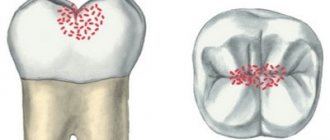
Cervical or basal caries is one of the most dangerous forms of the disease. With this diagnosis, the pathological focus is located in the area of the tooth adjacent to the edge of the gum. It is more difficult to treat due to the difficulty of accessing the carious cavity. The putrefactive process quickly spreads to the root and, faster than other forms, ends with a fracture of the base, that is, loss of the tooth.
What type of caries is this?
Cervical caries is a clinical form of the carious process localized in the neck of the tooth - a small space between the root and crown, covered by the gum. It is also called basal caries. The disease develops regardless of age. Even an infant can get sick if he is fed haphazardly and often given sweetened water.
Based on the number of lesions, cervical dental caries is divided into:
- single – from 1 to 3;
- multiple – from 3 to 10;
- systemic – 10 or more.
The disease may be:
- primary – develops for the first time;
- secondary – develops again after treatment has already been carried out.
And:
- uncomplicated - if the destruction involves only hard tooth tissues - enamel and dentin;
- complicated - when infection penetrates into the dental cavity, root canals and periodontium with the development of inflammation in these tissues (pulpitis, periodontitis).
Cervical caries
Features of filling caries near the gums
Placing fillings in the area near the gums is much more difficult than with other types of caries - approximal or fissure. This is due to some factors that arise during the work process:
- the area near the gums is inconvenient for filling, especially on the upper teeth;
- Saliva gets on the affected area all the time, even placed cotton rolls do not help;
- During the treatment process, blood is always released, which also enters the working area.
The closer to the root a tooth is damaged, the more difficult it is to treat. Due to the fact that cervical caries most often affects the front teeth, you need to choose the color of the material with special care - it should ideally match the color of the enamel, since the aesthetic visual effect plays a role here.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of cervical caries is a bacterial infection that constantly lives in the oral cavity. If the crowns of the teeth are not completely cleared of food, then colonies of bacteria settle on them, forming soft and hard (tartar) plaque. Bacteria secrete enzymes that destroy tooth enamel and penetrate first deep into hard tissues and then into the dental cavity, affecting the pulp, root canals and moving onto the periodontium (the ligament that holds the tooth in the cell).
The localization of the carious process in the neck of the tooth determines the characteristics of its occurrence and course. This:
- the area with the thinnest layer of enamel - about 0.01 mm (average thickness in the crown area - 2 mm);
- the part of the tooth next to the gum is difficult to clean during daily hygiene procedures, so food debris accumulates in it, first soft and then hard plaque (tartar) is formed, destroying the gums, forming pockets between the gum and tooth, where even more food debris accumulates - it creates an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, and their waste products destroy the enamel;
- the neck is covered by the gum, so the onset of the carious process occurs unnoticed, the carious process is detected already at advanced stages, when the body signals it with pain;
- The pathological process proceeds very quickly with the development of complications.
Factors predisposing to the development of caries in the cervical region are:
- poor oral hygiene;
- frequent consumption of sweets without subsequent rinsing of the mouth;
- use of certain medications (glucocorticoids, antibiotics, etc.)
- smoking - poor circulation in the gums contributes to their inflammation and the formation of pockets between the gums and teeth where food gets stuck; smoking also destroys and stains enamel yellow;
- defects in the development of enamel - a thin layer or completely absent, slit-like depressions;
- immunity disorders;
- constant dry mouth, which develops for various reasons - saliva washes away bacteria;
- endocrine disorders of the thyroid and pancreas (diabetes mellitus);
- pregnancy - calcium is used to build fetal tissue.
- occupational hazards - persons at risk are those who work in industries with acids, heavy metals (lead, copper, brass), industrial dust and gases, sudden temperature changes, and infections.
