptions after tooth socket curettage –
- NSAID-based analgesics (for pain),
- 0.12-0.2% Chlorhexidine solution for antiseptic rinses (2-3 times a day for 1 minute),
- Antibiotics: usually either Amoxiclav 625 mg tablets (2 times a day for 5-7 days) or Unidox-solutab 100 mg (2 times a day for 5-7 days) are prescribed. These antibiotics are better, but not cheap. Inexpensive ones are Lincomycin capsules 0.25 (2 capsules 3 times a day), but keep in mind that after this antibiotic, problems with the stomach and intestines develop more often.
Method for creating a secondary blood clot -
However, there are 2 situations in which a different treatment method can be used.
This method involves the creation of a secondary blood clot in the socket and, accordingly, if successful, the socket will heal much faster than after constantly placing iodoform turundas into it for 2-3 weeks. It is preferable to use this method only in the following two situations... Firstly, when you consulted a doctor immediately after, for example, you rinsed a clot out of the hole or it fell out on its own (i.e. when the hole is not yet filled with infection and food debris , and there is no necrotic clot disintegration or suppuration). Secondly, when the patient has a sluggish alveolitis for a long period of time, and the socket is filled with inflammatory granulations.
How this technique is carried out - if the hole is empty, then under anesthesia the bone walls of the hole are scraped out with a curettage spoon to create bleeding and the hole fills with blood (video 3). If the hole is filled with granulations, then they are carefully scraped out, i.e. do the same curettage (video 4). Then, in both cases, after the hole is filled with blood, an anti-inflammatory medicine (Alvogel) is placed deep into the hole, and several sutures are placed on the mucous membrane to bring the edges of the wound closer together. Antibiotics are immediately prescribed.
Curettage to create a secondary blood clot: video 3-4
Summary: i.e. In both the first and second methods, curettage of the hole is carried out in the same way, but in the first case, the hole heals slowly under iodoform turundas, and in the second case, a blood clot forms in the hole for the second time, and the hole heals, as it should do under normal conditions .
Procedures for continuing treatment at home
Treatment of alveolitis at home is carried out when acute symptoms have been eliminated, antiseptic turundas are no longer needed and the goal is to speed up the healing of the hole. For this use:
- Mouth rinses with infusions of chamomile, calendula, and sage. These medicinal plants have anti-inflammatory properties and accelerate healing processes. Rinsing is carried out several times during the day, always after meals.
- Applications with dental adhesive paste Solcoseryl. The drug belongs to the group of tissue regeneration stimulators: it accelerates healing, improves the supply of cells with oxygen and nutrients. The paste has a pleasant mint taste and contains the anesthetic component polidocanol 600. To properly apply the paste, you need to dry the hole with a gauze swab and fill it with Solcoseryl, lightly moisten the paste with water on top. The procedure is repeated several times a day as necessary; the paste is able to protect the socket throughout the day from mechanical and chemical influences.
- Taking vitamin preparations. You can purchase any vitamin and mineral complex at the pharmacy (Vitrum, Duovit, Complivit); Vitamins are taken to increase the body's defenses and shorten the recovery period.
Additional physiotherapy treatment (click to expand)
Physiotherapeutic treatment is an important addition to drug therapy; with the help of physiotherapy, the intensity of inflammation can be significantly reduced and healing time can be accelerated. For alveolitis, the following techniques are used:
- UV therapy - the hole is irradiated with short-wave ultraviolet light, which kills pathogenic microorganisms and reduces the level of inflammation.
- SMV therapy is a method of treatment with an electromagnetic field, based on the effect of centimeter waves on the area of inflammation. The procedure helps improve blood circulation and metabolism, due to which toxic substances are removed from tissues faster and regeneration processes are accelerated. SMV therapy also has an analgesic effect.
- UHF therapy – the body is exposed to a high-frequency electromagnetic field. For alveolitis, UHF therapy is used if the patient's regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Electrophoresis – medications are injected into inflamed tissue using electrical impulses. For post-extraction alveolitis, electrophoresis is used to reduce pain. For this purpose, solutions of novocaine, lidocaine, trimecaine are used.
- Fluctuarization is a treatment technique with pulsed currents of a sinusoidal shape with a low frequency. As a result of the procedure, blood circulation and lymph flow improves, swelling resolves, and the level of inflammation decreases.
- Laser therapy - the hole is exposed to infrared laser radiation, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces swelling and redness of soft tissues, and accelerates healing.
Complications of alveolitis
If alveolitis is not treated in a timely manner, the following complications may develop:
- Odontogenic sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary sinus caused by the spread of infection from the inflamed sockets after the removal of premolars or molars of the upper jaw;
- Phlegmon - purulent inflammation spreads to the surrounding soft tissues;
- Acute periostitis - pus accumulates in the periosteum area;
- Odontogenic osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic lesion of the jaw bone;
- Sepsis - an infection enters the bloodstream, causing it to become infected.
Alveolitis itself is not so dangerous, but its complications are life-threatening. Therefore, if you notice symptoms of alveolitis, contact your doctor immediately.
Symptoms of alveolitis
An objective diagnosis of the disease can be made on the third day after removal. Before this, slight swelling and pain are normal. If the symptoms intensify, the patient has reason to suspect that everything is going wrong, and should consult a doctor.
Signs of the disease:
- Acute pain that increases after eating.
- Location - at the site of removal with distribution along the jaw.
- Often the pain radiates to the trigeminal nerve, making it difficult to move the jaw.
