Temporary teeth
Timing of teething
Dental buds are formed during the period of intrauterine development. The eruption of the first teeth begins at the twenty-fifth week of the baby’s life. The lower incisors appear first, followed by the upper ones by eight months. The age at which baby teeth, called premolars, erupt varies from one to two years. The last to appear are the canines and second premolars, which occurs from sixteen to thirty months.
This teething schedule is optimal, but it is impossible to determine the exact timing. The process depends on the characteristics of the child’s body, the health of the mother during pregnancy and genetic factors.
Timing of teething in children in the table
| Type of tooth | Lower jaw | Upper jaw |
| Medial incisor | 6 – 10 months | 7 – 12 months |
| Lateral incisor | 7 – 16 months | 9 – 13 months |
| Fang | 16 – 23 months | 16 – 22 months |
| First premolar (baby molar) | 12 – 18 months | 13 – 19 months |
| Second premolar (baby molar) | 20 – 31 months | 25 – 33 months |
The order of teething in children
The teeth follow the principle of pairing, for example, if one fang appears, a second one should be expected soon. The sequence of teething is determined by nature based on the practical significance of dental units for survival.
The front teeth of the lower row grow first, then the upper ones come. The lateral incisors disrupt the order of teeth eruption; their appearance begins with the upper jaw. Then comes the eruption of chewing teeth - the first premolars. The last to emerge are the canines and molars. The process of teething in children is completed by the age of 2-3 years.
Diagram of baby teeth eruption in children
Reasons for violation
The lower and upper teeth are formed in children at different times. The main factor that influences this is heredity, that is, the predisposition is laid down in genes, as is the quality of dentin, as well as the enamel layer. If mom or dad, grandfather or grandmother, or other relatives had cases of deviation from the order of appearance of chewing organs, this can be inherited by the toddler. Therefore, the child’s teeth grow out of order.
Of course, relatives are always worried when the growth process is delayed and goes astray from the generally accepted schedule. But dentists say that non-standard situations are also normal:
- When the appearance of units occurs several months earlier or later;
- If the order of appearance of the masticatory organs is disrupted;
- When the rate of growth of units does not coincide with the announced scheme;
Since the process of growth of incisors, canines, and molars begins at 12 weeks of pregnancy, it is influenced by the health of the mother. Influenza, bad habits of the mother in labor, and infectious diseases have a negative impact. Artificial feeding has a bad effect on the newborn's body. After all, sucking the mother's breast actively develops the facial muscles, and the correct development of the lower jaw occurs. Sucking from bottles occurs only with the help of the lips. As a result, the first tooth may appear in the top row. In this case, therapy is not needed. It is important that all 20 time units appear.
Remember! Medicine does not know of cases where children were left without chewing organs due to their untimely appearance. The units will appear, you just need to wait.
It wouldn't hurt to go to the dentist. If necessary, bite correction in children is carried out. In addition, a non-standard order can be observed in babies if their parents are of different nationalities, or if the climate is not suitable for the newborn. Many parents see disordered teething as a sign of rickets. Doctors explain that with rickets, babies have a large head, protruding ribs, and excessive sweating. If the pediatrician does not find these signs, then there is no reason to worry. But sometimes the absence of the first units up to a year indicates:
- Vitamin D deficiency in the body;
- Violation of metabolic processes;
- Gastrointestinal problems;
- Chronic diseases;
- Infectious diseases such as measles, scarlet fever;
- Lack of rudiments of future chewing organs;
- Horizontal position of the unit in the gum;
- Bite abnormalities;
- Dysfunction of the endocrine gland system;
- Slow development of the body;
Diagnosis and consultation with a pediatrician or pediatric dentist will clarify the situation and eliminate the problem.
Permanent teeth
Timing of teething in children
The first permanent teeth appear several months before the baby teeth fall out—the molars, or “sixes,” erupt. This occurs at the age of six. By the age of eight or nine years, it is the turn of the incisors. When a child is ten to twelve years old, premolars and canines erupt. Next come the second molars, the eruption of molars is completed by adulthood.
Important!
Wisdom teeth appear much later, after twenty years. However, their complete absence is also the norm.
Timing of teething in the table
| Name | Lower jaw - time of eruption | Upper jaw - eruption time |
| Medial incisor | 6 - 7 years | 7 - 8 years |
| Lateral incisor | 7 - 8 years | 8 - 9 years |
| Fang | 9 - 10 years | 11 - 12 years |
| First premolar | 10 - 12 years | 10 - 11 years |
| Second premolar | 11 - 12 years | 11 - 12 years |
| First molar | 6 - 7 years | 6 - 7 years |
| Second molar | 11 – 13 years | 12 - 13 years old |
| Third molar | 17 – 21 years old | 17 – 21 years old |
Teething order
The pairing principle also applies to permanent dental units. The correct sequence of teething is important for the formation of the bite; it is necessary to carefully monitor the time of loss of baby teeth and the order of growth of molars.
