11/24/2017 As you know, a person’s teeth grow twice throughout their life. By the age of 6-7 years, the primary bite is fully formed; by the age of 12-13 years, “children’s teeth” are replaced by “adult teeth” - by this time the formation of a permanent bite is completed. Somewhat later, up to the age of 20, 4 more “wisdom” teeth may grow. Their name reflects the late period of growth. They are the last in the row, but very often there is not enough space for them and their growth is associated with many problems.
How do dental tissues develop in humans?
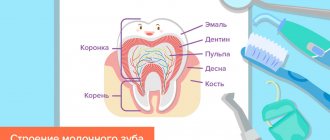
Anatomically, a human tooth consists of a crown, neck and root. The visible part of the tooth is surrounded by hard tissues - enamel, dentin and cement, which protect the soft tissue - pulp. It extends from the crown of the tooth to its roots, has a large number of vessels and nerve endings and is directly involved in the nutrition of the entire tooth. Unfortunately, all tooth tissues undergo age-related changes, so in this case we are dealing with complex aging.
Dental development begins in the prenatal period. Already in the second month, the fetus develops an oral cavity with a dental plate. The rudiments of baby teeth form on it. By the fourth month, clear cell differentiation occurs. We can find anameloblasts, which are responsible for the formation of enamel, and dentinoblasts, which form the basis for dentin. By the sixth month, the outer and inner layers of dentin with a network of tubules are formed, and the gradual formation of pulp occurs, in particular the formation of collagen fibers.
In what cases may they appear earlier/later and why?
If at least one tooth has grown by the age of one year, there is no reason to worry.
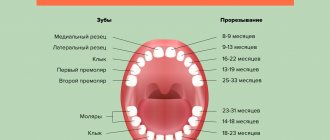
According to statistical data, in modern babies the period of eruption of the first teeth differs slightly from generally accepted normative indicators. White surfaces of the incisors are observed from 8.5 months of age.
Accordingly, the process of replacing dairy units with permanent units is also shifting. Pediatric dentists do not see any problems if by the age of one year the child has at least one tooth , and by the age of three the entire milk group has been formed.
In the complete absence of units, a thorough examination of the baby is carried out to identify provoking factors.
A discrepancy in the timing of teething may be due to a genetic factor or other reasons. Among the main provocateurs of process delays:
- previous infectious diseases;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract that occurred over a long period of time;
- problems with the metabolic functions of the body;
- lack of vitamin D (when diagnosing rickets);
- pituitary insufficiency.
It is not only the late teething that is alarming, but also their earlier appearance. Most often this occurs as a result of a disorder of the endocrine system (for example, Albright's syndrome, hyperthyroidism, hypergonadism).
A growing tumor (for example, eosinophilic granuloma) can provoke the eruption of one or a whole group of incisors before the age of six months.
Until what age do human teeth grow?
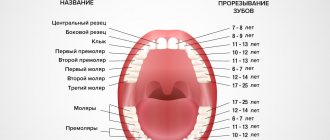
Baby teeth begin to erupt before one year of age. As a rule, at 2-2.5 years a child receives a full set of baby teeth. The molars are located immediately behind the milk teeth: between them there is a partition that is destroyed during the eruption of permanent teeth. The change of teeth in a person begins at the age of 6-7 years: the upper incisors usually fall out first. The milk bite is replaced by a permanent one at about 12-13 years of age. Molars develop more slowly than baby teeth, and the roots of wisdom teeth can continue to form up to 23 years of age and even later.
Typical problems
Usually in this age period the formation of the dental-jaw system proceeds without problems. There is not a single temporary tooth left in the mouth of a twelve-year-old child, and this period is the most favorable for treating malocclusion with braces. Since jaw growth begins to slow down by the age of 15, orthodontic treatment must be carried out before this age in order to avoid the removal of permanent teeth.
Lack of space for the eruption of the canine and permanent premolars occurs if temporary molars were removed in childhood and the corresponding correction was not carried out. The canine is the last one to erupt and it is the one that lacks space. Crowding of teeth is formed in the anterior part of the jaws and the fangs in this case can erupt closer to the lip outside the dental arch.
The formation or aggravation of crowding of teeth is possible in the case of incorrect location of the rudiment of the third molar on the lower jaw. As a result, the pressure exerted by the wisdom tooth on the second molar can lead to an anterior displacement of the entire dentition. Since there is not enough space in the row for an incorrectly positioned wisdom tooth, its complete eruption is impossible. And its retention, that is, incomplete eruption, leads to poor oral hygiene and, as a consequence, the development of carious processes both on the eighth tooth and on the adjacent second molar.
