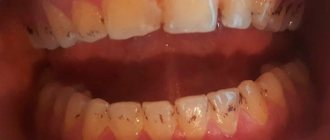
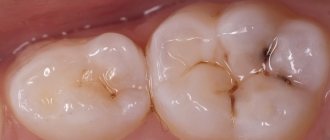
Caries is a pathological process characterized by damage to the hard tissues of the tooth and further formation of a cavity in it. In recent years, caries of primary teeth has become a fairly common problem. By the age of 6-7 years, until permanent teeth begin to appear, more than 70% of children have lesions on their baby teeth, and most of them go to the dentist with complications or an advanced process. Most often, caries of primary teeth is detected at 2-3 years of age, but sometimes it can also occur in children who are not yet two years old. In different regions of the country, the prevalence of this form of caries by the age of four is 20-80%. How can such problems be avoided and what do parents need to know?
Causes of caries
Most often, caries of primary teeth can form under the influence of several factors simultaneously. Its most common causes are:
- Damage to tooth germs in the prenatal period. In the embryo, tooth buds begin to form in the first trimester of pregnancy. That is why any illnesses of the expectant mother that she suffered during this period, as well as the use of medications, can contribute to the fact that the fetus’s proper development of teeth is disrupted.
- Insufficient oral hygiene or its absolute absence. In this case, food particles remain on the teeth, and this is an excellent environment for the life and proliferation of bacteria.
- Incorrect eating habits - using pacifiers for a long time. Those children who are unable to switch from drinking from a bottle to a sippy cup or cup for a long time, and especially those who have learned to fall asleep every evening with a bottle or pacifier in their mouth, are at risk of developing bottle caries. With this pathology, through prolonged contact with the teeth of the liquid from the bottle (especially if it is sweet), the front teeth are affected by caries, and the process spreads along the circumference of the crown part of the tooth (along the perimeter of its visible part).
- Insufficient amounts of food in the daily diet, which requires intense chewing and leads to increased salivation, due to which the teeth are cleaned naturally. This factor is inherent in children under two years of age; it is one of the causes of early caries.
- Lack of calcium in food and water - the main building material of teeth and fluorides, which strengthen tooth enamel and protect against caries, preventing the possibility of its development.
- Rickets – with this pathology in children, tooth tissue is easily destroyed.
- Physiologically determined low resistance of children's dental tissue to agents that cause caries.
- Anomalies of dentition and bite.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Chronic diseases, as well as frequent respiratory diseases, which reduce the overall resistance of the body.
- Excessive amounts of carbohydrates in a child’s food contribute to the development of caries in two ways simultaneously: they feed bacteria, and in the process of their decay, organic acids are formed that damage tooth enamel. For the formation of caries, it is not so much the total amount of carbohydrates consumed that matters, but the frequency of their intake.
Without a doubt, a child who is not yet three years old should not snack between meals, especially food containing a high amount of carbohydrates (sweets, chocolate, etc.). Instead, it is better to offer your baby fruits, marshmallows, marmalade, pastries, and dried goods. It is better to eat sweets after breakfast or dinner, and then brush your teeth after a while. Almost all children do not grow up without sweets, but their consumption should be limited and reasonable.
What is caries of primary teeth?
Caries affects not only the permanent teeth of adults, it is truly merciless to children’s delicate milk teeth. The principle of development of the disease is absolutely the same as in adults. If there are bacteria in the child’s mouth that cause caries, then they, feeding on carbohydrates from leftover food - and this also applies to breast milk, produce acids, which, in turn, destroy tooth enamel. This process goes much faster in children, because... their enamel is more fragile and cannot withstand an aggressive environment. And if several unfavorable factors confluence at once, then caries in children progresses very quickly.
