A method such as tooth remineralization therapy allows you to strengthen the tooth and maintain its healthy appearance. Preparations for tooth remineralization contain fluorides, phosphates and calcium (calcium gluconate solution, calcium glycerophosphate, calcium phosphate containing gels).
This method of preventive treatment, such as remineralization, has its advantages and is important because it is this method that allows you to prevent the occurrence and development of a pathological process in the tooth. The demineralization process entails many consequences - impaired sensitivity of tooth enamel, cracks and damage, and the development of a pathological process such as caries.
What kind of caries is this and why does it occur?
The front teeth include the incisors (denies incisivi) and canines (dentes canini), the purpose of which is to bite off individual pieces of food. The main difference from the lateral teeth (premolars (dentes praemolares) and molars (dentes molares)) is the absence of a tuberous chewing surface for grinding. Therefore, caries forms on the crown in the form of a chisel (incisors) or slopes (fangs), in the interdental space, at the junction of the visible part of the tooth and the gum (cervical caries of the front teeth). The tooth is gradually destroyed, “pockets” form at the “neck” - caries spreads deeper, destroying the root.
Modern dentistry is based on the theory of W. D. Miller (1883), who, while conducting experiments, noticed that if an extracted tooth was placed in a fermenting mixture of bread and saliva, something similar to caries appeared on it. At the same time, the density and structure of dental tissue provide protection of teeth from destruction.
Caries is, first of all, problems in the neurohumoral regulation of the body. Normally, the hypothalamus, with the help of the pituitary gland, controls the parotid salivary glands, which secrete parotin. With the help of this substance (in medicine “hormone”), calcium metabolism in the blood-bone tissue-organs system is controlled and stimulates the movement of dental lymph through microscopic tubules inside the teeth. This cleanses and strengthens the dental tissue. Therefore, the main cause of caries is a delay in the production of dental lymph and subsequent demineralization of the tooth. Then the weak tooth in the aggressive environment of the oral cavity is destroyed from the outside.
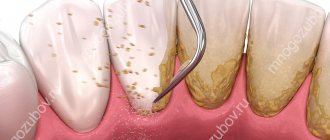
Caries on front teeth
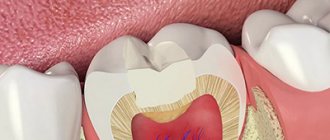
The dental lymph contains monoblasts, with the help of which the enamel and dentin are nourished. In order for the tooth to be cleaned from the inside, the microscopic structures of monoblasts work like a pump. The nutritious fluid released from the blood is pumped through the dentinal tubules and, under capillary pressure, is pushed towards the enamel, strengthening it. In case of disorders, when capillary pressure decreases, the amount of mineral substances decreases, plaque is literally attracted to the tooth walls (the enamel is like a fine-mesh sieve and allows oral fluid to pass into the tooth).
According to classical dental textbooks, caries is classified as an infectious bacterial disease. Recent research confirms that caries:
- odontoporosis (decreased density of dental tissue);
- odontoclasia (destruction of all layers of the tooth).
Factors influencing the intensity of caries development on the front teeth:
- Excessive consumption of confectionery products without cleaning the mouth for 4 hours (maximum time for the formation of soft plaque). In addition, excess sugar inhibits the normal functioning of the pituitary gland.
- Inflammatory process or removal of the salivary glands (saliva contains a complex of antimicrobial factors, neutralizes the acids of dental plaque and is involved in enamel calcification).
- Environmentally unpleasant factors and work in the metallurgical, mining, coal, chemical industries.
- Reduced general resistance (resistance) of the body.
- Improper development of the jaw, crowded teeth, making it difficult to clean the mouth.
How does caries manifest on the front teeth?
Caries on the front teeth most often appears on the enamel surface, but in older people or people with periodontal disease, the exposed surfaces of the tooth roots are also where the disease develops.
Symptoms:
- Whitish matte spots, initial carious lesion (white spot lesion, incipient lesion). Due to plaque on smooth surfaces, as well as the frequent location on proximal surfaces (when interdental caries of the anterior teeth develops), only a dentist can determine the initial stage of development of the disease. The surface layer of enamel at the site of a carious lesion loses mineralization, the enamel becomes weaker by 1-10%.
- Formation of a carious cavity due to demineralization of the enamel with subsequent infiltration of bacteria deep into the dentin.
- Unpleasant sensations. The tooth reacts with pain to cold, hot, sweet or sour foods. The tongue can feel a change in the surface of the tooth (it can be injured). Food particles and floss get stuck.