- concomitant diseases - at risk are persons suffering from diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, dysfunction of the salivary glands, vitamin deficiency, as well as those with a family history (having close relatives with multiple or systemic caries).
Additional reasons for the development of caries under the gum
In addition to factors directly related to the impact on the teeth, there are also third-party causes that can provoke the occurrence of a carious process between the gum and tooth.
Let's name the most common ones:
- hormonal or endocrine disorders in the body;
- use of medications that increase enamel porosity;
- lack of certain vitamins, especially group B;
- poor quality of drinking water;
- heredity;
- increased acidity of the body;
- age factor and others.
Taking into account these additional reasons, the treatment of gum caries should not be limited only to the work of the dentist. In this case, it should be comprehensive with the involvement of several specialists, for example, an endocrinologist and others. If the cause is not eliminated, the pathology will return again and again.
Symptoms
A stain on a tooth is a sign of caries
First, if you look closely at the tooth, you can see a small white spot on its frontal surface near the gum. But very often it is covered by gums or tartar, so only a dentist can notice it (this is why it is so important to undergo medical examinations twice a year). The tooth doesn't hurt.
After this, thin enamel and dentin are destroyed quite quickly with infection penetrating into the pulp (soft tissue penetrated by nerve endings and blood vessels). This is a complicated carious process. A person experiences pain when eating cold, hot, sour and sweet foods. The pain is severe and does not go away immediately after rinsing.
The next thing that appears is severe throbbing pain, sometimes accompanied by an increase in body temperature - a sign of periodontitis. If it is not treated promptly, the infection can spread to the soft tissues and bones of the jaw.
Content:
- When the roots are at risk
- Causes
- Symptoms of the disease
- Treatment of cervical caries
- What to do for root caries of incisors
- Preventive measures
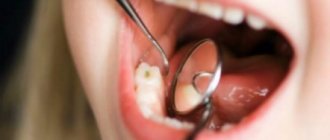
If the carious cavity is located at the base of the tooth (directly in the cervical area), dentists talk about root caries. Compared to other types of carious process, it is considered the most dangerous and rapidly progressing. That is why, when it appears, it is unacceptable to postpone a visit to the dentist until later.
Stages
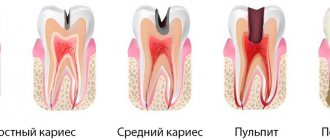
Cervical caries: medium, deep and complicated
Cervical caries occurs in stages. They replace each other faster than in the carious process of other localizations and cause complications more quickly.
Spot stage
The main symptom is a white spot on the enamel. The stain is matte - the enamel loses not only calcium, but also its shine. There are no complaints, only occasionally there is a feeling of a sore throat. If the patient does not visit the dentist for preventive purposes during this period, cervical caries may not be noticed.
Surface
The enamel continues to lose minerals and gradually deteriorates, its surface becoming slightly rough. The color may change from white to yellowish. The sore throat intensifies, and it hurts when eating very cold or hot food. At this stage, the patient may already suspect something is wrong if he carefully listens to the signals of his body. But this rarely happens, so this stage in most cases remains without treatment.
Average
At this stage, there is already complete destruction of the enamel and deepening of the carious cavity to the middle of the dentin layer. The defect is black in color and visible in the form of a hole in the tooth. It can only be missed if the cavity is covered by gums. At this stage, it hurts from the effects of temperature and chemical (sour, sweet foods) irritants, but the pain goes away quite quickly. It is at this stage that most patients turn to the dentist.
Deep
The carious cavity increases in width and depth, reaching the dentin border. A thin layer of dentin separates it from the dental cavity with pulp. The pain intensifies, the tooth reacts to all types of irritants, including mechanical ones - pressure when chewing. The tooth can hurt for a long time and quite severely. Food gets stuck in the resulting cavity.
Circulatory
Circulatory caries in a child with a broken tooth
This caries of the cervical region has its own characteristic features. There is a circular damage to the enamel and dentin of the cervical area and the teeth simply break off. The front teeth are mainly affected, the disease proceeds unnoticed and very quickly, reaching deep stages in weeks and even in a matter of days.