Age-related changes in dental growth and development
As soon as teeth (both milk and permanent) begin to erupt, they become vulnerable to the external environment, but at the same time they acquire a protector in the form of saliva, which not only helps destroy bacteria, but is also directly involved in saturating the teeth with various minerals. The first to experience age-related changes are enamel and dentin. Every year, due to the erosion of enamel, our teeth decrease in height. The average is about 0.035 millimeters per year, but some people experience increased tooth wear due to anatomical features and bad habits. The color and structure of the enamel change: more and more dyes accumulate in it, which leads to yellowing and loss of shine. Cracks and microdamages form on the surface of the enamel, where plaque penetrates. Over time, it mineralizes and prevents the penetration of organic substances and beneficial microelements into the enamel. It should be remembered that enamel cannot be restored, so in case of damage or illness, you should consult a doctor promptly and not wait for complications to arise. As for dentin, over the years it regenerates more and more slowly, and the quality of replacement dentin also becomes worse.
The main differences between baby teeth and permanent teeth
Unlike 28 permanent teeth, the primary dentition requires the presence of 20 units. At the same time, they have a number of characteristic features.
- Smaller in size compared to permanent teeth.
- White with a slightly blue tint (permanent units have a slightly yellowish tint).
- Less developed and slightly short roots compared to permanent teeth.
- The enamel of primary teeth is poorly formed - thinner.
- Milk units can be erased (permanent ones can too, but this is considered a pathology).
As the child grows, baby teeth fall out on their own - this is the norm. The permanent dentition units should not fall out on their own.
Age-related changes in dental pulp
Regressive and age-related changes in the dental pulp also affect dental health. Over the years, the pulp decreases, and fibrous changes are often observed in its tissues. Mineral deposition negatively affects the condition of blood vessels and capillaries. Atherosclerosis of pulp vessels occurs in many people over 50 years of age. Because of this, tooth tissues no longer receive proper nutrition, which is why they become more fragile and vulnerable. Many people are interested in how to determine a person’s age by looking at their teeth. Only a medical examination can provide more or less accurate data. It is very difficult to determine a person’s age by looking at their teeth, since even relatively young people’s teeth can be in very poor condition, and vice versa.
What are molars?
They are formed from the epithelial dental plate: molar rudiments appear only by the fifth month of the mother’s pregnancy. They are divided into two types: replacement - incisors, canines and molars, and additional - molars. The first ones repeat similar teeth in the “milk” set, the second ones have no predecessors.
The rudiments of replacement molars grow in the same alveolus as milk teeth, behind the lingual surface, and over time they are isolated by bone tissue. The rudiments of additional ones are formed only after a year, since the jaw by that time increases in size.
Age-related changes in bone tissue and gums
In addition to age-related changes in teeth, over the years a person, as a rule, decreases bone density and its height. Osteoporosis of the jaw often occurs in older people. The clinical picture is aggravated by adentia (partial or complete) and poor-quality dentures, due to which the distribution of the chewing load is disrupted. Changes can affect not only hard but also soft tissues. Age-related gum recession occurs both due to previous diseases (for example, periodontitis), and due to poor genetics, poor lifestyle and bad habits, especially smoking. At an advanced stage, this leads to loosening and loss of teeth.
Features of the development of dental tissue
The structure of each molar includes a crown - the outer part, a neck, as well as a root section, which ensures fixation in the bone tissue and nutrition of the element. The crown is covered with a protective layer - outer enamel, cement and dentin, designed to protect the pulp chamber from external influences. The sufficiency of nutrients entering the dental tissue depends on the condition of the pulp; in addition, it contains nerve endings that go to the root of the tooth, therefore, during inflammatory processes or damage affecting this layer, severe pain occurs. Age-related changes in dental tissue are an integral part of the natural aging of the body.
How can you avoid age-related changes with the help of modern dentistry?
Even though our teeth age along with the rest of our bodies over the years, this does not mean that it is impossible to maintain an attractive and healthy smile in old age. Rule number one is good daily hygiene. Rule number two is regular preventive visits to the dentist. Professional cleaning will help remove hard plaque and prevent the development of caries, and the remineralization procedure improves the condition of the enamel. Laser and physical therapy are now actively used to strengthen gums, therefore, if you have problems with periodontal disease, it is recommended not only to visit a specialized specialist, but also to monitor the health of your gums at home. Rule number three is a balanced and healthy diet, coupled with taking vitamin complexes. This will help not only the teeth and oral cavity, but also other systems of the body.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Yaroslav Ikonnikov
Useful tips on how to preserve teeth from childhood
The most important requirements are regular hygiene and preventive examinations at the dentist.