The Forbidden fruit is sweet…
In order not to tempt your baby with “forbidden fruits,” simply do not buy them or consume them yourself. There is no doubt that your friends and relatives all bring sweets to the child solely with the best intentions. Try to talk to them and explain that instead of candy, you can bring your child, for example, a toy or an interesting book. Due to poor or complete lack of oral hygiene, the plaque that remains on the teeth after eating food turns into dental plaque containing bacteria that produce lactic acid, which damages the enamel and contributes to the development of caries. As soon as a child has his first teeth, he should immediately have age-appropriate toothpaste and a brush. Developing the habit of brushing your teeth at an early age twice a day (in the morning and also in the evening, after meals) will prevent many problems.
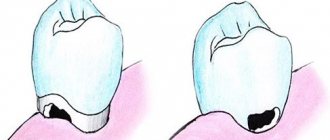
Installation of a filling for initial caries
Treatment of initial dental caries in most situations does not require the use of a drill, but in some cases filling is performed. This usually occurs at the dark spot stage, when the doctor is not confident in the success of remineralizing therapy, and for some reason treatment using Icon technology cannot be carried out. Light filling for initial caries is considered the most effective, since it has high functional and aesthetic indicators.
Signs of caries
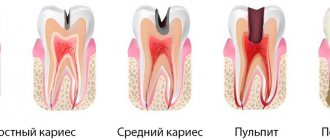
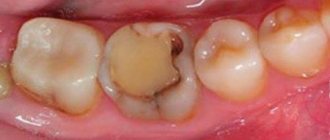
Caries of primary teeth according to the depth of damage can be divided into the following types:
- Initial caries - in this case, white spots of different sizes and shapes appear on the enamel, but there is no pain. If left untreated, the process progresses and the spots darken, become black or brown. If you start timely treatment, you can stop the further development of caries.
- Superficial caries - a defect in dental tissues can be detected exclusively within the enamel. Pain occurs when exposed to sour, sweet, salty foods. A carious cavity can be dark or light. Treatment consists of filling the cavity.
- Medium caries - damage to tooth enamel and part of the dentin (intradental tissue) is detected. Painful sensations arise from hot, cold, salty, sweet. With this type of caries, the cavity is filled.
- Deep caries - the enamel is affected, as well as most of the dentin. When choosing a treatment method, the condition of the pulp is assessed and, depending on whether, filling or conservative treatment is carried out, in which therapeutic pads are used, and then delayed filling.
In children, multiple dental lesions are possible (20 baby teeth may be affected at once). In addition, during childhood, several carious cavities can occur in one tooth. Due to the physiological and anatomical structure of teeth, some children have a thinner layer of dentin and enamel, so hard tissues have a higher permeability, which is why the carious process quickly spreads along the surface of the tooth and deeper. This contributes to the spread of the process to deeper tissues and the development of periodontitis and pulpitis.
A new way to solve the problem of early dental caries
The wide prevalence caries in young children determines the relevance of searching for ways to prevent this disease. caries is a long-term chronic process, which is the focus and source of infection and allergization of the child’s body, since with food the child constantly swallows a large number of microorganisms, as well as decomposition products of tooth tissue and food that linger in the carious cavity. In addition, these same microorganisms, their toxins and waste products are absorbed into the blood through the mucous membrane of the mouth and at the points of contact between the tooth and the jaw. Constant infection of the body and its sensitization contribute to the development in children of chronic tonsillitis, rheumatism, kidney diseases, joints, gastrointestinal tract and weakened vision.
The first signs of dental caries may appear in children during the eruption of baby teeth. The number of carious teeth in one child, as well as the number of carious cavities in one tooth, varies and determines the degree of caries . With a compensated course of caries, a 10-12 year old child in the oral cavity has no more than 4 teeth affected by caries , with subcompensated - up to 8-9 teeth. The decompensated form of caries is characterized not only by a large number of affected teeth (more than half of the total number), but also by a large number of carious cavities. There may be a large number of decayed teeth devoid of pulp. When treating such teeth, it is difficult to achieve good fixation of fillings; the teeth do not withstand optimal physical stress and are quickly destroyed. Therefore, it is very important to prevent caries to the stage of decompensated form. Of particular importance is the prevention of caries , starting from an early age.
