Untimely treatment of caries in children leads to the development of pulpitis - inflammation of tooth tissue, including blood vessels and nerve bundles. The lower molars are most often affected, but the disease occurs even on the anterior elements. Therefore, pulpitis in children occurs even more often than in adults. This is due to a number of factors:
- thin weak enamel;
- large volume of pulp;
- wide root canals;
- less mineralization;
- weak immunity.
In addition to caries, pulpitis can be caused by trauma, including poor treatment.
Treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis in children by our experienced pediatric therapists:
- treatment with a smile, no stress for the child , no tears
- pediatric doctors become friends for young patients
- doctors save baby and permanent teeth
- more than 7,890 children who are happy to have their teeth treated with us
- While the child is getting his teeth treated, the parents go about their business
- quality treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo
Treatment of primary teeth Medvedkovo, Babushkinskaya
Features of treatment of baby teeth
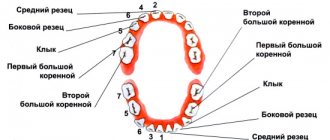
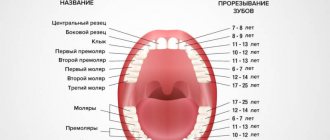
Teeth begin to fall out at the age of 5-6 years.
And this process ends when the child reaches 10-12 years old. The first to fall out are the central incisors, then the lateral incisors, then the canines, after which it is the turn of the first and second molars. A tooth that should fall out at age 10 will not fall out before that age. But troubles can arise. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the prevention of baby teeth. It is necessary to take care of the condition of the child’s teeth during pregnancy. The expectant mother is recommended to consume various foods that contain a lot of calcium, fluorine and phosphorus. It is these elements that influence the formation of milk teeth and the rudiments of permanent teeth. A balanced menu with the addition of vitamin and mineral complexes is necessary.
1 year
. By this age, the first teeth erupt. This may be accompanied by swollen gums and discomfort. Special gels relieve symptoms, so you can take your baby to the dentist for the first time before reaching one year of age. The doctor will recommend special pastes, brushes, and talk about proper prevention and oral hygiene.
Immediately after teething, the mother should begin to care for them. You can use special wipes to remove food debris and plaque. It is recommended to buy a special brush; it is placed on an adult’s finger, after which parents brush their children’s teeth themselves.
2 years
. At this time, most of the baby teeth appear (20 in total). At the same age, the first signs of caries may appear. The following procedures help stop the development of the disease:
- Fluoridation.
- Silvering.
- Fissure sealing.
These and other manipulations help keep baby teeth healthy until they naturally fall out.
3 years
. At this age, all baby teeth appear. Since children often love sweets, and parents do not always control the consumption of foods with sugar, carious lesions often occur. If you take care of your teeth and visit the dentist regularly, you can do without drilling and filling.
4-5 years
. In addition to caries, pulpitis often occurs. It is important to preserve the root parts, so partial tooth extraction and fillings can be installed. It is best that by this age the child retains all his milk teeth; after 5 years, they already fall out on their own, this is an ideal option for future permanent teeth.
Since it is difficult for children under 6-7 years of age to brush their teeth and take care of them on their own, this should be done by parents and a dentist. Visit your doctor every six months to monitor the normal development of baby teeth.
Treatment
In the early stages of caries development, drilling can be avoided. But if this cannot be avoided, there is no need to be afraid. Modern pediatric dentistry is completely painless. And doctors are real professionals who even remove caries-affected tissues and perform fillings in such a way that for a child it all turns into a game and entertainment, teaching from childhood not to be afraid of the dental chair and the clinic.
Modern materials are used to fill baby teeth. You can even make colored fillings. It is important from an early age to accustom your child to oral hygiene, dental care and preventive visits to the dentist. This will minimize the treatment of baby teeth.
Modern methods of dental treatment provide painless procedures, this may require anesthesia; safe, but effective and effective methods are offered for children that do not cause fear and from an early age form in children a positive attitude towards dentists and dental treatment. Even better, if you go to the clinic in the early stages of the disease, then everything will be done to save your teeth.
Where to treat
Dental clinic VitaDent offers all types of treatment for baby teeth. We employ pediatric dentists with extensive experience. The most modern technologies, methods and materials are used and a guarantee is provided. Our children are not afraid to have their teeth treated; they do it with interest. All this allows you to treat baby teeth on time, efficiently and effectively.
