X-rays allow you to make the correct diagnosis, prescribe appropriate treatment, and also monitor the results of treatment.
Myth about the dangers of X-rays in dentistry
It is important to note that x-rays are an absolutely painless procedure that does not require patient preparation and takes only a few minutes. Many people believe that x-rays are harmful to health. Actually this is not true. Of course, if you take an x-ray every day, there may be unpleasant consequences for the body, but x-rays in dentistry rarely require repeated examination, and therefore are completely harmless to the body.
The X-ray rooms of our dental clinic are equipped with the most modern equipment, which allows you to take an image of the oral cavity without harm to the patient.
Why is X-ray examination needed in dentistry?
X-ray examination (dental x-ray) is the basis of quality treatment with a good prognosis.
Without high-quality x-ray diagnostics, it is almost impossible to create a competent treatment plan. Our clinics have the best equipment, innovative software, and we use artificial intelligence for accurate diagnostics.
Dental x-rays can reveal:
- inflammatory process inside the tooth;
- presence, size and location of the cyst;
- presence of a tumor;
- quality of dental canal filling;
- how deep is the caries;
- abscess in periodontal elements;
- crack in the tooth;
- the presence of unerupted teeth (including wisdom teeth);
- various anomalies in the structure of bones;
Only after an adequate X-ray examination has been carried out can the doctor make a diagnosis with complete confidence and prescribe the correct treatment.
Dental X-rays are necessary during therapeutic treatment (especially during root canal treatment), prosthetics, implantation, and also before starting orthodontic treatment (bite correction).
In addition, X-ray diagnostics allows the doctor to confirm the effectiveness of the treatment.
Patient Interview
The primary research method is the patient interview. Further diagnostic work is based on the data obtained during the first examination.
During the survey, special attention is paid to several aspects to identify the clinical picture and assess the presence of changes in all areas:
- Soreness . Since pain is the most common complaint, it is isolated first. At the same time, its nature, localization, severity and duration, as well as the presence of irradiation, are determined.
- Quality of birth (if the child is examined).
One of the main causes of orthodontic anomalies is trauma during childbirth or intracranial hemorrhage, which leads to disruption of the development of the dental system. Therefore, the doctor must find out all the necessary details of this process. - Type of feeding .
Determining the type and period of breastfeeding allows us to determine the root cause of the orthodontic abnormality. With artificial feeding, the muscles work differently than with breastfeeding, which negatively affects the development of the jaw. - Compliance of child development with standards . Each parameter, starting from the first independent step, a spoken word or an erupted tooth, shows the degree of development of all the child’s systems.
- Diseases that were suffered in childhood . Some of them lead to disruption of metabolic processes, which affects the growth of the jaw and teeth.
- Having bad habits such as sucking a pacifier for a long time, regularly biting pencils, etc. Very often these factors are the cause of malocclusion.
- Condition of the patient's upper respiratory tract . Pathological changes in occlusion can be provoked by prolonged mouth breathing.
All data obtained is entered into the medical history, where the results of other diagnostic methods will also be displayed.
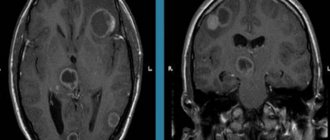
Types of X-ray examinations in dentistry
Dentists use several options for x-ray examinations, which allow them to study both one tooth individually and the entire jaw: bone structures, joints, connective tissues.
- Sight shot
is the most common type. It is performed on a visiograph with low radiation dose. This method is used to make a diagnosis in the area of 1-2 teeth. - CBCT (computed tomogram, 3D image).
This is the standard in dentistry today. CBCT will be required for volumetric therapeutic treatment, in preparation for implantation, prosthetics, and orthodontics. It can be used to identify deep dental lesions, bone changes, and malocclusion. - Panoramic
dental x-ray is a 2D overview image of the entire oral cavity. The doctors at our clinic work according to world standards, so we plan treatment based on 3D image data (CBCT). But we don’t take panoramic photographs in our clinic - this diagnosis is not enough for accurate planning.
Comments
How many times a year can dental x-rays be taken and how dangerous is it in terms of radiation exposure?
Timur (02/23/2020 at 11:21 pm) Reply to comment
- Dear Timur! Pictures today are taken using modern devices that have a minimal radiation dose. It's completely safe. So, for example, by taking one targeted image of 1 tooth, the patient will receive a radiation dose of approximately 5 μSv, one panoramic image - about 35 μSv, and a comprehensive computed tomography scan of the upper and lower jaw - 60 μSv. According to the standards, the maximum radiation exposure per year for an adult should not exceed 1000 μSv for prevention purposes. It turns out that in theory it is possible to take more than 100 images per year, but even with complex implantation such a number is not required.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (02/27/2020 at 09:12) Reply to comment
Should the doctor take a second X-ray after cleaning the canals? The dentist only took the initial photo and that’s it. But after the treatment I feel discomfort, so I would like to know if a repeat scan was necessary? And wasn’t this the doctor’s mistake?
Galina (03/20/2020 at 10:07 am) Reply to comment
At 30 weeks of pregnancy, I was told that taking a spot image of a tooth would be almost harmless with modern equipment. Is it so? I don’t want to risk the baby’s health, but the tooth hurts very badly.
Maria (03/20/2020 at 10:52 am) Reply to comment
What should you do if the picture was taken poorly and the dentist asks you to take another one? Will a damaged photo need to be paid in full or is it the dentist’s fault?