Development of caries
To date, sufficiently convincing evidence has been obtained for the role of microorganisms in the occurrence of caries . For the occurrence and development of caries, the following conditions are necessary [1]:
- Presence of cariogenic microflora.
- Intake from food and retention of easily digestible carbohydrates on the surface of tooth enamel.
- Reduced resistance to the effects of cariogenic factors.
It is believed that the causative agent of caries is the bacteria Streptococcus mutans (Str. mutans). The theory of the microbial etiology caries has long been the subject of debate, but currently the role of microorganisms in the occurrence of caries can be considered proven. In particular, the relationship between the presence of Str. mutans in saliva, the formation of microbial plaque and the development caries .
Bacteria Str. mutans are transmitted from person to person, infection usually occurs at an early age, often Str. mutans are found in a child's mouth even before the first teeth erupt.
Two oppositely directed processes continuously occur in teeth - demineralization and restoration of mineralization (remineralization): due to the action of microorganisms, first on the tooth enamel, and then on the hard tissues of the tooth, mineral substances, for example, calcium, are washed out, i.e. the teeth are demineralized. Saliva has a neutralizing effect on this process: excess minerals in its composition are deposited back into the hard substance of the teeth - remineralization of the teeth occurs. A shift in balance towards demineralization leads to weakening of tooth enamel.
Caries infection begins with infection of the oral cavity by bacteria Str. mutans. A feature of these bacteria is their high adhesiveness to oral tissues, which allows them to form dental plaque - yellowish or grayish deposits on the surface of the teeth. Dental plaque is a type of biofilm. Bacteria Str. mutans, which have a high adhesive ability, due to coadhesion, create favorable conditions for attachment to the tissues of the oral cavity and other microorganisms that are not able to stay in the oral cavity on their own. Thus, various pathogenic microflora can be retained, including pathogens of otitis media, pneumonia, and stomach ulcers. Soft plaque does not adhere tightly to the cells of the oral cavity, so it is relatively easy to remove. If this is not done, dental plaque contributes to the formation of dental plaque - a pathological conglomerate consisting of microorganisms, the polysaccharides they produce, as well as food debris. Dental plaque is attached to the surface of the tooth quite tightly and is much more difficult to remove than plaque.
At the site of plaque formation - that is, in practically anaerobic conditions, isolated from the external environment - acidic metabolites secreted by bacteria, in particular lactic acid, begin to destroy tooth enamel. Str. mutans not only produce organic acids, but are also acid tolerant and are able to survive in acidic plaque conditions at a pH below 5.5. Under the influence of acids, a defect in the tooth tissue begins to form at the site of the dental plaque, and a carious cavity appears. The most common places for caries are natural depressions on human teeth, most often on the chewing surface, the space between the teeth, and the area of the tooth neck along the gingival edge.
Demineralized areas of the tooth surface appear as white spots. to recognize caries at this stage; white spots on the teeth can easily be confused with the manifestation of fluorosis. Caries on a child's first teeth develops slowly and the process can take months. Subsequently, as the infection progresses, these white spots may turn brown. Noticeable damage to the teeth means that the pathological process has gone very far. Subsequently, caries will spread much faster, and it will become much more difficult to fight it. Therefore, the best way to protect your child’s teeth from caries is to prevent damage. The most effective and feasible strategy to combat caries is the introduction of healthy oral hygiene habits and the promotion of dental care practices at home. Leftover food, which is a nutrient medium for Str. mutans must be removed regularly and on time. Parents and caregivers should provide regular oral hygiene to their children. In order for the procedure to take hold and become firmly established in the daily care routine, the oral hygiene product must be effective, safe, convenient and, most importantly, must be positively perceived by the child. Xylitol CH2OH(CHOH)3CH2OH, a safe natural sweetener, has proven itself well as a means of caries
The mechanism of the anti-caries effect of xylitol
Unlike regular sugars (found in milk, juice, and most baby formulas), which have a chemical structure of six carbon atoms, xylitol has only five carbon atoms. Str. mutans uses six-carbon carbohydrates as an energy source. Xylitol, which contains five carbon atoms, is absorbed by bacteria very slowly, moreover, it inhibits the growth and reproduction of Str. mutans. It has been shown that consumption of xylitol practically does not reduce the pH of dental plaque [3]. Regular use of xylitol actually stops the growth of bacteria that cause tooth decay and gum disease. Xylitol competes with hexaatomic sugars during transmembrane transport, as well as in metabolic processes inside the cell. Unlike the metabolism of hexaatomic sugars, which releases energy and promotes bacterial growth, when broken down by Str. mutans xylitol energy is only consumed, but not released. Moreover, during xylitol metabolism, intermediate compounds that provide energy sources are absorbed but not reproduced [5].
