Have you already met the tooth fairy, who brings you a coin for a lost baby tooth? Sleepless nights are over, your baby pleases you with twenty temporary teeth and you are starting to think about when to expect permanent ones? Let's try to figure it out when baby teeth fall out
, what you need to remember and what to pay attention to when your child changes
baby teeth
to permanent ones.
How it all happens
First of all, a little anatomy. Baby teeth are formed in the prenatal period, but the formation of permanent teeth begins after the baby is born. Thus, when you rejoice at the first tooth that has erupted, its replacement is already waiting in the wings. The time and order of eruption of permanent teeth, as well as milk teeth, is individual for each child. But temporary teeth fall out in approximately the same order as they appeared. The permanent first molars appear first. There is no milk analogue for these teeth, because in a small child’s jaw there was simply not enough space for them. The baby grows, the gaps in the dentition increase and the first adult teeth appear in the mouth - the so-called “sixes”. After the molars have erupted, it is time to replace the baby teeth with permanent ones. Loss occurs, as a rule, in the same order as appearance.
Teething order: what to pay attention to
As long as the puppy feeds exclusively on milk, it does not need teeth.
2-3 weeks after birth, complementary foods are introduced into the diet. The period of teething begins. In total, babies should grow 28 teeth - 14 for each jaw. They appear in a certain order.
Sequence of teething in dogs
| Sequence | During what period (weeks) | Name | Quantity per jaw |
| 1 | 2-3 | incisors | 6 |
| 2 | 4 | fangs | 2 |
| 3 | 5-6 | premolars | 6 |
Sometimes there are deviations from the norm. In some breeds, the order in which the premolars and canines appear is different. In dwarf and decorative dogs, the first teeth appear a little later than in large individuals - at the age of one and a half months.
As soon as the puppies' canines erupt, they are separated from their mother to avoid injury to the nipples.
The procedure and timing of changing baby teeth to permanent ones
When does it make sense to wait for the first permanent teeth to appear? As we said above, the first molars to erupt are the teeth that are not included in the primary set. This happens around the age of six. The next ones to wait for are the front teeth, which displace the milk teeth. Tooth loss in children
It begins with the temporary root gradually resolving, making room for the permanent tooth. The baby tooth becomes loose, falls out, and very soon your child will be able to boast a real, adult set of teeth.
Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
If new teeth do not appear for a long time, this is due to one of three reasons:
- Edentia. This is the absence of a molar tooth germ. The disease is diagnosed using x-rays. Adentia is rare in children and is easily eliminated with prosthetics.
- Retention. This is a disease in which part of the tooth is either not visible from the gum tissue at all, or is only slightly visible. You need to contact a dentist who will make the correct diagnosis and, possibly, resort to surgery.
- Impact. If the crowns of the teeth are too close together to leave no room for new tooth growth, this is an indication of impaction. It is diagnosed using x-rays.
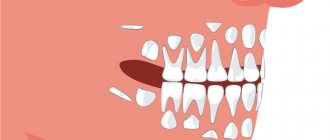
Tooth loss chart
Here is an approximate order of loss of temporary teeth, which is preceded by the resorption of their roots:
- the roots of the upper and lower central incisors begin to decrease from 4-5 years. As a rule, this process lasts about two years and they fall out by the age of 6-7 years;
- the upper and lower lateral incisors become loose from the age of six and their permanent analogues should be expected at the age of 7-8 years;
- The first molars above and below can be prepared for replacement within three years. The process of root resorption begins at the age of 7 and permanent ones appear by the age of 9-11;
- next in line are the upper and lower canines. The root dissolves starting at the age of eight and children show off new fangs by the age of 9-12;
- The second molars complete the process of tooth replacement. Baby teeth will fall out around the tenth year of life.
When do puppies start teething?
When introducing complementary foods, it is very important to note whether dogs have baby teeth. Until this moment, the pet is simply not able to chew solid food, so it is completely dependent on its mother.
The first snow-white teeth appear 20-25 days after birth and are fully grown by 1.5-2 months. The exact timing of eruption depends on the breed. In miniature dogs, this process is slightly delayed, occurring at 5-6 weeks of life.
Timing of permanent teeth eruption
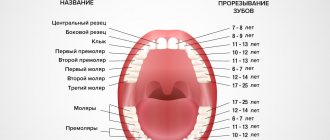
Permanent teeth in children erupt in the same order as baby teeth:
- central incisors above and below: permanent teeth appear in first-graders - at 6-7 years from below and at 7-8 years from above;
- the lateral incisors on both jaws change to permanent ones at 7-9 years of age;
- permanent first premolars appear by 6-11 years, and second ones should be expected no earlier than 10-12 years;
- at the age of nine to twelve, the upper and lower canines appear;
- The appearance of molars usually begins at the age of six and ends at the age of 21, when the third molars erupt.