- Headache, decreased performance, aches in muscles and joints. This is the result of intoxication, the source of which is an inflamed wound.
- Swelling of soft tissues.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Unpleasant putrid odor.
- Redness of the mucous membrane around the wound.
- Increase in body temperature to 38 degrees or more.
The manifestation of the disease is the complete or partial absence of a blood clot at the site of the extracted tooth. Inflammation provokes general intoxication of the body and deterioration of well-being.
The patient's role in the prevention of alveolitis
According to statistics, in most cases, the cause of the development of post-extraction alveolitis is the patient’s incorrect actions after tooth extraction, ignoring the recommendations of the attending physician. After tooth extraction it is prohibited:
- Remove the blood clot from the socket. The blood clot that forms in the hole after tooth extraction prevents microbes from entering the wound, and the healing process under it proceeds quickly and without complications. Patients can remove the clot by touching it with the tongue, with fingers, by vigorously rinsing the mouth immediately after tooth extraction, and also while eating solid foods.
- Do hard physical work, sports, take hot baths, go to the sauna. Intense loads and elevated temperatures provoke the opening of the wound, and bleeding resumes; pathogenic microorganisms can enter the wound.
- Smoking, drinking alcohol. Bad habits lead to excessive irritation of the mucous membranes, healing of the hole is much slower, and inflammation may occur.
To speed up healing and prevent the development of inflammation in the socket, you need to:
- In the first few days after tooth extraction, review your menu, excluding spicy, too salty, sour, and hot dishes. All food should be soft, pre-chopped;
- Maintain careful oral hygiene. The presence of chronic inflammation of the gums and carious teeth in the mouth can cause infection of the socket, so after tooth extraction you need to carry out antiseptic baths (they should be prescribed by a doctor);
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with clean water to remove any remaining food; this must be done very carefully so as not to remove the blood clot covering the hole;
- Brush your teeth carefully, trying not to touch the socket with the brush.
Alveolitis after tooth extraction: symptoms
As for the general symptoms, since alveolitis is not an acute inflammatory process, it usually does not cause fever or inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes. However, when it lasts for a long time, patients often feel weakness, fatigue, and the temperature may rise (but not higher than 37.5 degrees).
- Patient complaints include aching or throbbing pain in the area of the extracted tooth socket (of varying severity - from moderate to severe).
Sometimes alveolar pain can also spread to other areas of the head and neck. When alveolitis develops, pain usually occurs 2-4 days after removal, and can last from 10 to 40 days - in the absence of qualified treatment. Sometimes the pain is so severe that even very strong analgesics do not help. In addition, almost all patients report bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- When visually examining the socket, you can see an empty socket in which there is no blood clot (in this case, the alveolar bone in the depths of the socket will be exposed).
Or the socket may be completely or partially filled with food debris or necrotic disintegration of a blood clot. By the way, if the alveolar bone is exposed, it is usually extremely painful when touched, as well as when in contact with cold or hot water. In some cases, the edges of the mucous membrane converge so closely to each other above the hole that it is completely impossible to see what is happening in its depths. But when washing such a hole from a syringe with an antiseptic, the liquid will be cloudy, with a lot of food residue.
Dry socket after wisdom tooth removal –
Alveolitis after wisdom tooth removal may in addition have several more symptoms (in addition to those listed above). We are talking about difficulty opening the mouth or painful swallowing (24stoma.ru). Also, due to the fact that the socket of the 8th tooth is usually located deep in the soft tissues, suppuration from the socket often develops there (see video 2).
Alveolitis: video
In video 1 below you can see that there is no blood clot in the socket, there is exposed bone, and also in the depths of the socket it is filled with food debris. And in video 2 - alveolitis of the lower wisdom teeth, when the patient presses his finger on the gum in the area of 7-8 teeth, and copious purulent discharge comes from the holes.
The role of the doctor in excluding the possibility of alveolitis
Actions of the dental surgeon to exclude alveolitis:
- Thoroughly clean the socket so as not to leave a tooth fragment or cyst in it. After extracting a tooth, especially a damaged one, a control x-ray of the socket is often taken;
- Be careful and avoid injury. The tooth extraction was accompanied by bone injury due to the inept actions of the doctor. Usually the bone is injured during complex extraction, when tooth extraction cannot be carried out using conventional instruments. Difficult procedures include the removal of unerupted and incorrectly positioned wisdom teeth, multi-rooted teeth, and teeth with curved or destroyed roots. An inexperienced doctor may not understand the situation and damage the bone;
- Control during anesthesia. An overdose of anesthetic leads to a sharp decrease in the amount of blood released after tooth extraction and insufficient formation of a blood clot;
- Prescribing appropriate antibacterial drugs, especially if the tooth extraction was difficult or was carried out against the background of purulent inflammation.
Therefore, it is very important to seek help from competent and experienced specialists who are fully familiar with all the intricacies of the tooth extraction procedure.
Sometimes alveolitis can develop despite preventive measures taken due to certain reasons. These reasons include:
- Reduced immunity of the patient, inability of tissues to regenerate;
- Tendency to bleed, resulting in a blood clot not forming;
- An increase in the amount of the hormone estrogen in women when taking hormonal contraceptives or certain diseases, which leads to the destruction of a blood clot.
A timely visit to the dentist if alveolitis develops is the key to a quick cure. Patients of our clinic who have undergone tooth extraction surgery receive detailed recommendations on oral care; if they are strictly followed, the likelihood of developing alveolitis is excluded.