Children's teeth appear in a certain sequence and in pairs (for example, two central incisors or two canines). But often the timing of teething in children shifts upward: many parents begin to worry and get nervous, but this is not worth doing, since the deviation from the norm is explained by the individual characteristics of the body, the uncharacteristic course of pregnancy, or various injuries received during childbirth.
Teething in children and features of this process
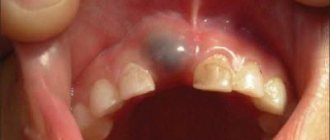
Quite often, a few weeks before the appearance of a baby or molar tooth, a lump filled with a clear or bluish liquid forms on the gum. Naturally, it worries parents, but there is no pathology in this formation, and the lump, which does not look very aesthetically pleasing, does not indicate the beginning of the inflammatory process. In most cases, no intervention by a doctor is required. You can contact the dentist if the lump increases in size: the doctor will make a small incision and release the liquid.
Baby teeth in children: order of eruption
Any newborn baby has follicles of milk teeth (20 pieces) and molars (16 pieces) inside the jaws. The remaining 16 rudiments will form later.
Teething in infants begins with the lower jaw: first the central incisors appear (6-10 months of the child’s life), then the canines (10-13 months), then comes the turn of the first (14-18 months) and second (17-23 months) molars .
Emerging teeth differ from adult teeth in having low-mineralized enamel. If you do not maintain oral hygiene, caries may begin to develop. In addition to careful adherence to hygiene rules, special gels and ointments that significantly accelerate the mineralization process will help make teeth stronger and more resistant to pathogenic microorganisms.
Teething
According to the tradition of many peoples of the world, there is a custom of giving gifts to a child on the occasion of the appearance of the first tooth. This ritual symbolizes wishes to the baby for health, happiness and long life. The appearance of a baby’s first tooth is a solemn moment for relatives and parents, but at the same time, teething can also be a “restless” period for parents and the baby. I would like to reassure parents and orient them to the fact that teething is a physiological process and must be approached philosophically. As if it were inevitable. And timely and correct teething is a guarantee of a healthy future child.
What is teething?
Teething is the process of vertical movement of a tooth from its origin and development within the jaw until a crown appears in the oral cavity. The process of teething begins after the crown has finally formed and is accompanied by its further development and growth of the jaw bones. Signs of physiological teething are: timeliness, sequence of eruption of certain groups of teeth and pairing.
There are temporary teeth (more often called milk teeth) and permanent teeth. According to the number of teeth, the primary teeth are 20, the permanent bite is 32 teeth. According to modern data, the period for the eruption of the first temporary teeth is usually considered to be from 4 months. The end of eruption is 3-3.5 years. Most often, the first teeth appear at the age of 6 months, and as a rule, the teeth on the lower jaw erupt first - the central incisors, then the lateral incisors, canines and molars. The timing of teething can vary from 4 months to 2 years (early teething) or from 8-10 months to 3.5-4 years (late teething).
Average time for eruption of primary teeth according to (R. Illingworth, 1997)
| tooth | Timing of eruption (month of life) | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | |
| Central incisor | 6 | 7,5 |
| Side cutter | 7 | 9 |
| First molar (chewing group of teeth) | 12 | 14 |
| Fang | 16 | 18 |
| Second molar (chewing group of teeth) | 20 | 24 |
It should be noted that the quality of nutrition, sanitary and hygienic conditions and pathological conditions of the child (rickets, hypovitaminosis, intoxication, states of oxygen starvation, the nature of feeding, etc.) significantly affect the process of teething. For example, disordered teething with disruption of the time intervals between groups of teeth, delayed eruption may be a manifestation of a pathology such as rickets.
Adverse effects during teething
Temporary teeth are not permanent, that’s why they are called that. As the child grows and develops, after a certain period of time, all 20 primary teeth will be replaced. As an exception, in individuals, milk teeth do not change, remaining in adulthood (most often this occurs due to the absence of the rudiments of permanent teeth).