In addition, as studies have shown, xylitol reduces the production of bacterial cells and the concentration in saliva of glycans, which ensure the attachment of the bacterial wall to the tooth surface.
Xylitol has also been shown to inhibit mother-to-child transmission of bacteria more effectively than chlorhexidine [6].
And finally, xylitol not only inhibits the growth of microorganisms that cause caries , but also promotes the remineralization of tooth enamel by increasing the buffering capacity of saliva.
The antibacterial properties of xylitol have been successfully used in Spiffies dental wipes. Spiffies are a new way to clean teeth and gums for both young children and adults when a toothbrush is not available. Spiffies wipes are convenient, easy to use and safe. It is recommended to use wipes starting from the age of 4 months. The impregnation of the napkins, which contains xylitol in concentrations of 20–40%, has a pleasant fresh taste, so the napkins are usually perceived positively by children. There are no other sweeteners in the composition. Research from the Harvard School of Dentistry has shown that xylitol is more effective in preventing tooth decay than a combination of xylitol and sorbitol [7]. The use of Spiffes wipes is a combination of mechanical removal of plaque and the creation of a healthy environment in the oral cavity that prevents the development of caries .
Spiffies wipes contain no artificial fragrances. The aroma of the napkins is created by adding natural aromatic substances that create the natural aromas of the corresponding fruits and berries. In a multi-stage purification process, all components that can cause allergic reactions are removed, leaving only low molecular weight esters that do not cause allergies. Sodium benzoate, widely used in the food industry, including baby food, is used as a preservative.
An adult cleanses the child's mouth. The method of using the napkin eliminates the risk that the napkin will slip off the finger and remain in the child’s mouth.
Spiffies wipes allow you to unobtrusively teach young children about oral hygiene, which is very important for their overall health. These wipes are a very convenient personal hygiene product for children aged 4–15 months, until the child gets used to the toothbrush. It is under no circumstances recommended to rinse your mouth after using the wipes, since the impregnation contains xylitol, which has a prolonged effect and helps prevent caries .
Massaging the gums with a Spiffies napkin also improves blood circulation in the tissues and is an important measure for the prevention of periodontal disease. Parents give this massage to a young child. Regular gum massage before the age of three subsequently forms in the child a strong habit of such procedures and a desire to follow them throughout his life. Irregular care is practically ineffective, since plaque has time to become saturated with salts and is difficult to remove; the harmful effects of food residues and microbes remain.
Spiffies wipes are recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Clinical trials have shown that Spiffies wipes are effective in removing plaque and are perceived more positively by children than a toothbrush [8].
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
E. K. Denyakina , Candidate of Chemical Sciences G. A. Sarkisyan Moscow State Medical and Dental University , Moscow
Stay vigilant
If you find plaque forming on your child’s teeth that you are unable to remove on your own, as well as brown or white spots, this indicates that the child urgently needs to be shown to a pediatric dentist. If the baby complains of discomfort that occurs when eating hot or cold food, this indicates the spread of caries into the deeper layers of the tooth. Parents should never ignore such complaints. It happens that a small child is not able to clearly communicate what is bothering him, so if he refuses food or a certain type of food, and also chews on one side, this may indicate toothache.