The lower molars appear first, then the upper ones. Next, the temporary teeth of the lower jaw fall out, the permanent teeth erupt, and only then the upper dental units are replaced.
This schedule for teething in children is not universal, but if there are significant deviations, you should consult a specialist.
Causes for concern
When a child remains without teeth after turning one year old, parents should take him to the doctor. Of course, the time at which chewing organs appear may vary. For example, in boys this process occurs more slowly than in girls. But, there are situations when medical consultation is absolutely necessary.
- An urgent visit to a pediatrician is necessary at a high temperature of more than 39 degrees.
- The baby should be shown to a doctor if symptoms such as frequent diarrhea and vomiting develop.
- An orthodontist is consulted if a malocclusion is suspected. Perhaps, after the eruption of incisors, canines, and molars, he needs therapy. In such situations, braces are used for children while the jaw apparatus is pliable.
- A specialist should examine a newborn whose units appeared in the prenatal period.
- A dentist is consulted if the organs are not formed in the dentition.
Therapy may consist of strengthening the health of the toddler, performing special exercises, and massaging the gums.
Signs of teething
Symptoms of teething in infants
The appearance of baby teeth is a little more difficult than that of permanent teeth, since the baby has not yet encountered pain and cannot understand what is happening to him. Teething in children under one year of age is accompanied by the following signs.
- The most common symptom of teething is fever. An increase to 38 degrees within three days is normal.
- Swelling of the gums. Often, when children are teething, their gums swell, their sockets itch, and they have a desire to chew hard objects. It is important to prevent the child from damaging the mucous membrane; it is better to buy a special teether to relieve discomfort.
- Decreased appetite. Children refuse to eat due to stress or itchy gums.
- Teething syndrome. Neurosis, tearfulness, anxiety, poor sleep and whims may indicate the imminent appearance of the first tooth, even if the child does not experience pain, fever or swelling of the gums.
Important!
An increase in white blood cell levels during teething should not be a cause for alarm. This is a common occurrence associated with a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of eruption of permanent teeth
A change in temporary bite is accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. The process has the following characteristics.
- Root resorption and loss of baby teeth. A sure signal of the appearance of a new tooth in the coming months.
- Increase in jaw bone size. Permanent teeth are larger than baby teeth, the jaw grows, creating conditions for a change in bite.
- Pain in the gums. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane are a reaction to teething.
Important!
Body temperature above 38 degrees, cramps, refusal to eat and difficulty breathing are not symptoms of the appearance of milk and permanent teeth. These are signs of an infectious disease. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
After a year, teeth appear with the following frequency:
- by 12-15 months – two pairs of first molars erupt;
- by 18-20 months – a pair of upper and a pair of lower canines are already clearly visible;
- 20-30 months is the period of appearance of two pairs of second molars.
How many teeth should a child have at 1 year 3 months? Ideally 12, but the number can change in one direction or the other, and this is not considered a deviation. The frequency of teething is influenced by many factors, including previous infections, heredity, climate, and health status.
The question of how many teeth a child should have at 1 year 8 months, or 20 months, also cannot be answered unambiguously. The answer will be approximate - about 16. Up to a year, parents should focus on the approximate formula: the number of months minus 4, with a reservation for the baby’s characteristics.
Painful teething: advice for parents
When faced with teething in children, many parents are at a loss. First of all, you need to call an ambulance and determine the reason for the baby’s poor health. If symptoms are confirmed, the specialist will prescribe medications for teething - antipyretics and painkillers.
You can treat your gums yourself with an anesthetic gel with a cooling effect to reduce itching and swelling of the mucous membrane. Ice will also help. To reduce gum irritation, there are special silicone fingertips made of hypoallergenic material.
Folk remedies for teething will effectively relieve painful sensations - a decoction of chamomile, sage, tincture of valerian and honey will soothe inflamed tissues.
Painkillers for teething are contraindicated in children; this can worsen their health.
Important!
Without a doctor's recommendation, antibiotics and other strong teething medications can cause an allergic reaction.
What should mom do?
When teeth erupt out of order, every parent should take this fact seriously. Pediatricians advise feeding your baby in a balanced manner. For six-month-old children, mother's milk is not enough. Complementary foods should be introduced gradually. Mothers should properly allocate time for wakefulness and sleep, and visit the doctor according to the schedule. A vitamin complex may be prescribed. It is prohibited to select medications on your own, since only a doctor can give an objective assessment of the baby’s condition.