When primary teeth erupt, the child is in a state of “stress” and can often manifest itself with general somatic disorders. The first signs of teething, often the main ones, are the appearance of swelling of the mucous membrane of the gums in the projection of the erupting teeth. Profuse salivation appears, the child may be irritated and tearful. The eruption of central teeth often occurs without any manifestations, except for swelling of the gums and profuse drooling. When the chewing group of teeth erupts and a larger area of the gum mucosa is involved, a secondary infection may occur if the resistance of the child’s body decreases. Symptoms such as increased body temperature, upset bowel movements, redness of the mucous membrane of the gums in the mouth, decreased appetite may appear. To relieve the annoying itch, the child begins to “drag” fingers and various objects into the mouth (toys, sucking the edge of clothing, a blanket) to scratch gums, thereby can damage and infect the mucous membrane. Which can manifest itself as erosive rashes. And aggravate this condition.
How can you help your child when they are teething?
To relieve itching of the gums in a child, it can be recommended to give hard vegetables or fruits (peeled apples, carrots), or a crust of bread to chew. It is good to massage the gums with special “teether” rings or a toothbrush (silicone, or a regular baby brush with soft bristles). Some rings can be pre-cooled, but you should carefully inspect these devices and purchase them in special places in order to avoid counterfeit, uncertified goods and subsequently not harm the baby’s health, so that the child does not get hurt. If the temperature rises, antipyretic drugs can be given. To reduce the sensitivity of the mucous membrane and reduce pain in pharmacies, pharmaceutical manufacturers offer special anesthetic gels for topical use. But we recommend using these drugs only as prescribed by a doctor, so as not to cause allergies in the baby and not miss more severe complications. Contact a pediatric dentist who will conduct an examination and give qualified prescriptions to improve your well-being.
Changing temporary teeth
Permanent teeth most often appear between 5.5 and 7 years of age. Their eruption practically occurs in the same sequence as temporary teeth. The lower central incisors appear first, then the upper central incisors, and in parallel, and sometimes earlier, the first large molars erupt (the first molars, or by their number, they are called “sixths”). Please note: The sixth teeth do not fall out! They should serve your child for life. Parents mistake them for temporary teeth, which is a misconception, especially in the case of absence or poor oral hygiene and damage to this group of teeth. Which can lead to a disastrous result – tooth loss. But this group of teeth - the “First molars” - are fundamental in the formation of a correct bite; they are also called the key of occlusion. The shape of permanent “young” teeth differs from more mature ones. The cusps and cutting edges of the crowns are more pronounced, especially the cutting edges of the central teeth have a scalloped (wavy edge), the size of a permanent tooth differs from a temporary tooth, it is larger. Some parents are alarmed by this fact. To which we answer, there is no reason to worry, literally a year after eruption, the enamel edge will become even and even. And regarding the size of the crowns of the teeth, while the child is small (the appearance of the first permanent teeth is 5.5-6 years old) relative to the facial skeleton, there is a certain disproportion; as the bones of the facial region grow and develop, a harmonious relationship between the face and teeth occurs.
Average time for the eruption of permanent teeth in children (according to Schroder, 1991)
| tooth | Timing of eruption (child's year of life) | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | |
| Central incisor | 6-7 | 7-8 |
| Side cutter | 7-8 | 8-9 |
| Fang | 10-12 | 11-13 |
| First premolar (small molar) | 10-11 | 9-10 |
| Second premolar (small molar) | 11-12 | 10-11 |
| First molar | 5-6 | 6-7 |
| Second molar | 12-13 | 12-14 |
| Third molar (wisdom tooth) | 15 and older | 15-16 and older |
1. In order for the teeth to last a long time and not have to “say goodbye” before the appointed time, they need careful care when they erupt.
2. Go ahead for a consultation with a pediatric dentist, who will select age-appropriate hygiene products (toothbrush and toothpaste) for your child. He will provide training in teeth brushing techniques.
3. Brush your child’s teeth at least 2 times a day (in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed). Helping clean hard-to-reach areas from an early age
4. Limit your child’s consumption of carbohydrate-containing foods (we do not recommend eating sweets for children under 3 years old)
5. If a child drinks liquid drinks before bed or at night, they must be replaced with regular drinking water, without added sugars.