Stages of caries on the front teeth
Caries on the front teeth develops in the following stages.
Spot stage
If you examine a stain after removing plaque using a dental probe, the roughness of the surface is noted, and when the probe is advanced, smoothness is noted. If you look at a section of a tooth under a polarizing microscope, a significant lack of minerals and an increase in the volume of enamel pores from 5 to 25% are found directly in the affected area. The components of saliva, water and proteins (protein elements) penetrate into these pores.
Initial stage of caries
Superficial caries
Over time, due to the penetration of foreign substances into the enamel, the stain darkens, but intensive cleaning cannot return the color. A carious cavity gradually forms, without affecting the dentin, since the surface layer of enamel at the site of a carious lesion is characterized by a loss of inorganic substances, reaching 1-10%.
Average caries
Caries spreads deeper. On an x-ray, the cavity exceeds half the thickness of the enamel, but does not yet affect the dentin. The rate of destruction of the dental crown at this stage slows down somewhat, since the so-called opaque (dark layer) of enamel is located here. Pores occupy almost 2-4% of it, they are small, because remineralization processes take place here. The tooth tries to recover on its own.
Deep caries
Destroys dentin, passing through the enamel-dentin border and spreading along the dentinal tubules towards the pulp. Dental pulp and dentin have their own protective mechanism. In dentin, sclerotization of the tubules begins, the processes of odontoblasts move away, and replacement irregular dentin is formed at the dentin-pulp boundary. The inflammatory process in the pulp, a reaction to the penetration of bacteria, is also a protective mechanism. If short-term pain occurs when eating cold food, it may be deep caries.
If we talk about caries of the roots of the front teeth (more often found on the canines than on the incisors), then the protective mechanism of the tooth works differently. The bare root surface, which has been exposed to the microbial-bacterial environment of the oral cavity for a long time, is covered with a thin layer of root cement. Strengthening (demineralization) of both the cement and the underlying enamel occurs, and the dentin becomes sclerotic. There are fewer dentinal tubules at the root, so the process proceeds more slowly and is initially shallow. However, over time, caries covers increasingly larger root surfaces.
The composition of plaque on root surfaces differs from the composition of the enamel surface; Aktmomyces fungus is especially common here.
Why is caries on the front teeth dangerous?
The process of caries spreading can occur much faster than on molars and premolars, since the incisors and canines do not have fissures. Due to the shape of the dental crown, the cavity reaches the dentin faster, destroying the tooth. In many cases, advanced caries leads to the fact that it becomes impossible to restore the tooth with filling materials; a crown must be installed. And in the worst case, tooth extraction and prosthetics or implantation.
Interdental and cervical caries involve adjacent teeth, and it is more difficult to treat this part of the dentition due to its specific shape, so treating caries on the front teeth is more expensive.
What is Remodent made from?
The material for the manufacture of the drug Remodent for teeth is animal bone tissue. The resulting biological material is dried by lyophilization. The method is that the material is first frozen and then placed in a vacuum chamber, where the material is dried by sublimation. During sublimation, the solvent evaporates, and the “dry residue” that we require in the case of Remodent remains. The process occurs without exposure to high temperatures. Thus, lyophilization products retain the integrity of their structure and their valuable properties. Lyophilized powder (for example, such as Remodent) when dissolved in water, restores its original properties. The drug Remodent contains the entire complex of iron, copper, sodium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, phosphorus and manganese ions, which is used for medicinal purposes.
The drug Remodent in sachets 3 grams
Types of caries in front teeth
Oral microorganisms metabolize small carbohydrate particles. The organic acids formed in this process (lactic, acetic, propionic) significantly influence the occurrence of caries. First, a sticky and sticky plaque (plaque) appears, which consists of bacterial cells and an intercellular substance called the matrix. There are two types of dental plaque:
- Supragingival (siipragingi-valis). Causes caries and gum inflammation (gingivitis);
- Subgingival (subgingivalis). Causes the occurrence of periodontal diseases.
Supragingival dental plaque settles in hard-to-clean places that contribute to the occurrence of caries (retention zones). A film appears on clean enamel in which colonies of bacteria form. The plaque becomes mature and cannot be removed without special cleaning. Over time, under the influence of saliva, plaque turns into tartar, and underneath it, the enamel is destroyed and bacteria penetrate. First of all, the grooves and pits on the surfaces of the teeth, the approximal and cervical surfaces of the teeth are subject to caries.
