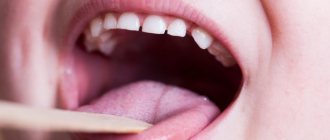
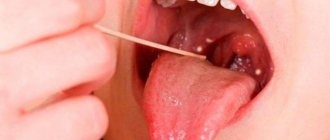
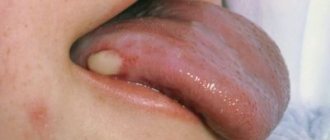
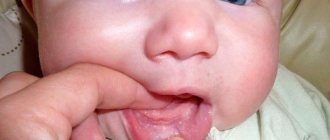
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
Why does my tongue hurt at the tip, bottom or side?
Among the causes of pain in various areas of the tongue, mechanical damage or thermal burns are most often noted. To find out exactly why the tongue hurts, in each specific case it is worth dealing with the support of an experienced doctor. As a result of examination, surveys and thorough diagnosis, it is possible to determine one of the following causes of pain:
- Accidental cuts, bruises, burns or bites while eating, getting cosmetic punctures or talking;
- Inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity of fungal or viral origin;
- Allergic reactions when taking specific foods or medications;
- Neuralgic reactions as a result of stressful situations or severe mental trauma;
- Improper functioning of the salivary glands;
- The presence of undiagnosed diseases of organs and body systems (digestive, cardiovascular, endocrine systems);
- Development of oncological diseases of the oral cavity.
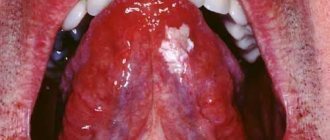
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
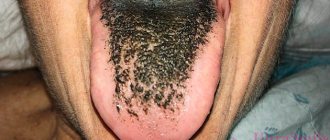
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Pain after puncture
Recently it has become fashionable to pierce the tongue, it is called piercing. We will skip moralizing on this topic and tell you briefly what this threatens.
Many patients complain that their tongue hurts for a long time after the puncture. This is considered normal, since a puncture, even the most skillful one, is a kind of injury that takes time to heal. In addition, the tongue is literally riddled with nerve endings, so the puncture site hurts especially strongly. It is impossible to say exactly how long the pain continues after the puncture; this happens individually for everyone: for some, the pain stops 2-3 days after the puncture, for others the pain lasts for 10-12 days. If your tongue is swollen and painful immediately after the piercing, this is normal. However, severe pain and swelling should gradually subside and disappear completely 4-5 days after the puncture. If the pain does not subside after a week or is acute and throbbing, you should immediately consult a doctor, as the possibility of infection cannot be ruled out.
Causes of pain after piercing:
- damage resulting from puncture of nerve endings located in the tongue;
- infection in the wound and development of the inflammatory process;
- allergy to the metal from which the jewelry is made.
In order to prevent the development of complications, you should contact only professionals. After all, not every cosmetologist knows how to properly pierce the tongue without damaging the nerve or developing inflammatory processes. If, after the piercing, the pain when speaking and swallowing does not go away, you should consult a dentist or surgeon.
It should be warned that the closer to the edges of the tongue the puncture is made, the more painful and dangerous complications it is. The easiest way to heal is a puncture made in the center of the tongue, because along the edges of the tongue there are arteries, damage to which can even lead to death. How far from the tip the puncture is made also plays a role. The closer to the root the tongue is pierced, the more it swells and hurts.
- If after piercing your tongue hurts on the side, left or right, you should definitely consult a doctor to see if the lateral arteries are damaged or if they are being pressed by a barbell.
- If the patient is suffering from pain in the tip of the tongue, but it is not swollen and there are no signs of inflammation, such pain must be endured and the puncture site must be given time to heal.
- If the tongue was pierced in the root area, you should expect that the pain at the base will be prolonged, and the healing itself will take 4-6 weeks.
Stitching pain in the tongue after piercing should alert you, as they most often indicate the development of an acute inflammatory process due to infection. Without timely treatment, an abscess may develop.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Organ structure
The tongue has 3 parts - the root, the body, and the apex. Each part is covered with epithelium and mucous membrane, the surface of which is equipped with various types of papillae (mushroom-shaped, filiform, groove-shaped, leaf-shaped).
- The entire surface of the organ is covered with filament papillae. Their structure resembles the shape of thin threads, which is why they got their name. The filament papillae do not have taste buds.
- Leaf-shaped papillae are located on the sides and back of the organ. They look like little folds. The leaf-shaped papillae have taste buds.
- The fungiform papillae are located in the center and at the top of the tongue. They are small red dots; taste buds are present in the epithelium of the fungiform papillae.
- The circumvallate papillae are located in the posterior part and in the body of the organ. Among all the others, the circumvallate papillae are the largest, but they also contain taste buds.
There are blood vessels throughout the muscle tissue of the tongue.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
When to see a doctor
If this is not the first time a burning sensation in the mouth has occurred, and the culprit is NOT spicy food, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. Based on the above reasons, doctors of various specialties can deal with this problem. First of all, these are therapists. A general practitioner, based on the history taken, will be able to exclude a number of pathologies and refer the patient to the right specialist. Among them are dentists, endocrinologists, infectious disease specialists, gastroenterologists and others.
Important! During the interview, the doctor should tell you about all concomitant diseases, lifestyle and medications you are taking. This information will help the doctor rule out a number of diseases and quickly identify the cause of the symptom.
Treatment methods for pain in the coccyx
Treatment of pain in the tailbone requires an integrated approach and consists not only of eliminating painful sensations, but also getting rid of the cause that led to them. The course of treatment is quite long.
