Toothache during pregnancy is common. During this period, changes in the hormonal background of metabolism occur, and the woman’s body becomes very vulnerable. Pregnancy often serves as a catalyst for oral problems. Teeth begin to react to cold and hot. Painful sensations occur during hygienic cleaning, and gums may bleed. The acidity of saliva increases, the dentition is exposed to increased bacterial load.
There are more than enough reasons for toothache. Even with regular oral care and visits to the dentist, almost half of women during pregnancy experience caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and other inflammatory dental pathologies. If your tooth hurts during pregnancy, you should immediately go to the dentist.
Toothache cannot be tolerated, especially during pregnancy. Painful attacks negatively affect the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems and can provoke involuntary contractions of the uterus and even premature birth. The opinion that it is undesirable to treat teeth during this period is a dangerous misconception. Even initial caries during pregnancy progresses much faster. Modern dentistry offers many effective means and treatment methods that are safe for the expectant mother and baby. The doctor selects treatment individually, according to the clinical picture and stage of pregnancy.
What symptoms should you consult a doctor for?
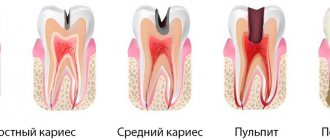
Any acute inflammatory diseases of teeth and gums are subject to urgent treatment. Even the smallest carious cavity is a source of infection, potentially dangerous for the developing fetus. If a carious tooth is not treated in a timely manner, pulpitis and periodontitis may develop, accompanied by severe pain and other symptoms.
You should immediately go to the dentist if the following symptoms appear:
- tooth reaction to cold, hot, sweet;
- pain (sharp, aching, throbbing);
- bleeding gums;
- pain when biting, chewing;
- redness, swelling of the gums;
- bad breath;
- purulent discharge
Urgent help
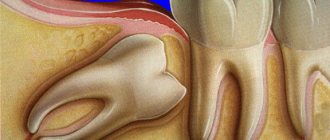
necessary for injuries - fracture of the tooth root, chips, cracks of the coronal part, damage to the pulp.
In the normal course of pregnancy, in the absence of risk factors for the mother and fetus, treatment of emergency or potentially dangerous conditions is carried out at any stage (in any trimester). The main contraindication to treatment is the threat of miscarriage. Each trimester has its own characteristics that determine the choice of treatment method.
Why do teeth hurt during pregnancy?
A pregnant woman may become a frequent visitor to the dentist. This is due to several factors:
- increased acidity of the oral cavity due to toxicosis;
- changes in hormonal levels, and, as a result, changes and metabolic disorders;
- lack of microelements and vitamins in the body.
All this provokes the occurrence of caries and inflammation of the gums and mucous membrane; may cause pain. You should not endure inconvenience: the psychological state of a pregnant woman is no less important than her physical health.
The changes that occur in the body due to pregnancy can also trigger the development of dental diseases.
How to relieve pain yourself
Rinsing with a soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per glass of warm water) will help temporarily relieve toothache during pregnancy. You need to rinse your mouth more often, every 2 hours. In addition to soda, you can use Furacilin solution, decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, oak bark, yarrow.
Not recommended
use herbs containing essential oils (sage, eucalyptus, peppermint, cloves, etc.), they can cause severe uterine cramps.
Severe dental pain during pregnancy can be treated with a suitable anesthetic. Steroid-based drugs and drugs that penetrate the placental barrier are contraindicated.
Treatment errors
Some measures that are generally considered useful are highly discouraged. Please note common mistakes:
- Applying Aspirin to the gum. The tablet is effective, but it has an aggressive effect. In this case, there is a high risk of gum burns.
- Drinking alcohol. Firstly, after it stops working, the pain will only get worse. Secondly, alcohol-containing drinks have an extremely negative effect on the body of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
- Applying a heating pad to the cheek. After this manipulation, inflammatory processes are even more disturbing.
- Consuming honey. Do not use folk remedies that contain this product, as it only promotes the development of caries.
- Rinse your mouth with cold water and apply ice to your cheek. Such actions lead to complications that have dangerous consequences.
It is not recommended to apply ice to the cheek as such actions lead to complications
Attention! It is also not recommended to press on the gums with your hands and chew on the sore side. Wash your hands thoroughly before touching a sore tooth or gum.
- How to store urine for analysis before submitting it to the laboratory for a child and an adult
What painkillers can pregnant women use for toothache?
The most suitable painkillers approved by WHO are Paracetamol, No-shpa
(or its analogue
Drotaverine
).