6. The use of toothpastes containing fluoride is very important for children of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug-Ugra
7. Visit the dentist 2 times a year!!!
The article was prepared by: pediatric dentist Malakhova A.A. Head of TOD - Mokrinskaya N.G.
Photos used in the article from satyov:
1. https://ladyspecial.ru
2. https://otvetymamam.ru
Approximate timing of eruption of permanent teeth
The first of the molar permanent teeth to appear are molars (at the 6th year of life), located at the end of the dentition. But it is they who are most susceptible to caries, since there are deep depressions on their surface where bacteria accumulate due to poor cleaning and neglect of flossing.
The second molar appears 4-6 years later, when the child reaches 11-13 years of age. Incisors erupt at 6-8 years of a person’s life, canines - after 9 years of age.
Like newly emerged milk teeth, permanent teeth contain few minerals (a tenth of their amount in a mature adult). It is for this reason that it is important to teach a child proper hygiene. It wouldn’t hurt to treat your teeth with gels containing a large amount of fluoride once a quarter.
When teeth start cutting
There is no exact answer as to what time a child’s teeth are cut – the timing varies from person to person. However, you can focus on the average, standard periods of eruption approved by WHO:
- the lower incisors appear at 6–7 months;
- upper – at 7–8 months;
- upper lateral incisors – at 8–9 months;
- the lower ones are closer to a year.
According to the standard, a one-year-old child must have eight baby teeth.
From one year to one and a half years, the child acquires larger teeth - upper and lower molars, and from fifteen to twenty months - upper canines, which are also called “ocular.” The fact is that the optic nerve runs next to them, so these teeth are often more difficult for the child than others. Irritation of the nerve causes sharp pain and sometimes watery eyes.
It can be difficult even for a doctor to understand that the first teeth are being cut. After all, this process is often accompanied by an increase in temperature, changes in stool and mood, and refusal to eat.
Teething in children: symptoms
The first signs of the imminent appearance of teeth appear about a week before their appearance. The symptoms will not stop until the tooth breaks through the gum lining.
Signs of teething in a baby are as follows:
- the child becomes irritable for no reason;
- sleep deteriorates (if the child cries at night and tosses and turns, there is no need to immediately start rocking him to sleep - it is better to give the baby the opportunity to calm down on his own);
- the gums become very swollen and swell at the site where the tooth appears;
- the appetite deteriorates, the baby may even refuse to eat altogether, feeling hungry;
- the child begins to chew on various objects to relieve severe itching in the gums;
- salivation increases;
- Due to drooling, a rash may appear around the mouth, chin and chest.
There are also additional ones, i.e. optional symptoms of teething in infants:
- heat. If the temperature has increased, this most likely indicates an inflammatory process that develops in parallel with teething and is in no way connected with it (it could be stomatitis or any cold).
When the temperature rises, you need to carefully examine the oral mucosa. If there are small bubbles filled with a cloudy liquid, erosion, and the gums themselves are bright red, then the child has herpetic stomatitis. Any baby receives antibodies to the herpes virus from its mother, but usually by the time the first teeth appear, their effect ends. Often the catalyzing factor in the development of stomatitis is trauma to the mucous membrane, which is inevitable when teeth appear. If the above signs cannot be detected, then it is recommended to give the baby Panadol (suppositories are the preferred form of medication). As practice shows, it is useless to call a pediatrician, since this is not their specialization. Only a dentist can determine the specific type of stomatitis (aphthous, herpetic, etc.).
- hematomas on the gums. Sometimes the gums become swollen, turning an eerie shade of blue. Despite their frightening appearance, hematomas do not require treatment. Doctor intervention is allowed only for large hematomas that do not decrease over a long time.
- vomit. The only acceptable cause of vomiting is excess saliva entering the stomach and esophagus. If vomiting begins against the background of elevated temperature and, especially, diarrhea, then these symptoms have nothing to do with teething - you need to call a doctor.
- coughing is not a natural cause when teeth appear, unless the child has swallowed saliva that has entered the respiratory tract.
- A runny nose is a sign of a cold, not teething.