A large accumulation of plaque above the gums leads to tooth decay
Caries between front teeth
Caries on the proximal surface is most common. Improper and untimely cleaning of the oral cavity leads to the rapid growth of plaque, which grows up and down, under the gum. Therefore, the carious cavity can be quite large, the tooth decay is so great that prosthetics are recommended.
Radical caries
The thickness of the enamel becomes thinner closer to the neck. Due to the anatomical structure of the dental crown, it is easier for colonies of bacteria to gain a foothold from below. Therefore, tartar forms here more often, and the carious cavity penetrates into the dentin much faster.
Contact
When there is not enough space in the plaque for an overgrown colony, it spreads to the neighboring tooth, “infecting it.” Usually, the adjacent tooth also has weakened areas of enamel, so caries begins there too.
Other types
There is still no single and universal classification of caries. Based on the analysis of clinical manifestations, as well as various forms of progression of caries of the anterior teeth, in addition to topographic (takes into account the anatomical localization, root, contact), we can also distinguish:
- dynamic caries (the degree of damage to the dental crown and root, as well as the speed of development of the disease are taken into account);
- chronological (takes into account the prevalence of caries depending on the age of the patient).
Diagnostics
Whether it will be painful to treat caries on a front tooth depends on the degree of damage. To diagnose it use:
- Fluorescent radiation. Due to the uneven reflection (the carious spot does not glow), the presence of the disease can be determined. The method is suitable for preventive examination.
- Vital staining with a mixture of methylene blue (1%) and red (0.5%) solutions. A carious stain is colored differently than healthy dental tissue. The method is cheap, it also allows you to identify areas of caries, but it is not used for prescribing treatment, because does not show the depth of the carious cavity.
- Electroodontometry. Check the condition of the pulp using an electric current.
- X-ray. The image shows the depth of destruction and the protective reaction of the tooth. The most accurate method by which treatment is prescribed in the most severe cases.
Instructions for use
- Rinsing the mouth. First, a solution is prepared: 3 grams of powder from a bag is dissolved in 100 milliliters of boiled or distilled water (this is half a glass). The result is a 3% solution of remodent. Rinse your mouth with the resulting solution for 5 minutes. The course of treatment consists of 10 rinses. 2 to 4 preventive courses are recommended.
- Applying the application to the affected areas. To do this, form a cotton swab of the required size, dip it into the Remodent solution, soak it in the medicine, and then apply it to the diseased tooth. The application is carried out for 15-20 minutes, the tampons are periodically renewed. Applications can be done 2-3 times a week.
Before carrying out procedures using Remodent, be sure to properly brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste! After the treatment procedure, it is recommended not to eat for 2 hours.
The prepared Remodent solution can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 14 days.
Treatment of caries of anterior teeth
The choice of treatment method depends on the location of the caries and the depth of its penetration. In this case, treatment must be comprehensive. In addition to dental treatment, patients must reduce their intake of easily fermented carbohydrates. Remineralizing therapy is also indicated.
Treatment of caries of anterior teeth
Sealing
Preparation of the cavity followed by filling is considered symptomatic treatment, since it does not eliminate the cause of the lesion. A cavity is an advanced state of the carious process, therefore, for the sake of protecting teeth, it is better not to bring it to this stage.
Caries between the front teeth involves both teeth, so it is common to have a cavity on both teeth at the same time. The best result is achieved with lingual access to the cavity (sometimes direct and vestibular), because The vestibular surface of the enamel is preserved and a higher aesthetic level is achieved.
To prepare a cavity, first pass through the enamel to the site of the lesion with a spherical bur, then excise the contact wall of the cavity with an enamel knife (or bur). The softened dentin is removed, cleaning the entire cavity. If necessary, retention points are formed (Latin retentio - retention, preservation) and an additional platform on the lingual surface. At the same time, they try to preserve the tissue of the contact surface of the tooth as much as possible. Enamel without underlying dentin is most often removed, since the likelihood that demineralization has spread to the entire tooth is quite high.
Then the prepared cavity is filled using contour matrices curved on a plane and interdental wedges so that the placed filling restores the surface of the dental crown and does not interfere. For filling use:
- composite materials (classes of macro- and microphiles, hybrids);
- ormokers and compomers (provide the most aesthetic result);
- glass ionomer cements (used when etching of tooth tissue is impossible. The cheapest filling).
Amalgam is only suitable for filling canines with lingual access.
For many, visiting the dental office means an unpleasant experience. Filling is a completely tolerable process, however, at the request of the patient (and if the caries cavity extends deep into the dentin), the dentist will inject an anesthetic.