Our doctors
Reviews about the clinic on independent portals:
Causes of occurrence and development of pulpitis
The main etiological factor that plays a role in the occurrence and development of pulpitis is untreated caries in a timely manner. Microbes living in a carious lesion penetrate into the pulp cavity, where they actively multiply and also produce toxic waste products that are destructive to the pulp fibers. In addition, pulpitis can occur due to the following reasons:
- retrograde penetration of infection into the pulp through the apical foramen during periodontitis;
- hematogenous spread of bacteria in the presence of chronic inflammatory foci in the body;
- iatrogenic damage to fibers during caries treatment (prolonged thermal exposure, overdrying, chemical burn, etc.);
- mechanical trauma to tissue (perforation of the cavity wall during drilling, dislocation of a segment, fracture of the crown, root), etc.
Treatment with a smile, no stress for the child, no tears
Pulpitis of primary and permanent teeth in pediatric dentistry is quite common; approximately 90% of children with advanced caries suffer from symptoms of this disease. Children's pulpitis is accompanied by excruciating toothache, which deprives you of joy. The use of painkillers will not solve the problem, so the only correct solution is to visit a dentist. The Novodenta dental clinic offers the services of a pediatric dentist who will not only treat pulpitis or periodontitis, but will also find an approach to every little patient.
How is dental nerve removal performed in children?
In modern pediatric dentistry, the pulp removal procedure includes the following steps:
- Examination, clarification of the diagnosis, and radiography.
- Pain relief using local anesthetics.
- Isolation of the tooth. This is done to prevent saliva microbes from entering the tooth during treatment.
- Removal of all affected tissue using a drill.
- Removal of pulp residues in the tooth cavity.
- Applying a “therapeutic” filling to the bottom of the cavity.
- Tooth filling using modern composite materials.
- Tooth polishing
At the Natadent clinic, treatment of pulpitis in a standard clinical situation is carried out at a time and lasts about 40 minutes. In this case, the child does not experience any pain, the procedure gives him no more discomfort than conventional caries treatment.
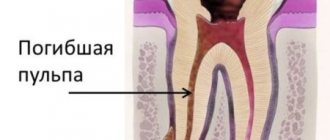
What is pulpitis
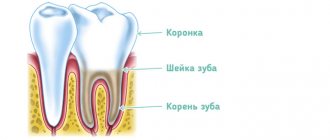
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the connective tissue that contains nerve endings, blood and lymphatic vessels. The pulp itself is located under a layer of dentin inside the tooth, consists of a cellular part, vascular and nerve bundles, the defeat of which causes severe and acute pain. In children, pulpitis occurs many times more often than in adults. The reason for this is the fact that baby teeth, like permanent teeth, have a thinner layer of enamel and dentin, which allows infection to quickly penetrate into the deep tissues of the tooth. The pulp is very important because it provides growth and nutrition to tooth tissue.
How to recognize pulpitis
Pulpitis can be diagnosed by the appearance of characteristic clinical signs:
- pain that gets worse at night;
- sharp reaction to stimuli;
- pain when chewing;
- darkening of the enamel;
- severe destruction of the crown walls;
- swelling of the mucous membrane around the segment;
- hypertrophied pulp tissues protrude above the chewing surface.
It is not always possible to recognize the disease on your own. If inflammation has developed under the filling, and the crown is slightly damaged or not damaged at all, then instrumental diagnostics are required.
Causes and symptoms of pulpitis in children
Inflammation of the pulp, according to pediatric dentists, can occur for several reasons, including:
- caries;
- acute infectious diseases that led to decreased immunity and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- dental injuries.
Symptoms of pulpitis in children are manifested by the following signs:
- sharp and throbbing pain in the area of the diseased tooth;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling, redness of the gums;
- general weakness, fever;
- increased sensitivity of teeth.
The main symptom of the disease is throbbing pain, which can occur at any time of the day. If you do not pay attention to the problem, this can lead to complications in the form of purulent inflammation, periodontitis and other consequences.
Potential complications of pulpitis in primary teeth
Not treating baby teeth (“after all, they will fall out anyway”) is the biggest mistake that parents can make regarding their child’s dental health. In particular, pulpitis that is not treated in time leads to a number of serious complications:
- periodontitis, purulent abscess, infection entering the bloodstream, which can even lead to death;
- deep infection can affect the primordia of the molars;
- Early loss of baby teeth affects the eruption of permanent teeth. As a result, the child may develop significant bite problems;
- pain and discomfort prevent the child from eating and communicating normally.
Classification
Pulpitis in children can affect both milk and permanent teeth and manifest itself in several forms - acute and chronic.
