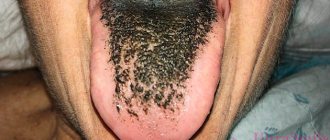
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Causes depending on the location of pain
Pediatric dentistry in St. Petersburg will understand every problem, find out the causes of the disease, and prescribe therapy. Provoking factors include:
- Organ damage in chronic and acute form. This could be inflammation or the negative effects of medications.
- Fungal and infectious diseases of internal organs, vitamin deficiency, dysbacteriosis.
- Poor hygiene, alcohol consumption, smoking.
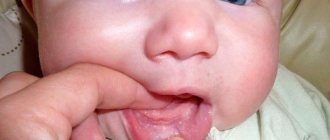
- Glossitis is inflammation of the outer layers of the mucous membrane. The disease occurs due to impaired blood circulation in the capillaries. It is provoked by a burn, cut, or injury. The disease goes away quickly, as saliva disinfects the wounds.
- Streptococci, staphylococci, viruses act pathogenically.
Main forms of pathological processes:
- Galvanic stomatitis;
- Geographical language;
The first disease develops against the background of staples, braces, and occlusion. A white coating and spots with pimples appear. If the form of the disease is severe, burning, erosion, irritation, and tooth marks on the lateral planes occur.
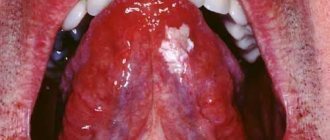
Geographic tongue is a disease of mucous tissue of a dystrophic and inflammatory nature. Desquamations appear on the surface of the organ, that is, areas with scaly peeling. In such areas the epithelium becomes red. They are surrounded by a rim of white epithelium, which peels off. The disease appears against the background of improper tissue nutrition, gastrointestinal diseases, and during the eruption of incisors, fangs, and molars.
The tip of the tongue hurts
The tip of the muscular organ is rich in taste buds and nerve plexuses. The ducts of the salivary anterior glands exit into this area. Every component can be damaged. If the tip of the tongue hurts, you can assume:
- Damage from trauma;
- Negative influence of physical factors;
- Allergies;
- Development of inflammatory processes;
- Glossalgia;
A child can be injured by hasty eating or inept use of cutlery. An accidental bite may cause bleeding. Damage is caused by salty, spicy foods, low and high temperatures. In such cases, children complain of pain and numbness. With reduced immunity, inflammation often develops. The aphthous form of stomatitis, which is caused by pathogenic agents, is often diagnosed. The disease manifests itself as deep ulcers, at the bottom of which plaque with a white tint accumulates. They heal slowly. Children's temperature rises and they feel unwell.
Viral pathogens cause herpes disease. The mucous membranes of the oral cavity are covered with colorless bubbles. After opening, ulcers form in their place and bleed. The baby may develop a fever.
The frenulum under the tongue hurts
If your child has pain in the frenulum under the tongue, you need to see a doctor to find out the cause of the problem. The main provoking factors are:
- Initial period of stomatitis;
- Incorrectly chosen mouthwash, brush or paste;
- An hysterical cry the day before, active singing;
- Microtraumas;
- Inflammation that appears as a result of an allergic reaction or enlarged lymph nodes;
- Caries, an infection of the gum tissue;
Problems arise due to a short frenulum. Insufficient ligament length can be corrected with conservative therapy or trimming. Specific gymnastics helps recovery: rolling a muscle organ into a ball, folding it into a tube. Exercises help stretch the ligament. Surgery is performed at any age, preferably in preschool. It is optimal to operate the ligament in infancy, since newborn children easily tolerate such manipulations.
Pain at the base of the tongue
Inflammation of the gums in a child is an unpleasant disease. The baby becomes capricious, whiny, his temperature may rise, and his appetite disappears. The sooner the parents show the little one to the doctor, the easier and faster the therapy will be. Children often complain of pain in the root area of the speech organ. This can happen when:
- The area of the base of the tongue is injured: wounds, injections, cuts. Children often suffer from foreign objects entering the oral cavity. If the injuries are serious, they are treated in a hospital.
- A viral or bacterial infection enters the body. The surface of the tongue becomes covered with ulcers and blisters. They interfere with swallowing food and speech. The pathology covers the tonsils, pharynx, and larynx.
- The salivary glands become clogged, which interferes with the swallowing process.
- Medicines are used uncontrollably.
- Neuralgia, allergies, anemia develop, and hormonal disorders appear.
