The enamel of baby teeth is thin and delicate. Therefore, the first teeth are susceptible to caries. Often, tooth decay occurs before the child begins to eat sweets: literally some time after teething. If in the first years it was possible to avoid caries, then at the age of 3–5 years the risk increases: children at this age already try chocolate and other desserts, and do not always brush their teeth thoroughly. However, it is not recommended to remove baby teeth ahead of time. How and why to treat them and how to decide which treatment is appropriate?
Baby teeth last for several years, but it is important to preserve them
Why do babies get caries?
Yes, caries in children under 3 years of age still surprises parents. "How so? After all, the baby doesn’t even know cigarettes and soda yet?” - they shrug their shoulders. In fact, there are two main groups of reasons for the appearance of caries in babies: poor lifestyle during pregnancy and insufficient oral care for the child after birth. Let's look at each group separately.
Pregnancy
The expectant mother should be especially attentive to herself. The baby's teeth begin to develop around the 12th week of pregnancy. It is important for a woman to understand that the process of feeding a child is a process that begins with conception.
For the health of the baby’s teeth, hair, nails, skin and other organs, the expectant mother should choose natural products that contain the daily requirements of essential vitamins and minerals:
- Dairy
. First of all, the expectant mother should choose cottage cheese, natural yogurt and hard cheeses. These treats contain calcium, protein, vitamins B, D, and Omega-3 polyunsaturated fats that baby’s teeth need.
- Nuts
- This is a storehouse of vitamins and nutrients necessary for the formation of teeth in a baby. Nuts contain selenium, magnesium, vitamin E, phytic acids and Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- Fish and seafood
. Everyone knows that fish contains the phosphorus needed by bones and teeth and beneficial vitamin D, which strengthens the nervous system of a pregnant woman and baby.
- Meat, liver
. Important cell building materials are meat and liver. These products contain the protein necessary for a growing body. The liver is rich in iron and B vitamins.
- Chicken and quail eggs
. These products contain more than 10 useful vitamins and microelements that affect the growth and abilities of the baby.
- Vegetables
. Vitamins, fiber, microelements and organic acids necessary for the development of healthy baby teeth are found in abundance in vegetables. Avocados, broccoli and carrots are especially useful for the expectant mother. These vegetables (in any form - raw or cooked) contain the most calcium, vitamins B, C and folic acid.
- Berries and fruits
– vitamin support for pregnant women and the key to the normal development of the child.
- Legumes
contain iron, folic acid and vitamin B-6, necessary for mother and baby.
- Cereals
rich in B vitamins, fiber and iron. Milk porridge will be very useful.
- Spinach.
The plant contains a lot of folic acid, calcium and vitamin A. In addition, the leaves are not at all difficult to grow at home on the balcony, and then enjoy them in the form of soups, purees and side dishes.
And, of course, the expectant mother should avoid taking antibiotics: such drugs can destroy the child’s health.
What is a fistula
A fistula (gingival fistula) is a small seal on the gum. It is characterized by the presence of an open canal, as well as the constant discharge of pus. In many cases, the presence of such a fistula can be recognized visually when a tubercle appears on the child’s gum, the diameter of which usually does not exceed 2 cm. It has a reddish tint, gradually becomes inflamed, and a small funnel appears. As inflammation progresses, more signs of a problem appear.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that a child has such a pathology as early as possible. If this problem is not detected, the fistula can cause serious complications that will have a significant negative impact on the child’s health.
This phenomenon is especially dangerous for the reason that it often occurs in children when they do not yet know how to speak and cannot complain to their parents or describe the essence of the problem.
Next, we will talk about why a child has fistulas on the gums, what to do to prevent them and properly treat them.
Oral care
Caries in children aged 2-3 years can also develop due to the inattentive attitude of parents. Let's look at the main mistakes that moms and dads make:
- Pacifiers and bottles in a dream.
To teach a child to sleep alone, parents give him a pacifier or even a bottle of milk at night. As a result, the child enjoys the sweet taste of the drink all night, and the teeth are slowly but surely destroyed. Such a habit, of course, will give mom and dad healthy sleep, but in the baby it can lead to bottle caries and malocclusion.
- Sweet life.
Of course, most kids are unfamiliar with the problem of excess weight. Therefore, grandparents strive to treat the child with additional cake or candy. And, as you know, bacteria on enamel love sugar with a tender love, and very soon children under 3 years old develop caries, which requires treatment.
- Insufficient dental care
. Many parents believe that there is no need to care for baby teeth at 2-3 years of age. As a result, plaque accumulates, and carious monsters spread over both grown and still growing teeth.