Children's gels will help reduce pain - Kamistad
,
Kalgel, Dentol-baby
. These are specialized products designed to reduce pain during teething. They pleasantly cool the gums and relieve inflammation.
You must understand that taking medication is a last resort before seeing a doctor. Tablets will temporarily relieve pain, but will not get rid of the underlying problem. Pregnancy is not a disease, but a special physiological state, so treating teeth during pregnancy is not only possible, but necessary.
Whims or symptoms of gingivitis during pregnancy?
The first symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women begin to appear between 8 and 12 weeks. Expectant mothers, as a rule, suffer from two forms - catarrhal and hypertrophic; ulcerative gingivitis develops less often.
Catarrhal gingivitis
This form of the disease is manifested by the formation of a fairly large amount of soft yellow plaque on the surface of the teeth, swelling of the gums, their soreness and significant bleeding when pressed with a sharp object. Catarrhal gingivitis is characterized by the spread of inflammation over the entire surface of the gums, sometimes the process affects the tissues of both the upper and lower jaws.
Hypertrophic gingivitis
The first symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis usually appear no earlier than the twentieth week of pregnancy. Inflammation affects the lower jaw, gums in the area of incisors, canines and small molars. The hypertrophic form of gingivitis is characterized by an increase in the volume of gum tissue, an inflammatory process in it and bleeding. Gum pockets also appear - grooves formed between the tooth and gum due to the growth of gum tissue.
Ulcerative gingivitis
The most severe form of gingivitis occurs in pregnant women. It occurs against the background of serious health problems accompanying pregnancy, in the last trimester, or under the influence of stressful situations. The main signs of ulcerative gingivitis are severe itching, burning, bleeding of the gums, swelling and ulceration.
When is the best time for pregnant women to have their teeth treated?
If a woman took a responsible approach to pregnancy and had her teeth treated in advance, she still needs to visit the dentist regularly for preventive examinations. This will allow you to detect pathology at an early stage and use the safest treatment methods. When performing any dental procedure, not only the woman’s well-being matters, but also the duration of pregnancy. Each trimester has its own characteristics and risks that determine the choice of treatment method.
First trimester
1st trimester
– period
from 1 to 12 weeks
inclusive. At this time, the formation of organs and structures of the embryo occurs. The placenta does not yet protect the fetus well enough from external influences, and the woman’s body undergoes serious changes: hormonal, physiological, metabolic. Any interventions, including medications, can negatively affect the pregnancy process and the health of the baby.
If a pregnant woman has a toothache in the 1st trimester, treatment is carried out mainly using gentle methods
(ICON, ozone therapy, air abrasive method). For pulpitis, periodontitis, accompanied by acute pain and purulent discharge, local anesthesia based on articaine (Ultracaine, Melivastesin, Mepifrine, Skadonest) is used.
Second trimester
2nd trimester
– period
from 13 to 24 weeks
.
This is the safest time
for dental treatment, gum treatment, professional hygiene and other dental interventions. The tissues, organs, and systems of the fetus have already been formed; the placenta reliably protects the baby from external factors. All planned procedures are recommended to be performed during this period.
Third trimester
3rd trimester
– the period
from 25 weeks to childbirth
, quite difficult for a pregnant woman.
The stress on the body increases, the placenta becomes more susceptible to external factors. Treatment is carried out exclusively for acute conditions
that are dangerous for the mother and child. Planned procedures are postponed until the baby is born.
If there is a need for dental treatment in a pregnant woman, a new generation of anesthetics based on articaine is used. The components of these drugs do not penetrate the placental barrier, do not affect the uterine and placental blood flow, do not increase the tone of the uterus, and are safe for the expectant mother and child. An alternative to local anesthesia is treatment under sedation (during sleep).
What procedures are allowed during this period, and which are strictly prohibited?
Pregnancy imposes a number of restrictions on treatment, including dental treatment.
Acceptable:
- Treatment of caries, especially in the very initial stages. If the tooth is barely touched, you can even do without anesthesia. In case of increased sensitivity, use a spray with a minimal content of adrenaline.
- Fluoridation, enamel whitening. These manipulations are classified as absolutely safe procedures.
- Gum treatment. It can be carried out in any trimester using anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Installation of crowns and removable dentures. It will not harm either the expectant mother or the child.
- Removal of a tooth. At the level of modern medicine, it is considered a relatively safe manipulation for pregnant women, but it is performed in extreme cases
Forbidden:
- Dental implantation due to the need to take strong medications.
- Removing "eights". Severe trauma to the jaw occurs: a large wound surface can become a source of infection.