Diana (03/20/2020 at 12:01 pm) Reply to comment
My child is 12 years old. His tooth hurt very much, he could not chew with it, although there were no visible changes in the tooth (no visible caries or anything else). We went to the municipal clinic. To fix the tooth, we went to the dentist twice in one week. The child also had dental x-rays taken twice a week. Tell me, how safe is it to have a child’s dental X-ray done in general and twice in one week?
Elena (03/20/2020 at 14:31) Reply to comment
About 3 years ago I finally decided to get all my teeth fixed. I went to the dentist for a month. At first she only filled, but when it came to 2 roots, which it was decided to build on... In general, I don’t know what dentists call it. I'll call it growing a tooth. So, before the extension of the first tooth, I was sent for an x-ray. Moreover, the picture didn’t work out the first time, only the second time. The doctor didn’t like the picture and she sent me for a repeat x-ray from a different angle. In total, I was “enlightened” 3 times. The root was fine, the tooth grew. However, when she sent me for an x-ray of the second tooth, or rather, its root, the x-ray room said that in a month they had given too much radiation through my head 3 times and advised me to come back in 3 weeks. As a result, I did not take an x-ray and have not treated the tooth until now. And you write in the comments about 100 pictures. So who is right?
Mikhail (03/20/2020 at 04:32 pm) Reply to comment
My wisdom tooth began to grow and displace the neighboring one, which was quite healthy and strong. The doctor said that it needed to be removed and sent him to take a picture. The tooth was removed on time, otherwise it would have grown in the second row. Probably, without a photo, such a procedure would not be easy to do.
Alla (03/20/2020 at 16:40) Reply to comment
Hello! Tell me, which method allows us to identify hidden tumor processes in the patient’s gums and jaws? I have a benign tumor of the salivary gland, is it possible to use sialography to analyze it, or is it better to have an ultrasound (I do it as planned once every six months)?
Eleanor (03/20/2020 at 5:51 pm) Reply to comment
I remember at an appointment at a dental clinic, the doctor removed a tooth without an x-ray. Another paid clinic sent me straight away for an x-ray. Does a doctor have the right to remove a tooth without sending the patient for a tomography?
Alexey (04/23/2020 at 07:39) Reply to comment
Any research methods that include x-rays carry a certain amount of radiation to the body. How safe are these devices described in the article for the patient?
Denis (04/23/2020 at 09:09) Reply to comment
Hello, can you write in more detail about multislice tomography? One more question: is it possible to get an appointment without a referral from a dentist? Can they tell right in the center with a tomograph what problems there are, or do they send this 3D image to the doctor?
Anita (04/23/2020 at 09:14) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Diagnocat artificial intelligence: fast CBCT analysis, accurate diagnosis
Our clinic uses Diagnocat artificial intelligence for CBCT analysis! The program uses 3D images to determine the condition of the teeth, finds problems and suggests how to treat them. In just a few minutes, Diagnocat will examine your CT scan, identify problem areas, and generate a report for each tooth. And the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis! More about Diagnocat here.
Initial consultation
To decide on treatment tactics, the dentist must first conduct an initial examination of the oral cavity using instruments that help determine the degree of damage to the dental tissues and mucous membranes. This is done for:
- determining the extent of previous diseases;
- analysis of the general condition of the patient’s oral cavity;
- establishing the fact of treatment using orthoconstructions earlier;
- clarification of the symptoms that forced the patient to see a dentist.
Visual diagnostics helps the doctor assess the condition of the teeth. The conclusion is made based on a number of criteria:
- pain syndrome (the point of localization of pain and the frequency of pain impulses are determined);
- condition of dental tissues, ratio of jaw sizes.
In addition, the dentist must pay attention to the symmetry of the nasolabial and chin folds.
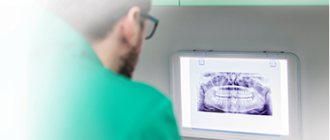
How is x-ray examination (dental x-ray) performed?
- The study can only be done in an X-ray room specially equipped for this purpose;
- The patient must remove all metal jewelry, removable plates, and piercings from the head;
- If you need a picture of one or more teeth, a radiologist places the visiograph sensor against a specific area;
- 3D scanning occurs using a rotating module (it is important to sit still);
- All images are immediately transferred to the computer;
- The duration of the study is only a couple of minutes.
Where can I get a dental x-ray done in Moscow and how much does it cost?
- You can take an X-ray of a tooth in Moscow at our Belgravia Dental Studio clinics;
- Our clinics are equipped with the most modern diagnostic equipment: safe and high-precision X-ray machines, visiographs, computed tomographs, allowing us to conduct all types of studies.
| X-ray diagnostics of dental condition: cost | |
| Sight radiography | 1 090 ₽ |
| BiteWing X-ray series | 1 790 ₽ |
Price list for Belgravia Dental Studio services
Our promotions
Using Models
To determine the exact position of the defect in the dentition, dentists often use impressions. They are made mainly from gypsum. Impression trays are made of metal or plastic.
These devices are used to establish the correctness of the dentition and clarify the previously made diagnosis.
Functional diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis and make the diagnosis correctly, dentists often use:
- masticationography (assessment of the state of bite);
- graphical recording (determining the level of activity of the muscles located in the area of the mandibular joint at the time of chewing food);
- electromyography (determining the number of contractions of the mouth muscles over a certain period of time).