Fluoridation as a method of treating caries in the spot stage
The method is somewhat similar to remotherapy. But if remineralization preparations usually contain calcium and phosphates, then the main component of fluoridation products is fluorine. It has the property of strengthening tooth enamel and ensuring its strength.
Fluoridation can be simple or deep. In the first case, you will have to visit the dentist four to fifteen times. During each procedure, the doctor coats the teeth with fluoride-containing gel or varnish for 20 minutes. After the manipulation, you should not drink or eat for an hour.
The deep fluoridation method is considered simpler and more effective. It is carried out using two drugs. One contains magnesium, fluorine and copper, the other contains calcium hydroxide. By reacting with each other, these agents seal the enamel, which allows the concentration of fluoride ions in it to increase several times. A significant advantage of deep fluoridation is the smaller number of procedures - from one to three.
Due to fluoridation, the resistance of tooth enamel to destruction by acids increases, the activity of cariogenic bacteria decreases, and the balance of mineral substances is normalized. To achieve maximum results in the treatment of initial caries, the dentist may recommend the combined use of remineralization and fluoridation methods.
Complications of caries
The most typical complications of caries are pulpitis and periodontitis.
Pulpitis is a pathological process in which the inflammatory process affects the soft dental tissue (pulp). Symptoms of pulpitis can develop over several hours. This is preceded by minor pain, then acute pain occurs, more often at night or as a result of exposure to temperature stimuli. Such signs indicate that the carious cavity is most likely very deep and the dental pulp is affected. In this case, urgent dental intervention is necessary.
In the event that toothache has been observed repeatedly, the child has swelling of the gums or cheeks, and a fistula with purulent discharge is visible on the mucous membrane near the tooth, pain occurs as a result of biting on the tooth, then this indicates the spread of the pathological process beyond the tooth and inflammatory the process developed in the tissues that surround the tooth and a pathology such as periodontitis arose. When treating it, the doctor will choose the treatment tactics individually, but such a baby tooth is unlikely to be cured and will need to be removed.
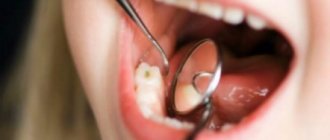
Diagnosis of initial caries
So, we have found out what caries looks like on teeth at the initial stage, now we need to tell you how the diagnosis is carried out. This is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. The clinical picture of initial caries is mild. The disease has practically no characteristic symptoms, and this is especially true for pain. Only occasionally the patient may feel slight discomfort after drinking cold drinks. Diagnosis of initial caries today is carried out using several methods.
Methods for diagnosing initial caries
- Drying.
A common visual assessment technique. The tooth is thoroughly dried with peroxide, after which the affected areas become visible. - X-ray.
Not the most reliable method, but dental x-rays are an integral part of the preparation. White spots are especially noticeable in targeted photographs. - Coloring.
After applying a solution of methylene blue, the affected areas turn a characteristic blue color. - Transillumination.
The teeth are scanned with a special fluorescent device, as a result of which areas of demineralized enamel and their boundaries are detected.
In addition, specialists can resort to differential diagnosis. This is a set of procedures aimed at distinguishing diseases that are similar in symptoms and clinical picture. In the case of initial caries, these are non-carious lesions of the enamel (fluorosis, hypoplasia, and the like).
Methods for treating caries
For caries in children at the initial stage of its development, enamel silvering can be used. In this case, a special solution containing silver ions is applied to the carious cavity (untreated). This is usually a temporary measure used to combat tooth decay. When using silver preparations, areas of the tooth affected by caries, that is, the carious stain itself, are persistently painted black, and this does not look very aesthetically pleasing. However, you don’t need to think that the entire tooth will turn black. Only the part affected by caries will darken, while the healthy part will remain unchanged white.