It mainly affects children from infants to preschool age, which is why its second name is bottle disease. In children in the first months and years of life, it is associated with improper frequent feeding without subsequent cleansing of the oral cavity. This leads to the accumulation of food debris on the crowns, the proliferation of bacteria and the destruction of several teeth at once.
In adults, circular cervical caries also occurs; its causes are: impaired immunity, smoking and alcohol abuse, poor oral hygiene, crowded teeth, and malocclusion.
When the roots are at risk
Damage to the cervical area occurs due to the pathological activity of the bacteria Streptococcus mutans. In this regard, this type of dental disorder is no different from the others. The only difference is in its location. So, if ordinary “holes” are located on the side of the dental crown or on its chewing surface, then the root lesion is located at the edge of the gum or even extends under it.
The enamel in this area is easily injured and is very vulnerable. The same can be said about dentin. This means that the destructive process reaches deep dental tissues in a short time. Then pulpitis develops. That is why, even with a slight dark spot, patients with basal caries complain of severe pain.
It is quite difficult to treat the disease due to the proximity of the gum line (especially if we are talking about molars or, even worse, wisdom teeth). The drill can injure the mucous membrane, which prolongs the subsequent rehabilitation period.
How dangerous is the disease?
If cervical caries is not treated, the following complications may quickly appear:
- Pulpitis is an inflammation of the soft tissue (pulp) located in the dental cavity. The infection enters the pulp when hard tissue is destroyed. Symptoms: severe excruciating pain in the tooth, appearing regardless of food intake, including at night.
- Periodontitis is an inflammation of the ligament that holds the tooth root in the cell (periodontal). The infection enters the periodontium through the root canals. The pain becomes unbearable, often pulsating, and intensifies with chewing (mechanical irritation). Fever and general malaise appear.
- An abscess at the root apex is a capsule filled with pus. Severe pain, severe fever, chills.
- Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the jaw bone. The condition is serious and urgent hospitalization is required.
- Periodontitis – inflammation spreads to the periodontal tissues, the gums become inflamed and bleed. Pockets form between the gum and neck, into which food becomes trapped, maintaining the infection. It is painful. Treatment takes a long time and is not always successful; much depends on the patient’s immunity.
- Lateral spread of infection to the necks of adjacent teeth, development of multiple caries.
- Circular lesion of the neck with crown fracture.
If you suspect the presence of a carious process under the gum, you should immediately contact your dentist: complications with this form of the disease develop very quickly!
How to determine the presence of a carious infection
Often this disease is accompanied by such symptoms as:
- pain when cold or hot;
- increased sensitivity of the affected part;
- aching pain that increases at night;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- change in tooth color.
In order to determine the presence of carious bacteria, it is best to contact trusted Dent Prestige dentists. Specialists diagnose the disease through a thorough examination and x-rays.
The presence of professional equipment contributes to the high-quality and quick implementation of the necessary procedures aimed at eliminating the problem.
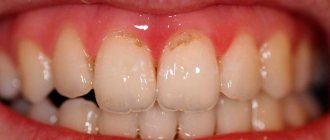
How to distinguish between cervical caries and wedge-shaped defect
Wedge-shaped defect before and after treatment
These pathological processes are similar, but there are a number of significant differences between them. A wedge-shaped defect is a non-carious process. The main reason for its development is the incorrect distribution of mechanical load on the teeth due to occlusion pathology, periodontal disease and endocrine pathology. It is necessary to distinguish cervical caries from a wedge-shaped defect, since these diseases require different approaches to treatment.