Teething: how to help your baby
This may require a fair amount of patience. During such a difficult period, you should take the baby in your arms more often, caress him, distract him from unpleasant sensations with toys, turn on pleasant, soothing music, and you can sing if natural abilities allow. A walk in the fresh air can also have a calming effect. Children who are breastfed, during teething, begin to cry more often and ask for the breast, and a loving mother needs to be patient, putting the baby to the breast every time, even if he grabs the nipple areola harder than usual during feeding. To satisfy the child’s need to chew something and hold something in his mouth, you can naturally use special rubber rings or toys, so-called teethers. You can offer your child dry food or baby cookies.
Currently, pharmaceutical companies offer a wide range of different products, primarily in the form of gels to “soothe the gums.” In general, most of these products contain painkillers such as lidocaine. You should not abuse these funds. They are not completely harmless; the anesthetics they contain can have an adverse effect on the child’s nervous and cardiovascular systems, and most importantly, they can cause serious allergic symptoms and contribute to the exacerbation of atopic dermatitis (diathesis) in children prone to allergies. In connection with the above, I can recommend, to reduce swelling and inflammation of the gums during teething, such special dental anti-inflammatory drugs for topical use as Cholisal gel, which can be applied to the baby’s gums 2-3 times a day, but must be rubbed in (not too much). of course) with light massaging movements over the entire surface of the gums, and not just putting it in the child’s mouth.
In addition, you can give a child suffering from teething special homeopathic drops, for example Dantinorm baby, according to the instructions for the drug. In any case, if the disturbing symptoms described above in this article appear, I advise you to play it safe once again and call a pediatrician to the home of a child with a high fever. A professional should give his diagnosis and recommendations.
Caring for children's teeth
The pattern of teething in children determines the approximate time of their appearance, but it is necessary to start observing oral hygiene as early as possible, without waiting for the teeth to erupt.
Breasts cannot take care of themselves, so they need help cleaning their gums. This is done either with the help of a fingertip, or, if there is none, with the help of an ordinary bandage dipped in warm boiled water and wound around the finger.
If teeth begin to erupt, you cannot do without the use of special products (baby pastes, brushes, etc.).
Taking care of your child's health
Parents often turn to dentists asking how to relieve teething pain in babies. There are several ways to help your child, including:
- application of a special gel for gums with a cooling effect
- using pacifiers or rubber toys, which help relieve itching from the gums for a while and distract attention
- massaging baby's gums
We also recommend cleaning your baby’s gums twice a day, morning and evening, using a special cloth fingertip soaked in boiled water.
Domostom family dentistry employs attentive and experienced doctors who find an approach to almost every child. At the appointment, the doctor will conduct a thorough examination and answer all the parents’ questions.
Types of teething disorders
Teething in children, the sequence of which is clearly defined, can occur with a delay caused by various reasons (illness of the mother during pregnancy, diseases suffered by the child, etc.). Due to the delay, deformation of the jaws may begin, because There is not enough free space for teeth that have not yet erupted. In this case, only the dentist can decide on treatment after a thorough visual examination of the child and analysis of the photograph taken.
The next very common disorder is enamel hypoplasia, which manifests itself in spots of different colors on newly emerging teeth, pits or grooves. Hypoplasia causes complications during pregnancy.
Why do teeth erupt with irregularities?
The condition of a child’s teeth in the first years of life depends on the health of the mother during pregnancy. The formation of hard dental tissues may be disrupted if a woman:
- suffered from toxicosis at the initial stage of pregnancy;
- experienced severe prolonged stress;
- was treated for kidney disease;
- suffered from rubella.
In addition to maternal diseases, the maturation of teeth and the development of the jaw system can be affected by:
- fetal prematurity or, conversely, delayed birth;
- conflict of Rh factors;
- sepsis suffered by a child in the first month of life;
- frequent colds, pneumonia;
- convulsions;
- toxicosis;
- refusal to breastfeed.
Often, parents, driven by the best intentions, want to alleviate the baby’s suffering by giving him medications. You must understand that any medicine, even if it seems completely safe, cannot be taken without consulting a pediatrician!