The most traditional methods of treating caries in primary teeth are removing the affected dental tissue with a drill using local anesthesia. The dentist decides on the need to use local or general anesthesia (anesthesia) individually in each case. Sometimes neither parents nor a doctor can persuade a child to open his mouth in order to treat or show his teeth. Most often, children under three years of age or those suffering from concomitant pathologies face this problem. Then it becomes necessary to treat teeth under general anesthesia. A child should not have any fear of the dentist. It is advisable that he become friends with him and understand that it is necessary to treat his teeth. After all, he will have to deal with this for the rest of his life. The child’s psychological mood largely depends on his parents and loved ones, who can convey to him their fear of visiting the dentist. Try to explain to your child the importance of a visit to the dentist and convince him that there is no need to be afraid of such a procedure.
Psychosomatics of caries in children
Children differ from adult patients in their increased emotionality and mobility. Treatment of caries is usually accompanied by feelings of anxiety and fear. Parents need to prepare their child for a visit to the dentist, and doctors need to provide emotional support during the treatment process.
- 1.5-2 years.
The baby's perception is associated with muscle sensations. He is afraid of falls: a sudden lowering of a chair or a bright light can frighten him. Parents go to treatment with their child: they hold hands and sit in a chair together.
- 3-4 years.
Children are sociable. The presence of a parent gives a sense of self-confidence and creates a sense of security.
- 5-6 years.
The child may be in the doctor's office without a parent. His behavior changes: before he wanted to touch everything, now he asks questions.
- 7-10 years.
The child becomes more balanced and can overcome the fear of dental procedures. When communicating with him, it is necessary to emphasize the importance of treatment.
- Adolescence.
It is characterized by hormonal changes in the body and frequent mood swings.
How to brush your teeth?
Each specialist has his own opinion about when to brush a child’s teeth using toothpaste. The composition of the toothpaste must correspond to the age of the baby - all information about this can be found on the packaging. Toothpastes for children under three years of age should not contain fluoride. Children at this age, not having the skills to rinse, swallow the paste. If a large amount of paste containing fluoride enters a child's body, serious health problems may arise, so in this case you should consult a doctor immediately. Children from about 4 years of age after brushing their teeth can partially spit out the remaining toothpaste. This is why toothpastes for this age contain fluorides. The maturation of tooth enamel is accelerated if hygiene products containing active fluoride are regularly used. This has been proven to help reduce the risk of tooth decay.
Children's toothbrushes are varied. For very small children, you can use special finger brushes, with which mother can easily remove plaque from her child’s teeth. By the age of 2.5-3 years, you gradually need to give the child a toothbrush in his hand and teach him to brush his teeth on his own.
Choose a toothbrush with soft bristles, the width of which corresponds to 2-3 teeth. It is recommended to change it every month, because frayed bristles can hurt your gums and are also a source of bacteria. The child should have an individual toothbrush; it should be stored separately, without a case, with the bristles facing up. Before brushing your teeth, as well as after the procedure, the brush should be rinsed well with running water. Oral care with additional hygiene products
- You can use dental floss or floss when all 20 baby teeth have erupted (most often at the age of 2-2.5 years). Dental floss should be used if the teeth fit tightly together. This must be done very carefully so as not to accidentally injure the gums.
- Dental rinses (elixirs) can be used as an additional hygiene product for children with a high risk of developing caries. Special children's elixirs contain fluoride in the amount that a child of a given age needs. You can use it twice a day after brushing your teeth or eating foods that contain a lot of sugar. Chewing gum should not be given to children until after 3 years of age. The sweeteners they contain (sorbitol, xylitol, etc.) have a beneficial effect on tooth enamel and prevent the occurrence of caries. Chewing gum also promotes increased salivation and self-cleaning of the oral cavity. They can be given to children regardless of the presence or absence of a filling in the mouth. Chewing duration is no more than 10-15 minutes.
Treatment of initial caries
Most patients are interested in how to get rid of initial caries if you have signs of its manifestation? Initial caries in the spot stage is quite easy to treat, and, importantly, today this rarely requires the use of a drill. Modern dentistry offers non-invasive methods that cope with the disease and do not require tooth preparation.
