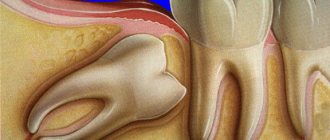
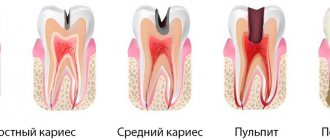
During pregnancy, the processes of destruction of her teeth are activated in a woman’s body, and problems with their treatment often arise. Why does this all happen and how to deal with this problem?
During pregnancy, hormonal changes begin in a woman's body, which are aimed at the full development of the fetus. However, such adjustments do not always go unnoticed for a woman and she develops some problems, for example with her teeth.
Naturally, not all women’s teeth begin to decay. This applies to those pregnant women who have previously completely and efficiently treated all their problem teeth and other diseases that appear in the oral cavity. But life makes its own adjustments to pregnancy: very often women do not treat their teeth enough, which, of course, will then have a very negative impact on the integrity of the teeth.
Why do teeth hurt during pregnancy?
Very often, the cause of toothache lies in the exacerbation of existing diseases - caries, periodontitis, gingivitis, pulpitis. A cutting wisdom tooth or tartar can also cause pain.
However, sometimes toothache is directly related to pregnancy.
There is such a thing as gingivitis in pregnant women - rapidly developing gum disease against the background of toxicosis and changes in hormonal balance, in which inflammation occurs more intensely than usual.
Another reason why pregnant women’s teeth literally begin to “crumble” is the formation of bones in the fetus and their active growth. If there is a deficiency of calcium, vitamins D3 and K in the body of a pregnant woman, the fetus has nothing to “build” a skeleton from, so it begins to “pull” the substances it needs from the mother’s body. And the depots of calcium and phosphorus are teeth and bones. Therefore, if the expectant mother’s diet does not have enough calcium, then the teeth will begin to decay very quickly.
Many pregnant women do not associate their toothache with calcium deficiency, since the expectant mother receives quite a lot of calcium - it is also found in milk, cheese, other dairy products, fish and even in some plants, for example, chia seeds. But in order for calcium to be absorbed, the body must have vitamins D3 and K, but a pregnant woman’s diet may not have enough of them, unless she takes specialized vitamin-mineral complexes. The fact is that the main sources of these vitamins are not very popular products. Thus, a person can get vitamin D3 from animal fats (fish oil, margarine), and their consumption during pregnancy is reduced so as not to gain excess weight. The main sources of vitamin K are spinach, cauliflower and nettle leaves, and its content in other vegetables and fruits is low. But vitamins D3 and K are consumed in huge quantities during pregnancy.
Also, early toxicosis of pregnant women greatly affects dental health: frequent vomiting oxidizes the environment of the oral cavity, provoking the development of diseases that already exist, but previously did not bother the woman, and pass without any special external manifestations. Nausea forces pregnant women to carefully choose food, often not paying attention to its nutritional value, only to the absence of irritating smells and tastes. Thus, the body may not receive vitamins, the lack of which provokes even more severe attacks of toxicosis.
But the reasons listed above do not mean at all that toothache is an obligatory companion for the expectant mother. Let's see what can be done to prevent toothache during pregnancy.
Fetal development destroys mother's teeth
What is the mechanism of tooth decay during fetal development during pregnancy? First of all, a developing baby, of course, eats. To build a full-fledged skeleton, the developing fetus has to take a lot of “building material,” in particular calcium, from the blood plasma of its mother. If the calcium content in the plasma becomes insufficient for the development of the child, this substance begins to be actively washed out of the bone tissue of the pregnant woman, and then is sent to the fetus.
In a normal situation, minerals are constantly washed out of the teeth, but at the same time, through saliva, these same elements re-enter the hard tissues of the teeth. However, during pregnancy the composition and amount of saliva also changes, which is no longer able to replenish the loss of calcium and other important elements. In addition, due to changes in the quality of saliva, its antibacterial and protective functions are disrupted, which are excellent for fighting germs in the mouth, and during pregnancy, bacteria begin to actively develop on the surface of the teeth and gums. These microorganisms, as a result of their vital activity, lead to the appearance and development of carious diseases.
How to save teeth during pregnancy
First of all, even if the teeth were in perfect order before pregnancy, the expectant mother should remember about prevention:
- brush your teeth not for twenty seconds, but for three minutes, thoroughly and regularly;
- use dental floss, preferably after every meal;
- use suitable gentle toothpastes, avoid whitening pastes;
- change your toothbrush once a month;
- try not to eat food that injures the gums and mucous membranes.
The second important point: take vitamins and minerals, especially vitamins D3 and K. It is most convenient to choose a vitamin and mineral complex for pregnant women, which will also contain other micronutrients necessary for the proper formation and development of the fetus.
