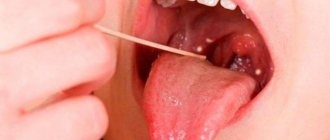
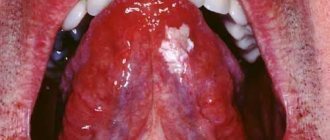
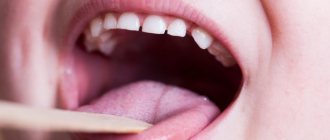
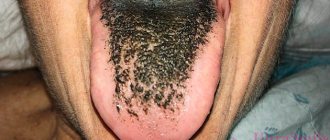
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Structure and functions
The tongue is a muscular organ without bones, covered with a mucous membrane.
Main functions:
- is directly involved in the pronunciation of sounds;
- determines the taste of what a person eats and drinks;
- is an integral element of the digestive system - it carries out the primary processing of food before it enters the esophagus.
The structure of the organ is quite simple, but very interesting. The tongue is divided into two parts: the back - the root and the front - the body or, as it is also called, the back, which has a velvety structure. The top is covered with papillae, which are responsible for taste buds.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
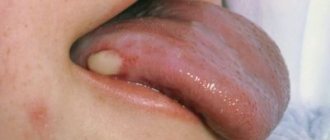
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Blue plaque in a child
Every young mother needs to make a daily morning examination of her child’s mouth a mandatory procedure. It should be borne in mind that a small whitish layer, which is easily removed by hygiene procedures or disappears on its own after eating, is the norm. But the appearance of a thick layer or a change in color should cause serious concern.
It is especially necessary to react quickly to a child’s blue tongue. Why should the blue tint of the tongue attract such increased attention? This shade serves as one of the main signals that can reflect the occurrence of a number of pathological problems that begin to progress in the important organs of the child. With such a change in color, problems with the respiratory system, heart (arrhythmias, angina pectoris, etc.), circulatory system, and kidneys can be suspected.
In such a situation, parents are advised to immediately consult a doctor. Young children are not always able to fully describe the sensations that arise, and young parents are not always able to correctly identify what the child is describing. That is why such an important signal should encourage parents to visit a medical facility. Another reason for a blue tongue in a small child may be disorders of the nervous system. With such problems, seizures or cerebrovascular accidents are usually observed simultaneously.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
What language should be normal?
A child who is completely healthy has a uniform pink tongue, without areas of inflammation. There should also be no plaque on the mucous membrane normally. Parents should be alert to the following changes in the tongue:
- Limited areas of inflammation;
- Neoplasms of various types;
- Uneven plaque, which consists of tiny particles of food and dead epithelium;
- Excessive growth of the epithelium in certain areas of the uvula.
You should pay attention to the localization of spots and areas of inflammation. This also has important diagnostic significance, since each part of the tongue is associated with the work of a specific organ.
- Liver and gallbladder – spots and plaque on the sides of the tongue;
- Intestines - changes affect the base of the uvula;
- Buds - spots located between the root and the middle of the tongue;
- Lungs - there are spots on the front of the tongue;
- The heart is connected to the tip of the organ.
Most often, spots on the tongue are caused by problems with the digestive tract. Such changes are not necessarily a sign of serious illness, but it is worth consulting your doctor about this.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Manifestations of chronic macroglossia
Often, tongue enlargement that is not cured in time leads to a severe chronic course of the disease. In this case, in an adult, the following manifestations of this pathology can be identified:
- the volume of the tongue is significantly increased, its movements are limited;
- the mouth is constantly slightly open;
- the lingual surface is rough, often with cracks or blue bloody blisters, with increased bleeding;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- permanent injury to the tongue tissue from dental crowns;
- speech is slurred, unclear, pronouncing words with difficulty.
Diseases that provoke Gunter-Miller glossitis
A smooth tongue is just an external manifestation of internal diseases, many of which are associated with an acute lack of one or another vitamin in the body. Let us list the main causes of pathology:
- Pernicious anemia: This is a malignant anemia associated with a deficiency of vitamin B12 as well as folic acid. Long-term use of medications, intestinal disorders, oncology in the gastrointestinal tract, autoimmune abnormalities, and congenital metabolic disorders can affect the absorption of these substances beneficial to the body. Moderate deficiency of these vitamins is often observed in vegetarians, malnutrition and alcoholism,
- pellagra: this is a disease that occurs due to a lack of nicotinic acid (vitamin B 3 or PP). At particular risk are people who abuse alcohol and cigarettes, as well as those who live in difficult living conditions and eat very little. The development of pellagra is promoted by acute and chronic gastrointestinal diseases, ultraviolet radiation, long-term use of antibiotics and antidepressants,
- sprue: a rare infectious disease characterized by a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. It is found in people who have visited endemically unfavorable areas of the Earth (the Caribbean, India, Asia).