Non-invasive methods for treating early caries
- Remineralization.
Before starting therapy, professional hygiene is carried out, which is designed to remove plaque and carious stains, as well as dry the teeth. The most common method is application with a solution of 10% calcium gluconate, as well as other drugs, for example, fluorides. To eliminate a stain, 10 to 20 procedures are usually required. In modern clinics, remineralization is often carried out using electrophoresis technology. It is also possible to carry out remineralization at home (for mild forms of the disease and for prevention). Usually special gels and pastes are used for this. - Deep fluoridation.
Application of preparations containing fluoride, copper hydroxide and calcium to the surface of teeth. To consolidate the result, fluoride-containing pastes are used. Fluoridation reduces the body's ability to absorb sugar, so the procedure is not recommended for people with diabetes, as well as for those with excess fluoride in the body. - Treatment using Icon technology.
This is an infiltration technique that involves treating the tooth with a special polymer composition that seals the carious cavity and prevents the development of the disease.
How to brush your teeth correctly?
It happens that trying to brush your teeth can sometimes cause a negative reaction. But you don't need to get upset about it. Better be patient and play. Remember that a child under three years of age, and older children too, learn about the world through play. Therefore, do not insist on brushing your teeth; it is unlikely that the baby will understand that this is important. Just play. For such games, a battery-powered brush and a toy on the handle are perfect. The movements performed by the brush for different groups of teeth should differ from each other. Cleaning the front teeth should be done from the gums with unidirectional vertical movements. Move the brush behind the cheeks in a circular manner, while the teeth should be closed. Cleaning the chewing surface of the teeth is carried out with horizontal movements from the inside (from the palate and tongue), back and forth, sweeping upward like a “broom”. But not only the movements that are performed are important, but also how much time is devoted to it. There are two ways to check whether your teeth are being brushed adequately:
- – in terms of time (you need to spend about 7-10 minutes brushing all your teeth), for this you can use an hourglass or any other clock
- – by the number of movements (for each area occupied by the bristles of the brush, 5-6 movements are needed).
Anesthesia
| In our Clinic, pediatric dentistry means comfort and convenience for patients. And pain relief is almost unnoticeable for children. The anesthesia site is first treated with an anesthetic gel with fruit and berry flavor (jam), which children really like. This is done to ensure that the moment of anesthesia (injection) is painless. Anesthesia is carried out with a special syringe with a thin needle containing an anesthetic. The Clinic uses only the latest generation of anesthetics (we use Ultracain DS, Ultracain DS Forte, Ubistezin, Scandonest). A special syringe is used - a cerviject, which is not like a regular one and does not frighten the child. With its help, the required amount of anesthetic is reduced by 7-10 times and there is no numbness in the child’s lips or tongue. |
Proper nutrition
One of the preventive measures for dental diseases is a balanced diet - one in which the daily diet contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins that are necessary for the formation and proper growth of dental tissues. In infants, this is breastfeeding. Older children need to include in their diet all the necessary types of complementary foods that are recommended for this age. Additional sources of fluoride can also be water and fluoridated salt; their use does not require special indications. The main sources of calcium are fermented milk products (cottage cheese, milk, cheese, etc.), buckwheat, gooseberries, potatoes, peas, oats, mineral water (some of its types).
What does bottle caries look like and where does it develop?
Bottle caries always begins its development in the most vulnerable part of a baby tooth, in the cervical area, since it is in this area that bacterial plaque accumulates. The vulnerability of the cervical part of the teeth is due to the fact that mineralization of the enamel here occurs after the birth of a child in new and not always favorable conditions. The mineralization process can be negatively affected by the nature of nutrition (natural breastfeeding or artificial), social conditions, as well as various diseases: acute respiratory infections, intestinal infections, etc. The neck of the tooth becomes weakened and after eruption the enamel becomes vulnerable.
