From this article you will learn:
- Why is it necessary to perform a gingivectomy?
- Indications for gingivectomy
- Contraindications to gingivectomy
- Methods of performing gingivectomy
- Rehabilitation after gingivectomy
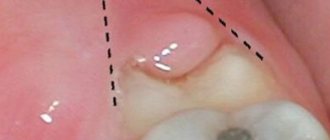
Plaque and food debris often accumulate in the necks of teeth and in the spaces between teeth. These irritants cause inflammation of the gums - gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivectomy is used to treat periodontal inflammation with irreversible changes, when the pathological process cannot be eliminated by professional hygiene and gentle curettage of periodontal pockets alone.
If the edge of the gum has changed, gingivectomy will help eliminate the affected tissue and stimulate the regeneration of the mucous membrane so that it tightly covers the teeth again, does not bleed, and returns to normal as much as possible.
Gingivectomy is an operation performed by a highly qualified dental surgeon or periodontist. It consists of excision, removal of the edge of the gum. At the same time, a sufficient amount of tissue remains for regeneration. The mucous membrane heals quickly, tightly surrounding the teeth. In this way, deep periodontal pockets and gum growths (as with hypertrophic gingivitis) can be removed.
How to get rid of a gum pocket
To get rid of the gum pocket, a surgical operation is performed - gingivectomy. It is possible with moderate severity of periodontitis, when cleaning the periodontal pocket from tartar, plaque and food debris, as well as medications no longer help. This can be explained by the fact that the gums, after removing stone and food debris, cannot immediately fit tightly to the body of the tooth. A person continues to consume food, and it again ends up in the gum pocket, rots and causes re-inflammation. To prevent this from happening, the edge of the gum must be trimmed a little, removing the gum pocket.
Get a gingivectomy at Dr. Granov's clinic!
Our dentists will carry out the necessary manipulations to get rid of the gum pocket, preventing more serious diseases!
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Initial consultation with a dentist
400 rubles
Postoperative care
During the recovery period, the patient must follow several rules:
- the periodontal bandage should be worn for 2–5 days;
- For the entire period of wearing the bandage, you should refrain from cleaning the operated area with a toothbrush, and instead perform oral baths with an antiseptic solution 2 times a day for 3–5 minutes;
- after removal of the bandage, local application of keratoplasty preparations is required as prescribed by a doctor.
A week after surgery, the wound should be epithelized or in the stage of epithelization. In this case, slight redness along the edge of the gum is allowed, and the surfaces of the teeth remain free from microbial plaque. After a month, the gums become pale pink and there is no pocket. For any deviations from this norm, you should consult your doctor [1].
When is gingivectomy prescribed?
Gingivectomy is recommended when all other therapeutic methods show ineffectiveness:
- taking antibiotics;
- curettage, i.e. cleaning gum pockets;
- scraping of tooth roots
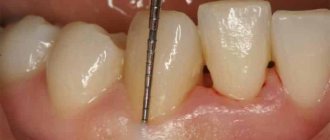
Also, an indication for gingivectomy is the depth of the gum pockets exceeding 4 mm. Deep periodontal pockets can accumulate pathogens that cause:
- gingivitis (when the gum tissue becomes inflamed);
- periodontitis (when the periodontal tissue becomes inflamed);
- periodontitis (when the bone tissue of the tooth begins to become inflamed).
In some cases, gingivectomy is used in aesthetic surgery. After it, the teeth visually become longer and the gums become smoother. However, this procedure has opponents among practicing dentists who claim that there are unjustified risks of gingivectomy on healthy teeth for aesthetic purposes - exposure of the tooth root, inflammation after surgery, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of gingivectomy
Periodontists value gingivectomy for its high effectiveness. If you do it on time and according to indications, you can achieve long-term sustainable results. Inflammatory processes are suppressed, gum pockets disappear - and, as a result, teeth become less mobile and strengthen in the alveolar bone. At the same time, the operation has several significant disadvantages:
- exposure of the necks of teeth and interdental spaces;
- unaestheticness of the operated area;
- frequent development of hypersensitivity of exposed roots to temperature, chemical and tactile stimuli.
Taking into account the shortcomings, many doctors consider it justified to use gingivectomy only on the lateral areas of the jaws [3].
For the patient, the leading symptom after treatment will be exposed roots, loosening of teeth and increased sensitivity.