- Bite correction. During pregnancy, a woman's body loses a lot of calcium, so braces are likely to cause tooth decay. If pregnancy occurs already during treatment, it is interrupted until the birth of the child.
- Use of general anesthesia for pain relief.
Carrying out local anesthesia with special preparations containing a minimum percentage of adrenaline and calculating the correct dosages is not considered dangerous to the fetus.
Is it possible to do x-rays?
Contrary to popular belief, X-rays can be taken during pregnancy. For this purpose, computer radiovisiographs are used. The radiation dose received by the patient when using a visiograph is minimal. If possible, the study should be carried out in the 2nd trimester
, excluding cases where urgent help is required - severe, acute pain in the teeth during pregnancy. X-ray examination is carried out observing all possible means of protecting the fetus.
“Fighting” radiation on the visiograph, women calmly fly south to eat fruit and bask in the sun. Not knowing that during a 2-3 hour flight a person receives 20-30 μSv. This is a radiation dose equivalent to 10-15 images on a visiograph. Ionizing radiation differs from light rays only in wavelength and has a damaging effect only under certain conditions.
Is it possible for pregnant women to have dental x-rays?
Pregnancy is not considered a contraindication for dental radiography. Images are taken using computer radiovisiographs, which deliver a very small dose of radiation. The woman’s body is covered with a special protective apron, and the radiation beam is directed towards the jaw area.
However, such a procedure should be performed only when absolutely necessary and should be limited to taking pictures of one or two teeth. Long-term planned treatment, which periodically requires radiography, is best postponed until the birth of the child and completion of breastfeeding.
Recommendations to help avoid problems
In order not to become one of the pregnant women suffering from gingivitis (and, according to statistics, there are more than 60%), you must adhere to simple rules.
- Carry out the necessary hygiene procedures regularly: brush your teeth using a toothbrush with soft bristles, and do this as thoroughly as possible, use floss and antiseptic rinses.
- Avoid excessive amounts of sweets and consume sweets, chocolate and cakes in moderation. It is strongly recommended to refrain from chewing toffee and caramel, since the remains of viscous delicacies can accumulate in the periodontal space of swollen gums, provoking particularly active proliferation of microorganisms.
- Eat more vegetables and fruits, paying special attention to foods containing vitamin C.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women cannot be postponed until later. Occurring due to changes in hormonal status and the growth of microbial microflora, it provokes even more active proliferation of bacteria, which in the most severe cases can cause intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Experts' opinion
As a result of clinical experiments using the Asepta series of products, conducted at the Kazan State Medical Academy, the complex use of anti-inflammatory drugs from the Asepta line contributed to faster relief of inflammation, the combined use of balm, gel, rinse, toothpaste and vitamin-mineral complex mutually enhanced the therapeutic effect did not require daily visits to the dentist.
Sources:
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
- https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennye-lechebno-profilakticheskie-sredstva-dlya-individualnoy-gigieny-polosti-rta Silantieva E.N., Berezina N.V., Krivonos S.M. Complex treatment of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis using drugs from the Asept line, Practical Medicine journal
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
How to treat?
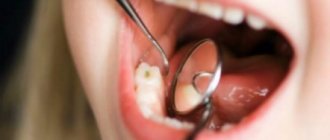
Gum treatment should be done in dentistry. First of all, you need to establish an accurate diagnosis, with a 90% probability that it will be gingivitis. This pathology is typical for pregnant women. First, you need to professionally clean the enamel from plaque and remove hard deposits using ultrasound. Don't worry, it's completely painless and not contraindicated when carrying a child.
In most cases, to eliminate the pathological process, you have to resort to drug therapy. The doctor prescribes only those drugs that are approved for use during pregnancy. Oral rinses with antiseptic solutions such as Miramistin are usually prescribed. Applications with anti-inflammatory plates are also indicated, and sometimes wound-healing ointments for topical use are indicated. In more serious cases, antibiotics may be needed.
Additionally, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs. Chamomile, sage or St. John's wort will do.
Preventive actions
To protect your oral health while bearing a child, you need to follow a number of preventive measures:
- During toxicosis, try to drink more water to maintain optimal microflora in the oral cavity.
- After eating carbohydrates, try to brush your teeth or use mouthwash.
- Buy toothpaste with extracts of medicinal herbs aimed at strengthening gums.
- Avoid eating foods that are too hot to avoid getting burned.
- Do not self-medicate. If you have problems with your gums, be sure to see a dentist.
- Massage your gums every day. An excellent massage effect can be achieved using an irrigator or finger pads. Such measures prevent stagnation and improve blood circulation in the gums.