Why bottle caries
develops only on the upper central teeth of the child? To do this, you need to remember how the sucking process occurs in young children. During the process of sucking and swallowing, the tongue is located between the lower teeth and the mother's breast (or pacifier, respectively), so the main load (impact) falls on the upper front teeth. It is in this area that food debris and plaque accumulate.
First visit to the dentist
A child’s first visit to the dentist is most often necessary for the following reasons: for a preventive examination upon admission to a preschool or if complaints arise. Don't wait until after the age of four to visit the dentist for the first time. Subsequently, the child needs such visits twice a year. If the baby has already begun the carious process, then during this time it will not be able to spread deeply, caries complications such as periodontitis and pulpitis will not arise, and the tooth can be saved. The sooner the doctor can detect caries, the more successful and painless the treatment will be. Sometimes, in the initial stages of superficial caries, treatment can be carried out without instrumental intervention using mineralizing agents. In this case, medicinal solutions of calcium and phosphorus are applied to damaged areas of enamel. The dentist’s task is not only to provide dental treatment, but also preventive measures that will help keep teeth and gums healthy:
- professional oral hygiene (removal of dental plaque);
- treatment of teeth with calcium and fluoride preparations
- prescribing general treatment if necessary (internal intake of vitamin and mineral complexes);
- teaching your child how to properly brush their teeth;
- correction of the composition and diet, identification of bad habits together with parents;
- sealing fissures (grooves that are located on the chewing surface of the tooth) is a prevention method that is aimed at preventing caries from affecting permanent teeth.
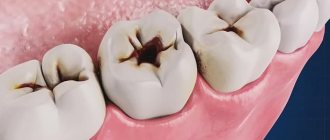
Initial stage of caries: clinical picture
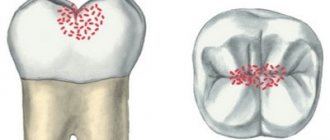
The main cause of any caries is the activity of acid-forming bacteria (Streptococcus mutans and others). Poor hygiene and consumption of large amounts of carbohydrates are the main factors in the formation of dental plaque with an increased concentration of pathogenic microorganisms. The disease clearly demonstrates the mechanism of decay: with initial caries, minerals and trace elements are “washed out” in the enamel. Demineralization of enamel provokes the formation of small light spots: they signal the beginning of the carious process. Under microscopic magnification, these areas appear more porous and rough compared to healthy enamel. The protective properties and aesthetics of the enamel are noticeably reduced, but its structure is not disturbed. This is how initial and superficial caries differ: with the latter, the enamel layer is destroyed, which leads to a corresponding reaction of the tooth (in particular, to a reaction to temperature stimuli).
Stages of initial dental caries
- Chalk spot stage.
At this stage, the stain is white, much lighter compared to healthy areas of enamel. - Dark spot stage.
A more serious form of early caries affecting the deeper layer of enamel. Food coloring penetrates there, causing the stain to become brown or brown.
The process of treating childhood caries
- Step 1: The cavity is treated with a water-cooled high-speed handpiece to remove decayed tooth tissue.
- Step 2. The resulting cavity is treated with an antiseptic solution and filled with filling material. To restore baby teeth, the Grandmed clinic uses special materials that release fluoride ions into the tooth. At the request of the parents and the baby, the filling can be colored.
- Step 3. Excess filling is removed and polished.
- Step 4. The final stage is to coat the filling with protective varnish.
In our clinic, during all stages of treatment, a small patient can watch cartoons. This is done to make dental treatment easier for children to understand.
Prevention of childhood caries
| Prevention begins with proper nutrition of the child - you need to remove all sugar-containing foods in the evening, you need to saturate the child's diet with milk, cheese, cottage cheese, which are rich in calcium and phosphorus, and vitamins for teeth - D, C, A, B and fluoride. We must not forget the importance of solid food. And, of course, one of the most important stages in preventing the development of caries in baby teeth is proper oral hygiene. Our doctors will tell parents and the little patient how to properly care for their teeth. |