Naturally, these symptoms are assessed sharply negatively by patients, so the patient should be warned about their development in advance when signing informed consent. In this case, emphasis should be placed on the temporary nature of the changes that occur. The increased sensitivity gradually disappears, the pathological mobility of the teeth also decreases, and the gingival papillae are fully or partially restored while maintaining the distance from the contact point to the alveolar ridge within 5–7 mm. Zakirov T.V., Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Orthodontics, USMU [4]
Gingivectomy is a rather complex intervention that requires highly qualified dentists and constant practice. To have it done, you should contact a trusted clinic.
List of sources:
- Workshop on periodontology at Tver State Medical University. // URL: https://studfile.net/preview/4106556/page:2/ (access date: 11/03/2020).
- Grudyanov A.I., Erokhin A.I. Surgical methods for the treatment of periodontal diseases. M.: Medical Information Agency, 2006. // URL: https://www.booksmed.com/stomatologiya/1001-xirurgicheskie-metody-lecheniya-zabolevanij.html (access date: 11/03/2020).
- Danilevsky N. F., Borisenko A. V. Periodontal diseases. Kyiv: Health, 2000. // URL: https://dental-ss.org.ua/load/kniga_stomatologia/terapevticheskaja/danilevskij_zabolevanija_parodonta/8-1-0-11 (date of access: 03.11.2020).
- Zakirov T.V. Features of the initial stage of treatment of patients with severe periodontitis. Professional dental online publication Dental Magazine // URL: https://dentalmagazine.ru/posts/osobennosti-nachalnogo-etapa-lecheniya-pacientov-s-tyazhelym-parodontitom.html (access date: 10/02/2020).
Contraindications for gingivectomy
Gingivectomy, like any other surgical procedure, has a number of contraindications:
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- blood diseases - bleeding disorders, anemia, leukemia, etc.
- connective tissue diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases - heart rhythm disturbances, recent heart attack, hypertension, etc.;
- acute infectious diseases.
In addition, gingivectomy cannot be done if the inflammatory process has already spread to the bone tissue.
Gingivotomy or gingivectomy
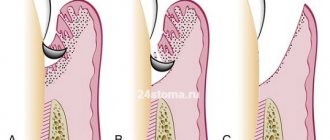
During gingivotomy, the tissue incision is performed vertically in the area of projection of the tooth root in the direction from the free edge of the gum (with or without indentation) to the fold of transition to the moving tissues.
The technique is relevant for the treatment of pathologically shaped periodontal pockets (deep and narrow), as well as for local periodontal and bone abscesses. Gingivectomy is performed primarily through a horizontal incision; it is intended for the surgical treatment of moderate periodontitis (pocket depth from 4 mm) affecting a large gum area. This operation allows you to remove non-viable excess mucous membranes with tissue suturing. Contraindicated for bone abscesses.
How is gingivectomy performed?
The entire procedure can be divided into three stages. The preparatory stage includes:
- professional teeth cleaning. It is carried out to remove tartar, plaque, food debris, that is, a breeding ground for the development of pathogenic bacteria. In our clinic we offer ultrasonic teeth cleaning;
- administration of an anesthetic drug. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, which lasts for several hours, but this is quite enough to perform all the necessary manipulations. On average, the procedure lasts from half an hour to an hour and a half, depending on the complexity of the case and the amount of work.
Operational stage:
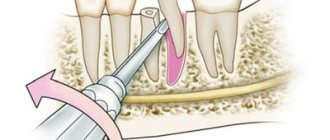
- the surgeon removes periodontal tissue partially or completely depending on the indications. A periodontal pocket can be removed either on one tooth or on several at once. Removal of gum pockets is performed with a scalpel or laser. Our clinic uses a laser - this allows us to minimize postoperative complications;
- After removing the gum tissue, the wound is treated with an antiseptic solution and covered with a special putty, and at the end a sterile bandage is applied. Thanks to all these manipulations, tissue regeneration occurs faster.
At the postoperative stage, the dental surgeon will explain to you how to care for your teeth during the rehabilitation period. In the postoperative period, close attention should be paid to oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth should be gentle - use a brush with soft bristles. Sometimes the doctor recommends not using a brush and thread at all for some time, but using only a special rinse solution.