Thus, in case of traumatic injuries, rest is required; hot baths and uncomfortable actions are prohibited. The condition will be improved by an orthopedic pillow.
Treatment of bruises will take approximately 1-1.5 months, uncomplicated fractures - about six months.
Fractures require bed rest with the installation of a fixing corset, splint, or plaster. If the spinal canal or nerve plexuses are damaged, the help of a neurologist is necessary.
Treatment of pain in the tailbone, regardless of its cause, includes:
- Including foods that prevent constipation in your diet: spinach, apples, prunes, walnuts, figs and others.
- If necessary, use orthopedic furniture and special devices to reduce pressure on the lower spine. So, if pain occurs in the tailbone when sitting, it is recommended to place a soft pillow under the buttocks.
Basically, treatment of pain in the coccyx is carried out with the help of drug therapy, physiotherapy, and surgery.
Drug therapy
When treating coccydynia, it is advisable to prescribe:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate pain and inflammation;
- muscle relaxants - specific medications to reduce the tone of skeletal muscles;
- local anesthetics in the form of creams, ointments, gels;
- microenemas and rectal suppositories to normalize intestinal function;
- antibiotics, in the presence of an infectious process;
- antidepressants to normalize the psycho-emotional state;
- immunostimulants to increase the body's protective functions and activate regenerative processes.
Chondroprotectors containing proteins necessary for articular cartilage, bone tissue and the entire musculoskeletal system are highly effective. Artracam demonstrated high efficiency. It is prescribed as part of complex therapy and as a preventive, supportive agent to strengthen the musculoskeletal system. Its mostly natural ingredients have virtually no side effects or contraindications.
Operation
The surgical treatment method is optimal for serious traumatic injuries:
- injury to a nearby organ;
- displacement, formation of fragments;
- extensive internal hemorrhage;
- improper fusion of tissues after fractures.
The need for complete or partial removal of the coccyx occurs in rare cases. The operation involves local frequency exposure (radiofrequency ablation).
Glossalgia
This term describes the occurrence of pain in the tip of the tongue for no apparent reason. Often accompanied by a feeling of dry mouth, itching, tingling, burning. Appears against the background of various problems with blood vessels and circulation, hormones, gastrointestinal tract, and during menopause. Basically, this condition develops with psychological disorders, depression and stress.
Glossalgia
Maintenance therapy consists of rinsing with herbal decoctions, performing pain-relieving applications, and rinsing the tongue with special medications prescribed by the doctor. But at the same time, it is worth calming the nervous system, since most often glossalgia is a psychological problem.
Survey
Initially, patients usually turn to a traumatologist, orthopedist or rheumatologist. Depending on the nature of the pain syndrome, the circumstances of its occurrence and the data obtained during the examination, the doctor may refer the patient for consultation or examination and treatment to an oncologist, gynecologist, urologist or proctologist. The list of diagnostic techniques for pain in the tailbone usually includes the following procedures:
- General inspection.
The specialist detects crepitus in fractures, signs of inflammation (edema, hyperthermia and hyperemia), fluctuation indicating fluid accumulation, space-occupying formations and fistula tracts. The doctor determines the exact location of the pain, specifies which structures it is associated with - the tailbone itself or the soft tissues. - Rectal examination
. It is performed in the absence of intense pain caused by suppuration in the area of the rectum and nearby tissues. During a rectal examination, tumors and infiltrates in inflammatory diseases are identified, the location and structure of the coccyx is assessed, and compacted ligaments in coccydynia are determined. - X-ray examination.
X-ray of the coccyx is a basic diagnostic technique and is recommended for all patients with pain of characteristic localization. To improve visualization, images are taken after colon cleansing. In the presence of fistulas, contrast fistulography is indicated. - Ultrasonography
. Ultrasound of the soft tissues of the coccygeal region is an inexpensive, accessible diagnostic method that allows one to assess the condition of soft tissues, identify areas with altered structure, cysts, abscess cavities and inflammatory infiltrates. - CT and MRI
. In case of uncertain radiographic data, to clarify the condition of solid structures, patients with suspected traumatic injury, neoplasm or degenerative process undergo a CT scan of the coccyx. For an in-depth study of soft tissues in inflammatory processes and tumors, MRI is performed.
The list of other methods varies significantly. The diagnostic search may include sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, irrigoscopy, proctodedecography and electrophysiological studies. If tumors are detected, a biopsy is required. According to indications, general blood and urine tests, blood biochemistry and other studies are prescribed.
CT coccyx
Mini injury
In this case, the pain is explained by an external mechanical effect on the muscle fibers of the tongue. The reasons may be banal biting with teeth (while eating, in a state of increased nervousness, in the habit of biting the tongue or when falling), unsuccessful piercing, the presence of fillings and dentures that have damaging edges, as well as burns after drinking hot drinks.
A large number of nerve cells in the tongue provoke pain after injury, which intensifies while eating, talking, and even when touching the teeth or palate.
Mini tongue injury
If the injury is very serious and accompanied by bleeding, proceed as follows:
- tilt your head forward so that blood does not enter the stomach,
- Apply a gauze or cotton swab dipped in cold water to the wound, press firmly,
- cold compresses are recommended - every half hour for 2-3 minutes during the first day,
- To ensure the wound is clean, rinse your mouth with a saline solution several times a day, starting on the second day after the cut.
While the wound is healing, avoid hot, cold, or too hard foods. Be sure to follow developments. If the situation worsens (swelling and pus appear, body temperature rises, etc.), consult a doctor immediately. Mandatory consultation with a doctor is also indicated if the wound is too deep and long, it was caused by a puncture, or a foreign object remains at the site of damage.