In addition, some complexes for expectant mothers help reduce the symptoms of toxicosis (nausea and vomiting, which affect the acid-base balance in the oral cavity), especially if they contain vitamin B6. For example, the Pregnoton Mama vitamin and mineral complex (designed so that it can be taken by women before, during and after pregnancy) contains vitamins B6, D3 and K, as well as other vitamins and minerals necessary for the body of a pregnant woman in precisely calculated doses . The fetus will not take them from the mother’s body, and toxicosis will minimally affect the acid-base balance, without provoking the development of caries, periodontitis and gingivitis.
As for calcium intake, as a rule, calcium is included in vitamin-mineral complexes for expectant mothers purely nominally, that is, in too small dosages. Therefore, discuss with your doctor whether you should take calcium supplements separately, or whether you need enough calcium in your diet.
Unfortunately, often expectant mothers do not think about prevention and “remember” their teeth when they have already become a source of trouble. So what to do if your teeth hurt, are loose, and your gums are red, painful or itchy?
Oral care during pregnancy
The oral cavity during pregnancy and lactation requires increased care and careful care. Basic hygiene rules do not differ from typical standards. But when a woman does not properly care for her teeth, she has serious problems. Gums may bleed and teeth may break off. At an appointment with a dentist, they identify and draw up a therapeutic plan, which includes activities to teach proper care. Observations have shown that insufficient hygiene activates the processes of crown destruction. When toxicosis occurs, many people undergo formal teeth cleaning. In addition, to get rid of nausea, women in labor constantly eat something. In such a situation, pathogenic bacteria quickly multiply, hard tissues are destroyed, and not only caries develops, but also periodontitis and pulpitis.
Today, dentists offer pregnant women caries treatment using the Icon system. Infiltration is used when the tissue is affected by no more than 1/3 of the thickness of the dentin layer. Pregnant women tolerate this therapy well. It does not harm the embryo, since no anesthesia is used. Caries of several units can be removed in one session. The procedure is painless and lasts 20-30 minutes. Basic principles of proper oral care:
- Since the enamel becomes thin and vulnerable, use a brush with soft or medium bristles.
- The brush must be changed after 2 months.
- It is not recommended to use pastes that contain a lot of fluoride, so as not to harm the little one.
- It is better to use pastes with a high calcium content.
- You should brush your teeth twice a day and rinse your mouth after eating.
- Once every 6 months you need to have your teeth professionally cleaned using approved methods.
- Promptly carry out therapy of masticatory organs using gentle technologies.
At the time of pregnancy, treatment of caries, non-carious lesions, periodontitis, and tooth extraction for medical reasons is allowed. The principles of hygiene during pregnancy do not change. But the procedures must be performed carefully, taking into account the processes that occur in the body of the expectant mother.
Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
The modern level of development of dentistry makes it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy. Of course, we are not talking about prosthetics or bite correction. But the dentist will be able to cope with caries, tartar or pulpitis. It is important to inform your doctor about your pregnancy, as this will help you choose the safest pain reliever that does not contain adrenaline.
The second trimester of pregnancy is traditionally considered the most appropriate time for dental treatment. This period is, in principle, the most stable of all nine months of gestation. But if a woman suffers from acute pain or the disease develops quickly, regardless of the trimester, she should consult a dentist and have the aching tooth treated.
Any inflammation takes away the body's strength, makes you experience pain and worry. All this affects both the woman and the unborn child, therefore, if a tooth hurts badly during pregnancy, there is no need to wait and hope that everything will go away on its own, it is better to consult a dentist as soon as possible.
Sources
- Kiselnikova L.P., Popova N.S. Dental status and prevention of dental diseases in pregnant women // Clinical dentistry. – 2011. – No. 1.
- Kuzmina E. M. Prevention of dental diseases in pregnant women and young children. Guidelines. – M., 1999. – 36 p.
- Ubertalli James T., Hingham, MA Gingivitis // MSD Handbook. The version is available at: https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/home/oral-and-dental diseases/periodontal diseases/gingivitis
THIS IS NOT AN ADVERTISING. THE MATERIAL WAS PREPARED WITH THE PARTICIPATION OF EXPERTS.
Other causes of tooth decay in expectant mothers
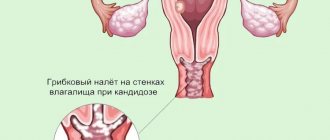
There are some other reasons that also lead to tooth decay in a woman during pregnancy. So, one of the additional issues may be gingivitis , that is, inflammation of the gums. With gingivitis, symptoms such as pain, bleeding, and redness are often observed. Bleeding gums occur when brushing your teeth and even while eating. These inflammatory conditions in the mouth promote the accumulation of microorganisms that begin to destroy teeth and worsen the symptoms of gingivitis. Also, in places called periodontal pockets, hard tartar begins to accumulate, on which even more pathological bacteria settle. Such processes, if treated insufficiently or completely absent, can lead to the loss of diseased teeth.
The infectious component present and accumulating in the mouth creates a permanent focus of the disease,
which can spread not only to neighboring teeth, but also to many other organs of the female body. Women who have inflammatory gum diseases, such as periodontal disease, gingivitis, periodontitis and others, can lead to the development of late toxicosis in the last weeks of pregnancy.