Chronic diseases can be associated with failure to comply with hygiene rules. In any case, parents need to show the child to a doctor for medical care.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
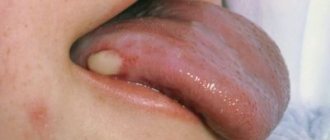
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Language functions
In order to find out why pain in this muscle organ may occur, it is necessary to understand its purpose. So, the functions of the language are as follows:
- Protective. The tongue prevents the penetration of germs and viruses through the mucous membrane.
- Sensitive. This organ is responsible for the sensitivity of tactile, thermal, pain and taste sensations.
- Plastic. The tongue helps to quickly restore cells and the upper layer of skin in case of mechanical damage.
- Suction. With the help of this organ, various substances enter the human body.
Language is a universal mechanism. It has a direct impact on the functioning of our body. That is why he needs to constantly pay attention and regularly care for him using hygiene procedures.
From the point of view of anatomical structure, the tongue is a muscle, on top of which there are many nerve endings, glands, fibers, papillae and taste buds. This organ has a direct connection with the gastrointestinal tract and affects its functioning. Our voice timbre also depends on the language.
This organ consists of two parts that do not have a clear boundary between each other. One of them is the back one. This is the root of the tongue, which on one of its sides fuses with the oral mucosa. The front part is the body. She is able to move freely in different directions. The upper surface of the tongue is called the dorsum.
This organ can be described as a litmus test, indicating the presence of diseases and malfunctions of various internal organs.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Viral stomatitis
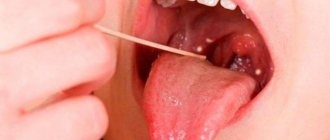
Often a child’s tongue hurts, and at the same time pimples and ulcers appear on it and on the oral mucosa. As a rule, the cause of this phenomenon is stomatitis. In children, this disease most often has a viral or aphthous form.
In the first case, the child’s tongue hurts, and yellowish ulcers can be seen on it, as well as in the oral cavity. These formations are very small in size. But despite this, they cause pain in the form of severe itching and burning. Similar local features of stomatitis appear with other signs of infection. For example, symptoms of fever, conjunctivitis, intoxication, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rash and other discomfort are likely to appear.
With stomatitis, the child’s tongue hurts and the body temperature may rise. Pediatricians often observe enlarged lymph nodes and increased salivation in their young patients. These children have an unhealthy odor from their mouth. They eat poorly or refuse food altogether and sleep restlessly. Also, with stomatitis, the child’s tongue and throat hurt.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Aphthous stomatitis
Why does my baby's tongue hurt? The cause may be aphthous stomatitis. Indeed, with this pathology, painful ulcers form on the tongue, as well as on the inside of the lips and cheeks. They are represented by a yellowish-white center, which is surrounded by an inflamed red stripe.
Pediatricians cannot pinpoint exactly what is the cause of this disease. As a rule, pathology develops due to such provoking factors as:
- allergies (drug, microbial and food);
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system;
- chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- staphylococcal infection.
The main symptoms of aphthous stomatitis are:
- burning and itching on the mucous membrane;
- temperature increase;
- child's refusal to eat;
- the formation of a cloudy film on the surface of the ulcers.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
Pediatricians do not recommend parents to independently diagnose their baby’s condition. If they have symptoms of the disease, they should consult a doctor. Only he can make the correct diagnosis.
Antiviral drugs taken orally are used to treat herpes stomatitis. Acyclovir is a fairly effective remedy, according to pediatricians. It should be given to the child for a week 4-5 times a day, 200 mg. In particularly severe cases, this drug is prescribed for intravenous drip administration.
Such treatment should be accompanied by local treatment of ulcers. For this purpose, drugs such as Zovirax and Oxolin are used. You can also lubricate the sores with sea buckthorn oil applied to a cotton swab. To reduce the level of intoxication in the body, pediatricians recommend taking immunoglobulins in the form of “Viferon” and “Anaferon”.
Quite often, children develop pimples on their tongues caused by an allergic reaction of the body.
If there is an allergy, the child's tongue becomes covered exclusively with white blisters. This is their main feature. First, you need to exclude foods that could cause allergies from your diet. You will also temporarily have to give up scented soaps, powders and other detergents of synthetic origin. Believe me, regular baby soap or laundry soap will be much more beneficial in this case. Try to wet clean your home and remove dust more often. It is recommended to treat blisters on the tongue of infants with a regular soda solution.
Dear mothers, do not forget that only a qualified specialist can accurately determine the cause of bubbles on the child’s tongue and prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Do not self-medicate at home, because the most valuable thing is at stake, namely the health of your baby! The main reasons for the formation of bubbles on a child’s tongue
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
Pediatricians point out to parents that the correct therapy for a child can be prescribed only after a comprehensive examination with the participation of a dentist, allergist and gastroenterologist. But in any case, local treatment will be needed.