Acute pulpitis of milk teeth or permanent teeth is divided into several types:
- Focal - attacks of pain last up to 30 minutes, most often appear after consuming cold or hot food or drinks.
- Diffuse – the middle layer of the pulp is damaged, the pain can last for several hours, and intensifies in the evening.
- Purulent - inflammation affects not only the pulp, but also affects the gums. Upon examination, you may notice a discharge of grayish or yellow liquid.
If you do not pay attention to the problem, the acute form quickly turns into chronic, which also has several forms:
- Fibrous – inflammation affects the root canals, tooth enamel quickly turns black, there is a reaction to hot and cold food, pain is practically not a concern.
- Hypertrophic – a polyp forms in the tooth cavity, the gums bleed, and there is a putrid odor from the mouth.
- Gangrenous is a dangerous type of disease when the pulp completely dies, and healthy tissue begins to be damaged.
Regardless of the form and type of the disease, treatment of pulpitis in milk or permanent teeth should be carried out as quickly as possible, this will help to eliminate the development of complications.
Treatment methods
The treatment of primary teeth in general does not differ from the treatment of permanent elements. If the child’s condition is serious, there is a threat of infection spreading throughout the body, amputation is performed. In most cases, the tooth is preserved to prevent malocclusion. Therapy is carried out in different ways:
- traditional. Involves treatment in three visits. During the first one, the nerve is opened, a devitalizing paste with arsenic is applied for 24-48 hours or without it for a period of up to 7 days. On the second visit, a pulp mummification mixture based on resorcinol-formalin is placed into the canals. At the last visit, a permanent filling is installed;
- modern. It takes place in 1 – 2 visits. If the child can sit quietly for a long time at the doctor and the roots of the tooth are formed, extraction is performed. The nerve is removed either on the first visit or after applying the paste. Next, the canals are carefully processed, infected tissue is removed, an anti-inflammatory paste (for example, zinc eugenol) is applied and closed with a filling. The composition will gradually dissolve along with the roots when changing teeth;
- partial vital amputation. The doctor removes the upper portion of the nerve and applies an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory medication that seals the remaining living pulp.
When treating teeth with immature roots, a different approach is chosen. This is due to several reasons:
- the apex of the roots has not yet closed and there is a risk of infection of the permanent tooth germ;
- the roots are short and the channels are wide;
- trauma to the upper zone of the root can lead to disturbances in its formation;
- It is impossible to remove the entire pulp and perform a complete canal treatment.
Most often, they choose amputation of the pulp by any method or biological treatment, when the tooth is cleaned of the affected tissue and a paste with calcium hydroxide is applied for several days. After this, a filling is installed.
Additional methods of conservative treatment of pulpitis
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used as an addition to the biological treatment method. The following procedures are shown:
- Helium-neon laser - its radiation has an analgesic effect, helps reduce swelling, reduce inflammation.
- Electrophoresis - using this method of electrotherapy, anesthetics are injected into the site of inflammation.
- Ultrasound therapy – low-frequency ultrasound stimulates regenerative processes and accelerates the delivery of medicinal substances to tissues.
After treatment of pulpitis with a biological method, patients must undergo electroodontic diagnostics in order to monitor the condition of the pulp. If the electrical excitability of the pulp is not restored after treatment and pulp death is diagnosed, a depulpation procedure (pulp removal) is performed.
What to do if baby teeth grow crookedly?
If parents notice that their child’s baby teeth are growing crookedly - for example, there is crowding or improper occlusion - this is a reason for a mandatory consultation with a pediatric orthodontist. It happens that due to anomalies of the facial skeleton (in particular, improper development of the jaws), defects are noticeable even with a primary bite, and with a permanent bite they will persist and worsen.
Therefore, it is recommended to show the child to an orthodontist from the age of three to determine whether there is pathology and find methods for its correction. There are malocclusions that are easily corrected at an early age and extremely difficult to correct in adults.
Treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth
Treatment of periodontitis in a permanent tooth involves removing the infection inside and outside the tooth, located in the ligament that holds the tooth.
Complaints. With this type of disease, complaints appear when biting on a tooth, a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth, pain in the gum next to the tooth, swelling and swelling of the gum, discharge of purulent contents from the tooth or from the gum. Signs of general intoxication of the body: fatigue, weakness, lethargy, temperature, enlarged regional lymph nodes.