Knowing all this, a woman should immediately consult a doctor when the first symptoms of dental and gum disease appear.
Treatment of caries during pregnancy at Dentistry on Shchelkovskaya
Finally, we will tell you what the main feature of visiting a dentist during pregnancy in our clinic is. The fact is that a pregnant woman is often subject to changes in her emotional state, so our dentists show sensitivity and attention to the patient’s condition, protecting her from any kind of physical pain and emotional stress. The dentists of the clinic on Shchelkovskaya perfectly understand the specific health and emotional background of a pregnant woman, so they do everything in their power to make your visit to the doctor calm and pleasant.
The most important thing that you should not do during pregnancy is to ignore toothache and allow the development of oral diseases. Remember that your baby’s health depends on your vigilance. Therefore, even if you feel slightly unwell, or have periodic aching pains, do not tolerate it, make an appointment with a dentist now! Treatment of caries during pregnancy at any stage of development is possible in our clinic. We work seven days a week, located in the Eastern Administrative District in the Izmailovo district at Shchelkovskoye Highway, building 44, building 5. Near us are Golyanovo, Pervomaiskaya, Partizanskaya, Cherkizovskaya.
Dental care if teeth begin to crumble.
The dentist will select the appropriate method for restoring the integrity and natural appearance of the tooth. The choice largely depends on the degree of its defeat.
Mineralization
A strengthening procedure during which applications containing calcium and fluoride are applied to damaged teeth.
Fluoride coating of teeth
The procedure also strengthens the enamel, but special fluoride-containing pastes are used.
Sealing
If a tooth is slightly crumbled, it can be restored using filling material.
Veneers
Used if the front tooth has crumbled. Ceramic onlays will perfectly restore the beauty of your smile.
Tabs
When the chewing tooth is destroyed by 50%, reliable inlays are saved. They are more durable and airtight than fillings.
Crowns
If the tooth is left with virtually no crown part, prosthetics should be performed with ceramic crowns - excellent for front teeth, and zirconium - for chewing teeth.
Removal followed by implantation
When a tooth has crumbled and only the destroyed root remains, it must be removed and, if possible, an implant and crown should be immediately installed on it.
What to do if the tooth is completely crumbled
The crown part of the tooth has completely crumbled, what should I do? You must make an appointment with a doctor at a dental clinic within two days. After the x-ray, it will be clear whether the root is preserved, what condition it is in, and whether removal is necessary. Then possible recovery options:
- prosthetics (stump inlays, pins, crowns and bridges);
- implantation (implantation of a titanium artificial root into bone tissue followed by installation of a crown).
In any case, modern techniques are sufficient to compensate for any loss of teeth.
Benefits of temporary prosthetics during pregnancy
- absolutely harmless and biocompatible product materials;
- no need for significant preparation of tooth tissue;
- relative ease of installation of prostheses in a short time (on average 3 days);
- elimination of imbalance and dysfunction of the lower jaw;
- prevention of unwanted movement of teeth to free areas of the jaw and changes in their inclination (all this may require additional orthodontic treatment after childbirth);
- ensuring complete chewing of food, which prevents gastrointestinal disorders and creates conditions for the proper absorption of vitamins and microelements necessary for the full development of the developing child;
- eliminating empty space between teeth, which prevents gum recession in adjacent teeth and bone atrophy;
- maintaining facial aesthetics;
- elimination of psychological discomfort: while expecting a child, it is useful to please yourself as often as possible; eliminating visual dental defects will help the expectant mother improve the quality of her emotional state;
- absence of discomfort and rapid adaptation of soft tissues in the oral cavity to the replacement structure in the area of the missing tooth.
Can pregnant women have anesthesia?
There are a large number of clinical studies on the safety of local anesthetics in the treatment and extraction of teeth in pregnant women. In Table No. 1, you can see 5 local anesthetics that can be used in pregnant women according to the FDA (corresponding to safety categories B and C). First of all, these are well-known anesthetics such as, for example, Lidocaine or Ultracaine DS, etc. The table also shows the permitted concentrations of vasoconstrictors.
Table No. 1 –
*according to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration, USA)
It should be noted that the use of a vasoconstrictor (vasoconstrictor component) not only allows you to reduce the dose of the administered anesthetic and increase the duration of its action. The presence of a vasoconstrictor makes it possible to reduce the possible systemic toxic effects of the anesthetic. This occurs due to the fact that the vasoconstrictor slows down the entry of the anesthetic into the bloodstream from the injection site, and therefore allows for a reduction in peak concentrations of the anesthetic in the blood (24stoma.ru).
The safety of the use of vasoconstrictors in pregnant women has been shown in many clinical studies (for example, the study by Haas D. “An update on local anesthetics in dentistry”). It is known that vasoconstrictors do not affect uterine blood flow - provided their dosages and anesthesia technique are observed. It is optimal to use the vasoconstrictor epinephrine at a concentration of 1:200,000, and to minimize the systemic effect of epinephrine in pregnant women, it is important to perform an aspiration test during each injection, because it will guarantee the absence of intravascular administration.