16.11.2019
Such a complication as stomatitis after tooth extraction is well known in dental practice. Moreover, the source of inflammation can appear not only on the gum, where the tooth used to be, but also on other places on the mucous surface of the oral cavity. The cause of the disease may be the unscrupulous work of the dentist. The patient himself can influence the formation of ulcerative defects. In any case, it is necessary to carry out full treatment of the disease.
The connection between surgery and stomatitis
It would seem, what could be the connection between tooth extraction surgery and stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa? The most direct one. Dentistry, which studies dental, jaw and other diseases of the oral cavity, has proven that all processes in the mouth are interconnected.
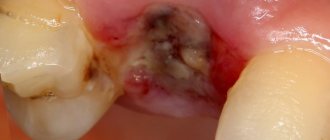
Accordingly, tooth extraction is quite capable of causing symptoms of stomatitis: painful ulcers, erosion, a specific white coating that hides bleeding wounds, and an unpleasant odor. Most often, defects appear on the gums or close to them: on the inside of the lips, palate, and floor of the mouth. The inner area of the cheek can also become inflamed if the disease occurs after the removal of a wisdom tooth. Without timely treatment, ulcers begin to spread throughout the mouth.
Of course, not every tooth extraction entails inflammation of certain areas of the oral mucosa. This requires additional conditions.
Catarrhal, ulcerative with the appearance of ulcers under the plaque, acute aphthous stomatitis
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis CHRAS Symptoms of stomatitis, causes
Oncological diseases and the appearance of stomatitis on the background of their treatment
Sore throat
Stomatitis is the name unites a whole group of diseases of the oral mucosa in both children and adults. The diagnosis of stomatitis can be made by either a general practitioner or a doctor's tooth in the examination room during initial treatment. Later, during the examination by a narrower specialist and after additional examination methods, the diagnosis is refined and sounds more accurate. The main signs of stomatitis are the same, regardless of the cause of this disease. At the clinic Denterum in Samara, an accurate diagnosis will always be made.
This is redness and swelling of the oral mucosa, white or gray patina in the mouth. If the defeat goes to the tongue, the plaque can cover it with a thick layer and then the diagnosis expands, as an additional diagnosis is made “glossitis”. The tongue is an extremely mobile organ and lesions of its mucous membrane are accompanied by severe soreness and a host of accompanying problems—it is painful to eat, talk, or just hot tea gets on the tongue, the pain immediately makes itself felt.
Types of stomatitis stomatitis herpes vesicles
Manifestations and stages of stomatitis formed the basis of clinical classification. The teeth of dentists are differentiated depending on the visible manifestations.
Catarrhal stomatitis
The causes can be very diverse, but usually catarrhal stomatitis develops against a background of numerous carious lesions and poor oral hygiene. The superficial epithelial layer of the mucous membrane suffers. There is always a large amount of soft plaque, there may be a hard plaque. On the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, edema and redness, white and gray coating, the gum between the teeth is swollen, and when the instrument is touched, blood is extracted from the interdental papilla. If catarrhal stomatitis lasts several days, an unpleasant odor from the mouth is attached.
Tooth doctors treat catarrhal stomatitis based on an obvious underlying cause. Our specialists, after anesthetizing the oral mucosa and gums, first conduct a gentle professional hygiene, removing visible plaque from the teeth and partially from the mucous membrane. More thorough cleaning of the teeth is difficult for the doctor, bleeding appears because of the presence of gingival inflammation. For the patient, the first visit can be painful. Further, mouth baths are prescribed at home for 2-3 days with antiseptic solutions. If the main cause-the virus or bacterial infection is established, a general appropriate etiologic treatment is prescribed. At the second visit the patient's gums bleed much less, they can easily anesthetize. Purification by ultrasound and AER-FLOU is carried out. Further treatment is carried out based on the specified diagnosis.