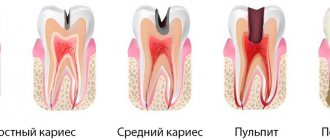
Symptoms of caries in babies
It can be difficult for parents to notice that their child’s teeth are affected by caries. Dentists distinguish several stages of the development of the disease:
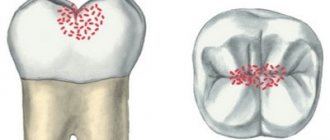
- Initial.
Subtle white spots appear on the baby's teeth. These spots can be large or very small, round or rectangular. The child does not experience any unpleasant sensations at the initial stage. Therefore, parents who do not examine their children's teeth skip this stage, and the enamel continues to deteriorate.
- Superficial
. At this stage of caries, teeth change more noticeably: dark spots appear on the top layer of enamel. Some children complain of pain when eating irritating foods (sour, salty and sweet). The enamel is damaged, the tooth cavity opens to bacteria.
- Average
. Caries bacteria reach the dentin (the tissue located inside the tooth). The baby complains of pain when eating foods that are too cold or too hot.
- Deep.
In children, deep caries is much more difficult than in adults. Most of the internal tissue of the tooth is damaged, and pulpitis develops sharply.
Unfortunately, in children under 3 years of age, unlike adults, caries often affects all teeth at once. Several holes may appear on one crown from different sides at once. Therefore, parents need to be extremely attentive to their children and devote time to oral care even before the first tooth appears.
Gap between teeth - diastema
Diastema is a fairly common phenomenon. In adults, you can often notice a gap, expressed to a greater or lesser extent. Statistics show that literally every second baby is at risk of developing a gap between the front teeth.
If the gap between the upper or lower front teeth is more than 1 mm and varies in width up to 10 mm (most often the limit is 2–6 mm), we can confidently speak of a diastema. The spaces between other teeth have another name - trema.
Due to the formation of a gap, all sorts of inconveniences arise in the implementation of everyday and vital functions. Diastema complicates the normal process of eating and affects diction, so if there is a sufficiently pronounced gap, the child speaks poorly. In addition, the gap is an additional stimulus for the occurrence of caries and periodontitis.
There is a classification of diastemas, including false ones: this involves the presence of a gap between the baby teeth, which naturally disappears during the change of teeth to molars.
If a gap occurs after the appearance of permanent teeth, measures should be taken to eliminate it as soon as possible. And although dentists eliminate diastema even in adulthood, it is most comfortable to carry out treatment in childhood.
What kind of gap could there be? The main division assumes the existence of symmetrical and asymmetrical diastemas. In the first case, the upper or lower incisors are at an equal distance from each other. In the second, only one tooth has an incorrect position, while the second remains in its rightful place.
Also, the spaces between the teeth can be conditionally divided according to the direction of growth of the incisors. The gap can be caused by the divergence of the incisors in different directions with parallel roots (lateral deviation of the crowns) or by a divergence starting from the roots (corpus lateral displacement).
In addition, a so-called medial tilt is possible, when teeth grow with rotation around their axis or have a clear direction to the side.
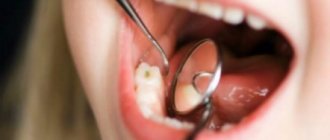
Treatment of caries in children under 3 years of age
The method of treating caries in children under 3 years of age depends on the stage of the disease, the individual characteristics of the child and, of course, his attitude towards dentists.
- At the stain stage, the doctor removes plaque and remineralizes the enamel using solutions or silvers the teeth.
- Superficial, medium and deep caries in children 1-3 years old (and older) are treated using a drill. If necessary, the doctor uses anesthesia. If a child suffers from aching toothache, canal depulpation is performed.
Remineralization
Remineralization is the restoration of damaged tooth enamel. To carry it out, the doctor cleans the surface of the affected area, and then covers the rows with a special composition with fluorine and calcium. The procedure is absolutely painless, most children tolerate it easily.
To avoid the development of caries in children, dentists recommend repeating remineralization every six months.
Silvering
This method enhances the protective abilities of enamel and is recommended for children who are afraid of dentists. The surface of the teeth is coated with silver nitrate. The substance provides a reliable antiseptic effect, but parents should be mentally prepared that after treatment the child’s teeth will turn black.
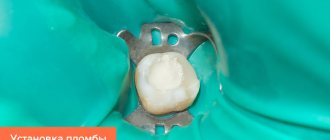
Sealing
For children over 1 year old, the dentist can fill damaged teeth. This treatment does not necessarily require the use of a drill. If the caries is shallow, the doctor applies a special solution with acid to the tooth. The substance corrodes the affected tooth surface, disinfects the carious cavity and applies photopolymer material.