Differences:
- wedge-shaped defect (CD) is localized more often on the lateral teeth (canines and molars), which have a high chewing load, and cervical caries (CC) - on the anterior ones;
- externally, the CD initially appears as a small yellowish area on the front surface of the neck of the lateral tooth under the gum; the enamel is not altered or rough; then a gradually deepening V-shaped defect appears; PC is first a white spot, then a black-brown carious cavity;
- CD lasts for years and decades, while cervical caries can reach a deep stage in a matter of weeks.
Diagnostics
The dentist begins by examining the patient's mouth using a dental mirror. If there is a defect in the crown, it is examined using a probe. After this, the doctor prescribes:
- X-ray diagnostics; if cervical caries of only one tooth has been detected, targeted radiovisiography is prescribed to determine its depth and volume; if a general X-ray of the jaw is necessary, an orthopantomogram is prescribed;
- electroodontodiagnostics (EDD) – determination of pulp viability and pain sensitivity of the affected tooth;
- laser fluorescence – illumination of pathological foci using a laser device;
- painting the stain with water-soluble paints (methylene blue or magenta); in places where the enamel is damaged, it becomes permeable to paint and the pathological focus acquires clear contours;
- X-raying the crown using a special lamp to detect any hidden cavities.
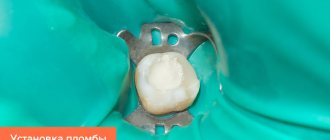
Treatment
Features of the treatment of this form of the disease are that the hard substance (enamel and dentin) in the area of the tooth neck has minimal thickness, so treatment of the resulting cavity may result in penetration into the pulp chamber and be complicated by pulpitis. The proximity of the gums also creates difficulties in treating and filling carious cavities. Cervical caries on the front teeth also requires restoration of the aesthetics of the tooth.
But there is good news: after local anesthesia, the entire treatment is absolutely painless. You can find out how cervical caries is treated and treatment methods at different stages of the disease below.
Treatment at the spot stage
Cervical caries begins with a process of demineralization (the enamel just begins to lose minerals). It can be suspended without instrumental intervention. To restore the enamel, professional teeth cleaning is carried out, then a course of remineralization is prescribed: applications with special products containing calcium and fluoride. To combat relapses, after treatment, the doctor recommends daily use of toothpaste with fluoride and minimal abrasive properties, as well as rinsing with light antiseptics or solutions with fluoride. The course of treatment is 10 procedures plus oral calcium supplements, followed by the use of fluoride-containing oral hygiene products for 1 to 2 months.
Treatment at the superficial stage
Enamel destruction requires instrumental treatment. First, professional teeth cleaning is also carried out, and then the resulting roughness on the enamel is sanded off. The doctor decides individually how cervical caries is treated further. Sometimes a course of remineralization is enough, but in some cases the doctor prepares the cavity, then etches its walls with acid, applying a special gel to improve the adhesion (sticking) of the filling material. Filling should be done with a liquid composite followed by light curing. The filling is ground and polished. Anesthesia is not performed, since enamel treatment is painless. But if gum separation is required, topical anesthesia is sometimes used. All treatment is carried out within half an hour.
Treatment at the middle and deep stages
The treatment process is carried out under local anesthesia. Average caries is treated in one session (30 – 40 minutes). It is carried out: removing plaque, if necessary, pushing back the gums with a special tool, opening and preparing the carious cavity, treating its walls with an antiseptic, etching with acid, applying an adhesive. Installation of a filling for cervical caries at this stage is usually performed on the same day.
Deep caries in the cervical area is treated in two visits. First, plaque is removed, the gums are necessarily pushed back, preparation and medicinal treatment of the cavity are carried out. To combat infection and mineral loss, fillings have to be done in two stages. First, a therapeutic pad with antiseptic and remineralizing properties and a temporary filling are installed at the bottom of the cavity. Return visit after 1 – 2 weeks. If there is no pain during this time, an insulating gasket is placed at the bottom of the prepared cavity. Then a permanent filling is performed.
What can you do at home?