Please note: the information above is approximate, and if your baby's teeth are not appearing on schedule, there is no reason to worry. In some children, permanent dentition forms earlier, in others - later. In any case, by the time they reach adulthood, most teenagers can already boast a full set of permanent teeth, and all that remains is to wait for the “eights” - wisdom teeth. However, more and more often, recently, wisdom teeth do not appear at all, as they are rudimentary and practically do not participate in the chewing process.
Types of bite in dogs
Not only its exterior, but also the animal’s health depends on the position in which the dog’s upper and lower jaws are in relation to each other. As a result of an incorrect bite, a dog can develop diseases of the digestive system, respiratory system, and sometimes the heart.
Main types of bite:
Normal or scissor.
In the process of evolution, wild dogs were forced to hunt other animals to feed themselves, as a result of which the structure of the jaws of dogs was designed to grab and hold prey. Therefore, for most dog breeds this bite is considered normal. With this type of jaw bite, the upper and lower jaws are equally developed. The front surface of the lower incisors is tightly adjacent to the back surface of the upper ones, the dog’s canines converge in a “lock”, the lower incisors rest against the base of the upper incisors. This type of bite is considered the norm for dogs - German and Caucasian, Doberman Pinschers, Pinschers, Terriers. Dogs with this type of malocclusion have less wear on their teeth, and owners of these breeds are less likely to go to the veterinary clinic with dental problems.
Pincer or level bite.
The position of the jaws in a straight bite is considered unacceptable for most dog breeds. Experts still classify this type of bite as a not too serious defect. With a pincer bite, the dog's upper and lower incisors are located on the same line and rest against each other, as a result of which the dog's teeth quickly wear down. This jaw position is considered unacceptable for most dog breeds. However, a pincer bite is still considered a not too serious defect. In this case, the dog’s lower and upper incisors are located on the same line and rest against each other, because of this they grind down very quickly. At the same time, a direct bite in dogs usually does not have a negative effect on the canines and molars. This type of bite in dogs can be either congenital or acquired. This type of bite in a puppy can be formed by the owners of the animal themselves as a result of too active games of tugging with the help of toys.
Underbite.
With an underbite, the dog's lower jaw is underdeveloped. Because of this, the dog has free space between the incisors. The lower canines are loosely adjacent to the edges of the upper jaw. An underbite in a dog can cause certain dental diseases. When a dog has an underbite, a large load falls on the molars and canines; in this case, they adjoin each other very tightly. With underbite in dogs, tartar often forms (treatment and prevention of tartar formation in dogs).
Undershot or bulldog-shaped.
An undershot is not a defect and is considered normal for bulldogs, Pekingese, and bull terriers. When overbiting, the dog's lower incisors protrude in front of the upper incisors. The dog's lower jaw protrudes forward. When a dog bites, the incisors and canines may even be exposed.
Early tooth loss
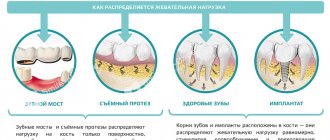
The time of tooth loss depends on the individual characteristics of the child’s body. However, premature tooth loss can be dangerous. The thing is that if a baby tooth is missing for a long time, then the neighboring teeth move, and there is simply no room left for the permanent one, which begins to grow in due course. This situation can cause a violation of the correct bite, distort the dentition and require long-term treatment by an orthodontist.
What causes premature tooth loss in children:
- various injuries;
- periodontal diseases;
- caries;
- infectious diseases suffered by a child in preschool age.
If a baby tooth has fallen out, and its permanent replacement is not expected soon, consult a dentist. In modern dentistry, there are special designs - plates that do not allow neighboring teeth to move and preserve space for a permanent tooth. Such systems do not injure tooth enamel, do not involve grinding of teeth and do not interfere with the baby while talking and eating.
Gum inflammation in dogs
Often a minor inflammatory process of the gums accompanies the entire period of changing teeth in a puppy. Clinically, this process in a puppy is manifested by redness and swelling of the gums, severe drooling, decreased appetite and the development of stomatitis (stomatitis in dogs).
Delayed tooth replacement or “stuck” baby teeth.
Sometimes a puppy’s baby teeth don’t have time to fall out before permanent ones “make their way” into their place. In addition to malocclusion, persistent teeth are dangerous due to additional injuries to the cheeks and inflammation of the gums. When examining the oral cavity, puppy owners discover baby teeth in the jaw at an age when they should no longer exist, as well as two processes from one tooth socket, one of which is baby teeth.
In the event that a dog owner cannot remove a loose tooth himself, it is necessary to contact a veterinary clinic about this problem.
Delay in loss of primary teeth
Your child is finishing school, but some of his baby teeth have not yet been replaced by permanent ones? It is worth making an appointment at a dental clinic. Temporary teeth that remain in their places for too long are a sign that there are disturbances in the functioning of the child’s body.