Cost of treatment
The final price of the operation is influenced by many factors: procedure technique, area of the operated area, type of anesthesia. If anesthesia or sedation is used, the cost will increase.
When using laser equipment, the price will be higher than when using a scalpel. However, the risk of complications is significantly reduced, and gum health will be restored faster.
Dental surgeons at our clinic use modern equipment. We use safe drugs for sedation or anesthesia. Prices are discussed with the patient before treatment begins.
Benefits of laser gingivectomy
Laser gingivectomy has a number of advantages compared to a similar operation performed traditionally:
- the possibility of more precise removal of the edges of the gums, thereby preventing inflammatory processes in very deep layers - dental canals, bone tissue;
- independent oral hygiene becomes more effective because there is access to areas of the tooth that were previously covered with gum pockets;
- Laser surgery is characterized by rapid tissue healing, low trauma and minimal likelihood of complications.
Procedure
The process of gingivectomy is an operation that must be performed by an oral surgeon as well as a periodontist. The doctor administers local anesthesia and then proceeds directly to the operation. Gingivectomy is performed both with conventional instruments and with a laser.
Simple:
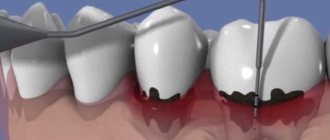
This method involves making wavy incisions of the gums and periosteum in a horizontal plane. The area of influence is the vestibule of the oral cavity and the oral cavity itself. The distance from the periodontal pocket is one millimeter.
Next, vertical incisions are made and the cut off part of the gum is removed. The next stage of the operation is curettage of the wound surface and bone pockets. This is followed by treatment with an antiseptic and the application of a special bandage for at least two days.
Partial / gentle:
This type of gingivectomy received widespread practical use in the mid-twentieth century, or more precisely, in 1962. The method is similar to simple gingivectomy. The main difference is that the excision of non-viable gum is not carried out along the entire wall of the periodontal pocket, but only along part of it (from two to three millimeters). Further manipulations are performed using curettage.
This method is less traumatic and provides an aesthetically more acceptable result, which allows you to include the front part of the gum in the area of treatment.
Radical gingivectomy:
This method has been known to dentists since the beginning of the twentieth century. This is an extremely serious surgical procedure. Six to seven teeth, as well as bone tissue, are simultaneously impacted.
As in the case of a simple gingivectomy, with a radical gingivectomy, wavy incisions are made, but the indentation increases to two millimeters. Along with the gingival margin, overgrown granular tissue, strands of epithelium, remaining dental plaque, and altered bone are removed. The edges of the alveolar arches are aligned at an angle to the outside.
Next, antiseptic treatment is performed. Hemostasis is performed in the wound area and an iodoform turunda or gum bandage is applied. Sometimes the turunda is fixed using an elastic periodontal tray.
Recently, this method has been used quite rarely - only if there are serious indications for radical gingivectomy, since flap periodontal surgery is often preferred.
Attention! Stitching the edges of the wound is highly discouraged. Also, radical gingivectomy is not recommended for the anterior part of the dentition due to aesthetic nuances.
Tools:
Straight scalpel; curved “eye” scalpel; scissors; tweezers for determining the depth of the periodontal pocket; laser.
Duration of the procedure: on average about 30 minutes.
What complications can occur after gingivectomy?
According to the observations of our dentists, complications develop quite rarely after gingivectomy. However, negative consequences can occur if the dentist is not aware of the patient's chronic immune system conditions. Periodontal disease and periodontitis are diseases that occur most often in patients with weakened immune systems. Gingivectomy can also cause complications in chronic connective tissue and cardiovascular diseases. This is explained by the fact that pathogenic bacteria can get into postoperative wounds. If the dentist has as much information as possible about the health status of his patient, he will be able to minimize the risk of such complications.
Gingivectomy - price in dentistry
A mandatory preliminary consultation with a specialist will determine how necessary gingivectomy is in general and which method is optimal in this particular case. Without serious indications, gingivectomy will not be performed.
The price for gingivectomy ranges from 300 rubles to 2,000 rubles for treating the area around one tooth.
Also, many clinics provide services to eliminate the consequences of poorly performed gingivectomy. Some institutions provide video and photographic materials of the gingivectomy operation to introduce the patient to the procedure.
Follow these guidelines after surgery
- Temporarily eliminate the consumption of solid foods, including fresh vegetables.