Ulcers in the mouth. Ulcerative stomatitis. Ulcers in the language of stomatitis Photo
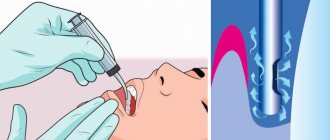
The appearance of ulcers under the plaque in the mouth suggests that catarrhal stomatitis has passed into the stage of ulcerative stomatitis. The mucous membrane of the mouth becomes inflamed to the full depth. Necrotic ulcers are extremely painful, covered with putrefactive gray bloom. Remove the plaque for antiseptic treatment is obtained with great difficulty due to the fact that it is closely welded to the walls of the ulcer, and the procedure itself causes severe suffering. The saliva becomes thick, the patient can only take liquid food. The smell from the mouth becomes sharply putrefactive, felt by the surrounding at a considerable distance. The pain that appears in the tongue of the ulcer causes extremely strong, the person can not talk, sometimes the tongue swells and does not fit in the mouth. Becomes dense and enlarges the lymph node inflammation is indicated near the ear and under the jaw, the temperature may rise. It also hurts to swallow because of the spread of inflammation from the mucous membrane of the mouth to the tonsils. Often the throat ache starts first and the patient consults the otorhinolaryngologist. The prescribed general treatment in the case of stomatitis and tonsillitis is very close, but to conduct a full-fledged hygiene of the oral cavity the ENT doctor can not-he does not have special tools, so recovery can be delayed. How to treat stomatitis ulcerative? To carry out the treatment of the affected areas, the tooth doctor first needs to conduct anesthesia mucosa. The mucous membrane is covered two to three times with an anesthetic gel, sometimes an injection of small doses of anesthetic is done. Injection system ARTI-DZHET allows you to make a very accurate calibration of the injected drug, and the needle is extremely thin.
After anesthesia, treatment with hydrogen peroxide 1% on tampons and rollers, mouth baths. In a large number of cases of acute stomatitis in the microbial landscape there is an anaerobic flora, oxygen containing preparations.
Acute aphthous stomatitis.
Most often, this disease accompanies other chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract gastritis, colitis, cholecystitis amid provoking local factors in the mouth and signs of seasonality. On the mucous membrane of the oral cavity appear rounded aphtha areas of inflammation, covered with a yellowish coating. They are surrounded by a red border. Aphids are moderately painful. Their periodic appearance in combination with diseases of the stomach and intestines gives reason to recall the unity of the innervation and trophism of the whole gastrointestinal tract. Consequently, similar aphthae can be present on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. But the oral cavity in this chain takes the first, starting place. It is in the mouth that the whole process begins. And if the dentist notices numerous carious lesions in the teeth, it should be reminded to the patient that the cause of many of his troubles in the stomach is a poorly sanitized oral cavity, where microorganisms rush along the entire length of the gastrointestinal tract, provoking his diseases.
Chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Very painful and dangerous disease, when his attacks and the appearance of aft in the mouth are replaced by remissions, but complete recovery does not occur.
If, in all the above cases, the physician achieves complete recovery with vigorous treatment of the general and local character, then in case of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis the disease returns again and again, despite carefully treated teeth, rejection of all bad habits and high level of oral hygiene. The causes of the disease are likely to be polyethiologic, multiple. The main ones are nervous overstrain (stress), hypovitaminosis in ascorbic acid and routine, carriage of some streptococcal strains in the oral cavity, more often hyaluronidase-producing. People with a second blood group are predisposed. The hereditary connection is traced. Very close to the symptoms of chronic herpetic stomatitis (see below). But with well-designed treatment, the herpes virus can be suppressed for a long time and the disease is clinically cured. In the case of chronic aphthous stomatitis, antiviral drugs are ineffective. There are different areas of rashes, with herpes marked by seasonality and the connection with common colds.
It is especially necessary to note the high probability of the appearance of severe forms of stomatitis against the background of treatment of oncological diseases. If at the same time there are traumatic factors in the mouth, a low level of hygiene, inflammation develops, up to necrotic lesions of the alveolar process.
In general, we must admit that chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis is not only a dental disease. In its treatment should be attended by doctors immunologists and gastroenterologists.
When the patient is to blame
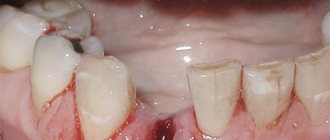
Stomatitis can occur even if the dentist has followed safety precautions and completely removed the tooth. Sometimes the patient himself is to blame. This can happen due to neglect of postoperative care for the affected tooth socket. After pulling out a tooth, you should not pick at the wound with foreign objects or rinse your mouth vigorously. Otherwise, a blood clot will fall out of the tooth socket - protection against pathogens.
Stomatitis after tooth extraction can occur due to ignoring the rules of personal hygiene: poor oral care, eating unwashed foods, eating with dirty hands.
Other circumstances
Other circumstances may also influence the development of stomatitis after tooth extraction. For example, a patient has an allergic reaction to local or general anesthesia. In this case, an allergic form of the disease manifests itself.