Where to find?
Where exactly to find the pale tongue in Dark souls 3 depends on whether you are ready to invade other worlds or not:
In single player
In this case, there are several options for how to obtain a pale tongue:
- find on location,
- knock out of the enemy.
Undead Settlement
You need to search in the part of the location where the battle with the Demon (DS 3 mini-boss) takes place along with Siegward. In a small area near the fireplace there are two corpses hanging, which can be knocked down with a ranged attack or climbed along the roofs. The desired item will drop from one of them.
After the demon is killed, the path to the hanging corpses is clear
Temple of the Depths
In the Temple of the Depths, you can take a pale tongue in two places at once:
- At the feet of the sleeping giant is a slave near the rise to the boss Deacons of the Deep.
- At the end of the roof on a corpse if you go up to the top of the temple. This path leads to the Rosary. You can get up here on a lift from the “Chapel of Purification” bonfire.
The sought-after giant
From this roof there are 2 passages to the dome at once
From the bodies of killed enemies
In addition, with a small chance it drops from an enemy called a dark spirit. They are found in several places:
- Farron Citadel.
- High Wall of Lothric.
- Before the entrance to the boss Guardians of the Abyss (location “Path of Sacrifices” bonfire “Border of the Farron Citadel”). They initially do not pay attention to the main character, but go to kill the Husks.
This is what the Dark Spirit looks like
Online mode
In many ways, the pale tongue in DS 3 is an online mode item, for this reason, it is 100% likely to drop in the following cases:
- After successfully invading the world of other players while in the covenant of the Fingers of the Rosary.
- After defeating other players without being in the Fingers of the Rosary.
But to get the artifact you will have to kill other players
What is it needed for
In Dark Souls 3, a pale tongue will be needed for several things at once:
- Increase your level in the Fingers of the Rosary covenant.
- Receiving the Key to the hall with the lift for the battle with the dark spirit from Leonhard. To do this, you must have at least 1 pale tongue in your inventory.
- Changes in the appearance and parameters of Rosaria, the mother of rebirth in the Temple of the Deep.
For this reason, if you want to do one of the things listed above, you need to find an artifact somewhere. We'll talk about this a little below.
How to spot early symptoms of tongue cancer
20.06.18
The fear of getting cancer is quite common and is called cancerophobia, or less commonly, cancrophobia. I would say, given the inclusion of cancer in the top five most common causes of death, that this fear is quite constructive if it prompts you to avoid risk factors and be regularly examined by an oncologist. This is good form - modern and responsible.
Tongue cancer is less common than many other types of cancer, but the fear of it is great due to the expected disability and significant impairment of quality of life.
What needs to be done to catch it at an early stage, at which it is possible to do without crippling methods of treatment?
Tongue cancer is insidious - its early manifestations are masked by harmless symptoms and require an active search even with regular examination. The greatest likelihood of detecting the first symptoms occurs during a regular dentist appointment. Firstly, he knows well what a healthy tongue should look like, and secondly, he knows what to do if he suspects the onset of a disease. It is important to understand that the dentist will notice early symptoms if you ask about it at the appointment, present complaints or concerns. If dangerous symptoms are detected, the dentist is obliged to refer the patient to an oncologist.
Particular attention to the tongue and oral cavity should be given to smokers, people working with carcinogens - asbestos, perchlorethylene, petroleum products and heavy metal salts. The second place among the risk factors for developing tongue cancer is microtrauma from sharp edges of teeth, poorly fitting dentures and fillings. The so-called precancerous diseases and conditions are important - erosion of the tongue, leukoplakia, papillomas, hyperkeratic and ulcerative-erosive forms of systemic lupus erythematosus and lichen planus, Bowen's disease.
Men suffer from tongue cancer 6-7 times more often than women. The reasons for this are poorly understood, it is assumed that they are more likely to be exposed to harmful factors, but it is possible that cancer is inherited on the Y chromosome.
Most often the lateral surface of the tongue is affected, less often the root or bottom of the tongue, and least often the surface. The tip of the tongue accounts for only 3% of identified cases. To identify tongue cancer at an early stage, let’s remember its three main manifestations:
- the presence of papillary growths or whitish spots, compactions or redness on the tongue, special attention to the lateral surfaces!