Infiltration method
Treatment of caries on the front teeth, when the destruction does not affect the dentin, is possible using Icon technology. The affected area of the tooth is not prepared, but treated with a special gel. Thanks to its mineralized chemical composition, the gel penetrates into the deep layers of enamel, destroying bacteria and sealing pores. At the same time, demineralization occurs with restoration of enamel thickness.
What can you do for caries in your front teeth at home?
To treat the initial stage of caries, remineralizing therapy is carried out at home. Typically, a 10% solution of calcium gluconate, a 2% solution of sodium fluoride, and Remodent are used. Before application, the teeth are mechanically cleaned, the tooth surface is treated with a 1% solution of hydrogen peroxide (attention: 3% is not suitable) and dried. Next use:
- Calcium gluconate. Apply cotton swabs soaked in the solution to the surface of the dental crown. Change every 5 minutes for 20 minutes. Then apply a tampon soaked in a 0.5-2% sodium fluoride solution.
- Sodium fluoride . A tampon soaked in the solution is applied for 10-12 minutes. Course: 3-4 applications every 3-5 days. Treatment is recommended every 3 months.
- Remodent. A tampon soaked in a 1,2, 3% solution is applied for 20 minutes, changing 3-4 times per procedure. Usually 15-20 procedures are required.
After the procedure, you should not eat food for 2 hours.
Attention! Home treatment has not been proven to be effective. By doing it, you can worsen the condition of your teeth.
How is remotherapy carried out?
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate inflammation and foci of caries. Sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out. To improve the penetration of the remineralizing drug, it is necessary to remove tartar and soft plaque covering the surface of the teeth. Air Flow hygienic cleaning or ultrasonic scaling is carried out.
1. Application remotherapy . A concentrated composition for remineralization is applied to the prepared surface of the teeth. If indicated, the teeth are coated with fluoride varnish at the end of the procedure. It is recommended to repeat the procedure approximately once every six months.
2. Remotherapy using a mouthguard . A sealed mouthguard is made individually based on impressions of the patient's jaws. The patient independently fills it with the remineralization composition, puts it on and takes it off. The duration of use of the mouthguard for remotherapy is determined by the dentist.
For a procedure such as remotherapy, special preparations are used to remineralize teeth: remineralizing toothpaste, special protective varnish, fluoride-containing discs, rocs remineralizing gel, remodent.
Remodent is a special substance in powder form that contains mineral compounds and is used for remotherapy. You can buy Remodent at a specialized pharmacy at an affordable price. Rocs remineralizing gel contains the necessary minerals - microelements, macroelements: magnesium, calcium, phosphorus. It is this composition of the gel that allows you to maintain the strength of the tooth.
Remineralizing preparations are used for rinsing and for local application and strengthening of teeth as a solution for applications or electrophoresis on the tooth area.
Rox gel is now widely used in dentistry for the reason that its composition is safe even for children, it does not contain fluoride, which is why it has gained its popularity. The use of rocs gel provides a bactericidal effect; its composition, among other things, contains xylitol. Because the drug is produced in the form of a gel; it is used in the form of applications to the tooth area, both at home and in a dental clinic. The gel is not fluid, so it adheres well to tooth enamel, creating a kind of film, and the beneficial components contained in the composition penetrate into the tooth enamel, strengthening it and making it healthier.
Indications for dental remotherapy According to dentists, one should prepare for dental remotherapy, and for the method to be effective, it is better to use it after whitening and removal of tartar. This method is especially recommended for use in pregnant women and adolescents, because their body is especially prone to losing minerals and nutrients.
Planned teeth whitening
Damage to enamel
· Hygienic teeth cleaning (after the procedure)
· Polishing, grinding and preparation of teeth for veneers, crowns (after the procedure)
· Pregnancy period
Dental hyperesthesia (increased enamel sensitivity)
Pathological abrasion, thinning of tooth enamel
Wedge-shaped defect
Erosion and other damage to enamel
· Caries in the spot stage
Prevention
To increase resistance to caries (caries resistance) it is recommended:
- Maintain oral hygiene (proper cleaning of the mouth, rinsing after meals);
- change your diet (reduce sweets, add solid vegetables and fruits);
- treat otitis media and diseases affecting the nasopharynx in a timely manner;
- take fluoride supplements.
Professional teeth cleaning is one of the preventive measures
Fluorine increases the resistance of enamel, forming fluorapatite. In addition, fluorides:
- normalize metabolism in dental tissue;
- inhibit the growth of microorganisms;
- reduce the rate of formation of acids that destroy teeth.