If the chewing organs do not appear according to the calendar, specialists prescribe certain tests to determine the cause of the failure. Mom should not neglect the doctor's recommendations. Its instructions should be followed exactly to stimulate the appearance of units. To do this you need:
- Include foods rich in vitamins in your diet;
- Correctly create a daily routine and monitor its implementation;
- Conduct comprehensive physical exercises with children;
- Regularly visit a doctor for preventive purposes;
- Treat illnesses in a timely manner;
Taking medications without a doctor's recommendation is dangerous and detrimental to a child's health. Only care and affection, proper care and feeding will allow you to raise a healthy child.
Deviations in teething
Minor changes in the timing and sequence of dental growth should not cause alarm. However, significant deviations from the norm in teething are a cause for concern.
- The tooth does not appear for a long time. Reason: genetic predisposition to long eruption or lack of rudiments.
- Too early appearance of teeth. Caused by disruption of the endocrine system.
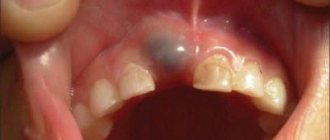
- Black or brown enamel surface color. Indicates high iron levels, poor salivation, or chronic inflammatory processes in the child’s body.
- Incorrect row position. Bite pathologies indicate a hereditary factor or deformation of the maxillofacial bone.
What microelements are needed for teeth growth?
Vitamins and microelements are a necessary component for the development and normal functioning of the child and adult body. The formation of dental tissue cannot do without:
Fluorine
Strengthens enamel, makes incisors resistant to bacteria, the destructive effects of acids, and prevents caries. Fluoride is taken in tablets or drops when a deficiency is diagnosed. Enters the body with sea fish, nuts, grape juice, spinach, and most vegetables.
Toothpastes with fluoride are not approved for use by children under 4–5 years of age. Children aged 1.5–3 years swallow the tasty mass when cleaning their mouths, and an excess of the element is formed in the blood. For foolish children, choose toothpastes without fluoride to protect them from the negative consequences of hygiene procedures.
Calcium
It is the building material of infants' teeth. Without calcium, mineralization in tissues is impossible. After finishing breastfeeding, a one-year-old child should receive dairy products daily, greens and fish at least three times a week.
Vitamin K
Necessary for complete absorption of calcium and protein synthesis. Found only in natural dairy products (cottage cheese, sour cream and others).
Teething for young parents seems like an extremely difficult and nervous process. They prepare for it mentally, they are afraid of hysterics and hyperthermia.
Young and inexperienced parents do not need to worry or be negative. It is better to study the issue of dentition in infancy in order to arm yourself with knowledge and understand why the baby cries and is nervous. In this case, jaw development will be perceived as a normal physiological stage of growth, which will be experienced easily and quickly.
What are the anatomical features of “children’s” molars?
- The first upper molars are smaller in size than the second ones. The first has two widely spaced roots, which sometimes merge to the apex. The rudiment of the first “adult” premolar is formed between the roots. Most often, the first upper molars have four root canals, although there are also three or two (in 19 and 5% of cases, respectively).
- The first lower molars differ from others by having an elongated prismatic crown. On their chewing surface there are four tubercles: lingual, higher, and buccal. The first “children’s” molar has 2 roots, with the medial one being longer and wider than the distal one. Often the first lower molars have three canals.
- The structure of the crown of the second upper molars of the dentition resembles the first upper permanent tooth. Four tubercles are clearly visible on the surface, and sometimes a fifth one is noticeable. The buccal surface is almost square with slightly convex sides. An enamel ridge is often visible on the palatal side. Such teeth have three roots, in 85% of cases there are 4 root canals, much less often - 3.
- The second lower molars already have five cusps with less deep grooves than those of “adult” teeth. Both roots are flattened and curved at the top. In 85% of cases, teeth have three canals, although there are exceptions.
With the eruption of permanent, “adult” molars, the change of teeth begins, which lasts from 5-7 to 12-14 years. It is the first molars, which do not have primary analogues, that hold the bite, ensuring the correct placement of the remaining permanent teeth in the arch.
Typical problems.
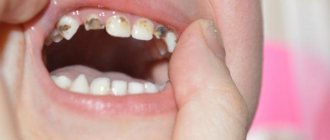
The most typical problem between the ages of 3 and 6 years is the development of caries of primary teeth in the area of the first and second primary molars. The narrow interdental spaces between the first and second primary molars, which are difficult for a child to reach, are an ideal place for plaque to accumulate. As a result, caries forms on the surface of the teeth hidden from the eyes of parents (between the 4th and 5th milk teeth). Being unnoticed, the carious process quickly progresses, complicated by inflammation of the nerve of the tooth (pulpitis).
With poor oral hygiene and a large number of carious teeth, caries of the permanent molar (6th tooth) often develops, high-quality treatment of which is only possible by a pediatric dentist.