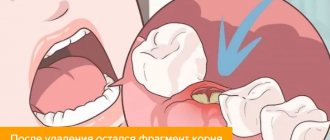
Sometimes, after a tooth is pulled out, a blood clot does not appear in the tooth socket. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to penetrate into the tissue of the unprotected hole, causing inflammation.
Kissing an infected person can also lead to stomatitis at the site of an extracted tooth. Or using dirty common items in a cafe, canteen, or home.
There is a high probability of the disease occurring if the patient has a weak immune system, and there are several wounds and they take a long time to heal. Most often this happens after the removal of a wisdom tooth. Due to its inaccessibility, the dentist sometimes has to cut the gum and part of the cheek before surgery.
Symptoms
Depending on the form of the disease and its intensity, a variety of symptoms may appear. First of all, a person should be alert to the following points: the presence of foci of inflammation, ulcers, changes in the appearance of the mucous membrane, swelling and redness, burning, acute or aching pain, etc.
Bacterial stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of small round ulcers, a viral disease manifests itself in the form of multiple blisters over the entire surface of the mucous membrane, and fungal stomatitis can additionally be accompanied by a dense white coating.
The patient may also notice an increase in bad breath, bleeding at the slightest contact with the gums, an increase in body temperature and a deterioration in general condition. With the right approach, the disease can be treated quickly enough, within a few weeks. If you do not seek help in time, there is a high risk of serious complications, which will be much more difficult to cope with.
The consequences are dangerous
Without timely treatment, seemingly harmless stomatitis can bring many negative consequences. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to secrete toxins - poison of biological origin.
Once in the blood or stomach, toxins poison the body. Intoxication leads to deterioration of health. Headaches and joint pains appear, appetite disappears, lethargy, nausea are felt, diarrhea begins, and the temperature may rise.
Other pathologies may develop: from inflammation of the throat or respiratory tract to destruction of the jaw bone or general infection of the circulatory system.
Comprehensive treatment of stomatitis will help to avoid complications. But before you begin self-therapy, you need to contact your dentist again. Or visit a therapist for adults, or a pediatrician for children. Only a doctor can determine the type of disease and prescribe appropriate medications.
Professional care and disinfection
Treatment of stomatitis that occurs after tooth extraction begins with the elimination of concomitant diseases in the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning. Then it is necessary to disinfect the surface of the mucous membrane using antiseptics:
- soda solution;
- brilliant greens;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- potassium permanganate solution;
- "Chlorhexidine";
- "Miramistina";
- "Furacilina".
This will minimize the number of pathogenic microorganisms, which will speed up recovery. Before treating stomatitis with any medication, you must obtain permission from your doctor.
What systemic diseases can manifest as aphthae?
- Reiter's syndrome
- Behçet's disease
- AIDS
- cyclic neutropenia
- PFAPA syndrome
The gastroenterologist is especially interested in the connection between recurrent ulcers and specialized systemic diseases.
Celiac disease is found in 5% , and for a long time canker sores may be the only manifestation of a reaction to gluten.
Let me remind you that the estimated prevalence of celiac disease in the general population is about 1%.
Enamel defects and aphthous stomatitis in celiac and healthy subjects: Systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies
Other important conditions that manifest as canker sores are inflammatory bowel diseases: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Extraintestinal Manifestations of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Prevalence, Presentation, and Anti-TNF Treatment
Vitamins are the key to health
At the same time as using disinfectants, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. This can be done with a diet rich in vitamins, macro and microelements. On the recommendation of a specialist, you can take a vitamin and mineral complex: “Alphabet”, Vitrum, “Multi Tabs”, “Centrum”.
Decoctions or extracts of echinacea, eleutherococcus, ginseng, and Schisandra chinensis will help. If necessary, the doctor prescribes drugs to enhance immunity: “Ribomunil”, “Imudon”, “Irs-19”, “Likopid”, “Derinat”, “Timaktide”.
If stomatitis occurs due to problems with the gastrointestinal tract, complex treatment should include drugs containing beneficial microorganisms - probiotics. They will help restore the microflora of the digestive tract. These include “Bifidumbacterin”, “Lactobacterin”, “Acilact”, “Bifilong”, “Narine”.
To speed up the healing of damaged mucosal surfaces, sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, vinylin, and propolis preparations are prescribed.