If a child comes to the doctor with deep caries, it will not be possible to do without drilling. Before starting treatment, the doctor gives the baby anesthesia, since baby teeth have nerve endings.
Treatment of caries in children 2-3 years of age and older can be supplemented with procedures such as
- preparation or opening of a cleaned carious cavity;
- depophoresis – introduction of an electric current of copper-calcium hydroxide ions;
- ozone therapy - treatment of carious cavities using a jet of ozone gas;
- photodynamic therapy – application of a special medicinal paste to a carious tooth and subsequent laser treatment of the area.
Why is caries of the front teeth dangerous?
Caries seems harmless until a person begins to feel discomfort. But destructive processes begin already in the first stages. First, the top layer becomes thinner, then depressions form on the surface of the tooth. Then the patient begins to feel pain.
Deep caries will lead to tooth destruction, endless sharp pain, an unpleasant odor will constantly emanate from the oral cavity (brushing, chewing gum and other fresheners will not help), and you will also notice a strong cosmetic defect. The longer you delay with the problem, the less chance you have of saving the tooth.
What if you don’t treat caries in a child?
Not treating caries on baby teeth means providing your child with a painful childhood. Firstly, caries suddenly “infects” other teeth, and secondly, it almost instantly turns into pulpitis and brings excruciating pain to the baby.
Untreated teeth in children can in the future provoke such serious diseases as:
- chronic allergic processes;
- inflammation in the oral cavity;
- periodontitis;
- chronic inflammation in the mouth.
Symptoms
If a “hole” has already formed on the teeth, then, most likely, caries led to pulpitis or periodontitis. Caries itself develops from a small spot - an area of weakened enamel. Over time, the damaged enamel dissolves and a “hole” is formed. At the earliest stage, the following symptoms appear:
- teeth become especially sensitive;
- pain occurs periodically;
- a stain appears on the enamel or the color changes;
- dental floss begins to get stuck between teeth;
- food gets into the interdental spaces.
Often caries grows from the interdental space, which is covered by the gum.
How to prepare a child for treatment?
Children intuitively feel the fear of adults and begin to be afraid of dentists even before their first glance at the dental chair. In order for the treatment of caries in a baby under 3 years old to go as smoothly as possible, it is necessary to prepare him for a visit to the doctor in advance.
- Find a trusted, good dentist who can establish contact with your child.
- Take your child for preventive examinations to the dentist, do not wait until the tooth hurts. Believe me, pain will greatly increase children's fear.
- Be calm at your doctor's appointment. Remember, all the fears of the parents are transmitted to the baby. There is no need to tell the child “don’t be afraid”, “it won’t hurt”, “like a mosquito will bite” even before he approaches the doctor.
- If your baby is already playing on his own, rehearse your visit to the dentist at home. Treat caries for a bear, bunny, or cat. Let your child get used to the atmosphere of the dental office a little.
- Tell your child that everyone goes to the dentist - mom, dad, and grandparents. And, most importantly, emphasize that visits to the doctor bring joy and relief to everyone.
- Choose a time to visit the doctor when your child is alert and cheerful. Believe me, the baby will not be happy to be in the doctor’s chair during the daytime nap or in the evening when he is already tired. By the way, during the visit the baby should be well-fed.
- If you nevertheless went to the dentist for the first time because of a toothache, convince your child that the doctor will definitely help him. Remember, the baby is already very scared, so there is no need to use the words “drill” or “acute pain”. Better tell a story about how a good doctor will save a child from carious monsters, and his teeth will become white and healthy.
We hope our tips for treating caries in children under 3 years of age will be useful to you. Teach your child not to be afraid of dentists and to take care of their teeth. May you and your children always have beautiful snow-white smiles.
And in order for a child to love brushing his teeth from a very early age, it is important to choose a tasty, high-quality toothpaste for him. ASEPTA baby toothpaste gel-paste is created specifically for children aged 0 to 3 years. The soft, sweet gel carefully cares for the child’s teeth and gums without damaging them, and the natural components of the paste provide protection against caries and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
The paste does not contain abrasives, fluorine, parabens, or sodium lauryl sulfate, so it is absolutely safe for crumbs. And the bright taste of “tutti-fruiti” will make brushing your teeth very pleasant for your baby.
Experts' opinion
The complex composition of ASEPTA Baby toothpaste allows you to simultaneously care for your gums and teeth. The product has:
- Certificate of state registration;
- Certificate of conformity No. ROSS RU. AG81.H01070.
The paste does not contain fluoride and does not require consultation with a doctor before use. The product is safe if swallowed, as it does not contain components harmful to the health of the baby.
Sources:
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of toothpaste “ASEPTA PLUS” GENTLE WHITENING” Author: doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)