It is very important for parents to develop the right habit in their child from childhood in order to maintain it for the rest of his life and protect his teeth from many dental problems. How to save teeth from childhood
| First visit to the dentist | The first visit to the dentist with your baby is necessary at the age of one year in order to make sure that the first teeth are growing and growing correctly. It is better to carry out medical examinations every six months, and after three years - every 3-4 months. This is explained by the fact that the tissues of baby teeth are quite soft and carious processes spread extremely quickly. |
| First visit to the orthodontist | You should visit an orthodontist for the first time at the age of 3-4 years. At this time, you can make the first attempts to correct the position of the jaws and elements of the dentition. Naturally, if there are serious congenital malocclusion pathologies, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible |
| When to start brushing your child's teeth | Hygienic procedures must be carried out from the moment the very first tooth appears. Many parents believe that cleaning can be neglected while the baby is on breast milk or until his firstborns are fully grown. But this is not so: the first teeth need especially careful hygiene - the growth and formation of a permanent bite largely depends on them. At the first stage, you can use a soft silicone cap, after 1-1.5 years - a baby brush with soft bristles, as well as a special paste selected according to age |
| Should a child get dentures? | Baby teeth not only need to be treated, but also replaced with children's dentures if they were removed too early. This will allow you to maintain the position of the others in the row and thereby form the correct permanent bite. |
| How often should you use a toothbrush? | You need to clean with a brush and paste 2 times a day: before breakfast and before bed, after all meals. In between, you need to use dental floss, irrigator and mouth rinse. |
| How often should you visit the dentist? | Adults need to visit a doctor every six months. Firstly, to examine the condition of the entire oral cavity, identifying problems at an early stage. Secondly, for comprehensive hygiene, which will better clean the enamel and gums from plaque |
Partial edentia
Adentia is the congenital absence of tooth buds. Most often, the top two “twos” are missing. Moreover, there may be a lack of both milk and permanent teeth, or both.
Adentia is a congenital condition; it occurs due to a malfunction in the embryonic period during the formation of the main organs and systems.
It is very difficult to notice partial edentia of baby teeth: the teeth are small, they are all of a similar shape, and others take the place of the missing ones. Such adentia does not harm the chewing process in any way.
If permanent teeth are missing, this is already noticeable visually. In this case, malocclusion may develop, since the “threes” are pulled up to replace the missing “twos”, and the following teeth are also displaced.
Partial edentia - absence of upper incisors
Partial edentia - there are no upper incisors, but “threes” have taken their place
The exception is wisdom teeth, also known as “eights.” Their functions are not so important; in most people they remain impacted, and if they are lost, they are not replaced with prosthetics. Their absence does not affect the health and aesthetics of the smile.
What to do?
If there is a partial lack of permanent teeth, it is most often necessary to correct the bite and prepare a place for prosthetics. If you do not make dentures, but cover the empty space with neighboring teeth, then this will not be a complete solution to the problem - the dentition will be narrower than it should have been.
Is it painful to have a wisdom tooth removed?
Is wisdom tooth extraction accompanied by pain? This is one of the most common questions.
The fact is that very rarely “eights” grow healthy; usually their eruption causes pathological processes that are dangerous to the patient’s health, so their removal is required. Surgical removal of the “eight” is always accompanied by pain, the process is especially difficult due to curvature and other disorders of the third molar. The procedure must be carried out with the use of painkillers. Most often, dentists use drugs based on articaine - “Ultracaine”, “Ubistezin”. The use of local anesthetics allows you to completely eliminate pain during surgery. However, the process of administering the drug itself may be accompanied by pain. In addition, when the anesthesia wears off (after about 6 hours), intense pain occurs.
Severe pain during the removal of the third molar is inevitable in cases where the patient has not consulted a specialist for a long time, the inflammatory process has started, resulting in purulent formations. Sometimes tooth extraction is performed under general anesthesia. In other situations, surgery is painless.
The upper “eights” are much easier to remove than the lower ones. This feature is due to the fact that wisdom teeth in the lower dentition have more powerful and sinuous roots. To properly carry out the procedure for removing the third molar, the dentist sends the patient for an x-ray before the operation.