It is impossible to cure cervical caries on your own. Even at the earliest stage, the patient himself will not be able to carry out high-quality demineralization at home; the process will quickly progress with the development of complications. But you can fight this process by preventing its appearance or identifying spots at the earliest stage. At home, the main thing is the prevention of cervical caries.
Clinical researches
The products in the Asept line have proven clinical effectiveness and are therefore sold in pharmacies. For example, multiple clinical studies have proven that regular use of preventive toothpaste ASEPTA ACTIVE for a month can reduce bleeding gums by 60%, improve the overall condition of the oral cavity by 44% and reduce inflammation by 33%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
Prevention
To combat the development and recurrence of the carious process, you need:
- stop consuming large amounts of easily digestible carbohydrates - sweets, baked goods, sweet carbonated drinks;
- do not have frequent snacks;
- regularly include dairy products in the diet, which the body needs as a source of calcium and phosphorus;
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush and use toothpaste recommended by your dentist (the choice of toothpaste depends on the condition of the teeth, heredity and the fluoride content of the water in the area);
- After each meal, rinse your mouth thoroughly and use dental floss or an irrigator to clean the interdental spaces;
- visit the dentist twice a year to identify and prevent the initial stages of cervical dental caries, and carry out professional cleaning.
If you regularly adhere to these requirements, you can maintain healthy teeth for a long time.
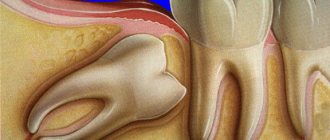
Wisdom tooth caries - treat or remove?
It is important to remember that the carious process cannot be left to chance even at the initial stage: the infection spreads quickly, and even healthy organs of the oral cavity can soon be affected. It's time to answer the question that torments many: if wisdom tooth caries is detected, what to do - therapy or removal?
Removal of a wisdom tooth with caries is indicated
- A wisdom tooth is a rudiment that is practically not used in the chewing process, and there is little benefit from it.
- Eights are located far away, access to them is limited, which makes it very difficult to provide quality treatment. This increases the likelihood of re-infection.
- The therapy is tiring for the patient because he has to sit with his mouth wide open throughout the entire procedure. This is especially true for the treatment of caries of the upper wisdom tooth.
As a rule, removal is indicated in cases where the tooth is dystopic and/or impacted, constantly injures the cheeks and tongue, and causes inflammatory processes due to difficult eruption. Whether to remove a wisdom tooth with caries, if it grows normally and does not cause any problems, should be decided individually together with a specialist.
What to do if a tooth hurts after treatment of cervical caries
If a slight pain after removal of cervical tooth caries lasts 2–3 days and gradually subsides, then this is normal. If there is severe, increasing pain, as well as an increase in body temperature or malaise, you should immediately consult a dentist. Possible reasons:
- insufficiently thorough treatment of the carious cavity before filling led to the spread of infection and relapse of the disease, including perforation of the dentin barrier, penetration into the pulp and the development of a complication - pulpitis; the dentist will remove the filling, open the tooth cavity and treat pulpitis; and only then can it be re-sealed;
- periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontal tissues) – the gums become swollen, painful, their edges move away from the crown, and bleeding may occur; this condition also requires dental treatment.
How does the removal work?
If there are indications for the removal of wisdom teeth with caries, the procedure is performed exclusively by a dental surgeon. Depending on the condition of the tooth and the characteristics of its development, simple or complex extraction can be performed.
Simple removal involves the usual manipulation of tooth extraction using forceps. But such a procedure is only possible if the only pathology is caries.
Most often, third molars require complex removal, which involves dental surgery and surgery. Complex removal is necessary for pathology of the root system, destruction of more than 50% of the tooth surface, dystopia or retention. During the procedure, the dentist may resort to cutting soft tissue, breaking the tooth and removing it in parts and other manipulations.
After removal of wisdom teeth with caries, an x-ray diagnosis is required to exclude remnants of parts of the tooth or root. After this, stitches are applied.