Late tooth loss can be caused by:
- abnormal location of the permanent tooth germ;
- regular stress;
- malnutrition and lack of vitamins and microelements;
- chronic diseases.
Do you want your child to have straight and healthy permanent teeth? Do not neglect preventive examinations at the dentist twice a year.
What to do if your teeth are uneven
Later or premature loss of baby teeth, individual characteristics of jaw development, trauma and many other factors lead to disruption of the position of the teeth. There is no need to worry too much if the emerging permanent teeth do not form a perfectly even row. Contact your orthodontist. Modern dental technologies make it possible to achieve a perfect smile with the help of braces or aligners. A child's jaw is still in the process of formation. Timely treatment is the key to quick and high-quality results.
What should parents do?
Losing primary teeth is a completely natural process and most often it is not accompanied by pain or complications. Nevertheless, in order to be sure of the baby’s health, you should follow a few simple rules:
- The teeth should fall out on their own. Do not pull out a tooth that has begun to loosen - you may accidentally damage a root that has not yet completely resolved and it will remain in the gum. You can help a tooth only if it really “hangs by one thread.” It’s even better if the tooth is removed by a pediatric dentist;
- After a tooth falls out, the wound may bleed. Give your baby a sterile gauze swab and ask him to bite down firmly - the bleeding will stop in a few minutes. Try not to feed your child for a couple of hours after losing a tooth. For the same period, you should give up hot, sour and salty foods;
- When changing teeth, it is very important to visit the dentist once every six months for preventive examinations. Your doctor will assess the general condition of your teeth and give recommendations on how to care for your baby and permanent teeth;
- Even though baby teeth are temporary, their condition must be treated very carefully. The health of temporary teeth directly affects the health of permanent teeth.
With each new permanent tooth, your child becomes more mature. Attentive attention to oral hygiene and regular dental checkups can give your child one of the main decorations: a healthy and beautiful smile.
Caring for a kitten during the period of teeth change
During the period of changing teeth, kittens' gums itch very much, just like people's gums (if adults remember this feeling). They try to chew on something to reduce the level of discomfort. At this time, owners need to be especially careful: the animal can harm itself, for example, by chewing electrical wires. There is also a danger of choking on a small object on which the kitten decided to scratch its gums. It is necessary to remove all such small items, wiring and other potentially dangerous things from the cat’s access area.
It is also necessary to pay attention to several issues: vaccination, nutrition and oral hygiene.
Nutrition
It is better to consult a veterinarian about the nutrition of a kitten during the period of teeth change. To build teeth, the animal’s body requires large amounts of calcium and phosphorus, so these elements can be slightly increased in the diet. However, you cannot overdo it: this is a serious burden on the kidneys. If parents or siblings had problems with the excretory system, then there is no need to introduce additional calcium and phosphorus.
If the kitten is accustomed to industrially produced food, then it should be fed dry food during this period. This will allow the pet to scratch its gums and, possibly, remove already loose teeth. There is no great danger in kittens swallowing teeth, but sometimes swallowed solids can harm the soft tissues of the digestive tract.
If the kitten has a natural diet, then it is recommended to give relatively large pieces of dietary meat. You can give fish twice a week, but you shouldn’t especially get used to such food. This is especially true for male kittens who are supposed to be castrated. In the future, fish will have to be completely excluded from the diet, and the animal should not get used to it.
You should also give your kitten plenty of dairy products rich in calcium. This can be cottage cheese, whole milk (if the animal tolerates it normally), yogurt, kefir with a low fat content.
In specialized stores you can find special bones that a kitten can chew on when its gums itch. In addition to the fact that it eliminates discomfort and helps teething, such products also contain useful additives that will improve the kitten’s health.
Vaccinations
Kittens should be vaccinated according to the schedule. The first vaccinations are given at two months; further procedures should be consulted with a veterinarian. As for vaccination during the period of teeth change, all veterinarians agree on this issue: while the milk teeth are falling out and the molars are growing, there is no point in getting vaccinated.
A visit to the veterinary clinic is stressful for the animal. And during the period of changing teeth, the kitten already feels somewhat weakened, even if everything is going fine. Therefore, vaccinations should be done before they begin to fall out, and then after the root ones grow.
Oral hygiene
To prevent tartar and other diseases of the oral cavity, teeth and gums, cats should brush their teeth regularly. Experts advise accustoming the animal to this procedure from infancy: then it will not experience discomfort, will get used to it and, perhaps, will even love cleaning.
Kittens need to brush their teeth with a special toothpaste and brush. Human toothpastes are not suitable for cats as they contain ingredients that are harmful to them. Each family member should have their own brush. There are also special gels for disinfecting the oral cavity for cats.
This should be done approximately once every three weeks. During the shift, you can purchase a special product containing anti-inflammatory and anesthetic components. Procedures with such a gel will significantly reduce the animal’s discomfort.