- Consume foods when they are warmed to room temperature.
- It is not recommended to drink hot or cold drinks.
- Until tissue restoration is complete, alcoholic drinks should be completely excluded from the diet.
- It is also not recommended to smoke until the rehabilitation period is complete.
- Minimize chewing loads on the healing area.
The recovery period for each individual case is different, primarily depending on the food used in the diet. Therefore, during the rehabilitation stage, doctors recommend consuming exclusively soft foods that cannot harm the gums. You also need to brush your teeth very carefully so as not to damage the sutures.
Possible complications
Laser gingivectomy is currently most recommended by doctors, since this type of intervention is the least traumatic.
The main types of common complications after gingivectomy can be:
- infection of gum tissue;
- periodontitis, periodontal disease;
- infection entering the bloodstream;
- reduced immunity;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies (usually cardiovascular).
Gingivectomy is a forced, although effective, measure for many periodontal pathologies. Carrying out this operation often saves the patient from many serious health problems. The main thing is not to neglect the condition of your gums and teeth. Properly performed gingivectomy eliminates the occurrence of postoperative complications. Experts especially recommend laser gingivectomy, which is as safe and painless as possible for patients. Take care of your gums!
Sources used:
- Gehrig, J., & Willmann, D. E. (2011). Foundations of Periodontics for the Dental Hygienist (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health
- Borovsky E. V. Gingivitis // Great Medical Encyclopedia, 3rd ed.
- Lemetskaya T.I., Periodontal diseases (periodontopathies), M., 1972
- National Library of Medicine (USA)
Existing indications for surgery
This surgical intervention becomes possible only if there are certain indications for gingivectomy, expressed in the following pathological changes:
- Hyperplasia of the gum margin (fibromatosis, periodontitis, hypertrophic gingivitis);
- Elongated natural tooth crown;
- Deformation and overhanging gums;
- Proliferation of the interdental papilla;
- Formation of periodontal pockets of pathological depth;
- For cosmetic and aesthetic purposes.
Despite the fact that this is a minor surgical intervention, it is not performed without special reasons. The purpose of the operation is justified if the problem cannot be solved with the help of drug treatment, or the depth of the periodontal pocket does not allow the use of the closed curettage technique.
Causes of excess gum growth
The main function of the gums is to protect the roots of the tooth from mechanical, temperature and microbial influences. Normally, the depth of the gum pocket, in which the roots are hidden, is 3-4 millimeters. However, if the walls of this “shelter” increase, covering the crown of the tooth, doctors talk about a pathology that needs to be treated.
There are several reasons for the proliferation of soft tissues. As a rule, this is a defensive reaction to some kind of influence. Most often, this is how the body tries to fight tartar. With insufficient oral hygiene, plaque is deposited on the tooth enamel, which over time hardens and turns into tartar. To stop plaque deposition, the body begins to actively grow periodontal tissue, which covers part of the tooth. However, this is fraught with the fact that microbes accumulate under the gum. They begin to actively decompose in the “shelter”, and this leads to inflammation of the gum pocket.
Among other reasons, doctors identify a genetic predisposition to gum hyperplasia (overgrowth), malocclusion, taking certain medications, a number of chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and metabolism, circulatory problems, cardiovascular diseases) and traumatic periodontal damage. during treatment or thermal, chemical exposure.
Risks of surgery
Many patients do not consider gum surgery to be serious. However, any operation has its risks. And operations in the oral cavity are characterized by the likelihood of bacteria entering the blood as quickly as possible. After all, anatomically, it is the oral cavity that has the most pronounced innervation and blood supply.
In this regard, the doctor usually takes especially seriously patients at risk. If patients have the following pathologies, the doctor has the right to decide for himself whether it is possible to undergo gingivectomy surgery at the moment. The risk group includes patients with the presence of:
- cords or frenulum at the surgical site;
- narrow gums;
- depth of bone pockets more than 5 mm;
- advanced periodontitis;
- heart disease;
- endocarditis;
- artificial heart valve;
- general weakening of the immune system;
- liver cirrhosis;
- implanted joints.
Often in these groups of patients the doctor is forced to additionally prescribe antibiotics before or after gingivectomy.
Also, gingivectomy is not performed for destruction of the alveolar bone. If the gum is excised in this pathology, the tooth will become mobile and may soon be completely lost.