Therefore, if there is a low level of fluoride in the water in the region, it is recommended to drink fluoridated water, and also more often add sea fish and canned food made from it, seaweed, parsley, and tea to your food. And also use toothpaste with fluoride.
Sodium fluoride intake is 250 days a year with a break in the summer months. Subject to compliance with the timing and method of application, a reduction (decrease) of caries of primary teeth by 70-93%, and of permanent teeth by 30-60% is ensured.
Hyperesthesia (increased tooth sensitivity) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of hyperesthesia is aimed at reducing the speed of fluid flow in the dentinal tubules. This can be achieved in the following ways:
- blockage of enamel micropores with the help of desensitizers - drugs that reduce tooth sensitivity;
- reducing the size of micropores using mineralizing agents, for example, gels with a high content of fluoride and calcium. These include gels ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse;
- closing or narrowing of dentinal tubules using a laser [14];
- preparation and filling of teeth for carious lesions;
- surgery on the gum when it recedes as a result of periodontal disease;
- correction of the bite.
In 1935, dentist L. Grossman identified the main properties of an ideal remedy for combating hyperesthesia [12]. In his opinion, it should act quickly and be effective for a long time, not irritate the pulp, not provoke pain and not change the color of the teeth. There are quite a lot of such drugs now. Desensitizing agents (reducing tooth sensitivity) are produced in the form of gel, toothpaste, rinse, varnish, etc. Toothpastes are most often used.
For mild hyperesthesia , as a rule, applications of various solutions are sufficient.
The drug Remodent in the form of a 3% aqueous solution for applications is applied to areas of hyperesthesia for 15-20 minutes. For the course of treatment to be effective, it is necessary to make 8-28 such applications (one 2 times a week) until a positive result is achieved. Sometimes a 3% solution of remodent is used as a rinse (4 times a week). The full course includes about 40 procedures.
Strontium chloride is used in the form of a 25% aqueous solution and 75% paste. When rubbing the paste, stable compounds of strontium appear with the hard tissue of the tooth. This remedy is a good prevention of hyperesthesia after tooth preparation and removal of dental plaque.
To eliminate hyperesthesia, a 30% aqueous solution of zinc chloride is also used. After this, an application is carried out with a 10% solution of potassium ferrocyanide. It seals the tubules with the resulting sediment. The duration of the applications is one minute. The use of a paste containing alkalis is also indicated: sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium, magnesium. It attracts dentinal fluid, which is contained in the micropores of the enamel, and reduces tooth sensitivity.
A modern treatment for hyperesthesia is bifluoride-12, a special colorless varnish containing fluoride, and fluocal, a dental gel containing sodium fluoride. They are carefully applied to the teeth with a brush or foam swab. Both products create a coating that saturates the enamel and dentin with fluoride ions, which leads to a decrease in sensitivity. Fluocal can also be used in the form of an application solution. Typically, a course of treatment with such applications includes only 2-3 procedures. Varnish is usually used as an auxiliary method that enhances the effect of the main drug [15].
Treatment of hyperesthesia with laser has been shown to be the preferred treatment method. It is aimed at narrowing the dentin tubules by combining the proteins of the dentin fluid, partially melting the hard tissues and relaxing the internal nerve receptors. Laser therapy has no side effects [15].
Treatment of generalized hyperesthesia is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, so it not only relieves symptoms, but also affects the course of the disease. Treatment must be comprehensive. In addition to treating the main cause of hyperesthesia, it is necessary to restore the mineral composition of enamel and dentin, and normalize the content of phosphorus and calcium in the body. For this purpose, calcium glycerophosphate, clamine or phytolon, as well as multivitamin preparations are prescribed. Taking phosphorus-calcium drugs throughout the course of treatment provides a good prognosis. Otherwise, restoration of normal sensitivity will take a long time.
To eliminate pain at the beginning of treatment, in addition to using toothpaste with phosphate, electrophoresis with a 2.5% solution of calcium glycerophosphate is required. The course of such physiotherapy is 10 sessions. In case of hyperesthesia against the background of impaired neurological status, the use of a galvanic collar according to Shcherbak is indicated (also at least 10 sessions).
Studies have shown that the effect of complex treatment of hyperesthesia occurs quickly and lasts for quite a long time. The content of phosphate and calcium in the dental tissues increases, the level of calcium and phosphate in the blood normalizes.
During the treatment of hyperesthesia of any degree it is necessary:
- select personal hygiene products;
- control bad habits (do not bite nails, pencils);
- adjust your diet (exclude soda, sticky sweets, consume vegetables, fruits and dairy products more often);
- wear a mouth guard at night (for bruxism) [14].