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes
- soreness in the tongue without clear localization. This symptom is rare, more often it is simply a feeling of discomfort, an unusual sensation in the tongue.
At this stage, the oncologist will do a smear test or biopsy to identify the type of cancer or rule it out. By the way, for the initiated, in 95% of histologically, tongue cancer is classified as squamous, i.e. develops rapidly and metastasizes quickly.
At the second stage, it is called “developed”, the symptoms are more distinct, but the treatment prognosis is worse.
- the pain becomes more localized, radiating to the ear, temple or oral organs
- salivation increases
- there will be a bad breath
- There is numbness in parts of the tongue, difficulty pronouncing sounds, pain when swallowing
- with the papillary form, a distinct growth will appear on the tongue (see illustration), with the ulcerative form, a growing ulcer with a distinct ridge along the edges (also shown in the illustration)
- in the infiltrative-ulcerative form, deep fissure ulcers appear on the tongue; in the infiltrative form, the body of the tongue thickens
The advanced stage is quite obvious and we will not consider it within the scope of this material.
Treatment for tongue cancer is always complex, including surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Prevention consists of quitting smoking, limiting alcoholic beverages, and regular dental and oral care.
Timely diagnosis allows for a favorable survival prognosis, which some authors note at 95%. But here, the sooner the patient applies, the better the prognosis. Attention to health, accuracy and systematic reasonable self-observation can give many years of active life.
Health diagnostics: signs of diseases by color
You can make a diagnosis based on the tongue by paying attention to changes in shade. They are associated with diseases as follows:
- Crimson is a sign of poisoning with an increase in temperature, the entry of a severe viral infection into the human body, which may indicate a severe stage of pneumonia.
- A bluish or bluish tint is an indicator of defects in the heart. This color may also indicate an increased risk of heart attack in middle-aged and older people.
- Red is a symptom of heart or lung problems, blood disorders or infections. The more intense and dark the shade, the more difficult the patient’s situation. If there are alternating white and red spots on the tongue, this may indicate scarlet fever.
- Purple color – chronic blood diseases and lung problems at a late stage.
- Black is a sign of possible cholera infection.
- A whitish surface indicates anemia and severe exhaustion. If a person experiences that the lower part of the organ becomes white, this indicates pathological changes in the liver or gall bladder.
Also, changes in shade may indicate problems with energy channels, improper flow of energy, which provokes a general deterioration in well-being and individual organs. Diagnostics of the body makes it possible to discover what disorders are being discussed in a particular case. So, dark brown is a symptom of vata dosha disorders, white indicates problems with kapha, and a red tint is a sign of pitta disorders.
Carrying out diagnostics
It is best to diagnose macroglossia in utero. Currently, with ultrasound of the fetus, norms for the size of any of its organs at various stages of pregnancy have been developed. There are optimal sizes for the length and width of the tongue. Often, during intrauterine examination, protrusion of the tongue outside the mouth is noticeable.
The final conclusion is given by specialists after several ultrasound examinations over 1 – 2 months.
More often, a full diagnosis can be established only by the 30th week of pregnancy.
After the birth of a baby with this pathology, he will need a number of consultations with an ENT doctor, an infectious disease specialist, a geneticist, an endocrinologist, and an oncologist.
And only after a detailed examination (using clinical analysis and instrumental methods) is a treatment plan for the disease developed.
Features of regular care
In order to maintain good health over a long period of time, it is necessary to pay considerable attention to hygiene, including the process of cleaning the tongue. To do this, you can use the following tools:
- Classic toothbrush.
- Plastic scrapers with a spatula tip.
- Spoons in the form of attachments for an irrigator.
- Devices that combine the functions of a brush and a scraper.
Modern medicine recommends cleaning after meals, in the morning and evening, to remove plaque and food debris. Cleaning is carried out evenly and smoothly; after cleaning, the instrument must be rinsed. It is advisable to change the device every 2 to 4 months for hygienic cleanliness.
Prevention
To avoid the reappearance of small red dots on the tongue, you must carefully follow a number of recommendations:
- Eliminating bad habits.
- Scrupulous personal hygiene of the oral cavity, as well as good quality toothpaste and brushes.
- Review your diet and get rid of fast food products that are rich in hot spices.
- Carbonated drinks should not be consumed, especially if they contain a large number of dyes.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Periodic visits to the doctor.
- It is recommended to harden children, carefully choose a diet, and also exclude the intake of any allergen.