Treatment method. Before dental treatment for periodontitis, local anesthesia is performed (if necessary). Demineralized tissue is removed from the carious cavity and access to the root canals is created for the purpose of high-quality mechanical, chemical and medicinal treatment. A medicinal paste is injected into the tooth canals for 7-10 days for the purpose of antiseptic and osteotropic effects, the treatment ends with the installation of a temporary filling. On the second visit, the medicinal paste is removed from the tooth, the root canals are filled with modern sealers (pastes) and fillers (gutta-percha pins) under X-ray control. After the treatment, the issue of restoring the crown part of the tooth is decided: a filling or a crown. Only a dentist, having assessed the condition of the tooth, will suggest one or another method of restoring the tooth.
Recommendations. Visit a dentist at least once every 6 months to examine the oral cavity in order to identify foci of inflammation, prevent complications and sanitation.
Medicines for the treatment of root canals in children
Today, pediatric dentists have a huge selection of medications for treating intracanal cavities at their disposal. The products most actively used by leading dental clinics in Moscow are represented by the following categories and types:
- antibiotics (Metronidazole, Gramicidin, Polymyxin M);
- bactericidal compounds (Chlorhexidine, Sodium hypochloride, iodine, Iodinol, Lugol's solution, hydrogen peroxide, 30% urea solution);
- anti-inflammatory (Dicamphen, Iodex, Camphorphen, Guaifen, Pulposeptin, Indextrol);
- calcium hydroxide (powder, solution or paste composition) and hydroxyapatites (Hydroxyapol, Kergap, Ostim-100);
- MTA preparations (mineral trioxide aggregate) – Biodentin, Restapex, Trioxident and others.
When choosing the optimal therapeutic drug, it is important not only to correctly assess the condition of the root canals and the general well-being of the patient, but also the nature of the problem. You should also take into account the quality of the substance used: biocompatibility, non-toxicity, moisture tolerance, hypoallergenicity, effectiveness, etc. Upon completion of medication treatment, it is imperative to re-examine the canals and perform their permanent obturation.
Indications for medicinal effects on the canals
The main method of endodontic treatment is mechanical cleaning of the canals with constant rinsing. Moreover, in some cases, dentists use medicinal preparations of various effects. These include the following diseases:
- acute form of chronic, traumatic, toxic or infectious periodontitis;
- chronic development of periodontitis with a predominance of anaerobic microflora, periapical defect of bone tissue or constant canal humidity;
- the need for endodontic treatment at the stage of incomplete root formation or its apex;
- traumatic damage to permanent or temporary teeth;
- perforation of the root wall, external or internal resorption.
Possible problems
Unfortunately, treatment of pulpitis in children is often carried out with errors, since it is not always possible to carry out all the necessary manipulations in full and with the required accuracy due to the child’s anxiety. The following problems occur:
- The devitalization paste is applied incorrectly (not to the nerve), as a result of which the pain does not decrease, and the paste has to be applied again.
- Due to the proximity of the gums, the paste can cause burns and quite severe pain.
- If the roots are unformed or if they begin to reabsorb, canal treatment manipulations can cause prolonged bleeding.
- Sometimes perforation of the root of a baby tooth occurs, which can result in periodontitis, as well as periostitis.
- Due to the inexperience of the doctor, a broken instrument may remain in the tooth canal.
Where does treatment begin?
After you decide to enroll in Faceline dentistry, the child is examined by a doctor and diagnoses the problem. We use:
- targeted and panoramic photographs of teeth (X-ray doses are minimal);
- indicators of dental plaque (determine visually invisible boundaries of dental lesions);
- caries markers (reveal hidden carious cavities).
Then the dentist offers the parent ways to solve the problem and explains how much it costs to treat permanent or baby teeth. Together with the parent, we approve an action plan and get to work.
Price table for pulpitis treatment in Moscow
| Name of service | Cost of pulpitis treatment | Price |
| Mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canal + filling the canal with gutta-percha pins | 1-channel tooth | 4030 |
| 2 channel | 5800 | |
| treatment of 3-channel pulpitis | 8420 | |
| Treatment of the canal (fur and medicinal) + filling it with Thermofil, MTA | single channel | 4930 |
| two-channel | 7880 | |
| three-channel | 11200 | |
| Crown restoration with fluoropolymers | from 4600 | |
How is pulpitis treated?
Treatment of tooth pulpitis is aimed at preserving the unit, relieving symptoms, and preventing the development of purulent inflammation. The most commonly used method is depulpation, i.e. removal of the pulp along with the neurovascular bundle. However, after such a procedure (due to loss of innervation and blood supply), the tooth becomes “dead” and gradually collapses. Therefore, if the pulp is slightly damaged, biological methods of its treatment are used, aimed at maintaining the viability of the structure. If serious complications develop, the question of tooth extraction may arise.