What should be done when diagnosing aphthous stomatitis in a child?
To alleviate the suffering of a small patient, doctors can prescribe him the drug “Vinilin”. This remedy is also called Shostakovsky's balm. Pediatricians consider this drug to be an effective antiseptic that produces a regenerating and antimicrobial effect. The product contains a substance such as polyvinox. Its action is aimed at disinfecting the mucous membrane, excluding re-infection of damaged areas. At the same time, the drug “Vinilin” is able to eliminate pain and accelerate tissue regeneration. The balm is applied to the sores, having first applied it to a gauze napkin.
A strong antiseptic that has a remarkable anti-inflammatory effect is also a remedy such as Iodinol. It is mixed with water and used as a rinse.
For children older than one year, pediatricians may recommend Cholisal (gel). Along with the anti-inflammatory effect, this remedy also has an anesthetic effect. Apply the drug to the affected areas of the tongue, squeezing a small strip out of the tube and carefully distributing the gel on the mucous membrane.
In addition, for aphthous stomatitis, pediatricians prescribe drugs that increase local and general immunity, as well as vitamins.
What symptoms should you pay attention to?
In addition to pain, other symptoms may occur, many of which are a reason to urgently consult a doctor or call an ambulance.
1. Increase in temperature
. This symptom is characteristic of many intestinal infections, acute pancreatitis, stomach diseases, pyelonephritis and many other diseases. Remember, if the temperature does not subside for a long time even after taking antipyretics, you need to contact an ambulance service.
2. Nausea and vomiting
. Similar symptoms can accompany all of the above diseases. Do not delay calling a doctor if there is blood in the vomit or the vomiting does not stop.
3. Diarrhea
. Increased bowel movements can accompany intestinal infections, pancreatitis, gastritis and other diseases. If the stool is black or contains blood, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Less dangerous symptoms that accompany pain in the left hypochondrium are bloating, heaviness after eating food (especially fried, fatty, salty), severe rumbling in the stomach, and heartburn.
“Throat and stomach hurt,” or what do you know about adenovirus
During seasonal ARVI, cough and sore throat are an “expected” phenomenon. But what if traditional respiratory symptoms are combined with diarrhea or vomiting? Perhaps it is an adenoviral infection.
Special signs
Adenovirus, unlike many respiratory viruses, affects not only the respiratory tract, but also the mucous membrane of the small intestine. In addition, the conjunctiva of the eye comes under attack.
It leads to:
- copious mucous discharge from the nose,
- sore and sore throat,
- cough (first dry, and later with sputum),
- symptoms of conjunctivitis, such as redness of the eyes, watery eyes, a feeling of dryness and “sand” in the eyes,
- as well as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting
- and fever, the duration of which can reach 2 weeks.
Moreover, if intestinal symptoms may not develop during the entire infection, then the “characteristic” eyes are an important distinguishing feature of the adenovirus.
Where can you get infected?
Adenovirus is extremely infectious and resistant in the external environment. And the source of infection can be sick people or household items on which the virus remains active for up to 8 days.
You can become infected:
- when the patient coughs and sneezes,
- consuming food prepared without sanitary standards (thorough hand washing is required),
- and even through contact with the feces of an infected person (for example, when changing a diaper for an infected child).
You can “catch” the virus even in a swimming pool if the water is not properly disinfected. And, obviously, this viral infection is not uncommon in children's groups.
How dangerous is this?
Adenovirus infection, in most cases, does not pose a threat to health or life. And it usually ends without consequences after 7-14 days. Whereas in weakened patients, the infection can drag on and reach 6 weeks.
This same category of patients most often develop complications in the form of:
- pneumonia,
- otitis,
- bronchospasm
- severe keratoconjunctivitis.
However, Rospotrebnazor experts note that complications of adenoviral infection are always associated with the addition of pathogenic bacterial flora (staphylococci, streptococci and others).
How to identify adenovirus
The classic symptoms of adenoviral infection, as a rule, do not require additional tests. And the help of laboratory diagnostic methods is mainly resorted to at the earliest stage of the infectious process or in case of doubt about the diagnosis.
The most informative analysis in this case is PCR diagnostics of the material (throat swab or feces) for adenovirus.
The study can be ordered separately or immediately in combination with other ARVI viruses (for example, “ARVI-Screen”), which will allow you to immediately carry out a differential diagnosis. True, the PCR technique sharply loses its reliability if treatment, both local (rinses, sprays) and general, has already begun.
A blood test for IgA antibodies to adenovirus does not have these shortcomings.
They appear in the blood during the initial period of the disease, and continue to circulate for some time after recovery.
However, children, as you know, “don’t like” blood tests, so this examination format is more suitable for adults.